Kherson
Encyclopedia
Kherson is a city
in southern Ukraine
. It is the administrative center
of the Kherson Oblast
(province
), and is designated as its own separate raion
(district) within the oblast. Kherson is an important port
on the Black Sea
and Dnieper River
, and the home of a major ship-building industry. The current estimated population is 329,000 (as of 2007).
. Kherson was founded in 1778 by Grigori Aleksandrovich Potemkin, on the orders of Catherine the Great
. The city was built under the supervision of General Ivan Gannibal
on the site of a small fortress called Aleksanderschanz. The name Kherson is a contraction of Chersonesos, an ancient Greek colony founded approximately 2500 years ago in the southwestern part of Crimea
. One of the first buildings in the Kherson Fort was the Church of St. Catherine where Potemkin was eventually buried. The last tarpan
was caught near Kherson in 1866.
, the ethnic groups living within Kherson are:
s. Two of them still carry mark of a colonial city
of Russia
.
, Poland
Zalaegerszeg
, Hungary
Shumen
, Bulgaria
Kent
, United States
Zonguldak
, Turkey
Oslo
, Norway
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
in southern Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
. It is the administrative center
Capital City
Capital City was a television show produced by Euston Films which focused on the lives of investment bankers in London living and working on the corporate trading floor for the fictional international bank Shane-Longman....
of the Kherson Oblast
Kherson Oblast
Kherson Oblast is an oblast in southern Ukraine, just north of Crimea. Its administrative center is Kherson. The area of the region is 29000 km², its population is 1.12 million.Important cities in the oblast include:...
(province
Oblast
Oblast is a type of administrative division in Slavic countries, including some countries of the former Soviet Union. The word "oblast" is a loanword in English, but it is nevertheless often translated as "area", "zone", "province", or "region"...
), and is designated as its own separate raion
Raion
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet countries. The term, which is from French rayon 'honeycomb, department,' describes both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district"...
(district) within the oblast. Kherson is an important port
Port
A port is a location on a coast or shore containing one or more harbors where ships can dock and transfer people or cargo to or from land....
on the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
and Dnieper River
Dnieper River
The Dnieper River is one of the major rivers of Europe that flows from Russia, through Belarus and Ukraine, to the Black Sea.The total length is and has a drainage basin of .The river is noted for its dams and hydroelectric stations...
, and the home of a major ship-building industry. The current estimated population is 329,000 (as of 2007).
History
Until 1774, the region belonged to the Crimean KhanateCrimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate, or Khanate of Crimea , was a state ruled by Crimean Tatars from 1441 to 1783. Its native name was . Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan...
. Kherson was founded in 1778 by Grigori Aleksandrovich Potemkin, on the orders of Catherine the Great
Catherine II of Russia
Catherine II, also known as Catherine the Great , Empress of Russia, was born in Stettin, Pomerania, Prussia on as Sophie Friederike Auguste von Anhalt-Zerbst-Dornburg...
. The city was built under the supervision of General Ivan Gannibal
Ivan Gannibal
Ivan Abramovich Gannibal was a Russian military leader and eminent Russian of African origin...
on the site of a small fortress called Aleksanderschanz. The name Kherson is a contraction of Chersonesos, an ancient Greek colony founded approximately 2500 years ago in the southwestern part of Crimea
Crimea
Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
. One of the first buildings in the Kherson Fort was the Church of St. Catherine where Potemkin was eventually buried. The last tarpan
Tarpan
Tarpan is an extinct subspecies of wild horse. The last individual of this subspecies died in captivity in Russia in 1909....
was caught near Kherson in 1866.
Demographics
As of Ukrainian National Census (2001)Ukrainian Census (2001)
The first Ukrainian Census was carried out by State Statistics Committee of Ukraine on 5 December 2001, twelve years after the last Soviet Union census in 1989....
, the ethnic groups living within Kherson are:
- UkrainiansUkrainiansUkrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens...
- 76.6% - RussiansRussiansThe Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
- 20.0% - Other - 3.4%
Population
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1790 | 24,000 |
| 1926 | 58,000 |
| 1939 | 97,000 |
| 1959 | 158,000 |
| 1981 | 361,000 |
| 2004 | 354,000 |
| 2007 | 329,000 |
Administrative divisions
There are three city raionRaion
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet countries. The term, which is from French rayon 'honeycomb, department,' describes both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district"...
s. Two of them still carry mark of a colonial city
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
of Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
.
- Dnipro Raion, named after the Dnieper riverDnieper RiverThe Dnieper River is one of the major rivers of Europe that flows from Russia, through Belarus and Ukraine, to the Black Sea.The total length is and has a drainage basin of .The river is noted for its dams and hydroelectric stations...
. - Komsomol Raion, named after the Russian Communist youth organization, KomsomolKomsomolThe Communist Union of Youth , usually known as Komsomol , was the youth division of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. The Komsomol in its earliest form was established in urban centers in 1918. During the early years, it was a Russian organization, known as the Russian Communist Union of...
. - Suvorov Raion, named after the RussianRussiansThe Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
GeneralGeneralA general officer is an officer of high military rank, usually in the army, and in some nations, the air force. The term is widely used by many nations of the world, and when a country uses a different term, there is an equivalent title given....
Suvorov.
Education
- Kherson state agrarian university
- Kherson state university
- Kherson national technical university
- International University of Business and Law
Main sights
- The Church of St. Catherine was built in the 1780s, supposedly to Ivan StarovIvan StarovIvan Yegorovich Starov was a Russian architect from St. Petersburg who devised the master plans for Yaroslavl, Voronezh, Pskov, Dnipropetrovsk, Mykolaiv, and many other towns in Russia and Ukraine...
's designs, and contains the tomb of Prince Potemkin. - Kherson TV Tower — is a famous construction located in the city.
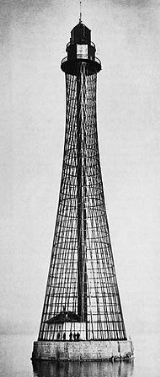
- Adziogol LighthouseAdziogol LighthouseAdziogol Lighthouse , also known as Stanislav Range Rear Light, is a vertical lattice hyperboloid structure of steel bars, serving as an active lighthouse, about from Kherson, Ukraine...
, hyperboloid structureHyperboloid structureHyperboloid structures are architectural structures designed with hyperboloid geometry. Often these are tall structures such as towers where the hyperboloid geometry's structural strength is used to support an object high off the ground, but hyperboloid geometry is also often used for decorative...
designed by V.G.ShukhovVladimir ShukhovVladimir Grigoryevich Shukhov , was a Russian engineer-polymath, scientist and architect renowned for his pioneering works on new methods of analysis for structural engineering that led to breakthroughs in industrial design of world's first hyperboloid structures, lattice shell structures, tensile...
, 1911
Famous people
- Georgy ArbatovGeorgy ArbatovGeorgy Arkadevich Arbatov was a Soviet and Russian political scientist who served as an adviser to five General Secretaries of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and was best known in the West during the Cold War era as a representative for the policies of the Soviet Union in the United...
(1923–2010), political scientist. - Sergei BondarchukSergei BondarchukSergei Fedorovich Bondarchuk was a Soviet film director, screenwriter, and actor.- Biography :Born in Belozerka, in the Kherson Governorate, Sergei Bondarchuk spent his childhood in the cities of Yeysk and Taganrog, graduating from the Taganrog School Number 4 in 1938. His first performance as an...
, Soviet, Ukrainian-born film director, screenwriter, and actor. - Abram Petrovich GannibalAbram Petrovich GannibalMajor-General Abram Petrovich Gannibal, also Hannibal or Ganibal or Ibrahim Hannibal or Abram Petrov , was brought to Russia as a gift for Peter the Great and became major-general, military engineer, governor of Reval and nobleman of the Russian Empire...
, founder of the city - Yefim GolïshevYefim GolïshevYefim Golyshev was a Ukrainian-born painter and composer who was mainly active in Europe.After a successful career as a child prodigy violinist and the Reger Prize from Berlin's Stern Conservatory, Golyshev became one of the founding members of the Dadaist November Group, painting "anti-art"...
(1897–1970) PainterPaintingPainting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a surface . The application of the medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush but other objects can be used. In art, the term painting describes both the act and the result of the action. However, painting is...
and composerComposerA composer is a person who creates music, either by musical notation or oral tradition, for interpretation and performance, or through direct manipulation of sonic material through electronic media...
associated with the DadaDadaDada or Dadaism is a cultural movement that began in Zurich, Switzerland, during World War I and peaked from 1916 to 1922. The movement primarily involved visual arts, literature—poetry, art manifestoes, art theory—theatre, and graphic design, and concentrated its anti-war politics through a...
movement in BerlinBerlinBerlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
. - Nikolai GrinkoNikolai GrinkoNikolai Grigoryevich Grinko or Mykola Hryhorovych Hrynko , was a Soviet/Ukrainian actor.He is well known for his roles in the films of Andrei Tarkovsky, including: Ivan's Childhood, Andrei Rubliov, Solaris, Mirror, and Stalker. He starred in the 1981 film Teheran 43.-External links:...
, Ukrainian Soviet-era film actor - John HowardJohn Howard (prison reformer)John Howard was a philanthropist and the first English prison reformer.-Birth and early life:Howard was born in Lower Clapton, London. His father, also John, was a wealthy upholsterer at Smithfield Market in the city...
(died in Kherson in 1790) - Mircea Ionescu-QuintusMircea Ionescu-QuintusMircea Ionescu-Quintus is a Romanian politician, former Senator and Minister of Justice.-External links:...
, a Romanian politicianPoliticianA politician, political leader, or political figure is an individual who is involved in influencing public policy and decision making...
, writerWriterA writer is a person who produces literature, such as novels, short stories, plays, screenplays, poetry, or other literary art. Skilled writers are able to use language to portray ideas and images....
, and juristJuristA jurist or jurisconsult is a professional who studies, develops, applies, or otherwise deals with the law. The term is widely used in American English, but in the United Kingdom and many Commonwealth countries it has only historical and specialist usage... - Evgeny KucherevskyEvgeny KucherevskyYevhen Mefodiyovych Kucherevskyi was a Ukrainian football coach. He is most famous for his spells managing Dnipro Dnipropetrovsk, which, under his helm, won the Soviet Championship in 1988, took 2nd place twice in 1987 and 1989, as well as the USSR Cup in 1989...
, Ukrainian football coach of Dnipro Dnipropetrovsk (died 2006) - Larisa Latynina, a Soviet gymnastGymnastGymnasts are people who participate in the sports of either artistic gymnastics, trampolining, or rhythmic gymnastics.See gymnasium for the origin of the word gymnast from gymnastikos.-Female artistic:Australia...
who was the first female athlete to win nine OlympicOlympic GamesThe Olympic Games is a major international event featuring summer and winter sports, in which thousands of athletes participate in a variety of competitions. The Olympic Games have come to be regarded as the world’s foremost sports competition where more than 200 nations participate...
gold medals - Tatiana LysenkoTatiana LysenkoTatiana Felixivna Lysenko is a Soviet and Ukrainian gymnast, who had her senior competitive career from 1990 to 1994.She is Jewish. Tatiana was known for her exceptional difficulty level and haughty style on the floor...
, a Soviet and Ukrainian gymnastGymnastGymnasts are people who participate in the sports of either artistic gymnastics, trampolining, or rhythmic gymnastics.See gymnasium for the origin of the word gymnast from gymnastikos.-Female artistic:Australia...
who won the gold medal on the balance beam at the 1992 Summer Olympics1992 Summer OlympicsThe 1992 Summer Olympic Games, officially known as the Games of the XXV Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event celebrated in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, in 1992. The International Olympic Committee voted in 1986 to separate the Summer and Winter Games, which had been held in the same...
in BarcelonaBarcelonaBarcelona is the second largest city in Spain after Madrid, and the capital of Catalonia, with a population of 1,621,537 within its administrative limits on a land area of...
. - Grigory Potyomkin, founder of the city
- Salomon Rosenblum, later known as Lieutenant Sidney ReillySidney ReillyLieutenant Sidney George Reilly, MC , famously known as the Ace of Spies, was a Jewish Russian-born adventurer and secret agent employed by Scotland Yard, the British Secret Service Bureau and later the Secret Intelligence Service . He is alleged to have spied for at least four nations...
, a secret agentSecret AgentSecret Agent is a British film directed by Alfred Hitchcock, loosely based on two stories in Ashenden: Or the British Agent by W. Somerset Maugham. The film starred John Gielgud, Peter Lorre, Madeleine Carroll, and Robert Young...
and international adventurer and playboy who was at one time employed by the British Secret Intelligence ServiceSecret Intelligence ServiceThe Secret Intelligence Service is responsible for supplying the British Government with foreign intelligence. Alongside the internal Security Service , the Government Communications Headquarters and the Defence Intelligence , it operates under the formal direction of the Joint Intelligence...
. He is reputed to be the real inspiration for Ian Fleming's spy character, James BondJames BondJames Bond, code name 007, is a fictional character created in 1953 by writer Ian Fleming, who featured him in twelve novels and two short story collections. There have been a six other authors who wrote authorised Bond novels or novelizations after Fleming's death in 1964: Kingsley Amis,...
. - Moshe SharettMoshe SharettMoshe Sharett on 15 October 1894, died 7 July 1965) was the second Prime Minister of Israel , serving for a little under two years between David Ben-Gurion's two terms.-Early life:...
, the second Prime Minister of IsraelPrime Minister of IsraelThe Prime Minister of Israel is the head of the Israeli government and the most powerful political figure in Israel . The prime minister is the country's chief executive. The official residence of the prime minister, Beit Rosh Hamemshala is in Jerusalem...
(1953–1955) - Sergei Stanishev, Ex-Prime Minister of Bulgaria
- Alexander SuvorovAlexander SuvorovAlexander Vasilyevich Suvorov , Count Suvorov of Rymnik, Prince in Italy, Count of the Holy Roman Empire , was the fourth and last generalissimo of the Russian Empire.One of the few great generals in history who never lost a battle along with the likes of Alexander...
, founder of the city - Lev Davidovitch Bronstein, Leon TrotskyLeon TrotskyLeon Trotsky , born Lev Davidovich Bronshtein, was a Russian Marxist revolutionary and theorist, Soviet politician, and the founder and first leader of the Red Army....
, BolshevikBolshevikThe Bolsheviks, originally also Bolshevists , derived from bol'shinstvo, "majority") were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which split apart from the Menshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903....
revolutionary and Marxist theorist was born in Kherson in 1879. - Mikhail YemtsevMikhail YemtsevMikhail Yemtsev - Soviet and Russian science fiction writer who worked mostly in collaboration with Yeremey Parnov.-Collaborative works with Yeremey Parnov:Collected stories...
, science fiction writer
Sister Cities
RzeszówRzeszów
Rzeszów is a city in southeastern Poland with a population of 179,455 in 2010. It is located on both sides of the Wisłok River, in the heartland of the Sandomierska Valley...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
Zalaegerszeg
Zalaegerszeg
In 2001 Zalaegerszeg had 61,654 inhabitants . The distribution of religions were, 71.1% Roman Catholic, 3.8% Calvinist, 1.6% Lutheran, 11.6% Atheist .-Notable people:* Lajos Botfy , mayor...
, Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
Shumen
Shumen
Shumen is the tenth-largest city in Bulgaria and capital of Shumen Province. In the period 1950–1965 it was called Kolarovgrad, after the name of the communist leader Vasil Kolarov...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
Kent
Kent, Washington
Kent is a city located in King County, Washington, United States, and is the third largest city in King County and the sixth largest in the state. An outlying suburb of Seattle, Kent is also the corporate home for companies such as REI and Oberto Sausage...
, United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Zonguldak
Zonguldak
Zonguldak is a city and the capital of Zonguldak Province in the Black Sea region of Turkey. Its population, according to the 2009 census, was 108,792. It is an important port on the Black Sea because of the coal mining in Zonguldak Province...
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
Oslo
Oslo
Oslo is a municipality, as well as the capital and most populous city in Norway. As a municipality , it was established on 1 January 1838. Founded around 1048 by King Harald III of Norway, the city was largely destroyed by fire in 1624. The city was moved under the reign of Denmark–Norway's King...
, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
External links
- Pictures of Kherson
- Kherson city administration website
- Kherson patriots
- Kherson info&shopping
- List of cities of Ukraine by population
- List of cities of Ukraine by subdivisions

