Demographics of Hungary
Encyclopedia
This article is about the demographic
features of the population
of Hungary
, including population density
, ethnicity
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
According to the demographers, about 80 percent of the population was made up of Hungarians before the Battle of Mohács
, however the Hungarian ethnic group became a minority in its own country after the Rákóczi's War for Independence
. Major territorial changes made Hungary ethnically homogeneous after World War I. Nowadays, more than nine-tenths of the population is ethnically Hungarian and speaks Hungarian as the mother tongue.
Note: The data refer to the territory of the Kingdom of Hungary
, not of present-day Hungary.
, which was decreased from 20.9 million to 7.6 million, and 31% (3.3 out of 10.7 million) of its ethnic Hungarians, Hungary lost five of its ten most populous cities.
 According to the census of 1910, the largest ethnic group in the Kingdom of Hungary were Hungarians, who were 54,5% of the population of Kingdom of Hungary, excluding Croatia-Slavonia.
According to the census of 1910, the largest ethnic group in the Kingdom of Hungary were Hungarians, who were 54,5% of the population of Kingdom of Hungary, excluding Croatia-Slavonia.
Although the territories of the former Kingdom of Hungary that were assigned by the treaty to neighbouring states in total had a majority of non-Hungarian population, they also included areas of Hungarian majority and significant Hungarian minorities, numbering 3,318,000 in total.
The number of Hungarians in the different areas based on census data of 1910. The present day location of each area is given in parenthesis.
The number of bilingual people was much higher, for example 1,398,729 people spoke German (17%), 399,176 people spoke Slovak (5%), 179,928 people spoke Croatian (2.2%) and 88,828 people spoke Romanian (1.1%). Hungarian was spoken by 96% of the total population and was the mother language of 89%. The percentage and the absolute number of all non-Hungarian nationalities decreased in the next decades, although the total population of the country increased.
After Word War II, about 200,000 Germans were deported to Germany according to the decree of the Potsdam Conference
. Under the forced exchange of population between Czechoslovakia and Hungary, approximately 73,000 Slovaks left Hungary. After these population movements Hungary became an ethnically almost homogeneous country except the rapidly growing number of Roma people in the second half of the 20th century.
(1938), two Vienna Awards
(1938
and 1940
), and aggression against Yugoslavia and Carpathian Ruthenia (1941).
The population of Northern Transylvania
, according to the Hungarian census from 1941 counted 53.5% Hungarians and 39.1% Romanians
.
The territory of Bacska had 789,705 inhabitants, and 45,4% or 47,2% declared themselves to be Hungarian native speakers or ethnic Hungarians.
The percentage of Hungarian speakers was 84% in southern Czechoslovakia and 15% in the Sub-Carpathian Rus.
in Communist Hungary.
 Unless otherwise indicated, vital statistics are from the Hungarian Statistical Office.
Unless otherwise indicated, vital statistics are from the Hungarian Statistical Office.
>
Year
Total Fertility Rate
1970–1975
2.09
1974–1977
2.28
1975–1980
2.12
1980–1985
1.81
1985–1990
1.82
1990–1995
1.73
1995–2000
1.38
2001–2005
1.30
2006–2008
1.34
2009
1.33
male:
1990: 65.1 years
2001: 68.2 years
2009: 70.1 years
female:
1990: 73.7 years
2001: 76.5 years
2009: 77.9 years
According to census data, the largest religion in Hungary is Catholicism
(54.5% — Roman Catholicism 51.9%; Greek Catholicism
2.6%). There is a significant Calvinist minority (16% of the population) and smaller Lutheran (3%),Baptist (0.2%), ortodox(0.015%) and Jewish (0.1%) minorities. However, these census figures are representative of religious affiliation rather than practice; fewer than 12% of Hungarians attend religious services at least once a week and fewer than 50% at least once a year, while 30% of Hungarians do not believe in God.
For historical reasons, significant Hungarian minority populations can be found in the surrounding countries, notably in Ukraine
(in Transcarpathia
), Slovakia
, Romania
(in Transylvania
), and Serbia
(in Vojvodina
). Austria
(in Burgenland
), Croatia
, and Slovenia
(Prekmurje
) are also host to a number of ethnic Hungarians.
 The following demographic statistics are from the CIA Factbook as of September 2009, unless otherwise indicated.
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA Factbook as of September 2009, unless otherwise indicated.
Population
:
9,905,596 (Only Hungarian citizens, 2009 est.)
Age structure:
0–14 years: 15% (male 763,553/female 720,112)
15–64 years: 69.3% (male 3,384,961/female 3,475,135)
65 years and over: 15.8% (male 566,067/female 995,768) (2009 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
15–64 years:
0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.57 male(s)/female
total population:
0.91 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
Ethnic groups:
Hungarian 93.2%, Roma 1.9%, other or unknown 5,8%.
Religion:
According to census data, the largest religion in Hungary is Catholicism
(54.5% — Roman Catholicism 51.9%; Greek Catholicism
2.6%). There is a significant Calvinist minority (16% of the population) and smaller Lutheran (3%), and Jewish (0.1%) minorities. However, these census figures are representative of religious affiliation rather than practice; fewer than 12% of Hungarians attend religious services at least once a week and fewer than 50% at least once a year, while 30% of Hungarians do not believe in a God.
Literacy
:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99.4%
male:
99.5%
female:
99.3% (2003 est.)
The majority of Hungarians became Christian in the 11th century. Hungary remained predominantly Catholic until the 16th century, when the Reformation
took place and, as a result, first Lutheranism
, then soon afterwards Calvinism
, became the religion of almost the entire population.
In the second half of the 16th century, however, Jesuits led a successful campaign of counterreformation among the Hungarians. Orthodox Christianity
in Hungary has been the religion mainly of some national minorities in the country, notably, Romanians
, Rusyns
, Ukrainians
, and Serbs
.
Faith Church
, one of Europe's largest Pentecostal churches, is also located in Hungary. Hungary has historically been home to a significant Jewish community.
. The main minority group
are the Roma. Other groups include: German
s, Slovaks
, Croats
and Bunjevci
s (0.2%), Romanians
(0.1%), Ukrainians
(0.1%), and Serbs
(0.1%).
and Avar
peoples. Written sources in the 9th century also suggest that some groups of the Onogurs
, and the Bulgars
occupied the valley of the river Mureş
at the time of the Magyars’ invasion. There is a question whether Romanian population existed in Transylvania during this time.
(See Origin of the Romanians)
tribes joined to the Hungarians and participated in the Hungarian conquest of Hungary. They settled mostly in Bihar county.
s migrated to the Carpathian Basin in the course of the 10th-12th centuries and they were composed of various ethnic groups. Most of them must have arrived from Volga Bulgaria
.
settlers ('Úzok' or 'Fekete Kunok/Black Cumans' in Hungarian) came to the Carphatian Basin from the middle of the 11th century. They were settled mostly in Barcaság
. The city of Ózd
got its name after them.
(Jász in Hungarian) people were a nomadic tribe which settled -with the Cumans- in the Kingdom of Hungary during the 13th century. Their name is almost certainly related to that of the Iazyges. Béla IV, king of Hungary granted them asylum and they became a privileged community with the right of self-government. During the centuries they were fully assimilated to the Hungarian population, their language disappeared, but they preserved their Jassic identity and their regional autonomy until 1876. Over a dozen settlements in Central Hungary (e.g. Jászberény
, Jászárokszállás
, Jászfényszaru
) still bear their name.
, a nomadic tribe who had opposed them, west of the Carpathian Mountains. There, the Cumans appealed to King Béla IV of Hungary for protection. In the Kingdom of Hungary, Cumans created two regions named Cumania
(Kunság
in Hungarian): Greater Cumania
(Nagykunság) and Little Cumania
(Kiskunság), both located the Great Hungarian Plain. Here, the Cumans maintained their autonomy, language and some ethnic customs well into the modern era. According to Pálóczi's estimation originally 70-80,000 Cumans settled in Hungary.
and this area was mentioned under different name (Olachi) in 1285. The first appearance of a supposed Romanian name 'Ola' in Hungary derives from a charter (1258). They were significant population in Transylvania
, Banat
, Maramaros
and Partium
. Jean W.Sedlar estimates that Vlachs (Romanians) constituted about two-thirds of Transylvania's population in 1241 on the eve of the Mongol invasion, however according to other researches Hungarian ethnic group was in majority in Transylvania before Battle of Mohács
.
people lived mainly in Upper Hungary
, northern parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. Regions of Vojvodina
and Banat
, Békés county had bigger Slovak groups from the 18th century. After WWII a major population exchange with Czechoslovakia
was carried out: about 73,000 Slovaks were transferred to Slovakia
, replaced by a comparable number of Hungarians.
threat, a large number of Serbs
migrated to the Hungarian Kingdom. After the Battle of Mohács
, most of the territory of Hungary got into Ottoman rule. In that time, especially in the 17th century, many Serb, and other Southern Slavic immigrants settled in Hungary. Most of the Ottoman soldiers in the territory of Hungary were South Slavs
(the Janissary
). After the Turkish
withdrawal, Kingdom of Hungary came under Habsburg
rule, a new wave of Serb refugees migrated to the area around 1690, as a consequence of the Habsburg-Ottoman war. In the first half of the 18th century, Serbs and South Slavs were ethnic majority in several cities in Hungary.
and in Southern Transylvania
(Transylvanian Saxons
).
The third, largest wave of German-speaking immigrants into Hungary occurred after the withdrawal of the Ottoman Empire
from Hungarian territory, after the Treaty of Karlowitz
. Between 1711 and 1780, German-speaking settlers immigrated to the regions of Southern Hungary, mostly region of Bánát
, Bács-Bodrog
, Baranya
and Tolna
counties (as well as into present-day Romania
and Yugoslavia
), which had been depopulated by the Ottoman wars
. At the end of the 18th century, the Kingdom of Hungary contained over one million German-speaking residents (collectively known as Danube Swabians
). In 2001, 62,105 people declared to be German in Hungary.
had lived mostly in Carpathian Ruthenia
, Northeast Hungary, however significant Rusyn population appeared in Vojvodina
from the 18th century.
was in personal union with Hungary from 1102. Croat
communities were spread mostly in the western and southern part of the country and along the Danube, including Budapest.
lived at the northern borders of Kingdom of Hungary from the arrival of the Hungarians.
(Vendek in Hungarian) lived in the western part of the Carpathian basin before the Hungarian conquest. In the 11th and 12th century, the current linguistic and ethnic border between the Hungarian and Slovene people was established. Nowadays, they live in Vendvidék (Slovenska krajina in Slovenians) between the Mura and the Rába
rivers. In 2001, there were around 5,000 Slovenes in Hungary.
came to Hungary from the Balkans in the 10 - 11th century.
 The Romani people arrived in Hungary in the fifteenth century from Turkey. Nowadays, the real number of Roma in Hungary is a disputed question. In the 2001 census only 190 046 (2%) called themselves Roma, but experts and Roma organisations estimate that there are between 450,000 and 1,000,000 Roma living in Hungary. Since then, the size of the Roma population has increased rapidly. Today every fifth or sixth newborn child belongs to the Roma minority. Based on current demographic trends, a 2006 estimate by Central European Management Intelligence claims that the proportion of the Roma population will double by 2050, putting the percentage of its Roma community at around 14-15% of the country's population.
The Romani people arrived in Hungary in the fifteenth century from Turkey. Nowadays, the real number of Roma in Hungary is a disputed question. In the 2001 census only 190 046 (2%) called themselves Roma, but experts and Roma organisations estimate that there are between 450,000 and 1,000,000 Roma living in Hungary. Since then, the size of the Roma population has increased rapidly. Today every fifth or sixth newborn child belongs to the Roma minority. Based on current demographic trends, a 2006 estimate by Central European Management Intelligence claims that the proportion of the Roma population will double by 2050, putting the percentage of its Roma community at around 14-15% of the country's population.
There are problems related to the Roma minority in Hungary, and the very subject is a heated and disputed topic.
Objective problems:
migrated to Kingdom of Hungary from the 15th and 16th centuries. Mass migrations did not occur until the 17th century, the largest waves being in 1718 and 1760-1770; they were primarily connected to the economic conditions of the period. It is estimated that 10,000 Greeks emigrated to Hungary in the second half of the 18th century.
and the surrounding villages were inhabited by Bulgarians since the Middle Ages
. However, present day Bulgarians
are largely descended from gardeners who migrated to Austria-Hungary
from the 18th century.
Demographics
Demographics are the most recent statistical characteristics of a population. These types of data are used widely in sociology , public policy, and marketing. Commonly examined demographics include gender, race, age, disabilities, mobility, home ownership, employment status, and even location...
features of the population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
of Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
, including population density
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
, ethnicity
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Historical
The population composition at the foundation of Hungary (895) depends on the size of the arriving Hungarian population and the size of the Slavic (and remains of Avar-Slavic) population at the time. One source mentions 200 000 Slavs and 400 000 Hungarians, while other sources often don't give estimates for both, making comparison more difficult. The size of the Hungarian population around 895 is often estimated between 120 000 and 600 000, with a number of estimates in the 400-600 000 range. Other sources only mention a fighting force of 25 000 Magyar warriors used in the attack, while declining to estimate the total population including women and children and warriors not participating in the invasion. In the historical demographics the largest earlier shock was the Mongol Invasion of Hungary, several plagues also took a toll on the country's population.According to the demographers, about 80 percent of the population was made up of Hungarians before the Battle of Mohács
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács was fought on August 29, 1526 near Mohács, Hungary. In the battle, forces of the Kingdom of Hungary led by King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia were defeated by forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent....
, however the Hungarian ethnic group became a minority in its own country after the Rákóczi's War for Independence
Rákóczi's War for Independence
Rákóczi's War for Independence was the first significant attempt to topple therule of Habsburg Austria over Hungary. The war was fought by a group of noblemen, wealthy and high-ranking progressives and was led by Francis II Rákóczi Rákóczi's War for Independence (1703–1711) was the first...
. Major territorial changes made Hungary ethnically homogeneous after World War I. Nowadays, more than nine-tenths of the population is ethnically Hungarian and speaks Hungarian as the mother tongue.
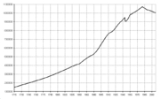
900–1910
| Time | Population | Percentage rate of Hungarians (without Kingdom of Croatia Kingdom of Croatia Kingdom of Croatia can refer to:* Kingdom of Croatia * Kingdom of Croatia * Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia... ) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| c. Circa Circa , usually abbreviated c. or ca. , means "approximately" in the English language, usually referring to a date... 900 AD Anno Domini and Before Christ are designations used to label or number years used with the Julian and Gregorian calendars.... |
c. Circa Circa , usually abbreviated c. or ca. , means "approximately" in the English language, usually referring to a date... 600,000 |
66% | |
| 1000 | 1,000,000-1,500,000 | ||
| 1222 | 2,000,000 | 70–80% | The time of the Golden Bull Golden Bull of 1222 The Golden Bull of 1222 was a golden bull, or edict, issued by King Andrew II of Hungary. The law established the rights of the Hungarian nobility, including the right to disobey the King when he acted contrary to law . The nobles and the church were freed from all taxes and could not be forced to... . The last estimate before the Tatar invasion Mongol invasion of Europe The resumption of the Mongol invasion of Europe, during which the Mongols attacked medieval Rus' principalities and the powers of Poland and Hungary, was marked by the Mongol invasion of Rus starting in 21 December 1237... . |
| 1242 | 1,200,000 | Population decreased after the Mongol invasion of Hungary(estimations about population loss are between 20% and 50%). | |
| 1300 | 2,000,000 | ||
| 1348 |
|
Before the plague (at the time of the Angevin Capetian House of Anjou The Capetian House of Anjou, also known as the House of Anjou-Sicily and House of Anjou-Naples, was a royal house and cadet branch of the direct House of Capet. Founded by Charles I of Sicily, a son of Louis VIII of France, the Capetian king first ruled the Kingdom of Sicily during the 13th century... kings.) |
|
| 1370 | c. Circa Circa , usually abbreviated c. or ca. , means "approximately" in the English language, usually referring to a date... 2,000,000 |
60–70% | |
| 1400 |
|
||
| 1490 |
|
|
Before the Ottoman conquest (about 3.2 million Hungarians). |
| 1600 |
|
Populations of Royal Hungary, Transylvania and Ottoman Hungary together. | |
| 1699 |
|
|
At the time of Treaty of Karlowitz Treaty of Karlowitz The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed on 26 January 1699 in Sremski Karlovci , concluding the Austro-Ottoman War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman side had been defeated at the Battle of Zenta... (not more than 2 million Hungarians). |
| 1711 |
|
|
At the end of Kuruc Kuruc The kuruc was a term used to denote the armed anti-Habsburg rebels in Royal Hungary between 1671 and 1711.... War, starting date of the organized resettlement. |
| 1720 |
|
|
|
| 1790 |
|
|
End of the organized resettlement, approximately 800 new German villages were established between 1711 and 1780. |
| 1828 | 11,495,536 | 40-45% | |
| 1837 |
Croatia Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ... ) |
||
| 1846 | 12,033,399 |
|
Two years before Hungarian Revolution of 1848 Hungarian Revolution of 1848 The Hungarian Revolution of 1848 was one of many of the European Revolutions of 1848 and closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas... . |
| 1880 | 13,749,603 | 46% | |
| 1900 | 16,838,255 | 51.4% | |
| 1910 | 18,264,533 |
|
5% Jews History of the Jews in Hungary Hungarian Jews have existed since at least the 11th century. After struggling against discrimination throughout the Middle Ages, by the early 20th century the community grew to be 5% of Hungary's population , and were prominent in science, the arts and business... (counted according to their mother tongue). |
Note: The data refer to the territory of the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
, not of present-day Hungary.
Ethnic structure of the territory of contemporary Hungary (1495-1910)
| Ethnic group | 1495 | 1715 | 1785 | 1880 | 1900 | 1910 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hungarians | 990,000 95,6 % |
1,176,000 79,1 % |
2,103,000 79 % |
4,402,364 82.4 % |
5,890,999 85.9 % |
6,730,299 88.4 % |
| Germans Germans The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages.... |
17,000 1.6 % |
136,600 9.2 % |
291,900 11 % |
606,363 11.3 % |
604,751 8.8 % |
553,179 7.3 % |
| Slovaks Slovaks The Slovaks, Slovak people, or Slovakians are a West Slavic people that primarily inhabit Slovakia and speak the Slovak language, which is closely related to the Czech language.Most Slovaks today live within the borders of the independent Slovakia... |
n.d n.d. |
37,700 2.5 % |
130,400 4.9 % |
199,788 3.7 % |
192,227 2.8 % |
165,317 2.2 % |
| Croats Croats Croats are a South Slavic ethnic group mostly living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and nearby countries. There are around 4 million Croats living inside Croatia and up to 4.5 million throughout the rest of the world. Responding to political, social and economic pressure, many Croats have... |
1,200 0.1 % |
58,900 4 % |
71,700 2.7 % |
59,251 1.1 % |
68,161 1 % |
62,018 0.8 % |
| Others | 23,800 2.4 % |
70,800 4.8 % |
66,214 2.4 % |
75,598 1.5 % |
98,277 1.5 % |
101,301 1.3 % |
| Total | 1,032,000 | 1,480,000 | 2,663,214 | 5,343,364 | 6,854,415 | 7,612,114 |
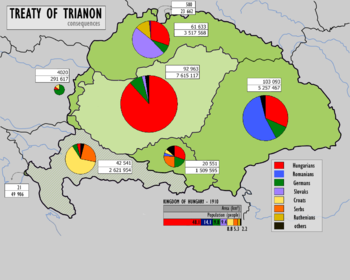
Treaty of Trianon
Hungary lost 64% of its total population in consequence of the Treaty of TrianonTreaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon was the peace agreement signed in 1920, at the end of World War I, between the Allies of World War I and Hungary . The treaty greatly redefined and reduced Hungary's borders. From its borders before World War I, it lost 72% of its territory, which was reduced from to...
, which was decreased from 20.9 million to 7.6 million, and 31% (3.3 out of 10.7 million) of its ethnic Hungarians, Hungary lost five of its ten most populous cities.

Although the territories of the former Kingdom of Hungary that were assigned by the treaty to neighbouring states in total had a majority of non-Hungarian population, they also included areas of Hungarian majority and significant Hungarian minorities, numbering 3,318,000 in total.
The number of Hungarians in the different areas based on census data of 1910. The present day location of each area is given in parenthesis.
- In Upper HungaryUpper HungaryUpper Hungary is the usual English translation for the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia...
(SlovakiaSlovakiaThe Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
): 885,000 - 30% - In TransylvaniaTransylvaniaTransylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
(RomaniaRomaniaRomania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
): 1,662,948 - 31.6% - In VojvodinaVojvodinaVojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
(SerbiaSerbiaSerbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
): 290,20 - 14.28% - In TranscarpathiaZakarpattia OblastThe Zakarpattia Oblast is an administrative oblast located in southwestern Ukraine. Its administrative center is the city of Uzhhorod...
(UkraineUkraineUkraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
): 183,000 - 30% - In CroatiaCroatiaCroatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
: 121,000 - 3.5% - In PrekmurjePrekmurjePrekmurje is a geographically, linguistically, culturally and ethnically defined region settled by Slovenes and lying between the Mur River in Slovenia and the Rába Valley in the most western part of Hungary...
(SloveniaSloveniaSlovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
): 14,065 - 15% - In BurgenlandBurgenlandBurgenland is the easternmost and least populous state or Land of Austria. It consists of two Statutarstädte and seven districts with in total 171 municipalities. It is 166 km long from north to south but much narrower from west to east...
(AustriaAustriaAustria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
): 26,200 - 9%
Non-Hungarian population in the Kingdom of Hungary, based on 1910 census data
Slovaks, Romanians, Ruthenians, Serbs, Croats and Germans, who represented the majority of the populations of the above-mentioned territories:- In Upper HungaryUpper HungaryUpper Hungary is the usual English translation for the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia...
(SlovakiaSlovakiaThe Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, CzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
): 1,687,977 Slovaks and 1,233,454 others (mostly Hungarians - 886,044, Germans, Ruthenians and Roma) [according to the 1921 census, however, there were 1,941,942 Slovaks and 1,058,928 others] - In Carpathian RutheniaCarpathian RutheniaCarpathian Ruthenia is a region in Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast , with smaller parts in easternmost Slovakia , Poland's Lemkovyna and Romanian Maramureş.It is...
(CzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
): 330,010 Ruthenians and 275,932 others (mostly Hungarians, Germans, Romanians, and Slovaks) - In TransylvaniaTransylvaniaTransylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
(RomaniaRomaniaRomania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
): 2,831,222 Romanians (53.8%) and 2,431,273 others (mostly Hungarians - 1,662,948 (31.6%) and Germans - 563,087 (10.7%). The 1919 and 1920 Transylvanian censuses indicate a greater percentage of Romanians (57.1%/57.3%) and a smaller Hungarian minority (26.5%/25.5%) - In VojvodinaVojvodinaVojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
and Croatia-Slavonia (YugoslaviaYugoslaviaYugoslavia refers to three political entities that existed successively on the western part of the Balkans during most of the 20th century....
): 2,756,000 Croats and Serbs and 1,366,000 others (mostly Hungarians and Germans) - In PrekmurjePrekmurjePrekmurje is a geographically, linguistically, culturally and ethnically defined region settled by Slovenes and lying between the Mur River in Slovenia and the Rába Valley in the most western part of Hungary...
(SloveniaSloveniaSlovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
): 74,199 Slovenes (80%), 14,065 Hungarians (15,2%), 2,540 Germans (2,7%) - In BurgenlandBurgenlandBurgenland is the easternmost and least populous state or Land of Austria. It consists of two Statutarstädte and seven districts with in total 171 municipalities. It is 166 km long from north to south but much narrower from west to east...
(AustriaAustriaAustria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
): 217,072 Germans and 69,858 others (mainly Croatian and Hungarian)
Minorities in post-Trianon Hungary
According to the 1920 census 10.4% of the population spoke one of the minority languages as mother language:- 551,212 German (6.9%)
- 141,882 Slovak (1.8%)
- 23,760 Romanian (0.3%)
- 36,858 Croatian (0.5%)
- 23,228 Bunjevac and Šokac (0.3%)
- 17,131 Serb (0.2%)
- 7,000 Slovenes (0,08%)
The number of bilingual people was much higher, for example 1,398,729 people spoke German (17%), 399,176 people spoke Slovak (5%), 179,928 people spoke Croatian (2.2%) and 88,828 people spoke Romanian (1.1%). Hungarian was spoken by 96% of the total population and was the mother language of 89%. The percentage and the absolute number of all non-Hungarian nationalities decreased in the next decades, although the total population of the country increased.
After Word War II, about 200,000 Germans were deported to Germany according to the decree of the Potsdam Conference
Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference was held at Cecilienhof, the home of Crown Prince Wilhelm Hohenzollern, in Potsdam, occupied Germany, from 16 July to 2 August 1945. Participants were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States...
. Under the forced exchange of population between Czechoslovakia and Hungary, approximately 73,000 Slovaks left Hungary. After these population movements Hungary became an ethnically almost homogeneous country except the rapidly growing number of Roma people in the second half of the 20th century.
From 1938 to 1945
Hungary expanded its borders into Czechoslovakia, Romania, and Yugoslavia at the outset of the war. These annexations were affirmed under the Munich AgreementMunich Agreement
The Munich Pact was an agreement permitting the Nazi German annexation of Czechoslovakia's Sudetenland. The Sudetenland were areas along Czech borders, mainly inhabited by ethnic Germans. The agreement was negotiated at a conference held in Munich, Germany, among the major powers of Europe without...
(1938), two Vienna Awards
Vienna Awards
The Vienna Awards are two arbitral awards by which arbiters of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy sought to enforce peacefully the claims of Hungary on territory it had lost in 1920 when it signed the Treaty of Trianon...
(1938
First Vienna Award
The First Vienna Award was the result of the First Vienna Arbitration, which took place at Vienna's Belvedere Palace on November 2, 1938. The Arbitration and Award were direct consequences of the Munich Agreement...
and 1940
Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award was the second of two Vienna Awards arbitrated by the Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. Rendered on August 30, 1940, it re-assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania from Romania to Hungary.-Prelude and historical background :After the World War I, the multi-ethnic...
), and aggression against Yugoslavia and Carpathian Ruthenia (1941).
The population of Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania is a region of Transylvania, situated within the territory of Romania. The population is largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians, and the region has been part of Romania since 1918 . During World War II, as a consequence of the territorial agreement known as...
, according to the Hungarian census from 1941 counted 53.5% Hungarians and 39.1% Romanians
Romanians
The Romanians are an ethnic group native to Romania, who speak Romanian; they are the majority inhabitants of Romania....
.
The territory of Bacska had 789,705 inhabitants, and 45,4% or 47,2% declared themselves to be Hungarian native speakers or ethnic Hungarians.
The percentage of Hungarian speakers was 84% in southern Czechoslovakia and 15% in the Sub-Carpathian Rus.
Communist/Socialist era (1949-1990)
According to some authors there was an enforced MagyarizationMagyarization
Magyarization is a kind of assimilation or acculturation, a process by which non-Magyar elements came to adopt Magyar culture and language due to social pressure .Defiance or appeals to the Nationalities Law, met...
in Communist Hungary.
Numbers about ethnic groups between 1920 and 1980
| Ethnic group | 1920 | 1930 | 1941The 1941 data refer to the Kingdom of Hungary Kingdom of Hungary The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders... after the territorial changes regarding North-Transylvania and other territories, all of which had been part of the Kingdom of Hungary Kingdom of Hungary The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders... until 1920. |
1949 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hungarians | 7 155 973 89.6 % |
8 000 335 92.1 % |
11 881 455 80.9 % |
9 076 041 98.6 % |
9 786 038 98.2 % |
10 166 237 98.5 % |
10 638 974 99.3 % |
| Germans | 550 062 6.9 % |
477 153 5.5, % |
533 045 3.6 % |
22 455 0.2 % |
50 765 0.5 % |
35 594 0.4 % |
11 310 0.1 % |
| Slovaks Slovaks The Slovaks, Slovak people, or Slovakians are a West Slavic people that primarily inhabit Slovakia and speak the Slovak language, which is closely related to the Czech language.Most Slovaks today live within the borders of the independent Slovakia... |
141 877 1.8 % |
104 786 1.2 % |
175 550 1.2 % |
25 988 0.3 % |
30 630 0.3 % |
21 176 0.2 % |
9 101 0.1 % |
| Romanians | 23 695 0.3 % |
16 221 0.2 % |
1 051 026 7.2 % |
14 713 0.2 % |
15 787 0.2 % |
12 624 0.1 % |
8 874 0.1 % |
| Ruthenians Ruthenians The name Ruthenian |Rus']]) is a culturally loaded term and has different meanings according to the context in which it is used. Initially, it was the ethnonym used for the East Slavic peoples who lived in Rus'. Later it was used predominantly for Ukrainians... |
- | - | 547 770 3.7 % |
- | - | - | - |
| Croats Croats Croats are a South Slavic ethnic group mostly living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and nearby countries. There are around 4 million Croats living inside Croatia and up to 4.5 million throughout the rest of the world. Responding to political, social and economic pressure, many Croats have... |
58 931 0.7 % |
47 337 0.5 % |
12 346 0.1 % |
20 423 0.2 % |
33 014 0.3 % |
17 609 0.2 % |
13 895 0.1 % |
| Serbs Serbs The Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in... |
17 132 0.2 % |
7 031 0.1 % |
213 585 1.5 % |
5 158 0.1 % |
4 583 0.1 % |
12 235 0.1 % |
2 805 0.0% |
| Slovenes | 6 087 0.1 % |
5 464 0.1 % |
94 000 0.1 % |
4 473 0.1 % |
- | 4 205 0.0 % |
1 731 0.0 % |
| Roma | 6 989 0.1 % |
7 841 0.1 % |
76 209 0.5 % |
21 387 0.2 % |
25 633 0.3 % |
34 957 0.3 % |
6 404 0.1 % |
| Others | 26 123 0.3 % |
18 946 0.2 % |
29 210 0.2 % |
14 161 0.1 % |
14 534 0.1 % |
17 462 0.2 % |
16 369 0.2 % |
| JewishExcept in the year 1941, Jewish people were not recognized as a minority, but only as a religion — assuredly, many Jews considered themselves as belonging to one of the recognized minorities. | - | - | 139 041 0.9 % |
- | - | - | - |
| Total | 7 986 875 | 8 685 109 | 14 679 573 | 9 204 799 | 9 961 044 | 10 322 099 | 10 709 463 |
Vital statistics

Births and deaths
| Average population (x 1000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918 | 128 000 | 207 000 | -79 000 | 15.3 | 25.7 | -10.4 | |
| 1919 | 7 860 | 217 000 | 157 000 | 60 000 | 27.6 | 20.0 | 7.6 |
| 1920 | 7 940 | 249 000 | 170 000 | 79 000 | 31.4 | 21.4 | 10.0 |
| 1921 | 8 020 | 255 000 | 170 000 | 85 000 | 31.8 | 21.2 | 10.6 |
| 1922 | 8 080 | 249 000 | 173 000 | 76 000 | 30.8 | 21.4 | 9.4 |
| 1923 | 8 170 | 239 000 | 159 000 | 80 000 | 29.2 | 19.5 | 9.7 |
| 1924 | 8 220 | 221 000 | 168 000 | 53 000 | 26.9 | 20.4 | 6.5 |
| 1925 | 8 300 | 235 000 | 142 000 | 93 000 | 28.3 | 17.1 | 11.2 |
| 1926 | 8 370 | 229 000 | 140 000 | 89 000 | 27.4 | 16.7 | 10.7 |
| 1927 | 8 490 | 219 000 | 151 000 | 68 000 | 25.8 | 17.8 | 8.0 |
| 1928 | 8 510 | 225 000 | 146 000 | 79 000 | 26.4 | 17.2 | 9.2 |
| 1929 | 8 580 | 215 000 | 153 000 | 62 000 | 25.1 | 17.8 | 7.3 |
| 1930 | 8 660 | 220 000 | 134 000 | 86 000 | 25.4 | 15.5 | 9.9 |
| 1931 | 8 730 | 207 000 | 145 000 | 62 000 | 23.7 | 16.6 | 7.1 |
| 1932 | 8 783 | 206 000 | 157 000 | 49 000 | 23.4 | 17.9 | 5.5 |
| 1933 | 8 845 | 194 000 | 130 000 | 64 000 | 21.9 | 14.7 | 7.2 |
| 1934 | 8 915 | 194 279 | 129 049 | 65 230 | 21.8 | 14.5 | 7.3 |
| 1935 | 8 980 | 189 479 | 136 923 | 52 556 | 21.1 | 15.2 | 5.9 |
| 1936 | 9 040 | 183 369 | 128 333 | 55 036 | 20.3 | 14.2 | 6.1 |
| 1937 | 9 100 | 182 449 | 128 049 | 54 400 | 20.0 | 14.1 | 6.0 |
| 1938 | 9 159 | 182 206 | 130 628 | 51 578 | 19.9 | 14.3 | 5.6 |
| 1939 | 9 217 | 178 633 | 124 591 | 54 042 | 19.4 | 13.5 | 5.9 |
| 1940 | 9 280 | 185 562 | 132 735 | 52 827 | 20.0 | 14.3 | 5.7 |
| 1941 | 9 340 | 177 047 | 123 349 | 53 698 | 19.0 | 13.2 | 5.7 |
| 1942 | 9 392 | 187 187 | 136 844 | 50 343 | 19.9 | 14.6 | 5.4 |
| 1943 | 9 440 | 173 295 | 127 158 | 46 137 | 18.4 | 13.5 | 4.9 |
| 1944 | 9 250 | 190 000 | 144 048 | 45 952 | 20.5 | 15.6 | 5.0 |
| 1945 | 9 055 | 169 091 | 211 323 | -42 232 | 18.7 | 23.3 | -4.7 |
| 1946 | 9 042 | 169 120 | 135 486 | 33 634 | 18.7 | 15.0 | 3.7 |
| 1947 | 9 093 | 187 316 | 117 537 | 69 779 | 20.6 | 12.9 | 7.7 |
| 1948 | 9 158 | 191 907 | 105 780 | 86 127 | 21.0 | 11.6 | 9.4 |
| 1949 | 9 249 | 190 398 | 105 718 | 84 680 | 20.6 | 11.4 | 9.2 |
| 1950 | 9 338 | 195 567 | 106 902 | 88 665 | 20.9 | 11.4 | 9.5 |
| 1951 | 9 423 | 190 645 | 109 998 | 80 647 | 20.2 | 11.7 | 8.6 |
| 1952 | 9 504 | 185 820 | 107 443 | 78 377 | 19.6 | 11.3 | 8.2 |
| 1953 | 9 595 | 206 926 | 112 039 | 94 887 | 21.6 | 11.7 | 9.9 |
| 1954 | 9 706 | 223 347 | 106 670 | 116 677 | 23.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 |
| 1955 | 9 825 | 210 430 | 97 848 | 112 582 | 21.4 | 10.0 | 11.5 |
| 1956 | 9 911 | 192 810 | 104 236 | 88 574 | 19.5 | 10.5 | 8.9 |
| 1957 | 9 840 | 167 202 | 103 645 | 63 557 | 17.0 | 10.5 | 6.5 |
| 1958 | 9 882 | 158 428 | 97 866 | 60 562 | 16.0 | 9.9 | 6.1 |
| 1959 | 9 937 | 151 194 | 103 880 | 47 314 | 15.2 | 10.5 | 4.8 |
| 1960 | 9 984 | 146 461 | 101 525 | 44 936 | 14.7 | 10.2 | 4.5 |
| 1961 | 10 029 | 140 365 | 96 410 | 43 955 | 14.0 | 9.6 | 4.4 |
| 1962 | 10 072 | 130 053 | 108 273 | 21 780 | 12.9 | 10.7 | 2.2 |
| 1963 | 10 104 | 132 335 | 99 871 | 32 464 | 13.1 | 9.9 | 3.2 |
| 1964 | 10 135 | 132 141 | 100 830 | 31 311 | 13.0 | 9.9 | 3.1 |
| 1965 | 10 160 | 133 009 | 108 119 | 24 890 | 13.1 | 10.6 | 2.4 |
| 1966 | 10 197 | 138 489 | 101 943 | 36 546 | 13.6 | 10.0 | 3.6 |
| 1967 | 10 223 | 148 886 | 109 530 | 39 356 | 14.6 | 10.7 | 3.8 |
| 1968 | 10 275 | 154 419 | 115 354 | 39 065 | 15.0 | 11.2 | 3.8 |
| 1969 | 10 316 | 154 318 | 116 659 | 37 659 | 15.0 | 11.3 | 3.7 |
| 1970 | 10 338 | 151 819 | 120 197 | 31 622 | 14.7 | 11.6 | 3.1 |
| 1971 | 10 368 | 150 640 | 123 009 | 27 631 | 14.5 | 11.9 | 2.7 |
| 1972 | 10 398 | 153 625 | 118 991 | 34 634 | 14.8 | 11.4 | 3.3 |
| 1973 | 10 432 | 156 224 | 123 366 | 32 858 | 15.0 | 11.8 | 3.1 |
| 1974 | 10 479 | 186 288 | 125 816 | 60 472 | 17.8 | 12.0 | 5.8 |
| 1975 | 10 532 | 194 240 | 131 102 | 63 138 | 18.4 | 12.4 | 6.0 |
| 1976 | 10 589 | 185 405 | 132 240 | 53 165 | 17.5 | 12.5 | 5.0 |
| 1977 | 10 637 | 177 574 | 132 031 | 45 543 | 16.7 | 12.4 | 4.3 |
| 1978 | 10 673 | 168 160 | 140 121 | 28 039 | 15.8 | 13.1 | 2.6 |
| 1979 | 10 698 | 160 364 | 136 829 | 23 535 | 15.0 | 12.8 | 2.2 |
| 1980 | 10 707 | 148 673 | 145 355 | 3 318 | 13.9 | 13.6 | 0.3 |
| 1981 | 10 700 | 142 890 | 144 757 | -1 867 | 13.3 | 13.5 | -0.2 |
| 1982 | 10 683 | 133 559 | 144 318 | -10 759 | 12.5 | 13.5 | -1.0 |
| 1983 | 10 656 | 127 258 | 148 643 | -21 385 | 11.9 | 13.9 | -2.0 |
| 1984 | 10 619 | 125 359 | 146 709 | -21 350 | 11.8 | 13.8 | -2.0 |
| 1985 | 10 579 | 130 200 | 147 614 | -17 414 | 12.3 | 14.0 | -1.6 |
| 1986 | 10 534 | 128 204 | 147 089 | -18 885 | 12.2 | 14.0 | -1.8 |
| 1987 | 10 486 | 125 840 | 142 601 | -16 761 | 12.0 | 13.6 | -1.6 |
| 1988 | 10 443 | 124 296 | 140 042 | -15 746 | 11.9 | 13.4 | -1.5 |
| 1989 | 10 398 | 123 304 | 144 695 | -21 391 | 11.9 | 13.9 | -2.1 |
| 1990 | 10 374 | 125 679 | 145 660 | -19 981 | 12.1 | 14.0 | -1.9 |
| 1991 | 10 373 | 127 207 | 144 813 | -17 606 | 12.3 | 14.0 | -1.7 |
| 1992 | 10 369 | 121 724 | 148 781 | -27 057 | 11.7 | 14.3 | -2.6 |
| 1993 | 10 357 | 117 033 | 150 244 | -33 211 | 11.3 | 14.5 | -3.2 |
| 1994 | 10 343 | 115 598 | 146 889 | -31 291 | 11.2 | 14.2 | -3.0 |
| 1995 | 10 329 | 112 054 | 145 431 | -33 377 | 10.8 | 14.1 | -3.2 |
| 1996 | 10 311 | 105 272 | 143 130 | -37 858 | 10.2 | 13.9 | -3.7 |
| 1997 | 10 290 | 100 350 | 139 434 | -39 084 | 9.8 | 13.6 | -3.8 |
| 1998 | 10 267 | 97 301 | 140 870 | -43 569 | 9.5 | 13.7 | -4.2 |
| 1999 | 10 238 | 94 645 | 143 210 | -48 565 | 9.2 | 14.0 | -4.7 |
| 2000 | 10 211 | 97 597 | 135 601 | -38 004 | 9.6 | 13.3 | -3.7 |
| 2001 | 10 198 | 97 047 | 132 183 | -35 136 | 9.5 | 13.0 | -3.4 |
| 2002 | 10 165 | 96 804 | 132 833 | -36 029 | 9.5 | 13.1 | -3.5 |
| 2003 | 10 129 | 94 647 | 135 823 | -41 176 | 9.3 | 13.4 | -4.1 |
| 2004 | 10 108 | 95 137 | 132 492 | -37 355 | 9.4 | 13.1 | -3.7 |
| 2005 | 10 088 | 97 496 | 135 732 | -38 236 | 9.7 | 13.5 | -3.8 |
| 2006 | 10 072 | 99 871 | 131 603 | -31 732 | 9.9 | 13.1 | -3.2 |
| 2007 | 10 056 | 97 613 | 132 938 | -35 325 | 9.7 | 13.2 | -3.5 |
| 2008 | 10 038 | 99 149 | 130 027 | -30 878 | 9.9 | 13.0 | -3.1 |
| 2009 | 10 022 | 96 450 | 130 350 | -33 900 | 9.6 | 13.0 | -3.4 |
| 2010 | 10 000 | 90 350 | 130 450 | -40 100 | 9.0 | 13.0 | -4.0 |
Infant mortality rate
The infant mortality rate (IMR) decreased considerably after WW II. In 1949, the IMR was 91.0. The rate decreased to 47.6 in 1960, 35.9 in 1970, 23.2 in 1980, 14.8 in 1990, 9.2 in 2000 and reached an all time low in 2009: 5.1 per 1000 live born children.http://portal.ksh.hu/pls/ksh/docs/eng/xstadat/xstadat_long/h_wdsd001a.htmlTotal fertility rates
| > | |
| Year | Total Fertility Rate Total Fertility Rate The total fertility rate of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates through her lifetime, and she... |
|---|---|
| 1900–1901 | 5.28 |
| 1910–1911 | 4.67 |
| 1920–1921 | 3.84 |
| 1930–1931 | 2.84 |
| 1940–1941 | 2.48 |
| 1948–1949 | 2.56 |
| 1950–1955 | 2.73 |
| 1955–1960 | 2.21 |
| 1960–1965 | 1.82 |
| 1965–1970 | 1.98 |
Total Fertility Rate
The total fertility rate of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates through her lifetime, and she...
Life expectancy at birth
male:
1990: 65.1 years
2001: 68.2 years
2009: 70.1 years
female:
1990: 73.7 years
2001: 76.5 years
2009: 77.9 years
The Hungarian census of year 2001
The census of 2001 recognized Hungarians along with sixteen other ethnic groups. The ethnic composition according to the 2001 census was as follows: (based on self-determination)- Hungarians: 9,416,045 or 93.2%
- Roma: 190,046 or 1.9%
- GermansGermansThe Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
: 62,233 or 0.6% - SlovaksSlovaksThe Slovaks, Slovak people, or Slovakians are a West Slavic people that primarily inhabit Slovakia and speak the Slovak language, which is closely related to the Czech language.Most Slovaks today live within the borders of the independent Slovakia...
: 17,693 or 0.17% - CroatsCroatsCroats are a South Slavic ethnic group mostly living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and nearby countries. There are around 4 million Croats living inside Croatia and up to 4.5 million throughout the rest of the world. Responding to political, social and economic pressure, many Croats have...
: 15,620 or 0.15% - RomaniansRomaniansThe Romanians are an ethnic group native to Romania, who speak Romanian; they are the majority inhabitants of Romania....
: 7,995 or 0.08% - Other nationalities in Hungary: 20 473 (0,2%)
- Foreign nationality: 16 081 (0,16%)
- No answer, unknown: 570 537 (5,6%)
According to census data, the largest religion in Hungary is Catholicism
Catholicism
Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole....
(54.5% — Roman Catholicism 51.9%; Greek Catholicism
Hungarian Greek Catholic Church
The Hungarian Greek Catholic Church is a Byzantine Rite sui juris particular Church in full union with the Catholic Church that uses Hungarian in the liturgy.-History:...
2.6%). There is a significant Calvinist minority (16% of the population) and smaller Lutheran (3%),Baptist (0.2%), ortodox(0.015%) and Jewish (0.1%) minorities. However, these census figures are representative of religious affiliation rather than practice; fewer than 12% of Hungarians attend religious services at least once a week and fewer than 50% at least once a year, while 30% of Hungarians do not believe in God.
For historical reasons, significant Hungarian minority populations can be found in the surrounding countries, notably in Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
(in Transcarpathia
Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia is a region in Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast , with smaller parts in easternmost Slovakia , Poland's Lemkovyna and Romanian Maramureş.It is...
), Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
(in Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
), and Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
(in Vojvodina
Vojvodina
Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
). Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
(in Burgenland
Burgenland
Burgenland is the easternmost and least populous state or Land of Austria. It consists of two Statutarstädte and seven districts with in total 171 municipalities. It is 166 km long from north to south but much narrower from west to east...
), Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
, and Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
(Prekmurje
Prekmurje
Prekmurje is a geographically, linguistically, culturally and ethnically defined region settled by Slovenes and lying between the Mur River in Slovenia and the Rába Valley in the most western part of Hungary...
) are also host to a number of ethnic Hungarians.
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics


Population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
:
9,905,596 (Only Hungarian citizens, 2009 est.)
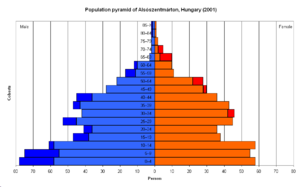
Age structure:
0–14 years: 15% (male 763,553/female 720,112)
15–64 years: 69.3% (male 3,384,961/female 3,475,135)
65 years and over: 15.8% (male 566,067/female 995,768) (2009 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
15–64 years:
0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.57 male(s)/female
total population:
0.91 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
Ethnic groups:
Hungarian 93.2%, Roma 1.9%, other or unknown 5,8%.
Religion:
According to census data, the largest religion in Hungary is Catholicism
Catholicism
Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole....
(54.5% — Roman Catholicism 51.9%; Greek Catholicism
Hungarian Greek Catholic Church
The Hungarian Greek Catholic Church is a Byzantine Rite sui juris particular Church in full union with the Catholic Church that uses Hungarian in the liturgy.-History:...
2.6%). There is a significant Calvinist minority (16% of the population) and smaller Lutheran (3%), and Jewish (0.1%) minorities. However, these census figures are representative of religious affiliation rather than practice; fewer than 12% of Hungarians attend religious services at least once a week and fewer than 50% at least once a year, while 30% of Hungarians do not believe in a God.
Literacy
Literacy
Literacy has traditionally been described as the ability to read for knowledge, write coherently and think critically about printed material.Literacy represents the lifelong, intellectual process of gaining meaning from print...
:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99.4%
male:
99.5%
female:
99.3% (2003 est.)
- See also : HungaryHungaryHungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
Religion
| Denominations | Population | % of total |
|---|---|---|
| Catholicism Catholicism Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole.... |
5,558,901 | 54.5 |
| Roman Catholics | 5,289,521 | 51.9 |
| Greek Catholics | 268,935 | 2.6 |
| Protestantism Protestantism Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the... |
1,985,576 | 19.5 |
| Calvinists | 1,622,796 | 15.9 |
| Lutherans | 304,705 | 3.0 |
| Baptists | 17,705 | 0.2 |
| Unitarians Unitarianism Unitarianism is a Christian theological movement, named for its understanding of God as one person, in direct contrast to Trinitarianism which defines God as three persons coexisting consubstantially as one in being.... |
6,541 | 0.1 |
| Other Protestants | 33,829 | 0.3 |
| Orthodox Christianity Orthodox Christianity The term Orthodox Christianity may refer to:* the Eastern Orthodox Church and its various geographical subdivisions... |
15,298 | 0.1 |
| Other Christians | 24,340 | 0.2 |
| Judaism Judaism Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people... |
12,871 | 0.1 |
| Other religions | 13,567 | 0.1 |
| Total religions | 7,610,553 | 74.6 |
| No religion | 1,483,369 | 14.5 |
| Did not wish to answer | 1,034,767 | 10.1 |
| Unknown | 69,566 | 0.7 |
| total | 10,198,315 | 100.00 |
The majority of Hungarians became Christian in the 11th century. Hungary remained predominantly Catholic until the 16th century, when the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
took place and, as a result, first Lutheranism
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Western Christianity that identifies with the theology of Martin Luther, a German reformer. Luther's efforts to reform the theology and practice of the church launched the Protestant Reformation...
, then soon afterwards Calvinism
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
, became the religion of almost the entire population.
In the second half of the 16th century, however, Jesuits led a successful campaign of counterreformation among the Hungarians. Orthodox Christianity
Orthodox Christianity
The term Orthodox Christianity may refer to:* the Eastern Orthodox Church and its various geographical subdivisions...
in Hungary has been the religion mainly of some national minorities in the country, notably, Romanians
Romanians
The Romanians are an ethnic group native to Romania, who speak Romanian; they are the majority inhabitants of Romania....
, Rusyns
Rusyns
Carpatho-Rusyns are a primarily diasporic ethnic group who speak an Eastern Slavic language, or Ukrainian dialect, known as Rusyn. Carpatho-Rusyns descend from a minority of Ruthenians who did not adopt the use of the ethnonym "Ukrainian" in the early twentieth century...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians
Ukrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens...
, and Serbs
Serbs
The Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in...
.
Faith Church
Faith Church, Hungary
Faith Church is a major Pentecostal church in Hungary. The community is one of Europe's largest pentecostal-evangelical Christian churches, and the country's fourth most supported church...
, one of Europe's largest Pentecostal churches, is also located in Hungary. Hungary has historically been home to a significant Jewish community.
Largest cities
| Name | Population (1949) | Top population | Population (2010) | Agglomeration | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Budapest BudapestBudapest Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter... |
1,590,316 | 2,059,226 (1980) | 1,721,556 | 2,503,105 (2009) | Capital city |
| Debrecen Debrecen Debrecen , is the second largest city in Hungary after Budapest. Debrecen is the regional centre of the Northern Great Plain region and the seat of Hajdú-Bihar county.- Name :... |
115,399 | 212,235 (1990) | 207,270 | 237,888 (2005) | Regional centre, county seat, urban county |
| Szeged Szeged ' is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county town of Csongrád county. The University of Szeged is one of the most distinguished universities in Hungary.... |
104,867 | 169,930 (1990) | 169,731 | 201,307 (2005) | Regional centre, county seat, urban county |
| Miskolc Miskolc Miskolc is a city in northeastern Hungary, mainly with heavy industrial background. With a population close to 170,000 Miskolc is the fourth largest city of Hungary It is also the county capital of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén and the regional centre of Northern Hungary.- Geography :Miskolc is located... |
109,841 | 208,103 (1980) | 169,226 | 216,470 (2005) | Regional centre, county seat, urban county |
 Pécs PécsPécs Pécs is the fifth largest city of Hungary, located on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the south-west of the country, close to its border with Croatia. It is the administrative and economical centre of Baranya county... |
89,470 | 170,039 (1990) | 157,680 | 179,215 (2005) | Regional centre, county seat, urban county |
| Győr Gyor -Climate:-Main sights:The ancient core of the city is Káptalan Hill at the confluence of three rivers: the Danube, Rába and Rábca. Püspökvár, the residence of Győr’s bishops can be easily recognised by its incomplete tower. Győr’s oldest buildings are the 13th-century dwelling tower and the... |
69,583 | 130,478 (2010) | 130,478 | 182,776 (2005) | Regional centre, county seat, urban county |
| Nyíregyháza Nyíregyháza - Tourist sights :Nyíregyháza also has several museums and exhibitions, showing the city's rich cultural heritage.* Collection of the International Medallion Art and Small Sculpture Creative Community of Nyíregyháza-Sóstó – periodic exhibitions of works of contemporary artists-Twin towns — Sister... |
56,334 | 118,795 (2001) | 117,832 | ||
| County seat, urban county | |||||
| Kecskemét Kecskemét Kecskemét is a city in the central part of Hungary. It is the 8th largest city of the country, and the county seat of Bács-Kiskun.Kecskemét lies halfway between the capital Budapest and the country's third-largest city, Szeged, 86 kilometres from both of them and almost equal distance from the two... |
61,730 | 112,233 (2010) | 112,233 | ||
| County seat, urban county | |||||
| Székesfehérvár Székesfehérvár Székesfehérvár is a city in central Hungary and is the 9th largest in the country. Located around southwest of Budapest. It is inhabited by 101,973 people , with 136,995 in the Székesfehérvár Subregion. The city is the centre of Fejér county and the regional centre of Central Transdanubia... |
42,260 | 108,958(1990) | 101,973 | ||
| Regional centre, county seat, urban county |
Language
For 93.6% of the population, the mother language is HungarianHungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
. The main minority group
Minority group
A minority is a sociological group within a demographic. The demographic could be based on many factors from ethnicity, gender, wealth, power, etc. The term extends to numerous situations, and civilizations within history, despite the misnomer of minorities associated with a numerical statistic...
are the Roma. Other groups include: German
Ethnic German
Ethnic Germans historically also ), also collectively referred to as the German diaspora, refers to people who are of German ethnicity. Many are not born in Europe or in the modern-day state of Germany or hold German citizenship...
s, Slovaks
Slovaks
The Slovaks, Slovak people, or Slovakians are a West Slavic people that primarily inhabit Slovakia and speak the Slovak language, which is closely related to the Czech language.Most Slovaks today live within the borders of the independent Slovakia...
, Croats
Croats
Croats are a South Slavic ethnic group mostly living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and nearby countries. There are around 4 million Croats living inside Croatia and up to 4.5 million throughout the rest of the world. Responding to political, social and economic pressure, many Croats have...
and Bunjevci
Bunjevci
Bunjevci are a South Slavic community and ethnic group living mostly in the Bačka region of Serbia and southern Hungary...
s (0.2%), Romanians
Romanians
The Romanians are an ethnic group native to Romania, who speak Romanian; they are the majority inhabitants of Romania....
(0.1%), Ukrainians
Ukrainians
Ukrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens...
(0.1%), and Serbs
Serbs in Hungary
The Serbs in Hungary are recognized as an ethnic minority, numbering 7,350 people or 0.1% of the total population . The number of Serbs in Hungary has drastically diminished; in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries large Serbian communities existed throughout Hungary, notably in Buda , Baja,...
(0.1%).
Ethnic groups during history of Hungary
When the Hungarians invaded the Carpathian Basin, it were inhabited by SlavicSlavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
and Avar
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
peoples. Written sources in the 9th century also suggest that some groups of the Onogurs
Onogurs
The Onogurs, also known as Utigurs, were a horde of equestrian nomads in the North Eurasian steppe east of the Don River during the 5th to 8th centuries. The Onogurs crossed the Volga and entered into Europe around the year 460 within the larger context of the Great Migrations and the Turkic...
, and the Bulgars
Bulgars
The Bulgars were a semi-nomadic who flourished in the Pontic Steppe and the Volga basin in the 7th century.The Bulgars emerge after the collapse of the Hunnic Empire in the 5th century....
occupied the valley of the river Mureş
Mures River
The Mureș is an approximately 761 km long river in Eastern Europe. It originates in the Hășmașu Mare Range in the Eastern Carpathian Mountains, Romania, and joins the Tisza river at Szeged in southeastern Hungary....
at the time of the Magyars’ invasion. There is a question whether Romanian population existed in Transylvania during this time.
(See Origin of the Romanians)
Kabars
Three KabarKabar
The Khavars or erroneously Kabars were Khazarians, therefore Turkic people who joined to the Magyars in the 8th century.- History :...
tribes joined to the Hungarians and participated in the Hungarian conquest of Hungary. They settled mostly in Bihar county.
Böszörménys
The Muslim BöszörményBöszörmény
Böszörmény, also Izmaelita or Szerecsen , is a name for the Muslims who lived in the Kingdom of Hungary in the 10-13th centuries. Some of the böszörmény probably joined the federation of the seven Magyar tribes during the 9th century, and later smaller groups of Muslims arrived to the Carpathian...
s migrated to the Carpathian Basin in the course of the 10th-12th centuries and they were composed of various ethnic groups. Most of them must have arrived from Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria, or Volga–Kama Bolghar, is a historic Bulgar state that existed between the seventh and thirteenth centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama rivers in what is now Russia.-Origin:...
.
Pechenegs
Communities of Pechenegs (Besenyő in Hungarian) lived in the Kingdom of Hungary from the 11-12th centuries. They were most numerous in the county of Tolna.Oghuz Turks
Smaller groups of Oghuz TurkOghuz Turks
The Turkomen also known as Oghuz Turks were a historical Turkic tribal confederation in Central Asia during the early medieval Turkic expansion....
settlers ('Úzok' or 'Fekete Kunok/Black Cumans' in Hungarian) came to the Carphatian Basin from the middle of the 11th century. They were settled mostly in Barcaság
Burzenland
The Burzenland is a historic and ethnographic area in southeastern Transylvania, Romania with a mixed population...
. The city of Ózd
Ózd
Ózd is a city in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county, Northern Hungary, away from county seat Miskolc. Ózd is the second largest city of the county.-History:The area has been inhabited since ancient times. The village Ózd was mentioned first in 1272...
got its name after them.
Jassics
The JassicJassic people
The Jassic people or Jász are an ethnic group of Hungarians who mostly live in the Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county of the Republic of Hungary. They are of Ossetic origin and originally spoke the Jassic dialect of the Ossetic language...
(Jász in Hungarian) people were a nomadic tribe which settled -with the Cumans- in the Kingdom of Hungary during the 13th century. Their name is almost certainly related to that of the Iazyges. Béla IV, king of Hungary granted them asylum and they became a privileged community with the right of self-government. During the centuries they were fully assimilated to the Hungarian population, their language disappeared, but they preserved their Jassic identity and their regional autonomy until 1876. Over a dozen settlements in Central Hungary (e.g. Jászberény
Jászberény
Jászberény is a city and market centre in Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county in Hungary.- Location :Jászberény is located in central Hungary, on the Zagyva River, a tributary of the Tisza River...
, Jászárokszállás
Jászárokszállás
Jászárokszállás is a town in Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county, in the Northern Great Plain region of central Hungary.-Geography:It covers an area of and has a population of 8267 people .-People:Famous actors from here are:* Jenő Balassa ,...
, Jászfényszaru
Jászfényszaru
Jászfényszaru is a town in Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county, in the Northern Great Plain region of central Hungary.-Geography:It covers an area of and has a population of 5887 people ....
) still bear their name.
Cumans
During the Russian campaign, the Mongols drove some 200,000 CumansCumans
The Cumans were Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation. After Mongol invasion , they decided to seek asylum in Hungary, and subsequently to Bulgaria...
, a nomadic tribe who had opposed them, west of the Carpathian Mountains. There, the Cumans appealed to King Béla IV of Hungary for protection. In the Kingdom of Hungary, Cumans created two regions named Cumania
Cumania
Cumania is a name formerly used to designate several distinct lands in Eastern Europe inhabited by and under the military dominance of the Cumans, a nomadic tribe who, with the Kipchaks, created a confederation. The Cumans were also known as the Polovtsians, or Folban...
(Kunság
Kunság
Kunság is a historical and geographical region in Hungary situated in the current Bács-Kiskun and Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok counties. Like other historical European regions called Cumania, it is named for the Cumans, a nomadic tribe of pagan Kipchaks that settled the area...
in Hungarian): Greater Cumania
Greater Cumania
Nagykunság is a historical and geographical region in Hungary situated in the current Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county between Szolnok and Debrecen. Like other historical European regions called Cumania, it is named for the Cumans, a nomadic tribe of pagan Kipchaks that settled the area.-See...
(Nagykunság) and Little Cumania
Little Cumania
Kiskunság is a historical and geographical region in Hungary situated in the current between Kalocsa and Szeged. Like other historical European regions called Cumania, it is named for the Cumans , a historically very significant nomadic tribe -See also:...
(Kiskunság), both located the Great Hungarian Plain. Here, the Cumans maintained their autonomy, language and some ethnic customs well into the modern era. According to Pálóczi's estimation originally 70-80,000 Cumans settled in Hungary.
Romanians
The oldest extant documents from Transylvania make reference to Vlachs too. Regardless of the subject of Romanian presence/non-presence in Transylvania prior to the Hungarian conquest, the first written sources about Romanian settlements derive from the 13th century, record was written about Olahteluk village in Bihar county from 1283. The 'land of Romanians', Terram Blacorum (1222,1280) showed up in FogarasFagaras
Făgăraș is a city in central Romania, located in Braşov County . Another source of the name is alleged to derive from the Hungarian language word for "partridge" . A more plausible explanation is that the name is given by Fogaras river coming from the Pecheneg "Fagar šu", which means ash water...
and this area was mentioned under different name (Olachi) in 1285. The first appearance of a supposed Romanian name 'Ola' in Hungary derives from a charter (1258). They were significant population in Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
, Banat
Banat
The Banat is a geographical and historical region in Central Europe currently divided between three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania , the western part in northeastern Serbia , and a small...
, Maramaros
Máramaros
Máramaros is the name of a historic administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is presently in north-western Romania and western Ukraine...
and Partium
Partium
Partium or Részek is the name given in Hungarian to the region located to the north and west of Transylvania.-Origin of the name:...
. Jean W.Sedlar estimates that Vlachs (Romanians) constituted about two-thirds of Transylvania's population in 1241 on the eve of the Mongol invasion, however according to other researches Hungarian ethnic group was in majority in Transylvania before Battle of Mohács
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács was fought on August 29, 1526 near Mohács, Hungary. In the battle, forces of the Kingdom of Hungary led by King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia were defeated by forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent....
.
Slovaks
The SlovakSlovaks
The Slovaks, Slovak people, or Slovakians are a West Slavic people that primarily inhabit Slovakia and speak the Slovak language, which is closely related to the Czech language.Most Slovaks today live within the borders of the independent Slovakia...
people lived mainly in Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary is the usual English translation for the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia...
, northern parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. Regions of Vojvodina
Vojvodina
Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
and Banat
Banat
The Banat is a geographical and historical region in Central Europe currently divided between three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania , the western part in northeastern Serbia , and a small...
, Békés county had bigger Slovak groups from the 18th century. After WWII a major population exchange with Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
was carried out: about 73,000 Slovaks were transferred to Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, replaced by a comparable number of Hungarians.
Serbs
From the 14th century, escaping from the OttomanOttoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
threat, a large number of Serbs
Serbs in Hungary
The Serbs in Hungary are recognized as an ethnic minority, numbering 7,350 people or 0.1% of the total population . The number of Serbs in Hungary has drastically diminished; in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries large Serbian communities existed throughout Hungary, notably in Buda , Baja,...
migrated to the Hungarian Kingdom. After the Battle of Mohács
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács was fought on August 29, 1526 near Mohács, Hungary. In the battle, forces of the Kingdom of Hungary led by King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia were defeated by forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent....
, most of the territory of Hungary got into Ottoman rule. In that time, especially in the 17th century, many Serb, and other Southern Slavic immigrants settled in Hungary. Most of the Ottoman soldiers in the territory of Hungary were South Slavs
South Slavs
The South Slavs are the southern branch of the Slavic peoples and speak South Slavic languages. Geographically, the South Slavs are native to the Balkan peninsula, the southern Pannonian Plain and the eastern Alps...
(the Janissary
Janissary
The Janissaries were infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops and bodyguards...
). After the Turkish
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
withdrawal, Kingdom of Hungary came under Habsburg
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
rule, a new wave of Serb refugees migrated to the area around 1690, as a consequence of the Habsburg-Ottoman war. In the first half of the 18th century, Serbs and South Slavs were ethnic majority in several cities in Hungary.
Germans
Three waves of German migration can be distinguished in Hungary before the 20th century. The first two waves of settlers arrived to the Hungarian Kingdom in the Middle Ages (11th and 13th centuries) in Upper HungaryUpper Hungary
Upper Hungary is the usual English translation for the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia...
and in Southern Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
(Transylvanian Saxons
Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania from the 12th century onwards.The colonization of Transylvania by Germans was begun by King Géza II of Hungary . For decades, the main task of the German settlers was to defend the southeastern border of the...
).
The third, largest wave of German-speaking immigrants into Hungary occurred after the withdrawal of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
from Hungarian territory, after the Treaty of Karlowitz
Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed on 26 January 1699 in Sremski Karlovci , concluding the Austro-Ottoman War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman side had been defeated at the Battle of Zenta...
. Between 1711 and 1780, German-speaking settlers immigrated to the regions of Southern Hungary, mostly region of Bánát
Banat
The Banat is a geographical and historical region in Central Europe currently divided between three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania , the western part in northeastern Serbia , and a small...
, Bács-Bodrog
Bács-Bodrog
Bács-Bodrog County was the administrative county of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary from 18th century to 1918. Its territory is currently in northern Serbia and southern Hungary. The capital of the county was Zombor .-Name:The county was named after two older counties: Bács and Bodrog...
, Baranya
Baranya
Baranya may refer to:*Baranya , a geographical region in Hungary and Croatia*Baranya , a county in Hungary*Baranya , a county in the historic Kingdom of Hungary...
and Tolna
Tolna
Tolna is a town in Tolna county, Hungary. It lies about north of Szekszárd and south of Budapest....
counties (as well as into present-day Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia refers to three political entities that existed successively on the western part of the Balkans during most of the 20th century....
), which had been depopulated by the Ottoman wars
Ottoman wars in Europe
The wars of the Ottoman Empire in Europe are also sometimes referred to as the Ottoman Wars or as Turkish Wars, particularly in older, European texts.- Rise :...
. At the end of the 18th century, the Kingdom of Hungary contained over one million German-speaking residents (collectively known as Danube Swabians
Danube Swabians
The Danube Swabians is a collective term for the German-speaking population who lived in the former Kingdom of Hungary, especially alongside the Danube River valley. Because of different developments within the territory settled, the Danube Swabians cannot be seen as a unified people...
). In 2001, 62,105 people declared to be German in Hungary.
Rusyns
RusynsRusyns
Carpatho-Rusyns are a primarily diasporic ethnic group who speak an Eastern Slavic language, or Ukrainian dialect, known as Rusyn. Carpatho-Rusyns descend from a minority of Ruthenians who did not adopt the use of the ethnonym "Ukrainian" in the early twentieth century...
had lived mostly in Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia is a region in Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast , with smaller parts in easternmost Slovakia , Poland's Lemkovyna and Romanian Maramureş.It is...
, Northeast Hungary, however significant Rusyn population appeared in Vojvodina
Vojvodina
Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
from the 18th century.
Croats
CroatiaCroatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
was in personal union with Hungary from 1102. Croat
Croats of Hungary
The Hungarian Croats are an ethnic minority in Hungary. According to the 2001 census, there were 25,730 Croats in Hungary or 0.26% of population....
communities were spread mostly in the western and southern part of the country and along the Danube, including Budapest.
Poles
The PolesPoles
thumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe...
lived at the northern borders of Kingdom of Hungary from the arrival of the Hungarians.
Slovenes
The SlovenesHungarian Slovenes
Hungarian Slovenes are an autochthonous ethnic and linguistic Slovene minority living in Hungary. The largest groups are the Rába Slovenes in the Rába Valley in western Hungary between the town of Szentgotthárd and the borders with Slovenia and Austria. They speak the Prekmurje dialect of Slovene...
(Vendek in Hungarian) lived in the western part of the Carpathian basin before the Hungarian conquest. In the 11th and 12th century, the current linguistic and ethnic border between the Hungarian and Slovene people was established. Nowadays, they live in Vendvidék (Slovenska krajina in Slovenians) between the Mura and the Rába
Rába
The Rába is a river in southeastern Austria and western Hungary and a right tributary of the Danube. Its source is in Austria, some kilometres east of Bruck an der Mur below Heubodenhöhe Hill. It flows through the Austrian states of Styria and Burgenland, and the Hungarian counties of Vas and...
rivers. In 2001, there were around 5,000 Slovenes in Hungary.
Jews
The first historical document about Jews of Hungary is the letter written about 960 to King Joseph of the Khazars by Hasdai ibn Shaprut, the Jewish statesman of Córdoba, in which he says Jews living in "the country of Hungarin".Armenians
The first ArmeniansArmenians in Hungary
Armenians in Hungary are ethnic Armenians living in the modern republic of Hungary. An estimated are up to 30,000 live in the nation today, making up roughly 0.01% of the population. Approximately two thirds of Hungary's Armenians population is found in Budapest and the surrounding Pest county...
came to Hungary from the Balkans in the 10 - 11th century.
The Roma minority


There are problems related to the Roma minority in Hungary, and the very subject is a heated and disputed topic.
Objective problems:
- Education/bad chances for work: slightly more than 80% of Roma children complete primary educationPrimary educationA primary school is an institution in which children receive the first stage of compulsory education known as primary or elementary education. Primary school is the preferred term in the United Kingdom and many Commonwealth Nations, and in most publications of the United Nations Educational,...
, but only one third continue studies into the intermediate (secondary) level. This is far lower than the more than 90% proportion of children of non-Roma families who continue studies at an intermediate level. Less than 1% of Roma hold higher educational certificates. - Poverty: most of the Roma people live in significantly worse conditions than others.
- Bad health conditions: life expectancy is about 10 years less compared to non-Romas
- Lack of debate regarding the subject: academic researchers and members of the mainstream press disregard any critics and study the subject in the canonical viewpoint. Critics don't have the funds necessary to perform alternative studies.
Greeks
GreeksGreeks in Hungary
Greeks in Hungary constitute one of the thirteen officially recognized ethnic minorities in Hungary since The Rights of National and Ethnic Minorities Act was enacted by the Hungarian parliament on July 7, 1993....
migrated to Kingdom of Hungary from the 15th and 16th centuries. Mass migrations did not occur until the 17th century, the largest waves being in 1718 and 1760-1770; they were primarily connected to the economic conditions of the period. It is estimated that 10,000 Greeks emigrated to Hungary in the second half of the 18th century.
Bulgarians
The town of SzentendreSzentendre
Szentendre is a riverside town in Pest county, Hungary, near the capital city Budapest. It is known for its museums , galleries, and artists. Due to its picturesque appearance and easy rail and river access, it has become a popular destination for tourists staying in Budapest...
and the surrounding villages were inhabited by Bulgarians since the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. However, present day Bulgarians
Bulgarians in Hungary
Bulgarians are one of the thirteen officially recognized ethnic minorities in Hungary since the Rights of National and Ethnic Minorities Act was enacted by the National Assembly of Hungary on 7 July 1993...
are largely descended from gardeners who migrated to Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
from the 18th century.
See also
- Hungarian diasporaHungarian diasporaHungarian diaspora is a term that encompasses the total ethnic Hungarian population located outside of current-day Hungary.There are two main groups of the diaspora...
- Demographics of the Kingdom of HungaryDemographics of the Kingdom of HungaryThis article is a list census data of counties in the Kingdom of Hungary during the time period between 1715 and 1910.The list contains only 39 counties of the total 72 counties of pre Trianon Hungary.-Abaúj-Torna:1910 census...
- History of HungaryHistory of HungaryHungary is a country in central Europe. Its history under this name dates to the early Middle Ages, when the Pannonian Basin was colonized by the Magyars, a semi-nomadic people from what is now central-northern Russia...
- Demographic history of SyrmiaDemographic history of Syrmia-Prehistory:Between 3000 BC and 2400 BC, Syrmia was a core area of Indo-European Vučedol culture. -6th-7th century:In 6th-7th century, entire Syrmia region was populated by Slavs. According to other source, it was also populated by Gepids, and Avars...
- MagyarizationMagyarizationMagyarization is a kind of assimilation or acculturation, a process by which non-Magyar elements came to adopt Magyar culture and language due to social pressure .Defiance or appeals to the Nationalities Law, met...

