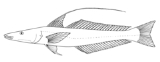
Gangetic whiting
Encyclopedia
The Gangetic whiting, Sillaginopsis panijus (also known as the flathead sillago), is a species
of inshore marine
and estuarine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae
. It is the most distinctive Asia
n member of the family due to its flattened head and trailing dorsal fin
s. Although first described in 1822, it was not placed in its own genus until 1861 when Theodore Gill
erected Sillaginopsis, a genus which is still monotypic. Gangetic whiting are of minor commercial importance
along the Southeast coast
of the Asian continent where it inhabits protected areas.
, containing all the smelt whitings. The Sillaginidae are part of the Percoidei
, a suborder of the order Perciformes
.
The Gangetic whiting was originally named Cheilodipterus panijus in 1822 by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton
from a holotype
taken from the Ganges estuary
in India
. The species was further examined by Gill in 1861 in the first review of the family, entitled "Synopsis of the Sillaginoids", which lead to the creation of the genus Sillaginopsis. This new classification changed the binomial name
to the currently accepted Sillaginopsis panijus.
of the species is highly depressed, like that of the flatheads
, with very small eyes well constricted by the orbits
. The first dorsal fin
contains ten spines including a large trailing second spine; the second dorsal fin has one spine and 25 to 27 soft rays. The anal fin has two spines and 24 to 27 soft rays. There are 84 to 90 lateral line
scales
and the species has a total of 42 vertebrae. The species is known to grow to a length of 44 cm.
Another unique feature of this species is its severe reduction or even absence of a swim bladder, which all other members of the family Sillaginidae possess. The Gangetic whiting also has a small mouth with a much shorter lower jaw
than upper jaw, with the two anteriormost teeth larger than the rest.
and the Ganges delta
, Myanmar
, Malaysia and occasionally as far south as the Indonesia
n archipelago
.
The species is often found on silt
y or mud
dy substrates in shallow, open bay
s and estuaries
along the coast. Juveniles
usually migrate into the upper reaches of estuaries for protection against predation
by larger species.
content analysis has found the Gangetic whiting consumes numerous small fish, benthic
and plankton
ic crustacean
s and algae
, with its small mouth size restricting the size of food portions.
The Gangetic whiting is the only known species of fish to host the intestinal parasite
Dichelyne alatae
, found in specimens in West Bengal
, with a number of other parasites identified from it.
Otolith
and size-age composition studies by Krishnayya (1963) of the commercial catches from the Hooghly River estuary and found that S. panijus probably spawn
s twice a year during the periods of November to February and August to September. The juveniles migrate toward the upper reaches during March and April and during December where they remain for two to three months. Sexual maturity
is attained at a length of about 120 mm.
exists along the coast of the Bay of Bengal
primarily near or on the river delta
s, with commercially important fish captured by nets
and longlines
in the Hooghly and Ganges delta. The Gangetic whiting is sold fresh in local market
s, rarely making its way to overseas markets. Juvenile Sillaginopsis panijus are also occasionally traded as brackish water
aquarium fish.
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
of inshore marine
Marine (ocean)
Marine is an umbrella term. As an adjective it is usually applicable to things relating to the sea or ocean, such as marine biology, marine ecology and marine geology...
and estuarine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae
Sillaginidae
The Sillaginidae, commonly known as the smelt-whitings, whitings, sillaginids, sand borers and sand-smelts, are a family of benthic coastal marine fishes in the order Perciformes. The smelt-whitings inhabit a wide region covering much of the Indo-Pacific, from the west coast of Africa east to Japan...
. It is the most distinctive Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
n member of the family due to its flattened head and trailing dorsal fin
Dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the backs of various unrelated marine and freshwater vertebrates, including most fishes, marine mammals , and the ichthyosaurs...
s. Although first described in 1822, it was not placed in its own genus until 1861 when Theodore Gill
Theodore Gill
Theodore Nicholas Gill was an American ichthyologist, mammalogist, malacologist and librarian.Born and educated in New York City under private tutors, Gill early showed interest in natural history. He was associated with J...
erected Sillaginopsis, a genus which is still monotypic. Gangetic whiting are of minor commercial importance
Fishery
Generally, a fishery is an entity engaged in raising or harvesting fish which is determined by some authority to be a fishery. According to the FAO, a fishery is typically defined in terms of the "people involved, species or type of fish, area of water or seabed, method of fishing, class of boats,...
along the Southeast coast
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
of the Asian continent where it inhabits protected areas.
Taxonomy and naming
The Gangetic whiting is the only species of the genus Sillaginopsis, which itself is one of three genera the family SillaginidaeSillaginidae
The Sillaginidae, commonly known as the smelt-whitings, whitings, sillaginids, sand borers and sand-smelts, are a family of benthic coastal marine fishes in the order Perciformes. The smelt-whitings inhabit a wide region covering much of the Indo-Pacific, from the west coast of Africa east to Japan...
, containing all the smelt whitings. The Sillaginidae are part of the Percoidei
Percoidei
Percoidei is one of eighteen suborders of bony fish in the order Perciformes. Many commercially harvested fish species are contained in this suborder, including the snappers, jacks, whitings, groupers, bass, perches and porgies.-Divisions:...
, a suborder of the order Perciformes
Perciformes
The Perciformes, also called the Percomorphi or Acanthopteri, is one of the largest orders of vertebrates, containing about 40% of all bony fish. Perciformes means perch-like. They belong to the class of ray-finned fish and comprise over 7,000 species found in almost all aquatic environments...
.
The Gangetic whiting was originally named Cheilodipterus panijus in 1822 by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton
Francis Buchanan-Hamilton
Dr Francis Buchanan, later known as Francis Hamilton but often referred to as Francis Buchanan-Hamilton was a Scottish physician who made significant contributions as a geographer, zoologist, and botanist while living in India.The standard botanical author abbreviation Buch.-Ham. is applied to...
from a holotype
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example of an organism, known to have been used when the species was formally described. It is either the single such physical example or one of several such, but explicitly designated as the holotype...
taken from the Ganges estuary
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. The species was further examined by Gill in 1861 in the first review of the family, entitled "Synopsis of the Sillaginoids", which lead to the creation of the genus Sillaginopsis. This new classification changed the binomial name
Binomial nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages...
to the currently accepted Sillaginopsis panijus.
Description
The distinct appearance of the Gangetic whiting makes it the easiest of the smelt whitings to identify. The headHead
In anatomy, the head of an animal is the rostral part that usually comprises the brain, eyes, ears, nose and mouth . Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do....
of the species is highly depressed, like that of the flatheads
Platycephalidae
Platycephalidae is a family of marine fishes, most commonly referred to as flatheads. They are relatives of the popular lionfishes, belonging to the order Scorpaeniformes....
, with very small eyes well constricted by the orbits
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
. The first dorsal fin
Dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the backs of various unrelated marine and freshwater vertebrates, including most fishes, marine mammals , and the ichthyosaurs...
contains ten spines including a large trailing second spine; the second dorsal fin has one spine and 25 to 27 soft rays. The anal fin has two spines and 24 to 27 soft rays. There are 84 to 90 lateral line
Lateral line
The lateral line is a sense organ in aquatic organisms , used to detect movement and vibration in the surrounding water. Lateral lines are usually visible as faint lines running lengthwise down each side, from the vicinity of the gill covers to the base of the tail...
scales
Scale (zoology)
In most biological nomenclature, a scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of an animal's skin to provide protection. In lepidopteran species, scales are plates on the surface of the insect wing, and provide coloration...
and the species has a total of 42 vertebrae. The species is known to grow to a length of 44 cm.
Another unique feature of this species is its severe reduction or even absence of a swim bladder, which all other members of the family Sillaginidae possess. The Gangetic whiting also has a small mouth with a much shorter lower jaw
Jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term jaws is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of...
than upper jaw, with the two anteriormost teeth larger than the rest.
Distribution and habitat
The Gangetic whiting is found on the southern Asian coast from Pondicherry in the east, northward along the Coromandel CoastCoromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the name given to the southeastern coast of the Indian Subcontinent between Cape Comorin and False Divi Point...
and the Ganges delta
Ganges Delta
The Ganges Delta is a river delta in the South Asia region of Bengal, consisting of Bangladesh and the state of West Bengal, India. It is the world's largest delta, and empties into the Bay of Bengal...
, Myanmar
Myanmar
Burma , officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar , is a country in Southeast Asia. Burma is bordered by China on the northeast, Laos on the east, Thailand on the southeast, Bangladesh on the west, India on the northwest, the Bay of Bengal to the southwest, and the Andaman Sea on the south....
, Malaysia and occasionally as far south as the Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
n archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
.
The species is often found on silt
Silt
Silt is granular material of a size somewhere between sand and clay whose mineral origin is quartz and feldspar. Silt may occur as a soil or as suspended sediment in a surface water body...
y or mud
Mud
Mud is a mixture of water and some combination of soil, silt, and clay. Ancient mud deposits harden over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone . When geological deposits of mud are formed in estuaries the resultant layers are termed bay muds...
dy substrates in shallow, open bay
Bay
A bay is an area of water mostly surrounded by land. Bays generally have calmer waters than the surrounding sea, due to the surrounding land blocking some waves and often reducing winds. Bays also exist as an inlet in a lake or pond. A large bay may be called a gulf, a sea, a sound, or a bight...
s and estuaries
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
along the coast. Juveniles
Juvenile (organism)
A juvenile is an individual organism that has not yet reached its adult form, sexual maturity or size. Juveniles sometimes look very different from the adult form, particularly in terms of their colour...
usually migrate into the upper reaches of estuaries for protection against predation
Predation
In ecology, predation describes a biological interaction where a predator feeds on its prey . Predators may or may not kill their prey prior to feeding on them, but the act of predation always results in the death of its prey and the eventual absorption of the prey's tissue through consumption...
by larger species.
Biology
GutGut (zoology)
In zoology, the gut, also known as the alimentary canal or alimentary tract, is a tube by which bilaterian animals transfer food to the digestion organs. In large bilaterians the gut generally also has an exit, the anus, by which the animal disposes of solid wastes...
content analysis has found the Gangetic whiting consumes numerous small fish, benthic
Benthic zone
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean or a lake, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. Organisms living in this zone are called benthos. They generally live in close relationship with the substrate bottom; many such...
and plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
ic crustacean
Crustacean
Crustaceans form a very large group of arthropods, usually treated as a subphylum, which includes such familiar animals as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill and barnacles. The 50,000 described species range in size from Stygotantulus stocki at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span...
s and algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
, with its small mouth size restricting the size of food portions.
The Gangetic whiting is the only known species of fish to host the intestinal parasite
Intestinal parasite
Intestinal parasites are parasites that populate the gastro-intestinal tract in humans and other animals. They can live throughout the body, but most prefer the intestinal wall. Means of exposure include: ingestion of undercooked meat, drinking infected water, and skin absorption...
Dichelyne alatae
Dichelyne alatae
Dichelyne alatae is a species of nematode, described on the basis of the worms recovered from the intestine of the whiting, Sillaginopsis panijus from the estuary of the Hooghly River at Kalyani, West Bengal, India...
, found in specimens in West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
, with a number of other parasites identified from it.
Otolith
Otolith
An otolith, , also called statoconium or otoconium is a structure in the saccule or utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular labyrinth of vertebrates. The saccule and utricle, in turn, together make the otolith organs. They are sensitive to gravity and linear acceleration...
and size-age composition studies by Krishnayya (1963) of the commercial catches from the Hooghly River estuary and found that S. panijus probably spawn
Spawn (biology)
Spawn refers to the eggs and sperm released or deposited, usually into water, by aquatic animals. As a verb, spawn refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, also called spawning...
s twice a year during the periods of November to February and August to September. The juveniles migrate toward the upper reaches during March and April and during December where they remain for two to three months. Sexual maturity
Sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the age or stage when an organism can reproduce. It is sometimes considered synonymous with adulthood, though the two are distinct...
is attained at a length of about 120 mm.
Relationship to humans
A local fisheryFishery
Generally, a fishery is an entity engaged in raising or harvesting fish which is determined by some authority to be a fishery. According to the FAO, a fishery is typically defined in terms of the "people involved, species or type of fish, area of water or seabed, method of fishing, class of boats,...
exists along the coast of the Bay of Bengal
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal , the largest bay in the world, forms the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. It resembles a triangle in shape, and is bordered mostly by the Eastern Coast of India, southern coast of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to the west and Burma and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to the...
primarily near or on the river delta
River delta
A delta is a landform that is formed at the mouth of a river where that river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, flat arid area, or another river. Deltas are formed from the deposition of the sediment carried by the river as the flow leaves the mouth of the river...
s, with commercially important fish captured by nets
Fishing net
A fishing net or fishnet is a net that is used for fishing. Fishing nets are meshes usually formed by knotting a relatively thin thread. Modern nets are usually made of artificial polyamides like nylon, although nets of organic polyamides such as wool or silk thread were common until recently and...
and longlines
Long-line fishing
Longline fishing is a commercial fishing technique. It uses a long line, called the main line, with baited hooks attached at intervals by means of branch lines called "snoods". A snood is a short length of line, attached to the main line using a clip or swivel, with the hook at the other end....
in the Hooghly and Ganges delta. The Gangetic whiting is sold fresh in local market
Market
A market is one of many varieties of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations and infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services in exchange for money from buyers...
s, rarely making its way to overseas markets. Juvenile Sillaginopsis panijus are also occasionally traded as brackish water
Brackish water
Brackish water is water that has more salinity than fresh water, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing of seawater with fresh water, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root "brak," meaning "salty"...
aquarium fish.

