Economy of Armenia
Encyclopedia
Armenia
is the second most densely populated of the former Soviet republics
. It is situated between the Black Sea
and the Caspian Sea
, bordered on the north and east by Georgia
and Azerbaijan
and on the south and west by Iran
and Turkey
.
According to Forbes magazine
Armenia had the second second worst economy in the world in 2011.
Until independence, Armenia's economy was based largely on industry
—chemicals
, electronic products
, machinery, processed food, synthetic rubber
and textiles; it was highly dependent on outside resources. Agriculture
accounted for only 20% of net material product and 10% of employment before the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991. Armenian mines produce copper
, zinc
, gold
and lead
. The vast majority of energy is produced with imported fuel, including gas and nuclear fuel (for its one nuclear power plant) from Russia; the main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. Small amounts of coal, gas and petroleum have not yet been developed.
Like other former States, Armenia's economy suffers from the legacy of a centrally planned economy and the breakdown of former Soviet trading patterns. Soviet investment in and support of Armenian industry has virtually disappeared, so that few major enterprises are still able to function. In addition, the effects of the 1988 earthquake, which killed more than 25,000 people and made 500,000 homeless, are still being felt. Although a cease-fire has held since 1994, the conflict with Azerbaijan
over Nagorno-Karabakh
has not been resolved. The consequent blockade along both the Azerbaijani and Turkish borders has devastated the economy, because of Armenia's dependence on outside supplies of energy and most raw materials. Land routes through Azerbaijan and Turkey are closed; routes through Georgia and Iran are inadequate or unreliable. In 1992-93, GDP fell nearly 60% from its 1989 level. The national currency, the dram
, suffered hyperinflation
for the first few years after its introduction in 1993.
Nevertheless, the Government of Armenia, helped by the cease-fire that has been in effect in Nagorno-Karabakh
since 1994, has been able to carry out wideranging economic reforms which paid off in dramatically lower inflation and steady growth. Armenia has registered strong economic growth since 1995, building on the turnaround that began the previous year, and inflation has been negligible for the past several years. New sectors, such as precious stone processing and jewelry making, information and communication technology, and even tourism are beginning to supplement more traditional sectors such as agriculture in the economy.
This steady economic progress has earned Armenia increasing support from international institutions. The IMF, World Bank
, EBRD, as well as other IFIs and foreign countries are extending considerable grants and loans. Total loans extended to Armenia since 1993 exceed $800 million. These loans are targeted at reducing the budget deficit, stabilizing the local currency; developing private businesses; energy; the agriculture, food processing, transportation, and health and education sectors; and ongoing rehabilitation work in the earthquake zone.
Continued progress will depend on the ability of the government to strengthen its macroeconomic management, including increasing revenue collection, improve the investment climate, and accelerate the privatization process. A liberal foreign investment law was approved in June 1994, and a Law on Privatization was adopted in 1997, as well as a program on state property privatization. The government has made major strides toward joining the World Trade Organization. By 1994, however, the Armenian Government had launched an ambitious IMF-sponsored economic liberalization program that resulted in positive growth rates in 1995-2005. Armenia joined the WTO in January 2003. Armenia also has managed to slash inflation, stabilize its currency, and privatize most small- and medium-sized enterprises. Armenia's unemployment rate, however, remains high, despite strong economic growth. The chronic energy shortages Armenia suffered in the early and mid-1990s have been offset by the energy supplied by one of its nuclear power plants at Metsamor
. Armenia is now a net energy exporter, although it does not have sufficient generating capacity to replace Metsamor, which is under international pressure to close. The electricity distribution system was privatized in 2002. Armenia's severe trade imbalance has been offset somewhat by international aid, remittances from Armenians working abroad, and foreign direct investment
. Economic ties with Russia
remain close, especially in the energy sector. The government made some improvements in tax and customs administration in 2005, but anti-corruption measures have been more difficult to implement. Investment in the construction
and industrial
sectors is expected to continue in 2006 and will help to ensure annual average real GDP growth of about 13.9%.
deposits (gold
, bauxite
) are small. The ongoing conflict with Azerbaijan over the ethnic Armenian-dominated region of Nagorno-Karabakh (which was part of Soviet Azerbaijan) and the breakup of the centrally directed economic system
of the former Soviet Union contributed to a severe economic decline in the early 1990s. By 1994, however, the Armenian Government had launched an ambitious IMF-sponsored economic program that has resulted in positive growth rates in 1995-99. Armenia also managed to slash inflation and to privatize most small- and medium-sized enterprises. The chronic energy shortages Armenia suffered in recent years have been largely offset by the energy supplied by one of its nuclear power plants at Metsamor. Continued Russian financial difficulties have hurt the trade sector especially, but have been offset by international aid, domestic restructuring and foreign direct investment.
emerged from the umbra
of the former Soviet Union
in 1991 and migrated from a centrally planned economy (Communist system) to a market economy
(capitalist
system). Both the nation
and the economy
are nascent
. Regional conflict retards economic growth
. In addition, the border with Turkey
is closed, making access to sea ports difficult and transportation logistics
challenging to a country largely dependent upon imports. In 2003, Armenia became a member of the WTO (World Trade Organization
). The nation is making substantial progress in privatizing ownership of what used to be State Owned industries under the former Soviet system. Despite marked progress, Armenia still suffers from a large trade imballance and is still largely dependent upon foreign aid and remittances from Armenian nationals working abroad, and members of the diaspora
donating aid through NGOs (non-governmental organizations) such as the church. There are some foreign capital inflows, but no robust foreign investment. Despite progress since the Soviet era, the unemployment rate still hovers near 30% and there remains a huge gulf between actual and potential Gross Domestic Product
.
, Namibia
, Georgia
, Serbia
and Pakistan
).
Despite pronouncements at the highest levels of government on the importance of free competition, Armenia is next to last in the effectiveness of its anti-monopoly policy according to the 2010 results of the World Economic Forum Global Competitiveness Report.
According to Vahram Nercissiantz, President Sarkisian's chief economic adviser, "Businessmen holding state positions have turned into oligarchs who have avoided paying sufficient taxes by abusing their state positions, distorted markets with unequal conditions, breached the rules of competition, impeded or prevented small and medium-sized business’ entry into manufacturing and thereby sharply deepened social polarization in the republic.
Following the advice of economic advisors who cautioned Armenia's leadership against the consolidation of economic power in the hands of a few, in January 2001, the Government of Armenia established the State Commission for the Protection of Economic Competition. Its members cannot be dismissed by the government.
or oligopoly
." "The result is the prices with us do not drop even if they do on international market, or they do quite belated and not to the size of the international market."
According to the estimate of a former prime minister
, Hrant Bagratian, 55 percent of Armenia's GDP is controlled by 44 families.
In early 2008, the State Commission for the Protection of Economic Competition named 60 companies having "dominant positions" in Armenia.
In October 2009, when visiting Yerevan
, the World Bank’s
managing director, Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
, warned that Armenia will not reach a higher level of development unless its leadership changes the "oligopolistic" structure of the national economy, bolsters the rule of law and shows "zero tolerance" towards corruption. "I think you can only go so far with this economic model," Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala told a news conference in Yerevan. "Armenia is a lower middle-income country. If it wants to become a high-income or upper middle-income country, it can not do so with this kind of economic structure. That is clear." She also called for a sweeping reform
of tax and customs administration, the creation of a "strong and independent judicial system" as well as a tough fight against government corruption. The warning was echoed by the International Monetary Fund
.
Major monopolies in Armenia include:
Former major monopolies in Armenia include:
of Armenia stood at 8.8 billion US dollars in 2010; with a population of 3.2 million, this amounts to a GDP per capita of $2,676 (purchasing power parity
$5,178). GDP growth for 2010 was at 2.9 percent, and inflation was at 8 percent.
GDP growth is expected to be around 3 percent in 2011, with inflation returning to 4-5 percent.
In comparison, in 2006, the GDP was estimated to be 6.6 billion USD per calendar year and the GDP per capita (purchasing power parity) was estimated at $5,400 US. The growth rate
was high at 13.4%, but the relatively low base must be considered. Low inflation
was maintained around 2.6% annually.
According to official figures, Armenia’s economy grew by 13.8 percent in 2007. According to research funded by the USAID CAPS project, Armenia's exceptionally high rate of economic growth during the last decade has been largely dependent on external factors (e.g. remittances, assistance from international financial and donor organization). Furthermore, the study concluded that despite its record growth on most macro-economic metrics, Armenia is "low and lagging" in competitiveness.
According to the National Statistical Service, the booming construction and service sectors remain the driving forces of the high growth rate of GDP.
sent back home from Armenians working abroad—mostly in Russia and the United States—are growing and contribute significantly to Armenia's Gross Domestic Product (between 15 to 30 percent). They help Armenia sustain double-digit economic growth and finance its massive trade deficit.
According to the Central Bank of Armenia
, during the first half of 2008, cash remittances sent back to Armenia by Armenians working abroad rose by 57.5 percent and totaled $668.6 million USD, equivalent to 15 percent of the country's first-half Gross Domestic Product. However, the latter figures only represent cash remittances processed through Armenian commercial banks. According to RFE/RL, comparable sums are believed to be transferred through non-bank systems, implying that cash remittances make up approximately 30 percent of Armenia's GDP in the first half of 2008.
In 2007, cash remittances through bank transfers rose by 37 percent to a record-high level of $1.32 billion USD. According to the Central Bank of Armenia, in 2005, cash remittances from Armenians working abroad reached a record-high level of $1 billion, which is worth more than one fifth of the country’s 2005 Gross Domestic Product.
Net private transfers decreased in 2009, but saw a continuous increase during the first six months of 2010. Since private transfers from the Diaspora tend to be mostly injected into consumption of imports and not in high value-added sectors, the transfers have not resulted in sizeable increases in productivity.
However, during the January to September 2010 period, the sector experienced a 5.2 percent year-on-year decrease, which according to the Civilitas Foundation
is an indication of the unsustainability of a sector based on an elite market, with few products for the median or low budgets. This decrease comes despite the fact that an important component of the government stimulus package was to support the completion of ongoing construction projects.
However, according to private tour operators and other individuals familiar with the country’s tourism industry, government claims that hundreds of thousands of foreign tourists visit Armenia each year are wide of the mark. Official statistics show that as many 575,000 tourists visited Armenia from abroad in 2009; the government stated earlier in 2010 that the figure will surpass 620,000 in 2010. However, data from the National Statistical Service shows that there were only 65,000 foreigners staying in Armenian hotels in 2009. Ara Vartanian, the chairman of the Armenian Trade and Industry Chamber, thinks that this measure is a far more objective indicator of the tourist influx into the country.
exports.
Armenia's agricultural output dropped by 17.9 percent in the period of January–September 2010. This was owing to bad weather, a lack of a government stimulus package, and the continuing effects of decreased agricultural subsidies by the Armenian government (per WTO
requirements).
through the United States Agency for International Development
and the Millennium Challenge Corporation
.
On March 27, 2006, the Millennium Challenge Corporation
signed a five-year, $235.65 million compact with the Government of Armenia. The single stated goal of the "Armenian Compact" is "the reduction of rural poverty through a sustainable increase in the economic performance of the agricultural sector." The Compact includes a $67 million to rehabilitate up to 943 kilometers of rural roads, more than a third of Armenia's proposed "Lifeline road network". The Compact also includes a $146 million project to increase the productivity of approximately 250,000 farm households through improved water supply, higher yields, higher-value crops, and a more competitive agricultural sector.
In 2010, the volume of US assistance to Armenia remained near 2009 levels; however, longer-term decline continued. The original Millennium Challenge Account commitment for $235 million had been reduced to about $175 million due to Armenia’s poor governance record. Thus, the MCC would not complete road construction. Instead, the irrigated agriculture project was headed for completion with apparently no prospects for extension beyond 2011.
According to the National Statistical Service, Armenia's trade deficit in 2006 was $1.2 billion with growth in exports being largely flat. During the first 11 months of 2006, net imports grew by 21 percent to $1.95 billion, while exports stood at $895 million, up 0.3 percent from the same period in 2005.
During January–February 2007, Armenia’s trade with the European Union
totaled $200 million. During the first 11 months of 2006, the European Union remained Armenia's largest trading partner, accounting for 34.4 percent of its $2.85 billion commercial exchange during the 11-month period.
During January–February 2007, Armenia’s trade with Russia
and other former Soviet republics was $205.6 million (double the amount from the same period the previous year), making them the country’s number one trading partner. During the first 11 months of 2006, the volume of Armenia’s trade with Russia was $376.8 million or 13.2 percent of the total commercial exchange.
During the first 11 months of 2006, U.S.-Armenian trade totaled $152.6 million.
As of late November 2009, the Armenian government's foreign debt was around $3 billion USD, having doubled in size over the course of the previous year. With the Armenian government needing more anti-crisis loans from the World Bank and other foreign donors, the debt-to-GDP ratio is expected to exceed 40 percent in 2010. According to a World Bank official, a country that has around 12 percent rate of growth or even lower, at the range of 7 to 8 percent, can afford a level of public debt of up to 50 percent. The official warned that the debt servicing payments of the Armenian government will surge by 2013 and absorb "quite significant part of tax revenues."
According to another estimate, the ratio between the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and the state's foreign debt has reached 46 percent. Economists generally agree that a country is insolvent
, if its foreign debt surpasses 50 percent of its GDP. Critics of the government say that the $500 million credit from Russia should have gone to develop industry, instead of going to the construction sector.
The only operational rail link into Armenia is from Georgia
. During Soviet times, Armenia's rail network connected to Russia's via Georgia through Abkhazia
along the Black Sea
. However, the rail link between Abkhazia and Georgia proper has been closed for a number of years, forcing Armenia to receive rail cars laden with cargo only through the relatively expensive rail-ferry services operating between Georgian and other Black Sea ports.
The Georgian Black Sea ports of Batumi
and Poti
process more than 90 percent of freight shipped to and from landlocked Armenia. The Georgian railway, which runs through the town of Gori in central Georgia, is the main transport link between Armenia and the aforementioned Georgian seaports. Fuel, wheat and other basic commodities are transported to Armenia by rail.
Armenia's main rail and road border-crossing with Georgia (at 41°13′41.97"N 44°50′9.12"E) is along the Debed river near the Armenian town of Bagratashen
and the Georgian town of Sadakhlo
.
The Upper Lars border crossing (at Darial Gorge
) between Georgia and Russia across the Caucasus Mountains
served as Armenia's sole overland route to the former Soviet Union and Europe. It was controversially shut down by the Russian authorities in June 2006, at the height of a Russian-Georgian spy scandal. Upper Lars is the only land border crossing that does not go through Georgia's Russian-backed breakaway regions of South Ossetia
and Abkhazia
. The other two roads linking Georgia and Russia run through South Ossetia and Abkhazia, effectively barring them to international traffic. This crossing is expected to reopen starting on March 1, 2010.
and Azerbaijan
has cut Armenia's rail link between Gyumri and Kars
to Turkey; the rail link with Iran through the Azeri exclave of Nakhichevan; and a natural gas and oil pipeline line with Azerbaijan. Also non-functioning are roads with Turkey and Azerbaijan. Despite the economic blockade of Turkey on Armenia, every day dozens of Turkish trucks laden with goods enter Armenia through Georgia.
In 2010, it was confirmed that Turkey will keep the border closed for the foreseeable future after the Turkey-Armenia normalization process collapsed.
has been completed, and a road to Iran through the southern city of Meghri
allows trade with that country. An oil pipeline to pump Iranian oil products is also in the planning stages.
As of October 2008, the Armenian government is considering implementing an ambitious project to build a railway to Iran. The 400 kilometer railway would pass through Armenia's mountainous southern province of Syunik
which borders Iran. Economic analysts say that the project would cost at least $1 billion (equivalent to about 40 percent of Armenia's 2008 state budget). As of 2010, the project has been continuously delayed, with the rail link estimated to cost as much as $4 billion and stretch 313 km (194.5 mi). In June 2010, Transport Minister Manuk Vartanian revealed that Yerevan is seeking as much as $1 billion in loans from China to finance the railway’s construction.
in Armenia for the first half of 2007 was 70,700 dram
s (about $210 USD).
As of April 24, 2008, the average monthly salary
is 75,000 drams (about $242 US dollars). According to the ROA National Statistical Service, the average monthly salary during January - June 2008 is 86,850 drams (about $287 at the time). About 62% of officially registered wage earners earn at least the average monthly wage, while only 19.6% receive a monthly salary of over 100,000 drams (about $330 at the time).
According to an OSCE survey, a typical Armenian migrant worker
is a married man aged between 41 and 50 years who "began looking for work abroad at the age of 32-33."
The AMD/USD exchange rate depreciated by 6.1 percent in the first three quarters of 2010 compared to the same period in 2009, before it began to show the expected end-of-the-year appreciation. In comparison between the January to October periods of 2010 and 2009, depreciation stands at 4.7 percent.
Many large companies have a privileged status when it comes to taxation. Big business is not taxed in proportion to its capacity and output, and the disproportionate burden falls on small and medium size businesses.
Armenian banking assets are very low and make up only 25 percent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
have allowed the success of this process.
In August 2002, the Armenian government sold an 80 percent stake in the Armenian Electricity Network (AEN) to Midland Resources, a British offshore-registered firm which is said to have close Russian connections.
In September 2002, the Armenian government handed over Armenia’s largest cement factory to the Russian ITERA
gas exporter in payment for its $10 million debt for past gas deliveries.
On November 5, 2002, Armenia transferred control of 5 state enterprises to Russia in an assets-for-debts transaction which settled $100 million of Armenian state debts to Russia. The document was signed for Russia by Prime Minister Mikhail Kasyanov
and Industry Minister Ilya Klebanov
, while Prime Minister Andranik Markarian and defense and security strongman Serge Sarkisian signed for Armenia. The five enterprises which passed to 100 percent Russian state ownership are:
In January 2003, the Armenian government and United Company RUSAL
signed an investment cooperation agreement, under which United Company RUSAL (which already owned a 76% stake) acquired the Armenian government's remaining 26% share of RUSAL ARMENAL
aluminum foil mill, giving RUSAL 100% ownership of RUSAL ARMENAL.
On November 1, 2006, the Armenian government handed de facto control of the Iran-Armenia gas pipeline to Russian company Gazprom
and increased Gazprom's stake in the Russian-Armenian company ArmRosGazprom
from 45% to 58% by approving an additional issue of shares worth $119 million. This left the Armenian government with a 32% stake in ArmRosGazprom. The transaction will also help finance ArmRosGazprom's acquisition of the Hrazdan electricity generating plant’s fifth power bloc (Hrazdan-5), the leading unit in the country.
In October 2008 the Russian bank Gazprombank
, the banking arm of Gazprom, acquired 100 percent of Armenian bank Areximbank after previously buying 80 percent of said bank in November 2007 and 94.15 percent in July of the same year.
Political observers say that Armenia's economic cooperation with Russia has been one of the least transparent areas of the Armenian government’s work. The debt arrangements have been personally negotiated by (then) Defense Minister (and now President) Serge Sarkisian, Kocharian’s closest political associate. Other top government officials, including Prime Minister Andranik Markarian, had little say on the issue. Furthermore, all of the controversial agreements have been announced after Sarkisian’s frequent trips to Moscow, without prior public discussion.
Finally, while Armenia is not the only ex-Soviet state that has incurred multimillion-dollar debts to Russia over the past decade, it is the only state to have so far given up such a large share of its economic infrastructure to Russia. For example, pro-Western Ukraine
and Georgia
(both of which owe Russia more than Armenia) have managed to reschedule repayment of their debts.
GDP $: $12.07 billion (2008)
GDP - real growth rate: 7.6% (2008)
GDP(per capita): $6,400 (2008)
GDP by sector
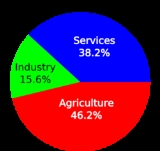
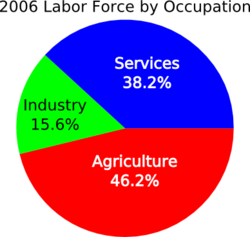
Agriculture: 17.2%
Industry: 36.4%
Services: 46.4%
Unemployment: 7.1% (2007)
Labour Force: 1.2 million (2007)
Labour Force - by occupation:
Population below poverty line:
Inflation: 4.4%
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 1.6%
highest 10%: 41.3% (2004)
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
Investment (gross fixed):
Central bank discount rate:
Stock of money:
Industries: Diamond processing, metal-cutting machine tools, forge-pressing machines, electric motors, tires, knitted wear, hosiery, shoes, silk fabric, chemicals, trucks, instruments, microelectronics, jewellery manufacturing, software development, food processing, brandy.
Agriculture - products:
Fruit
(especially grape
s and apricot
s), vegetables, livestock
, wheat
, wine
, brandy
Value of stock exchange: $42.8 million (2005)
Pig iron, unwrought copper
, nonferrous metals, cut diamond
s, mineral
products, foodstuffs, energy
Imports - commodities:
Natural gas
, petroleum
, tobacco
products, foodstuffs
, uncut diamond
s
Exports: $1.225 billion f.o.b. (2008)
country comparison to the world: 147
Imports: $3.546 billion f.o.b. (2008)
country comparison to the world: 132
Current account balance:
$-877 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 117
Export partners: Russia 17.5%, Netherlands 14.9%, Germany 14.7%, Ireland 11.1%, Belgium 8.7%, Georgia 7.6%, US 6.6%, Switzerland 4.3%, Bulgaria 4.1%, Ukraine 4% (2007)
Import partners: Russia 17.5%, Netherlands 14.9%, Germany 14.7%, Ireland 11.1%, Belgium 8.7%, Georgia 7.6%, US 6.6%, Switzerland 4.3%, Bulgaria 4.1%, Ukraine 4% (2007)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$1.657 billion (2007)
Debt - external:
$1.372 billion (2007)
Currency:
dram (AMD)
Currency code:
AMD
Exchange rates:
Armenian dram
per US dollar - 310.00 (2008), 457.69 (2005), 533.45 (2004), 578.76 (2003), 573.35 (2002), 555.08 (2001), 539.53 (2000)
5.544 GWh (2007)
country comparison to the world: 108
Electricity - consumption:
4.539 GWh (2006)
country comparison to the world: 109
Electricity - exports:
322.6 GWh; note - exports an unknown quantity to Georgia
; includes exports to Nagorno-Karabakh
(2007)
Electricity - imports:
400.6 GWh; note - imports an unknown quantity from Iran
(2007)
Oil - production:
0 oilbbl/d (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
Oil - consumption:
41090 oilbbl/d (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
Oil - exports:
0 oilbbl/d (2005)
country comparison to the world: 207
Oil - imports:
44670 oilbbl/d (2005)
country comparison to the world: 90
Natural gas - production:
0 m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
Natural gas - consumption:
2.05 billion m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
Natural gas - exports:
0 m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
Natural gas - imports:
2.05 billion m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
Armenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
is the second most densely populated of the former Soviet republics
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. It is situated between the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
and the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
, bordered on the north and east by Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan , officially the Republic of Azerbaijan is the largest country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west, and Iran to...
and on the south and west by Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
.
According to Forbes magazine
Forbes
Forbes is an American publishing and media company. Its flagship publication, the Forbes magazine, is published biweekly. Its primary competitors in the national business magazine category are Fortune, which is also published biweekly, and Business Week...
Armenia had the second second worst economy in the world in 2011.
Until independence, Armenia's economy was based largely on industry
Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
—chemicals
Chemical substance
In chemistry, a chemical substance is a form of matter that has constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. It cannot be separated into components by physical separation methods, i.e. without breaking chemical bonds. They can be solids, liquids or gases.Chemical substances are...
, electronic products
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, machinery, processed food, synthetic rubber
Synthetic rubber
Synthetic rubber is is any type of artificial elastomer, invariably a polymer. An elastomer is a material with the mechanical property that it can undergo much more elastic deformation under stress than most materials and still return to its previous size without permanent deformation...
and textiles; it was highly dependent on outside resources. Agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
accounted for only 20% of net material product and 10% of employment before the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991. Armenian mines produce copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
and lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
. The vast majority of energy is produced with imported fuel, including gas and nuclear fuel (for its one nuclear power plant) from Russia; the main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. Small amounts of coal, gas and petroleum have not yet been developed.
Like other former States, Armenia's economy suffers from the legacy of a centrally planned economy and the breakdown of former Soviet trading patterns. Soviet investment in and support of Armenian industry has virtually disappeared, so that few major enterprises are still able to function. In addition, the effects of the 1988 earthquake, which killed more than 25,000 people and made 500,000 homeless, are still being felt. Although a cease-fire has held since 1994, the conflict with Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan , officially the Republic of Azerbaijan is the largest country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west, and Iran to...
over Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, lying between Lower Karabakh and Zangezur and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains...
has not been resolved. The consequent blockade along both the Azerbaijani and Turkish borders has devastated the economy, because of Armenia's dependence on outside supplies of energy and most raw materials. Land routes through Azerbaijan and Turkey are closed; routes through Georgia and Iran are inadequate or unreliable. In 1992-93, GDP fell nearly 60% from its 1989 level. The national currency, the dram
Armenian dram
The dram is the monetary unit of Armenia and the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic. It is subdivided into 100 luma . The word "dram" translates into English as "money" and is cognate with the Greek drachma...
, suffered hyperinflation
Hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is inflation that is very high or out of control. While the real values of the specific economic items generally stay the same in terms of relatively stable foreign currencies, in hyperinflationary conditions the general price level within a specific economy increases...
for the first few years after its introduction in 1993.
Nevertheless, the Government of Armenia, helped by the cease-fire that has been in effect in Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, lying between Lower Karabakh and Zangezur and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains...
since 1994, has been able to carry out wideranging economic reforms which paid off in dramatically lower inflation and steady growth. Armenia has registered strong economic growth since 1995, building on the turnaround that began the previous year, and inflation has been negligible for the past several years. New sectors, such as precious stone processing and jewelry making, information and communication technology, and even tourism are beginning to supplement more traditional sectors such as agriculture in the economy.
This steady economic progress has earned Armenia increasing support from international institutions. The IMF, World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
, EBRD, as well as other IFIs and foreign countries are extending considerable grants and loans. Total loans extended to Armenia since 1993 exceed $800 million. These loans are targeted at reducing the budget deficit, stabilizing the local currency; developing private businesses; energy; the agriculture, food processing, transportation, and health and education sectors; and ongoing rehabilitation work in the earthquake zone.
Continued progress will depend on the ability of the government to strengthen its macroeconomic management, including increasing revenue collection, improve the investment climate, and accelerate the privatization process. A liberal foreign investment law was approved in June 1994, and a Law on Privatization was adopted in 1997, as well as a program on state property privatization. The government has made major strides toward joining the World Trade Organization. By 1994, however, the Armenian Government had launched an ambitious IMF-sponsored economic liberalization program that resulted in positive growth rates in 1995-2005. Armenia joined the WTO in January 2003. Armenia also has managed to slash inflation, stabilize its currency, and privatize most small- and medium-sized enterprises. Armenia's unemployment rate, however, remains high, despite strong economic growth. The chronic energy shortages Armenia suffered in the early and mid-1990s have been offset by the energy supplied by one of its nuclear power plants at Metsamor
Metsamor
Metsamor is a city in the Armavir Province of Armenia. Armenia's Nuclear Power Plant called Metsamor Nuclear Power Plant is located in this city. Metsamor was built in 1979 to house workers from the Metsamor Nuclear Power Plant. The power plant was closed in 1989 after an earthquake prompted...
. Armenia is now a net energy exporter, although it does not have sufficient generating capacity to replace Metsamor, which is under international pressure to close. The electricity distribution system was privatized in 2002. Armenia's severe trade imbalance has been offset somewhat by international aid, remittances from Armenians working abroad, and foreign direct investment
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
. Economic ties with Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
remain close, especially in the energy sector. The government made some improvements in tax and customs administration in 2005, but anti-corruption measures have been more difficult to implement. Investment in the construction
Construction
In the fields of architecture and civil engineering, construction is a process that consists of the building or assembling of infrastructure. Far from being a single activity, large scale construction is a feat of human multitasking...
and industrial
Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
sectors is expected to continue in 2006 and will help to ensure annual average real GDP growth of about 13.9%.
Overview
Under the old Soviet central planning system, Armenia had developed a modern industrial sector, supplying machine tools, textiles, and other manufactured goods to sister republics in exchange for raw materials and energy. Since the implosion of the USSR in December 1991, Armenia has switched to small-scale agriculture away from the large agroindustrial complexes of the Soviet era. The agricultural sector has long-term needs for more investment and updated technology. The privatization of industry has been at a slower pace, but has been given renewed emphasis by the current administration. Armenia is a food importer, and its mineralMineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
deposits (gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, bauxite
Bauxite
Bauxite is an aluminium ore and is the main source of aluminium. This form of rock consists mostly of the minerals gibbsite Al3, boehmite γ-AlO, and diaspore α-AlO, in a mixture with the two iron oxides goethite and hematite, the clay mineral kaolinite, and small amounts of anatase TiO2...
) are small. The ongoing conflict with Azerbaijan over the ethnic Armenian-dominated region of Nagorno-Karabakh (which was part of Soviet Azerbaijan) and the breakup of the centrally directed economic system
Economic system
An economic system is the combination of the various agencies, entities that provide the economic structure that defines the social community. These agencies are joined by lines of trade and exchange along which goods, money etc. are continuously flowing. An example of such a system for a closed...
of the former Soviet Union contributed to a severe economic decline in the early 1990s. By 1994, however, the Armenian Government had launched an ambitious IMF-sponsored economic program that has resulted in positive growth rates in 1995-99. Armenia also managed to slash inflation and to privatize most small- and medium-sized enterprises. The chronic energy shortages Armenia suffered in recent years have been largely offset by the energy supplied by one of its nuclear power plants at Metsamor. Continued Russian financial difficulties have hurt the trade sector especially, but have been offset by international aid, domestic restructuring and foreign direct investment.
History of the modern Armenian economy
ArmeniaArmenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
emerged from the umbra
Umbra
The umbra, penumbra and antumbra are the names given to three distinct parts of a shadow, created by any light source. For a point source only the umbra is cast.These names are most often used to refer to the shadows cast by celestial bodies....
of the former Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
in 1991 and migrated from a centrally planned economy (Communist system) to a market economy
Market economy
A market economy is an economy in which the prices of goods and services are determined in a free price system. This is often contrasted with a state-directed or planned economy. Market economies can range from hypothetically pure laissez-faire variants to an assortment of real-world mixed...
(capitalist
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
system). Both the nation
Nation
A nation may refer to a community of people who share a common language, culture, ethnicity, descent, and/or history. In this definition, a nation has no physical borders. However, it can also refer to people who share a common territory and government irrespective of their ethnic make-up...
and the economy
Economy
An economy consists of the economic system of a country or other area; the labor, capital and land resources; and the manufacturing, trade, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of that area...
are nascent
Nascent market
Nascent markets are small, newly developing markets. Companies can exploit nascent markets three ways: by making the company and market synonymous, by creating a clear perimeter for the firm by demarcating the market, with the use of alliances and controlling the market by setting applicable...
. Regional conflict retards economic growth
Economic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
. In addition, the border with Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
is closed, making access to sea ports difficult and transportation logistics
Logistics
Logistics is the management of the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of destination in order to meet the requirements of customers or corporations. Logistics involves the integration of information, transportation, inventory, warehousing, material handling, and packaging, and...
challenging to a country largely dependent upon imports. In 2003, Armenia became a member of the WTO (World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
). The nation is making substantial progress in privatizing ownership of what used to be State Owned industries under the former Soviet system. Despite marked progress, Armenia still suffers from a large trade imballance and is still largely dependent upon foreign aid and remittances from Armenian nationals working abroad, and members of the diaspora
Diaspora
A diaspora is "the movement, migration, or scattering of people away from an established or ancestral homeland" or "people dispersed by whatever cause to more than one location", or "people settled far from their ancestral homelands".The word has come to refer to historical mass-dispersions of...
donating aid through NGOs (non-governmental organizations) such as the church. There are some foreign capital inflows, but no robust foreign investment. Despite progress since the Soviet era, the unemployment rate still hovers near 30% and there remains a huge gulf between actual and potential Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
.
Global competitiveness
The Armenian economy's competitiveness is low and stagnating according to the Global Competitiveness Index, in which Armenia's ranking slipped from 80th out of 132 countries in 2006-2007 index to 93rd out of 131 countries in the 2007-2008 index (just below LibyaLibya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, Namibia
Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia , is a country in southern Africa whose western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. It gained independence from South Africa on 21 March...
, Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
, Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
).
Domestic business environment
Armenia's economy is highly anticompetitive with government-connected individuals enjoying de facto monopolies over the import and distribution of basic commodities and foodstuffs, and under-reporting revenue to avoid paying taxes.Despite pronouncements at the highest levels of government on the importance of free competition, Armenia is next to last in the effectiveness of its anti-monopoly policy according to the 2010 results of the World Economic Forum Global Competitiveness Report.
According to Vahram Nercissiantz, President Sarkisian's chief economic adviser, "Businessmen holding state positions have turned into oligarchs who have avoided paying sufficient taxes by abusing their state positions, distorted markets with unequal conditions, breached the rules of competition, impeded or prevented small and medium-sized business’ entry into manufacturing and thereby sharply deepened social polarization in the republic.
Following the advice of economic advisors who cautioned Armenia's leadership against the consolidation of economic power in the hands of a few, in January 2001, the Government of Armenia established the State Commission for the Protection of Economic Competition. Its members cannot be dismissed by the government.
Monopolies
According to one analyst, Armenia's economic system is anticompetitive due to the structure of the economy being a type of "monopolyMonopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
or oligopoly
Oligopoly
An oligopoly is a market form in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of sellers . The word is derived, by analogy with "monopoly", from the Greek ὀλίγοι "few" + πόλειν "to sell". Because there are few sellers, each oligopolist is likely to be aware of the actions of the others...
." "The result is the prices with us do not drop even if they do on international market, or they do quite belated and not to the size of the international market."
According to the estimate of a former prime minister
Prime Minister of Armenia
The Prime Minister of Armenia is the most senior minister within the Armenian government, and is required by the constitution to "oversee the Government's regular activities and coordinate the work of the Ministers." The Prime Minister is appointed by the President of Armenia, but can be removed by...
, Hrant Bagratian, 55 percent of Armenia's GDP is controlled by 44 families.
In early 2008, the State Commission for the Protection of Economic Competition named 60 companies having "dominant positions" in Armenia.
In October 2009, when visiting Yerevan
Yerevan
Yerevan is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously-inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and industrial center of the country...
, the World Bank’s
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
managing director, Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala was appointed in July 2011 as Nigeria's “de facto prime minister” and the new Minister of Finance for the Federal Republic of Nigeria. Prior to this appointment, she was the Managing Director of World Bank and has also held the position of a Finance Minister and Foreign...
, warned that Armenia will not reach a higher level of development unless its leadership changes the "oligopolistic" structure of the national economy, bolsters the rule of law and shows "zero tolerance" towards corruption. "I think you can only go so far with this economic model," Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala told a news conference in Yerevan. "Armenia is a lower middle-income country. If it wants to become a high-income or upper middle-income country, it can not do so with this kind of economic structure. That is clear." She also called for a sweeping reform
Reform
Reform means to put or change into an improved form or condition; to amend or improve by change of color or removal of faults or abuses, beneficial change, more specifically, reversion to a pure original state, to repair, restore or to correct....
of tax and customs administration, the creation of a "strong and independent judicial system" as well as a tough fight against government corruption. The warning was echoed by the International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
.
Major monopolies in Armenia include:
- Natural gasNatural gasNatural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
import and distribution, held by ArmRosGazpromArmrosgazpromArmRosGazprom was founded in 1997 as a joint Russian-Armenian natural gas pipeline project. The company organizes the gas supply for Armenia's domestic gas market. Director General is currently Karen Karapetian. The company is registered in Armenia as a ЗAО ArmRosGazprom (ARG) was founded in 1997...
(ARG) (controlled by Russian monopoly GazpromGazpromOpen Joint Stock Company Gazprom is the largest extractor of natural gas in the world and the largest Russian company. Its headquarters are in Cheryomushki District, South-Western Administrative Okrug, Moscow...
) - Armenia's railway, held by the Russian-owned South Caucasus Railway (SCR) (formerly Russia’s state-run rail company, RZD)
- OilOilAn oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils....
import and distribution (claimed by Armenian opposition parties to belonging to a handful of government-linked individuals, one of which - "Mika Limited" - is owned by Mikhail Baghdasarian, while the other - "Flash" - is owned by Barsegh Beglarian, a "prominent representative of the Karabakh clan")- AviationAviationAviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Aviation is derived from avis, the Latin word for bird.-History:...
keroseneKeroseneKerosene, sometimes spelled kerosine in scientific and industrial usage, also known as paraffin or paraffin oil in the United Kingdom, Hong Kong, Ireland and South Africa, is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid. The name is derived from Greek keros...
(supplying to Zvartnots airportZvartnots International AirportZvartnots International Airport is located near Zvartnots, west of Yerevan, the capital city of Armenia. The airport was built in 1961. It is now the busiest airport in Armenia and the Caucasus. The draftsmen of the airport included architects M. Khachikyan, A. Tarkhanyan, J. Sheqhlyan, L....
), held by Mika Limited
- Aviation
- Various basic foodstuffs such as riceRiceRice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
, sugarSugarSugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, wheatWheatWheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
, cooking oilCooking oilCooking oil is purified fat of plant origin, which is usually liquid at room temperature ....
and butterButterButter is a dairy product made by churning fresh or fermented cream or milk. It is generally used as a spread and a condiment, as well as in cooking applications, such as baking, sauce making, and pan frying...
(the Salex Group enjoys a de facto monopoly on imports of wheat, sugar, flour, butter and cooking oil. Its owner is parliament deputy Samvel Aleksanian (a.k.a. "Lfik Samo") a figure close to the country’s leadership.) - Newspaper distribution, held by Haymamul (some newspaper editors believe that Haymamul deliberately refuses to print more newspaper copies in order to minimize the impact of unfavorable press coverage of the government)
- Civil aviation, held by ArmaviaArmaviaAir Company "Armavia" is an airline with its head office on the grounds of Zvartnots International Airport in Zvartnots, Armenia, near Yerevan. It operates international passenger services from Yerevan to destinations in Europe and Asia...
national airline (owned by Mikhail Baghdasarov, who is thought to be close to President Serge Sarkisian)
Former major monopolies in Armenia include:
- Wireless (mobile) telephony, held by Armentel until 2004
- Internet access, held by Armentel until September 2006
- Fixed-line telephony, held by Armentel until August 2007
GDP
The Gross Domestic ProductGross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
of Armenia stood at 8.8 billion US dollars in 2010; with a population of 3.2 million, this amounts to a GDP per capita of $2,676 (purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
$5,178). GDP growth for 2010 was at 2.9 percent, and inflation was at 8 percent.
GDP growth is expected to be around 3 percent in 2011, with inflation returning to 4-5 percent.
In comparison, in 2006, the GDP was estimated to be 6.6 billion USD per calendar year and the GDP per capita (purchasing power parity) was estimated at $5,400 US. The growth rate
Economic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
was high at 13.4%, but the relatively low base must be considered. Low inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
was maintained around 2.6% annually.
Growth
After a decade of double-digit growth, Armenia's economy declined by 14.4 percent in 2009. The year-to-date growth as of October 2010 was 2.8 percent. In 2010, the main macro deficiencies of the Armenian economy — namely, unsustainable growth drivers, a narrow and resource-dominated export base, and overdependence on private transfers — were still prevalent.According to official figures, Armenia’s economy grew by 13.8 percent in 2007. According to research funded by the USAID CAPS project, Armenia's exceptionally high rate of economic growth during the last decade has been largely dependent on external factors (e.g. remittances, assistance from international financial and donor organization). Furthermore, the study concluded that despite its record growth on most macro-economic metrics, Armenia is "low and lagging" in competitiveness.
According to the National Statistical Service, the booming construction and service sectors remain the driving forces of the high growth rate of GDP.
Cash remittances
Cash remittancesRemittances
A remittance is a transfer of money by a foreign worker to his or her home country. Note that in 19th century usage a remittance man was someone exiled overseas and sent an allowance on condition that he not return home....
sent back home from Armenians working abroad—mostly in Russia and the United States—are growing and contribute significantly to Armenia's Gross Domestic Product (between 15 to 30 percent). They help Armenia sustain double-digit economic growth and finance its massive trade deficit.
According to the Central Bank of Armenia
Central Bank of Armenia
The Central Bank of Armenia is the central bank of Armenia with its headquarters in Yerevan. The CBA is an independent institution responsible for issuing all banknotes and coins in the country, overseeing and regulating the banking sector and keeping the government's currency reserves...
, during the first half of 2008, cash remittances sent back to Armenia by Armenians working abroad rose by 57.5 percent and totaled $668.6 million USD, equivalent to 15 percent of the country's first-half Gross Domestic Product. However, the latter figures only represent cash remittances processed through Armenian commercial banks. According to RFE/RL, comparable sums are believed to be transferred through non-bank systems, implying that cash remittances make up approximately 30 percent of Armenia's GDP in the first half of 2008.
In 2007, cash remittances through bank transfers rose by 37 percent to a record-high level of $1.32 billion USD. According to the Central Bank of Armenia, in 2005, cash remittances from Armenians working abroad reached a record-high level of $1 billion, which is worth more than one fifth of the country’s 2005 Gross Domestic Product.
Net private transfers decreased in 2009, but saw a continuous increase during the first six months of 2010. Since private transfers from the Diaspora tend to be mostly injected into consumption of imports and not in high value-added sectors, the transfers have not resulted in sizeable increases in productivity.
Construction sector
Armenia experienced a construction boom during the latter part of the 2000s. According to the National Statistical Service, Armenia's booming construction sector generated about 20 percent of Armenia's GDP during the first eight months of 2007. According to a World Bank official, 30 percent of Armenia's economy in 2009 came from the construction sector.However, during the January to September 2010 period, the sector experienced a 5.2 percent year-on-year decrease, which according to the Civilitas Foundation
Civilitas Foundation
thumb|alt=Civilitas Foundation Logo| The Civilitas Foundation.The Civilitas Foundation is an Armenian non-profit organization based in Yerevan, Armenia, and established in October 2008 by Armenia's former Minister of Foreign Affairs, Vartan Oskanian...
is an indication of the unsustainability of a sector based on an elite market, with few products for the median or low budgets. This decrease comes despite the fact that an important component of the government stimulus package was to support the completion of ongoing construction projects.
Retail trade
In 2010, retail trade turnover was largely unaltered compared to 2009. The existing monopolies throughout the retail sector have made the sector non-responsive to the crisis and resulted in near zero growth. The aftermath of the crisis has started to shift the structure in the retail sector in favor of food products.Services sector
In the 2000s, along with the construction sector, the services sector was the driving force behind Armenia's recent high economic growth rate. In 2010, the volume of services increased as much as 7.4 percent from January to September, over the same period in 2009.Tourism
According to official data, in 2007, a record-high 500,000 tourists visited Armenia — most of them ethnic Armenians from Europe, Russia and the United States. 2010 saw a noticeable increase in the number of Iranian tourists visiting Armenia – estimated to be 80,000.However, according to private tour operators and other individuals familiar with the country’s tourism industry, government claims that hundreds of thousands of foreign tourists visit Armenia each year are wide of the mark. Official statistics show that as many 575,000 tourists visited Armenia from abroad in 2009; the government stated earlier in 2010 that the figure will surpass 620,000 in 2010. However, data from the National Statistical Service shows that there were only 65,000 foreigners staying in Armenian hotels in 2009. Ara Vartanian, the chairman of the Armenian Trade and Industry Chamber, thinks that this measure is a far more objective indicator of the tourist influx into the country.
Industrial sector
Industrial output was relatively positive throughout 2010, with year-on-year average growth of 10.9 percent in the period January to September 2010, due largely to the mining sector where higher global demand for commodities led to higher prices. According to the National Statistical Service, during the January–August 2007 period, Armenia's industrial sector was the single largest contributor to the country's GDP, but remained largely stagnant with industrial output increasing only by 1.7 percent per year. In 2005, Armenia's industrial output (including electricity) made up about 30 percent of GDP.Mining
40 percent of Armenia's exports in 2009 were miningMining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
exports.
Agricultural sector
As of 2010, the agricultural production comprises on average 25 percent of Armenia's GDP. In 2006, the agricultural sector accounted for about 20 percent of Armenia's GDP.Armenia's agricultural output dropped by 17.9 percent in the period of January–September 2010. This was owing to bad weather, a lack of a government stimulus package, and the continuing effects of decreased agricultural subsidies by the Armenian government (per WTO
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
requirements).
United States
The Armenian government receives foreign aid from the government of the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
through the United States Agency for International Development
United States Agency for International Development
The United States Agency for International Development is the United States federal government agency primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid. President John F. Kennedy created USAID in 1961 by executive order to implement development assistance programs in the areas...
and the Millennium Challenge Corporation
Millennium Challenge Corporation
The Millennium Challenge Corporation is a bilateral United States foreign aid agency created by the George W. Bush administration in 2004, applying a new philosophy towards foreign aid.-Background and formation:...
.
On March 27, 2006, the Millennium Challenge Corporation
Millennium Challenge Corporation
The Millennium Challenge Corporation is a bilateral United States foreign aid agency created by the George W. Bush administration in 2004, applying a new philosophy towards foreign aid.-Background and formation:...
signed a five-year, $235.65 million compact with the Government of Armenia. The single stated goal of the "Armenian Compact" is "the reduction of rural poverty through a sustainable increase in the economic performance of the agricultural sector." The Compact includes a $67 million to rehabilitate up to 943 kilometers of rural roads, more than a third of Armenia's proposed "Lifeline road network". The Compact also includes a $146 million project to increase the productivity of approximately 250,000 farm households through improved water supply, higher yields, higher-value crops, and a more competitive agricultural sector.
In 2010, the volume of US assistance to Armenia remained near 2009 levels; however, longer-term decline continued. The original Millennium Challenge Account commitment for $235 million had been reduced to about $175 million due to Armenia’s poor governance record. Thus, the MCC would not complete road construction. Instead, the irrigated agriculture project was headed for completion with apparently no prospects for extension beyond 2011.
European Union
With curtailment of the MCC funding, the European Union may replace the US as Armenia’s chief source of foreign aid for the first time since independence. From 2011 to 2013, the European Union is expected to advance at least €157.3 million ($208 million) in aid to Armenia.Exports
In 2010, Armenia’s exports remained resource-dependent, largely because the non-resource-intensive sectors were significantly less competitive. Armenia has not succeeded in increasing and diversifying exports beyond raw materials thus leaving room for a greater vulnerability to external shocks. There was a 43.9 percent increase in overall exports during the January to September period. The main three export destinations were Bulgaria with 15.2 percent of total exports, followed by Germany with 14.2 percent and Russia with 13.9 percent. Raw minerals were the main export sent to Bulgaria and Germany.Imports
The global economic crisis has had less impact on imports because the sector is more diversified than exports. In the first nine months of 2010, imports grew about 19 percent, just about equal to the decline of the same sector in 2009.Deficit
During the first half of 2008, Armenia's widening current-account trade deficit grew by 66 percent to $1.39 billion USD, with a 40 percent rise in imports. Furthermore, Armenian exports fell by about one percent to $520 million USD.According to the National Statistical Service, Armenia's trade deficit in 2006 was $1.2 billion with growth in exports being largely flat. During the first 11 months of 2006, net imports grew by 21 percent to $1.95 billion, while exports stood at $895 million, up 0.3 percent from the same period in 2005.
European Union
In 2010, EU countries accounted for 32.1 percent of Armenia’s foreign trade. Germany is Armenia’s largest trading partner among EU member states, accounting for 7.2 percent of trade; this is due largely to mining exports. Armenian exports to EU countries have skyrocketed by 65.9 percent, making up more than half of all 2010 January to September exports. Imports from EU countries increased by 17.1 percent, constituting 22.5 percent of all imports.During January–February 2007, Armenia’s trade with the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
totaled $200 million. During the first 11 months of 2006, the European Union remained Armenia's largest trading partner, accounting for 34.4 percent of its $2.85 billion commercial exchange during the 11-month period.
Russia and former Soviet republics
Bilateral trade with Russia stood at more than $700 million for the first nine months of 2010 – on track to rebound to $1 billion mark first reached in 2008 prior to the global economic crisis.During January–February 2007, Armenia’s trade with Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and other former Soviet republics was $205.6 million (double the amount from the same period the previous year), making them the country’s number one trading partner. During the first 11 months of 2006, the volume of Armenia’s trade with Russia was $376.8 million or 13.2 percent of the total commercial exchange.
China
As of early 2011, trade with China is dominated by imports of Chinese goods and accounts for about 10 percent of Armenia's foreign trade. The volume of Chinese-Armenian trade soared by 55 percent to $390 million in January–November 2010. Armenian exports to China, though still modest in absolute terms, nearly doubled in that period.Iran
In 2010, the volume of bilateral trade with Iran was $200 million - which is approximately equal to the trade between Armenia and Turkey. The number of Iranian tourists has risen in recent years, with an estimated 80,000 Iranian tourists in 2010.Turkey
In 2010, the volume of bilateral trade with Turkey was about $200 million, with trade taking place without open borders, across Georgian territory. This figure is not expected to increase significantly so long as the land border between the Armenia and Turkey remains closed.United States
From January–September 2010, bilateral trade with the United States measured approximately $150 million, on track for about a 30 percent increase over 2009. An increase in Armenia’s exports to the US in 2009 and 2010 has been due to shipments of aluminum foil.During the first 11 months of 2006, U.S.-Armenian trade totaled $152.6 million.
Georgia
The volume of Georgian-Armenian trade remains modest in both relative and absolute terms. According to official Armenian statistics, it rose by 11 percent to $91.6 million in January–November 2010. The figure was equivalent to just over 2 percent of Armenia’s overall foreign trade.Foreign debt
Armenia's national debt has increased significantly since 2008 when public external debt consisted of only 13.5 percent of GDP. By the end of 2010, Armenia’s external debt is projected to form about 42 percent of GDP, and 50 percent in 2012.As of late November 2009, the Armenian government's foreign debt was around $3 billion USD, having doubled in size over the course of the previous year. With the Armenian government needing more anti-crisis loans from the World Bank and other foreign donors, the debt-to-GDP ratio is expected to exceed 40 percent in 2010. According to a World Bank official, a country that has around 12 percent rate of growth or even lower, at the range of 7 to 8 percent, can afford a level of public debt of up to 50 percent. The official warned that the debt servicing payments of the Armenian government will surge by 2013 and absorb "quite significant part of tax revenues."
According to another estimate, the ratio between the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and the state's foreign debt has reached 46 percent. Economists generally agree that a country is insolvent
Insolvency
Insolvency means the inability to pay one's debts as they fall due. Usually used to refer to a business, insolvency refers to the inability of a company to pay off its debts.Business insolvency is defined in two different ways:...
, if its foreign debt surpasses 50 percent of its GDP. Critics of the government say that the $500 million credit from Russia should have gone to develop industry, instead of going to the construction sector.
Internal
Since early 2008, Armenia's entire rail network is managed by the Russian state railway.Through Georgia
Russian natural gas reaches Armenia via a pipeline through Georgia.The only operational rail link into Armenia is from Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
. During Soviet times, Armenia's rail network connected to Russia's via Georgia through Abkhazia
Abkhazia
Abkhazia is a disputed political entity on the eastern coast of the Black Sea and the south-western flank of the Caucasus.Abkhazia considers itself an independent state, called the Republic of Abkhazia or Apsny...
along the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
. However, the rail link between Abkhazia and Georgia proper has been closed for a number of years, forcing Armenia to receive rail cars laden with cargo only through the relatively expensive rail-ferry services operating between Georgian and other Black Sea ports.
The Georgian Black Sea ports of Batumi
Batumi
Batumi is a seaside city on the Black Sea coast and capital of Adjara, an autonomous republic in southwest Georgia. Sometimes considered Georgia's second capital, with a population of 121,806 , Batumi serves as an important port and a commercial center. It is situated in a subtropical zone, rich in...
and Poti
Poti
Poti is a port city in Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the region of Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti in the west of the country. Built near the site of the ancient Greek colony of Phasis, the city has become a major port city and industrial center since the early 20th century. It is also...
process more than 90 percent of freight shipped to and from landlocked Armenia. The Georgian railway, which runs through the town of Gori in central Georgia, is the main transport link between Armenia and the aforementioned Georgian seaports. Fuel, wheat and other basic commodities are transported to Armenia by rail.
Armenia's main rail and road border-crossing with Georgia (at 41°13′41.97"N 44°50′9.12"E) is along the Debed river near the Armenian town of Bagratashen
Bagratashen
Bagratashen is a town in the Tavush Province of Armenia, on the border of the Republic of Georgia. The town was renamed in honor of Bagrat Vardanian , Hero of Socialist Labor.- References :* – World-Gazetteer.com...
and the Georgian town of Sadakhlo
Sadakhlo
Sadakhlo is a village in Georgia located in the south-east part of country in the administrative territory of Marneuli District near the border to Armenia.- Demography :...
.
The Upper Lars border crossing (at Darial Gorge
Darial Gorge
The Darial Gorge is the gorge on the border between Russia and Georgia. It is at the east base of Mount Kazbek, pierced by the river Terek for a distance of 8 metres between vertical walls of rock and is located South of present-day...
) between Georgia and Russia across the Caucasus Mountains
Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains is a mountain system in Eurasia between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea in the Caucasus region .The Caucasus Mountains includes:* the Greater Caucasus Mountain Range and* the Lesser Caucasus Mountains....
served as Armenia's sole overland route to the former Soviet Union and Europe. It was controversially shut down by the Russian authorities in June 2006, at the height of a Russian-Georgian spy scandal. Upper Lars is the only land border crossing that does not go through Georgia's Russian-backed breakaway regions of South Ossetia
South Ossetia
South Ossetia or Tskhinvali Region is a disputed region and partly recognized state in the South Caucasus, located in the territory of the South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast within the former Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic....
and Abkhazia
Abkhazia
Abkhazia is a disputed political entity on the eastern coast of the Black Sea and the south-western flank of the Caucasus.Abkhazia considers itself an independent state, called the Republic of Abkhazia or Apsny...
. The other two roads linking Georgia and Russia run through South Ossetia and Abkhazia, effectively barring them to international traffic. This crossing is expected to reopen starting on March 1, 2010.
Through Turkey and Azerbaijan
An economic blockade with TurkeyTurkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan , officially the Republic of Azerbaijan is the largest country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west, and Iran to...
has cut Armenia's rail link between Gyumri and Kars
Kars Gyumri Akhalkalaki railway line
The Kars–Gyumri–Tbilisi railway line is a railway line that runs from the city of Kars in Turkey to the Armenian city of Gyumri, then from there on to Tbilisi, Georgia....
to Turkey; the rail link with Iran through the Azeri exclave of Nakhichevan; and a natural gas and oil pipeline line with Azerbaijan. Also non-functioning are roads with Turkey and Azerbaijan. Despite the economic blockade of Turkey on Armenia, every day dozens of Turkish trucks laden with goods enter Armenia through Georgia.
In 2010, it was confirmed that Turkey will keep the border closed for the foreseeable future after the Turkey-Armenia normalization process collapsed.
Through Iran
A new gas pipeline to IranIran-Armenia Natural Gas Pipeline
The Iran–Armenia gas pipeline is a long pipeline from Iran to Armenia. The long Iranian section runs from Tabriz to the Iran–Armenia border. The Armenian section runs from the Meghri region to Sardarian, and another of pipeline is planned to reach the center of the country, where it will link up...
has been completed, and a road to Iran through the southern city of Meghri
Meghri
Meghri is a city in southern Armenia, located in the Syunik province, near the border with Iran. The city's economy is based on the food industry, and contains a bread-baking factory, canneries and a winery. Meghri has a significantly milder climate than the rest of the cities in Armenia, and...
allows trade with that country. An oil pipeline to pump Iranian oil products is also in the planning stages.
As of October 2008, the Armenian government is considering implementing an ambitious project to build a railway to Iran. The 400 kilometer railway would pass through Armenia's mountainous southern province of Syunik
Syunik
Syunik is the southernmost province of Armenia. It borders the Vayots Dzor marz to the north, Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan exclave to the west, Karabakh to the east, and Iran to the south. Its capital is Kapan. Other important cities and towns include Goris, Sisian, Meghri, Agarak, and Dastakert...
which borders Iran. Economic analysts say that the project would cost at least $1 billion (equivalent to about 40 percent of Armenia's 2008 state budget). As of 2010, the project has been continuously delayed, with the rail link estimated to cost as much as $4 billion and stretch 313 km (194.5 mi). In June 2010, Transport Minister Manuk Vartanian revealed that Yerevan is seeking as much as $1 billion in loans from China to finance the railway’s construction.
Labor

Monthly wages
According to the state-owned Armenpress news agency, the average monthly wageWage
A wage is a compensation, usually financial, received by workers in exchange for their labor.Compensation in terms of wages is given to workers and compensation in terms of salary is given to employees...
in Armenia for the first half of 2007 was 70,700 dram
Armenian dram
The dram is the monetary unit of Armenia and the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic. It is subdivided into 100 luma . The word "dram" translates into English as "money" and is cognate with the Greek drachma...
s (about $210 USD).
As of April 24, 2008, the average monthly salary
Salary
A salary is a form of periodic payment from an employer to an employee, which may be specified in an employment contract. It is contrasted with piece wages, where each job, hour or other unit is paid separately, rather than on a periodic basis....
is 75,000 drams (about $242 US dollars). According to the ROA National Statistical Service, the average monthly salary during January - June 2008 is 86,850 drams (about $287 at the time). About 62% of officially registered wage earners earn at least the average monthly wage, while only 19.6% receive a monthly salary of over 100,000 drams (about $330 at the time).
Unemployment
According to research commissioned by the Yerevan office of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, at least one in three working-age Armenians was unemployed as of February 2005 despite several consecutive years of double-digit economic growth. The finding sharply contrasts with government's official unemployment rate of about 10 percent. A 2003 household survey conducted by the National Statistical Survey found that the real unemployment rate is about 33 percent.Migrant workers
Since gaining independence in 1991, hundreds of thousands of Armenia's residents have gone abroad, mainly to Russia, in search of work. Unemployment has been the major cause of this massive labor emigration. OSCE experts estimate that between 116,000 and 147,000 people left Armenia for economic reasons between 2002 and 2004, with two-thirds of them returning home by February 2005. According to estimates by the National Statistical Survey, the rate of labor emigration was twice as higher in 2001 and 2002.According to an OSCE survey, a typical Armenian migrant worker
Migrant worker
The term migrant worker has different official meanings and connotations in different parts of the world. The United Nations' definition is broad, including any people working outside of their home country...
is a married man aged between 41 and 50 years who "began looking for work abroad at the age of 32-33."
Appreciation and depreciation of the dram
In 2010, the value of the Armenian Dram (AMD) was artificially kept high during the height of the global economic crisis. Had the AMD been allowed to depreciate to its market level, exports would have become more competitive and the purchasing power of the majority of the population who are dependent on remittances from abroad would have increased. Instead, the value of the AMD was kept high, out of a fear of inflation and concern about alienating the powerful government-connected importers of oil, sugar, flour, cigarettes and beverages.The AMD/USD exchange rate depreciated by 6.1 percent in the first three quarters of 2010 compared to the same period in 2009, before it began to show the expected end-of-the-year appreciation. In comparison between the January to October periods of 2010 and 2009, depreciation stands at 4.7 percent.
Government revenue and taxation
The Armenian government collected 383.5 billion drams ($1.26 billion) in various taxes in the first nine months of 2008 (a 33.2 percent increase from the same period last year).Many large companies have a privileged status when it comes to taxation. Big business is not taxed in proportion to its capacity and output, and the disproportionate burden falls on small and medium size businesses.
New VAT tax
Over half of the tax revenues in the January–August 2008 time period were generated from value-added taxes (VAT tax). By comparison, corporate profit tax generated less than 16 percent of the revenues. This suggests that tax collection in Armenia is improving at the expense of ordinary citizens, rather than wealthy citizens (who have been the main beneficiaries of Armenia's double-digit economic growth in recent years).Tax evasion
Many Armenian companies, especially those owned by government-connected tycoons, have long reported suspiciously low earnings, thereby avoiding paying larger taxes.Environmental issues
Armenia is trying to address its environmental problems. It has established a Ministry of Environment and has introduced a pollution fee system by which taxes are levied on air and water emissions and solid waste disposal, with the resulting revenues used for environmental protection activities. Armenia is interested in cooperating with other members of the Commonwealth of Independent States (a group of 12 former Soviet republics) and with members of the international community on environmental issues. The Armenian Government is working toward closing the Armenian Nuclear Power Plant as soon as alternate energy sources can be identified.Banking
Armenia's financial system is not integrated into the global network. According to the head of the Armenian Central Bank’s (CBA) department for financial system policies and analyses (Vahe Vardanyan) Armenian banks have no large asset concentrations in foreign markets, particularly in capital markets. They nearly have no purchased securities (so-called securitized packages). For this reason, Armenia was virtually unaffected by the Liquidity crisis of September 2008.Armenian banking assets are very low and make up only 25 percent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Takeover of Armenian industrial property by the Russian state and Russian companies
In implementing its strategy to regain political dominance over post-Soviet countries by taking over their economic infrastructure, the Russian state, since 2000, has acquired several key assets in the energy sector and Soviet-era industrial plants. Property-for-debt or equity-for-debt swaps (acquiring ownership by simply writing off the Armenian government's debts to Russia) are usually the method of acquiring assets. The failure of market reforms, clan-based economics, and official corruption in ArmeniaCorruption in Armenia
Political corruption in Armenia is a widespread and growing problem in Armenian society. The United Nations Development Programme in Armenia views corruption in Armenia as "a serious challenge to its development."- Corruption levels :...
have allowed the success of this process.
In August 2002, the Armenian government sold an 80 percent stake in the Armenian Electricity Network (AEN) to Midland Resources, a British offshore-registered firm which is said to have close Russian connections.
In September 2002, the Armenian government handed over Armenia’s largest cement factory to the Russian ITERA
ITERA
ITERA is the acronym for the International Telecommunications Education and Research Association. ITERA is a 501 non-profit organization and was founded on the principle that leading educational institutions can greatly benefit from cooperative development of curricular and research...
gas exporter in payment for its $10 million debt for past gas deliveries.
On November 5, 2002, Armenia transferred control of 5 state enterprises to Russia in an assets-for-debts transaction which settled $100 million of Armenian state debts to Russia. The document was signed for Russia by Prime Minister Mikhail Kasyanov
Mikhail Kasyanov
Mikhail Mikhailovich Kasyanov - was the Prime Minister of Russia from May 2000 to February 2004.He is the leader of the People's Democratic Union and an ex-member of the opposition coalition "The Other Russia".-Political career:...
and Industry Minister Ilya Klebanov
Ilya Klebanov
Ilya Iosifovich Klebanov is a Russian politician. He currently is the Plenipotentiary Presidential Envoy to the Northwestern Federal District of the Russian Federation....
, while Prime Minister Andranik Markarian and defense and security strongman Serge Sarkisian signed for Armenia. The five enterprises which passed to 100 percent Russian state ownership are:
- Armenia's largest thermal power plant which is in the town of HrazdanHrazdanHrazdan is the capital of the Kotayk province of Armenia. The name Hrazdan is derived from the Middle-Persian name Frazdan. Farzdan is connected to the Zoroastrian mythology. With a population of 52,900 it is the fifth-largest city in Armenia by population. It has lost significant population since...
and is gas-burning - the Mars electronics and robotics plant in Yerevan, a Soviet-era flagship for both civilian and military production
- three research-and-production enterprises—for mathematical machines, for the study of materials, and for automated control equipment—these being Soviet-era military-industrial plants
In January 2003, the Armenian government and United Company RUSAL
United Company RUSAL
United Company RUSAL is the world's largest aluminium company, with headquarters in Moscow, Russian Federation. UC RUSAL accounts for almost 11% of the world's primary aluminium output and 13% of the world’s alumina production. The United Company was formed by the merger of RUSAL , SUAL, and the...
signed an investment cooperation agreement, under which United Company RUSAL (which already owned a 76% stake) acquired the Armenian government's remaining 26% share of RUSAL ARMENAL
RUSAL ARMENAL
RUSAL ARMENAL is a wholly owned subsidiary of RUSAL which runs an aluminum foil mill in the Arabkir district of Yerevan, Armenia. The premises of the mill was formerly known as the Kanaker aluminum smelter, which was commissioned in 1950, and became one of the largest aluminum foil mills in the...
aluminum foil mill, giving RUSAL 100% ownership of RUSAL ARMENAL.
On November 1, 2006, the Armenian government handed de facto control of the Iran-Armenia gas pipeline to Russian company Gazprom
Gazprom
Open Joint Stock Company Gazprom is the largest extractor of natural gas in the world and the largest Russian company. Its headquarters are in Cheryomushki District, South-Western Administrative Okrug, Moscow...
and increased Gazprom's stake in the Russian-Armenian company ArmRosGazprom
Armrosgazprom
ArmRosGazprom was founded in 1997 as a joint Russian-Armenian natural gas pipeline project. The company organizes the gas supply for Armenia's domestic gas market. Director General is currently Karen Karapetian. The company is registered in Armenia as a ЗAО ArmRosGazprom (ARG) was founded in 1997...
from 45% to 58% by approving an additional issue of shares worth $119 million. This left the Armenian government with a 32% stake in ArmRosGazprom. The transaction will also help finance ArmRosGazprom's acquisition of the Hrazdan electricity generating plant’s fifth power bloc (Hrazdan-5), the leading unit in the country.
In October 2008 the Russian bank Gazprombank
Gazprombank
Gazprombank is the largest Russian non-state owned bank, which is among the three largest banks in Russia. It is a joint stock bank founded in 1990. The bank is owned by the Russian gas company Gazprom, which controls 62.59% of shares directly and also retains shares through its subsidiaries...
, the banking arm of Gazprom, acquired 100 percent of Armenian bank Areximbank after previously buying 80 percent of said bank in November 2007 and 94.15 percent in July of the same year.
Controversy over non-transparent deals
Critics of the Kocharian government say that the Armenian administration never considered alternative ways of settling the Russian debts. According to economist Eduard Aghajanov, Armenia could have repaid them with low-interest loans from other, presumably Western sources, or with some of its hard currency reserves which then totaled about $450 million. Furthermore, Aghajanov points to the Armenian government's failure to eliminate widespread corruption and mismanagement in the energy sector – abuses that cost Armenia at least $50 million in losses each year, according to one estimate.Political observers say that Armenia's economic cooperation with Russia has been one of the least transparent areas of the Armenian government’s work. The debt arrangements have been personally negotiated by (then) Defense Minister (and now President) Serge Sarkisian, Kocharian’s closest political associate. Other top government officials, including Prime Minister Andranik Markarian, had little say on the issue. Furthermore, all of the controversial agreements have been announced after Sarkisian’s frequent trips to Moscow, without prior public discussion.
Finally, while Armenia is not the only ex-Soviet state that has incurred multimillion-dollar debts to Russia over the past decade, it is the only state to have so far given up such a large share of its economic infrastructure to Russia. For example, pro-Western Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
(both of which owe Russia more than Armenia) have managed to reschedule repayment of their debts.
Background
GDP(pp.): $18.92 billion (2008)GDP $: $12.07 billion (2008)
GDP - real growth rate: 7.6% (2008)
- country comparison to the world: 22
GDP(per capita): $6,400 (2008)
GDP by sector
Agriculture: 17.2%
Industry: 36.4%
Services: 46.4%
Unemployment: 7.1% (2007)
- country comparison to the world: 88
Labour Force: 1.2 million (2007)
- country comparison to the world: 88
Labour Force - by occupation:
- agriculture: 46.2%
- industry: 15.6%
- services: 38.2% (2006)
Population below poverty line:
- 26.5% (2006 est.)
Inflation: 4.4%
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 1.6%
highest 10%: 41.3% (2004)
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
- 37 (2006)
Investment (gross fixed):
- 34.1% of GDP (2008)
- country comparison to the world: 13
Central bank discount rate:
- 7.25% (2008)
- country comparison to the world: 55
Stock of money:
- $1.507 billion (2007)
- country comparison to the world: 106
Production
Industrial production growth rate:- 3% (2008 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 105
Industries: Diamond processing, metal-cutting machine tools, forge-pressing machines, electric motors, tires, knitted wear, hosiery, shoes, silk fabric, chemicals, trucks, instruments, microelectronics, jewellery manufacturing, software development, food processing, brandy.
Agriculture - products:
Fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
(especially grape
Grape
A grape is a non-climacteric fruit, specifically a berry, that grows on the perennial and deciduous woody vines of the genus Vitis. Grapes can be eaten raw or they can be used for making jam, juice, jelly, vinegar, wine, grape seed extracts, raisins, molasses and grape seed oil. Grapes are also...
s and apricot
Apricot
The apricot, Prunus armeniaca, is a species of Prunus, classified with the plum in the subgenus Prunus. The native range is somewhat uncertain due to its extensive prehistoric cultivation.- Description :...
s), vegetables, livestock
Livestock
Livestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
, wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
, wine
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
, brandy
Brandy
Brandy is a spirit produced by distilling wine. Brandy generally contains 35%–60% alcohol by volume and is typically taken as an after-dinner drink...
Value of stock exchange: $42.8 million (2005)
Trade
Exports - commodities:Pig iron, unwrought copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, nonferrous metals, cut diamond
Diamond
In mineralogy, diamond is an allotrope of carbon, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a variation of the face-centered cubic crystal structure called a diamond lattice. Diamond is less stable than graphite, but the conversion rate from diamond to graphite is negligible at ambient conditions...
s, mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
products, foodstuffs, energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
Imports - commodities:
Natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
products, foodstuffs
Foodstuffs
Foodstuffs is a group of three New Zealand grocery and liquor retailers' cooperatives based in Auckland, Wellington and Christchurch which collectively control an estimated 57% of the New Zealand grocery market...
, uncut diamond
Diamond
In mineralogy, diamond is an allotrope of carbon, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a variation of the face-centered cubic crystal structure called a diamond lattice. Diamond is less stable than graphite, but the conversion rate from diamond to graphite is negligible at ambient conditions...
s
Exports: $1.225 billion f.o.b. (2008)
country comparison to the world: 147
Imports: $3.546 billion f.o.b. (2008)
country comparison to the world: 132
Current account balance:
$-877 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 117
Export partners: Russia 17.5%, Netherlands 14.9%, Germany 14.7%, Ireland 11.1%, Belgium 8.7%, Georgia 7.6%, US 6.6%, Switzerland 4.3%, Bulgaria 4.1%, Ukraine 4% (2007)
Import partners: Russia 17.5%, Netherlands 14.9%, Germany 14.7%, Ireland 11.1%, Belgium 8.7%, Georgia 7.6%, US 6.6%, Switzerland 4.3%, Bulgaria 4.1%, Ukraine 4% (2007)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$1.657 billion (2007)
Debt - external:
$1.372 billion (2007)
Currency:
dram (AMD)
Currency code:
AMD
Exchange rates:
Armenian dram
Armenian dram
The dram is the monetary unit of Armenia and the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic. It is subdivided into 100 luma . The word "dram" translates into English as "money" and is cognate with the Greek drachma...
per US dollar - 310.00 (2008), 457.69 (2005), 533.45 (2004), 578.76 (2003), 573.35 (2002), 555.08 (2001), 539.53 (2000)
Energy
Electricity - production:5.544 GWh (2007)
country comparison to the world: 108
Electricity - consumption:
4.539 GWh (2006)
country comparison to the world: 109
Electricity - exports:
322.6 GWh; note - exports an unknown quantity to Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
; includes exports to Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, lying between Lower Karabakh and Zangezur and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains...
(2007)
Electricity - imports:
400.6 GWh; note - imports an unknown quantity from Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
(2007)
Oil - production:
0 oilbbl/d (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
Oil - consumption:
41090 oilbbl/d (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
Oil - exports:
0 oilbbl/d (2005)
country comparison to the world: 207
Oil - imports:
44670 oilbbl/d (2005)
country comparison to the world: 90
Natural gas - production:
0 m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
Natural gas - consumption:
2.05 billion m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
Natural gas - exports:
0 m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
Natural gas - imports:
2.05 billion m³ (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44

