Classical Athens
Encyclopedia
The city of Athens during the classical period of Ancient Greece (508-322 BC
) was a notable polis
(city-state
) of Attica
, Greece
, leading the Delian League
in the Peloponnesian War
against Sparta
and the Peloponnesian League
. Athenian democracy
was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes
following the tyranny of Hippias
. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC
(aftermath of Lamian War
) . The peak of Athenian hegemony
was achieved in the 440s
to 430s BC
, known as the Age of Pericles
.
In the classical period
, Athens
was a center for the arts, learning and philosophy
, home of Plato
's Akademia
and Aristotle
's Lyceum
, Athens was also the birthplace of Socrates
, Pericles
, Sophocles
, and many other prominent philosophers, writers and politicians of the ancient world. It is widely referred to as the cradle
of Western Civilization
, and the birthplace of democracy
, largely due to the impact of its cultural and political achievements during the 5th and 4th centuries BC on the rest of the then known European continent.
established a dictatorship in 514 B.C., which proved very unpopular, and was eventually overthrown with the help of an army from Sparta
, in 510 B.C. A radical politician of aristocratic background, Cleisthenes
, then took charge and established democracy in Athens. The reforms of Cleisthenes replaced the traditional four "tribes" (phyle
) with ten new ones, named after legendary heroes of Greece and having no class basis, which acted as electorates. Each tribe was in turn divided into three trittyes, while each trittys
had one or more deme
s (see deme
) - depending on their population - which became the basis of local government. The tribes each selected fifty members by lot for the Boule
, the council which governed Athens on a day-to-day basis. The public opinion
of voters could be influenced by the political satire
s written by the comic poets and performed in the city theaters. The Assembly
or Ecclesia was open to all full citizens and was both a legislature and a supreme court, except in murder cases and religious matters, which became the only remaining functions of the Areopagus. Most offices were filled by lot, although the ten strategoi
(generals) were elected.
 Prior to the rise of Athens, Sparta
Prior to the rise of Athens, Sparta
, a city-state with a militaristic culture, considered itself the leader of the Greeks, and enforced an hegemony
. In 499 BC Athens sent troops to aid the Ionia
n Greeks of Asia Minor
, who were rebelling against the Persian Empire
(see Ionian Revolt
). This provoked two Persian invasions of Greece, both of which were repelled under the leadership of the soldier-statesmen Miltiades
and Themistocles
(see Persian Wars). In 490 the Athenians, led by Miltiades
, prevented the first invasion of the Persians, guided by king Darius I, at the Battle of Marathon
. In 480 the Persians returned under a new ruler, Xerxes I
. The Hellenic League led by the Spartan King Leonidas led 7,000 men to hold the narrow passageway of Thermopylae
against the 100,000-250,000 army of Xerxes. Simultaneously the Athenians led an indecisive naval battle off Artemisium
. However, this delaying action was not enough to discourage the Persian advance which soon marched through Boeotia
, setting up Thebes
as their base of operations, and entered southern Greece. This forced the Athenians to evacuate Athens, which was taken by the Persians, and seek the protection of their fleet. Subsequently the Athenians and their allies, led by Themistocles
, defeated the Persian navy at sea in the Battle of Salamis
. It is interesting to note that Xerxes had built himself a throne on the coast in order to see the Greeks defeated. Instead, the Persians were routed. Sparta's hegemony was passing to Athens, and it was Athens that took the war to Asia Minor. These victories enabled it to bring most of the Aegean and many other parts of Greece together in the Delian League
, an Athenian-dominated alliance.
- an Athenian general, politician and orator - distinguished himself above the other personalities of the era, men who excelled in politics
, philosophy
, architecture
, sculpture
, history
and literature
. He fostered arts and literature and gave to Athens a splendor which would never return throughout its history. He executed a large number of public works projects and improved the life of the citizens. Hence, he gave his name to the Athenian Golden Age. Silver mined in Laurium
in southeastern Attica contributed greatly to the prosperity of this "Golden" Age of Athens.
During the time of the ascendancy of Ephialtes
as leader of the democratic faction, Pericles
was his deputy. When Ephialtes was assassinated
by personal enemies, Pericles stepped in and was elected general, or strategos
, in 445 BC
; a post he held continuously until his death in 429 BC
, always by election of the Athenian Assembly.
 Resentment by other cities at the hegemony of Athens led to the Peloponnesian War
Resentment by other cities at the hegemony of Athens led to the Peloponnesian War
in 431, which pitted Athens and her increasingly rebellious sea empire against a coalition of land-based states led by Sparta
. The conflict marked the end of Athenian command of the sea
. The war between Athens and the city-state Sparta ended with an Athenian defeat after Sparta started its own navy.
Athenian democracy was briefly overthrown by the coup
of 411, brought about because of its poor handling of the war, but it was quickly restored. The war ended with the complete defeat of Athens in 404. Since the defeat was largely blamed on democratic politicians such as Cleon
and Cleophon, there was a brief reaction against democracy, aided by the Spartan army (the rule of the Thirty Tyrants
). In 403, democracy was restored
by Thrasybulus
and an amnesty declared.
and Corinth
, became her allies. Argos
, Thebes
and Corinth
, allied with Athens
, fought against Sparta
in the decisive Corinthian War
of 395 BC - 387 BC. Opposition to Sparta enabled Athens to establish a Second Athenian League. Finally Thebes
defeated Sparta in 371 in the Battle of Leuctra
. However, other Greek cities, including Athens, turned against Thebes
, and its dominance was brought to an end at the Battle of Mantinea (362 BC)
with the death of its leader, the military genius Epaminondas
.
was becoming dominant in Athenian affairs, despite the warnings of the last great statesman of independent Athens, Demosthenes
. In 338 BC the armies of Philip II
defeated Athens at the Battle of Chaeronea
, effectively limiting Athenian independence. Athens and other states became part of the League of Corinth
. Further, the conquests of his son, Alexander the Great, widened Greek horizons and made the traditional Greek city state obsolete. Antipater
dissolved the Athenian government and established a plutocratic system in 322 BC (see Lamian War
and Demetrius Phalereus
). Athens remained a wealthy city with a brilliant cultural life, but ceased to be an independent power.
In the 2nd century BC, following the Battle of Corinth (146 BC)
, Greece was absorbed into the Roman Republic
as part of the Achaea Province, concluding 200 years of Macedonian supremacy.
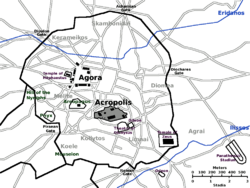 Athens was in Attica
Athens was in Attica
, about 30 stadia
from the sea, on the southwest slope of Mount Lycabettus
, between the small rivers Cephissus
to the west, Ilissos
to the south, and the Eridanos
to the north, the latter of which flowed through the town. The walled city measured about 1.5 km (0.93205910497471 mi) in diameter, although at its peak the city had suburbs extending well beyond these walls. The Acropolis
was just south of the centre of this walled area. The city was burnt by Xerxes
in 480 BC
, but was soon rebuilt under the administration of Themistocles
, and was adorned with public buildings by Cimon and especially by Pericles
, in whose time (461
-429 BC
) it reached its greatest splendour. Its beauty was chiefly due to its public buildings, for the private houses were mostly insignificant, and its streets badly laid out. Towards the end of the Peloponnesian war
, it contained more than 10,000 houses, which at a rate of 12 inhabitants to a house would give a population of 120,000, though some writers make the inhabitants as many as 180,000.
Athens consisted of two distinct parts:
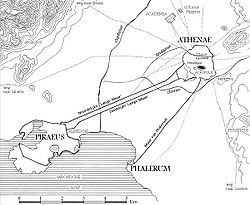 The Long Walls
The Long Walls
consisted of two walls leading to Piraeus
, 40 stadia
long (4.5 miles, 7 km), running parallel to each other, with a narrow passage between them. In addition, there was a wall to Phalerum on the east, 35 stadia long (4 miles, 6.5 km). There were therefore three long walls in all; but the name Long Walls seems to have been confined to the two leading to the Piraeus, while the one leading to Phalerum was called the Phalerian Wall. The entire circuit of the walls was 174.5 stadia (nearly 22 miles, 35 km), of which 43 stadia (5.5 miles, 9 km) belonged to the city, 75 stadia (9.5 miles, 15 km) to the long walls, and 56.5 stadia (7 miles, 11 km) to Piraeus, Munichia, and Phalerum.
, also called Cecropia from its reputed founder, Cecrops
, was a steep rock in the middle of the city, about 50 meters high, 350 meters long, and 150 meters wide; its sides were naturally scarped on all sides except the west end. It was originally surrounded by an ancient Cyclopean
wall said to have been built by the Pelasgians
. At the time of the Peloponnesian war
only the north part of this wall remained, and this portion was still called the Pelasgic Wall; while the south part which had been rebuilt by Cimon, was called the Cimonian Wall. On the west end of the Acropolis, where access is alone practicable, were the magnificent Propylaea
, "the Entrances," built by Pericles
, before the right wing of which was the small Temple of Athena Nike. The summit of the Acropolis was covered with temples, statues of bronze and marble, and various other works of art. Of the temples, the grandest was the Parthenon
, sacred to the "Virgin" goddess Athena
; and north of the Parthenon was the magnificent Erechtheion, containing three separate temples, one to Athena Polias, or the "Protectress of the State," the Erechtheion proper, or sanctuary of Erechtheus
, and the Pandroseion
, or sanctuary of Pandrosos, the daughter of Cecrops. Between the Parthenon and Erechtheion was the colossal Statue of Athena Promachos
, or the "Fighter in the Front," whose helmet and spear was the first object on the Acropolis visible from the sea.

, and to the southeast they ran along beside the Ilissos
.


 The period from the end of the Persian Wars to the Macedonian conquest marked the zenith of Athens as a center of literature, philosophy (see Greek philosophy
The period from the end of the Persian Wars to the Macedonian conquest marked the zenith of Athens as a center of literature, philosophy (see Greek philosophy
) and the arts (see Greek theatre). Some of the most important figures of Western cultural and intellectual history lived in Athens during this period: the dramatists Aeschylus
, Aristophanes
, Euripides
and Sophocles
, the philosophers Aristotle
, Plato
and Socrates
, the historians Herodotus
, Thucydides
and Xenophon
, the poet Simonides
and the sculptor Phidias
. The leading statesman of this period was Pericles
, who used the tribute paid by the members of the Delian League to build the Parthenon
and other great monuments of classical Athens. The city became, in Pericles's words, "the school of Hellas [Greece]."
322 BC
Year 322 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rullianus and Curvus...
) was a notable polis
Polis
Polis , plural poleis , literally means city in Greek. It could also mean citizenship and body of citizens. In modern historiography "polis" is normally used to indicate the ancient Greek city-states, like Classical Athens and its contemporaries, so polis is often translated as "city-state."The...
(city-state
City-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
) of Attica
Attica
Attica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
, Greece
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
, leading the Delian League
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in circa 477 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, members numbering between 150 to 173, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Greco–Persian Wars...
in the Peloponnesian War
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War, 431 to 404 BC, was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases...
against Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
and the Peloponnesian League
Peloponnesian League
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance in the Peloponnesus from the 6th to the 4th centuries BC.- Early history:By the end of the 6th century, Sparta had become the most powerful state in the Peloponnese, and was the political and military hegemon over Argos, the next most powerful state...
. Athenian democracy
Athenian democracy
Athenian democracy developed in the Greek city-state of Athens, comprising the central city-state of Athens and the surrounding territory of Attica, around 508 BC. Athens is one of the first known democracies. Other Greek cities set up democracies, and even though most followed an Athenian model,...
was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes was a noble Athenian of the Alcmaeonid family. He is credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508/7 BC...
following the tyranny of Hippias
Hippias (son of Pisistratus)
Hippias of Athens was one of the sons of Peisistratus, and was tyrant of Athens in the 6th century BC.Hippias succeeded Peisistratus in 527 BC, and in 525 BC he introduced a new system of coinage in Athens. His brother Hipparchus, who may have ruled jointly with him, was murdered by Harmodius and...
. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC
322 BC
Year 322 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rullianus and Curvus...
(aftermath of Lamian War
Lamian War
The “Lamian War”, also referred to as the “Hellenic War” and the “War against Antipater”, was fought by the Athenians and their Aetolian, Locrian, and Phocian allies against the Macedonians in Thessaly during the winter of 323–322 BC...
) . The peak of Athenian hegemony
Hegemony
Hegemony is an indirect form of imperial dominance in which the hegemon rules sub-ordinate states by the implied means of power rather than direct military force. In Ancient Greece , hegemony denoted the politico–military dominance of a city-state over other city-states...
was achieved in the 440s
440s BC
-Births:* 446 BC** Aristophanes, Greek playwright ** Marcus Furius Camillus, Roman soldier and statesman -Deaths:* 449 BC** Appius Claudius, former decemvir, suicide...
to 430s BC
430s BC
-Births:* 436 BC** Isocrates, Athenian orator ** Artaxerxes II, king of Persia * 435 BC – Philoxenus of Cythera, Greek dithyrambic poet...
, known as the Age of Pericles
Age of Pericles
Fifth-century Athens refers to the Greek city-state of Athens in the period of roughly 480 BC-404 BC. This was a period of Athenian political hegemony, economic growth and cultural flourishing formerly known as the Golden Age of Athens or The Age of Pericles. The period began in 480 BC when an...
.
In the classical period
Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a 200 year period in Greek culture lasting from the 5th through 4th centuries BC. This classical period had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire and greatly influenced the foundation of Western civilizations. Much of modern Western politics, artistic thought, such as...
, Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
was a center for the arts, learning and philosophy
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
, home of Plato
Plato
Plato , was a Classical Greek philosopher, mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the...
's Akademia
Platonic Academy
The Academy was founded by Plato in ca. 387 BC in Athens. Aristotle studied there for twenty years before founding his own school, the Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenistic period as a skeptical school, until coming to an end after the death of Philo of Larissa in 83 BC...
and Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
's Lyceum
Lyceum
The lyceum is a category of educational institution defined within the education system of many countries, mainly in Europe. The definition varies between countries; usually it is a type of secondary school.-History:...
, Athens was also the birthplace of Socrates
Socrates
Socrates was a classical Greek Athenian philosopher. Credited as one of the founders of Western philosophy, he is an enigmatic figure known chiefly through the accounts of later classical writers, especially the writings of his students Plato and Xenophon, and the plays of his contemporary ...
, Pericles
Pericles
Pericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
, Sophocles
Sophocles
Sophocles is one of three ancient Greek tragedians whose plays have survived. His first plays were written later than those of Aeschylus, and earlier than or contemporary with those of Euripides...
, and many other prominent philosophers, writers and politicians of the ancient world. It is widely referred to as the cradle
Cradle of Civilization
The cradle of civilization is a term referring to any of the possible locations for the emergence of civilization.It is usually applied to the Ancient Near Eastern Chalcolithic , especially in the Fertile Crescent , but also extended to sites in Armenia, and the Persian Plateau, besides other Asian...
of Western Civilization
Western culture
Western culture, sometimes equated with Western civilization or European civilization, refers to cultures of European origin and is used very broadly to refer to a heritage of social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, religious beliefs, political systems, and specific artifacts and...
, and the birthplace of democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
, largely due to the impact of its cultural and political achievements during the 5th and 4th centuries BC on the rest of the then known European continent.
Rise to power (510–448 BC)
HippiasHippias (son of Pisistratus)
Hippias of Athens was one of the sons of Peisistratus, and was tyrant of Athens in the 6th century BC.Hippias succeeded Peisistratus in 527 BC, and in 525 BC he introduced a new system of coinage in Athens. His brother Hipparchus, who may have ruled jointly with him, was murdered by Harmodius and...
established a dictatorship in 514 B.C., which proved very unpopular, and was eventually overthrown with the help of an army from Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
, in 510 B.C. A radical politician of aristocratic background, Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes was a noble Athenian of the Alcmaeonid family. He is credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508/7 BC...
, then took charge and established democracy in Athens. The reforms of Cleisthenes replaced the traditional four "tribes" (phyle
Phyle
Phyle is an ancient Greek term for clan or tribe. They were usually ruled by a basileus...
) with ten new ones, named after legendary heroes of Greece and having no class basis, which acted as electorates. Each tribe was in turn divided into three trittyes, while each trittys
Trittys
Trittyes were population divisions in ancient Attica, established by the reforms of Cleisthenes in 508 BC. The name means "thirtieth," and there were in fact thirty trittyes in Attica. Each tribe, or phyle of Athens was composed of three trittyes, one from the coast, one from the city, and one...
had one or more deme
Deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or demos was a subdivision of Attica, the region of Greece surrounding Athens. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in...
s (see deme
Deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or demos was a subdivision of Attica, the region of Greece surrounding Athens. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in...
) - depending on their population - which became the basis of local government. The tribes each selected fifty members by lot for the Boule
Boule (Ancient Greece)
In cities of ancient Greece, the boule meaning to will ) was a council of citizens appointed to run daily affairs of the city...
, the council which governed Athens on a day-to-day basis. The public opinion
Public opinion
Public opinion is the aggregate of individual attitudes or beliefs held by the adult population. Public opinion can also be defined as the complex collection of opinions of many different people and the sum of all their views....
of voters could be influenced by the political satire
Political satire
Political satire is a significant part of satire that specializes in gaining entertainment from politics; it has also been used with subversive intent where political speech and dissent are forbidden by a regime, as a method of advancing political arguments where such arguments are expressly...
s written by the comic poets and performed in the city theaters. The Assembly
Ecclesia (ancient Athens)
The ecclesia or ekklesia was the principal assembly of the democracy of ancient Athens during its "Golden Age" . It was the popular assembly, opened to all male citizens over the age of 30 with 2 years of military service by Solon in 594 BC meaning that all classes of citizens in Athens were able...
or Ecclesia was open to all full citizens and was both a legislature and a supreme court, except in murder cases and religious matters, which became the only remaining functions of the Areopagus. Most offices were filled by lot, although the ten strategoi
Strategos
Strategos, plural strategoi, is used in Greek to mean "general". In the Hellenistic and Byzantine Empires the term was also used to describe a military governor...
(generals) were elected.

Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
, a city-state with a militaristic culture, considered itself the leader of the Greeks, and enforced an hegemony
Hegemony
Hegemony is an indirect form of imperial dominance in which the hegemon rules sub-ordinate states by the implied means of power rather than direct military force. In Ancient Greece , hegemony denoted the politico–military dominance of a city-state over other city-states...
. In 499 BC Athens sent troops to aid the Ionia
Ionia
Ionia is an ancient region of central coastal Anatolia in present-day Turkey, the region nearest İzmir, which was historically Smyrna. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements...
n Greeks of Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
, who were rebelling against the Persian Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
(see Ionian Revolt
Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC...
). This provoked two Persian invasions of Greece, both of which were repelled under the leadership of the soldier-statesmen Miltiades
Miltiades the Younger
Miltiades the Younger or Miltiades IV was the son of one Cimon, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer. Miltiades considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, and is known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon; as well as his rather tragic downfall afterwards. His son Cimon was a major Athenian...
and Themistocles
Themistocles
Themistocles ; c. 524–459 BC, was an Athenian politician and a general. He was one of a new breed of politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy, along with his great rival Aristides...
(see Persian Wars). In 490 the Athenians, led by Miltiades
Miltiades the Younger
Miltiades the Younger or Miltiades IV was the son of one Cimon, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer. Miltiades considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, and is known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon; as well as his rather tragic downfall afterwards. His son Cimon was a major Athenian...
, prevented the first invasion of the Persians, guided by king Darius I, at the Battle of Marathon
Battle of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. It was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate...
. In 480 the Persians returned under a new ruler, Xerxes I
Xerxes I of Persia
Xerxes I of Persia , Ḫšayāršā, ), also known as Xerxes the Great, was the fifth king of kings of the Achaemenid Empire.-Youth and rise to power:...
. The Hellenic League led by the Spartan King Leonidas led 7,000 men to hold the narrow passageway of Thermopylae
Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas of Sparta, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I over the course of three days, during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place simultaneously with the naval battle at Artemisium, in August...
against the 100,000-250,000 army of Xerxes. Simultaneously the Athenians led an indecisive naval battle off Artemisium
Battle of Artemisium
The Battle of Artemisium was a series of naval engagements over three days during the second Persian invasion of Greece. The battle took place simultaneously with the more famous land battle at Thermopylae, in August or September 480 BC, off the coast of Euboea and was fought between an alliance of...
. However, this delaying action was not enough to discourage the Persian advance which soon marched through Boeotia
Boeotia
Boeotia, also spelled Beotia and Bœotia , is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. It was also a region of ancient Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, the second largest city being Thebes.-Geography:...
, setting up Thebes
Thebes, Greece
Thebes is a city in Greece, situated to the north of the Cithaeron range, which divides Boeotia from Attica, and on the southern edge of the Boeotian plain. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others...
as their base of operations, and entered southern Greece. This forced the Athenians to evacuate Athens, which was taken by the Persians, and seek the protection of their fleet. Subsequently the Athenians and their allies, led by Themistocles
Themistocles
Themistocles ; c. 524–459 BC, was an Athenian politician and a general. He was one of a new breed of politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy, along with his great rival Aristides...
, defeated the Persian navy at sea in the Battle of Salamis
Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis was fought between an Alliance of Greek city-states and the Persian Empire in September 480 BCE, in the straits between the mainland and Salamis, an island in the Saronic Gulf near Athens...
. It is interesting to note that Xerxes had built himself a throne on the coast in order to see the Greeks defeated. Instead, the Persians were routed. Sparta's hegemony was passing to Athens, and it was Athens that took the war to Asia Minor. These victories enabled it to bring most of the Aegean and many other parts of Greece together in the Delian League
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in circa 477 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, members numbering between 150 to 173, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Greco–Persian Wars...
, an Athenian-dominated alliance.
Athenian hegemony (448–430 BC)
PericlesPericles
Pericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
- an Athenian general, politician and orator - distinguished himself above the other personalities of the era, men who excelled in politics
Politics
Politics is a process by which groups of people make collective decisions. The term is generally applied to the art or science of running governmental or state affairs, including behavior within civil governments, but also applies to institutions, fields, and special interest groups such as the...
, philosophy
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
, architecture
Architecture
Architecture is both the process and product of planning, designing and construction. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural and political symbols and as works of art...
, sculpture
Sculpture
Sculpture is three-dimensional artwork created by shaping or combining hard materials—typically stone such as marble—or metal, glass, or wood. Softer materials can also be used, such as clay, textiles, plastics, polymers and softer metals...
, history
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
and literature
Literature
Literature is the art of written works, and is not bound to published sources...
. He fostered arts and literature and gave to Athens a splendor which would never return throughout its history. He executed a large number of public works projects and improved the life of the citizens. Hence, he gave his name to the Athenian Golden Age. Silver mined in Laurium
Laurium
Laurium or Lavrio is a town in southeastern part of Attica, Greece. It is the seat of the municipality of Lavreotiki...
in southeastern Attica contributed greatly to the prosperity of this "Golden" Age of Athens.
During the time of the ascendancy of Ephialtes
Ephialtes
Ephialtes of Trachis was the son of Eurydemus of Malis. He betrayed his homeland by showing the Persian forces a path around the allied Greek position at the pass of Thermopylae, which helped them win the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC.-Trail:The allied Greek land forces, which Herodotus states...
as leader of the democratic faction, Pericles
Pericles
Pericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
was his deputy. When Ephialtes was assassinated
Assassination
To carry out an assassination is "to murder by a sudden and/or secret attack, often for political reasons." Alternatively, assassination may be defined as "the act of deliberately killing someone, especially a public figure, usually for hire or for political reasons."An assassination may be...
by personal enemies, Pericles stepped in and was elected general, or strategos
Strategos
Strategos, plural strategoi, is used in Greek to mean "general". In the Hellenistic and Byzantine Empires the term was also used to describe a military governor...
, in 445 BC
445 BC
Year 445 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augurinus and Philo...
; a post he held continuously until his death in 429 BC
429 BC
Year 429 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Tricipitinus and Fidenas...
, always by election of the Athenian Assembly.
Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC)

Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War, 431 to 404 BC, was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases...
in 431, which pitted Athens and her increasingly rebellious sea empire against a coalition of land-based states led by Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
. The conflict marked the end of Athenian command of the sea
Command of the sea
A naval force has command of the sea when it is so strong that its rivals cannot attack it directly. Also called sea control, this dominance may apply to its surrounding waters or may extend far into the oceans, meaning the country has a blue-water navy...
. The war between Athens and the city-state Sparta ended with an Athenian defeat after Sparta started its own navy.
Athenian democracy was briefly overthrown by the coup
Athenian coup of 411 BC
The Athenian coup of 411 BC was a revolutionary movement during the Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta that overthrew the democratic government of ancient Athens by replacing it with a short-lived oligarchy known as The Four Hundred....
of 411, brought about because of its poor handling of the war, but it was quickly restored. The war ended with the complete defeat of Athens in 404. Since the defeat was largely blamed on democratic politicians such as Cleon
Cleon
Cleon was an Athenian statesman and a Strategos during the Peloponnesian War. He was the first prominent representative of the commercial class in Athenian politics, although he was an aristocrat himself...
and Cleophon, there was a brief reaction against democracy, aided by the Spartan army (the rule of the Thirty Tyrants
Thirty Tyrants
The Thirty Tyrants were a pro-Spartan oligarchy installed in Athens after its defeat in the Peloponnesian War in 404 BC. Contemporary Athenians referred to them simply as "the oligarchy" or "the Thirty" ; the expression "Thirty Tyrants" is due to later historians...
). In 403, democracy was restored
Phyle Campaign
The Phyle Campaign was the civil war that resulted from the Spartan imposition of a narrow oligarchy on Athens and resulted in the restoration of Athenian democracy.-Prelude:...
by Thrasybulus
Thrasybulus
Thrasybulus was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a primary leader of the successful democratic resistance to that coup...
and an amnesty declared.
Corinthian War and the Second Athenian League (395–355 BC)
Sparta's former allies soon turned against her due to her imperialist policies, and Athens's former enemies, ThebesThebes, Greece
Thebes is a city in Greece, situated to the north of the Cithaeron range, which divides Boeotia from Attica, and on the southern edge of the Boeotian plain. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others...
and Corinth
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
, became her allies. Argos
Argos
Argos is a city and a former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. It is 11 kilometres from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour...
, Thebes
Thebes, Greece
Thebes is a city in Greece, situated to the north of the Cithaeron range, which divides Boeotia from Attica, and on the southern edge of the Boeotian plain. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others...
and Corinth
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
, allied with Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
, fought against Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
in the decisive Corinthian War
Corinthian War
The Corinthian War was an ancient Greek conflict lasting from 395 BC until 387 BC, pitting Sparta against a coalition of four allied states; Thebes, Athens, Corinth, and Argos; which were initially backed by Persia. The immediate cause of the war was a local conflict in northwest Greece in which...
of 395 BC - 387 BC. Opposition to Sparta enabled Athens to establish a Second Athenian League. Finally Thebes
Thebes, Greece
Thebes is a city in Greece, situated to the north of the Cithaeron range, which divides Boeotia from Attica, and on the southern edge of the Boeotian plain. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others...
defeated Sparta in 371 in the Battle of Leuctra
Battle of Leuctra
The Battle of Leuctra was a battle fought on July 6, 371 BC, between the Boeotians led by Thebans and the Spartans along with their allies amidst the post-Corinthian War conflict. The battle took place in the neighbourhood of Leuctra, a village in Boeotia in the territory of Thespiae...
. However, other Greek cities, including Athens, turned against Thebes
Thebes, Greece
Thebes is a city in Greece, situated to the north of the Cithaeron range, which divides Boeotia from Attica, and on the southern edge of the Boeotian plain. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others...
, and its dominance was brought to an end at the Battle of Mantinea (362 BC)
Battle of Mantinea (362 BC)
The Battle of Mantinea was fought on July 4 362 BC between the Thebans, led by Epaminondas and supported by the Arcadians and the Boeotian league against the Spartans, led by King Agesilaus II and supported by the Eleans, Athenians, and Mantineans...
with the death of its leader, the military genius Epaminondas
Epaminondas
Epaminondas , or Epameinondas, was a Theban general and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state of Thebes, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a preeminent position in Greek politics...
.
Athens under Macedon (355–322 BC)
By mid century, however, the northern kingdom of MacedonMacedon
Macedonia or Macedon was an ancient kingdom, centered in the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, the region of Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south....
was becoming dominant in Athenian affairs, despite the warnings of the last great statesman of independent Athens, Demosthenes
Demosthenes
Demosthenes was a prominent Greek statesman and orator of ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual prowess and provide an insight into the politics and culture of ancient Greece during the 4th century BC. Demosthenes learned rhetoric by...
. In 338 BC the armies of Philip II
Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon "friend" + ἵππος "horse" — transliterated ; 382 – 336 BC), was a king of Macedon from 359 BC until his assassination in 336 BC. He was the father of Alexander the Great and Philip III.-Biography:...
defeated Athens at the Battle of Chaeronea
Battle of Chaeronea (338 BC)
The Battle of Chaeronea was fought in 338 BC, near the city of Chaeronea in Boeotia, between the forces of Philip II of Macedon and an alliance of Greek city-states...
, effectively limiting Athenian independence. Athens and other states became part of the League of Corinth
League of Corinth
The League of Corinth, also sometimes referred to as Hellenic League was a federation of Greek states created by Philip II of Macedon during the winter of 338 BC/337 BC after the Battle of Chaeronea, to facilitate his use of military forces in his war against Persia...
. Further, the conquests of his son, Alexander the Great, widened Greek horizons and made the traditional Greek city state obsolete. Antipater
Antipater
Antipater was a Macedonian general and a supporter of kings Philip II of Macedon and Alexander the Great. In 320 BC, he became Regent of all of Alexander's Empire. Antipater was one of the sons of a Macedonian nobleman called Iollas or Iolaus and his family were distant collateral relatives to the...
dissolved the Athenian government and established a plutocratic system in 322 BC (see Lamian War
Lamian War
The “Lamian War”, also referred to as the “Hellenic War” and the “War against Antipater”, was fought by the Athenians and their Aetolian, Locrian, and Phocian allies against the Macedonians in Thessaly during the winter of 323–322 BC...
and Demetrius Phalereus
Demetrius Phalereus
Demetrius of Phalerum was an Athenian orator originally from Phalerum, a student of Theophrastus and one of the first Peripatetics...
). Athens remained a wealthy city with a brilliant cultural life, but ceased to be an independent power.
In the 2nd century BC, following the Battle of Corinth (146 BC)
Battle of Corinth (146 BC)
The Battle of Corinth was a battle fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek state of Corinth and its allies in the Achaean League in 146 BC, that resulted in the complete and total destruction of the state of Corinth which was previously so famous for its fabulous wealth...
, Greece was absorbed into the Roman Republic
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
as part of the Achaea Province, concluding 200 years of Macedonian supremacy.
Overview

Attica
Attica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
, about 30 stadia
Stadion (unit of length)
The stadion, Latinized as stadium and anglicized as stade, is an ancient Greek unit of length. According to Herodotus, one stade is equal to 600 feet. However, there were several different lengths of “feet”, depending on the country of origin....
from the sea, on the southwest slope of Mount Lycabettus
Mount Lycabettus
Mount Lycabettus, also known as Lycabettos, Lykabettos or Lykavittos , is a Cretaceous limestone hill in Athens, Greece. At 277 meters above sea level, the hill is the highest point in the city that surrounds it. Pine trees cover its base, and at its peak are the 19th century Chapel of St...
, between the small rivers Cephissus
Cephissus (Athenian plain)
Cephissus , Kifissós) or Cephisus Kifisos), a river flowing through the Athenian plain.In his summary of Greek mythology Apollodorus declares that Erechtheus' wife Praxithea was daughter of Phrasimus by Diogenia daughter of Cephissus.This river is found in the western part of the...
to the west, Ilissos
Ilissos
The Ilissos or Ilissus is a river in Athens, Greece. Originally a tributary of the Kifissos River, it is now largely channeled underground.-Ancient Athens:...
to the south, and the Eridanos
Eridanos (Athens)
Eridanos was the small stream that flowed from a source in the foothills of the Lykabettos, through the Agora of ancient Athens in Greece to the archaeological site of the Kerameikos, where its bed is still visible...
to the north, the latter of which flowed through the town. The walled city measured about 1.5 km (0.93205910497471 mi) in diameter, although at its peak the city had suburbs extending well beyond these walls. The Acropolis
Acropolis of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens or Citadel of Athens is the best known acropolis in the world. Although there are many other acropoleis in Greece, the significance of the Acropolis of Athens is such that it is commonly known as The Acropolis without qualification...
was just south of the centre of this walled area. The city was burnt by Xerxes
Xerxes I of Persia
Xerxes I of Persia , Ḫšayāršā, ), also known as Xerxes the Great, was the fifth king of kings of the Achaemenid Empire.-Youth and rise to power:...
in 480 BC
480 BC
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus...
, but was soon rebuilt under the administration of Themistocles
Themistocles
Themistocles ; c. 524–459 BC, was an Athenian politician and a general. He was one of a new breed of politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy, along with his great rival Aristides...
, and was adorned with public buildings by Cimon and especially by Pericles
Pericles
Pericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
, in whose time (461
461 BC
Year 461 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gallus and Cornutus...
-429 BC
429 BC
Year 429 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Tricipitinus and Fidenas...
) it reached its greatest splendour. Its beauty was chiefly due to its public buildings, for the private houses were mostly insignificant, and its streets badly laid out. Towards the end of the Peloponnesian war
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War, 431 to 404 BC, was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases...
, it contained more than 10,000 houses, which at a rate of 12 inhabitants to a house would give a population of 120,000, though some writers make the inhabitants as many as 180,000.
Athens consisted of two distinct parts:
- The City, properly so called, divided into The Upper City or AcropolisAcropolis of AthensThe Acropolis of Athens or Citadel of Athens is the best known acropolis in the world. Although there are many other acropoleis in Greece, the significance of the Acropolis of Athens is such that it is commonly known as The Acropolis without qualification...
, and The Lower City, surrounded with walls by Themistocles. - The port city of PiraeusPiraeusPiraeus is a city in the region of Attica, Greece. Piraeus is located within the Athens Urban Area, 12 km southwest from its city center , and lies along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf....
, also surrounded with walls by Themistocles and connected to the city with the Long WallsLong WallsThe Long Walls , in Ancient Greece, were walls built from a city to its port, providing a secure connection to the sea even during times of siege. Although long walls were built at several locations in Greece—Corinth and Megara being two of the best known examples—the phrase "long...
, built under CononCononConon was an Athenian general at the end of the Peloponnesian War, who presided over the crucial Athenian naval defeat at Battle of Aegospotami; later he contributed significantly to the restoration of the political and military power.-Defeat at Aegospotami:Conon had been sent out following the...
and PericlesPericlesPericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
.
The Long Walls

Long Walls
The Long Walls , in Ancient Greece, were walls built from a city to its port, providing a secure connection to the sea even during times of siege. Although long walls were built at several locations in Greece—Corinth and Megara being two of the best known examples—the phrase "long...
consisted of two walls leading to Piraeus
Piraeus
Piraeus is a city in the region of Attica, Greece. Piraeus is located within the Athens Urban Area, 12 km southwest from its city center , and lies along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf....
, 40 stadia
Stadion (unit of length)
The stadion, Latinized as stadium and anglicized as stade, is an ancient Greek unit of length. According to Herodotus, one stade is equal to 600 feet. However, there were several different lengths of “feet”, depending on the country of origin....
long (4.5 miles, 7 km), running parallel to each other, with a narrow passage between them. In addition, there was a wall to Phalerum on the east, 35 stadia long (4 miles, 6.5 km). There were therefore three long walls in all; but the name Long Walls seems to have been confined to the two leading to the Piraeus, while the one leading to Phalerum was called the Phalerian Wall. The entire circuit of the walls was 174.5 stadia (nearly 22 miles, 35 km), of which 43 stadia (5.5 miles, 9 km) belonged to the city, 75 stadia (9.5 miles, 15 km) to the long walls, and 56.5 stadia (7 miles, 11 km) to Piraeus, Munichia, and Phalerum.
The Acropolis (Upper city)
The AcropolisAcropolis of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens or Citadel of Athens is the best known acropolis in the world. Although there are many other acropoleis in Greece, the significance of the Acropolis of Athens is such that it is commonly known as The Acropolis without qualification...
, also called Cecropia from its reputed founder, Cecrops
Cecrops I
Cecrops was a mythical king of Athens who is said to have reigned for fifty-six years. The name is not of Greek origin according to Strabo, or it might mean 'face with a tail': it is said that, born from the earth itself, he had his top half shaped like a man and the bottom half in serpent or...
, was a steep rock in the middle of the city, about 50 meters high, 350 meters long, and 150 meters wide; its sides were naturally scarped on all sides except the west end. It was originally surrounded by an ancient Cyclopean
Cyclopean masonry
Cyclopean masonry is a type of stonework found in Mycenaean architecture, built with huge limestone boulders, roughly fitted together with minimal clearance between adjacent stones and no use of mortar...
wall said to have been built by the Pelasgians
Pelasgians
The name Pelasgians was used by some ancient Greek writers to refer to populations that were either the ancestors of the Greeks or who preceded the Greeks in Greece, "a hold-all term for any ancient, primitive and presumably indigenous people in the Greek world." In general, "Pelasgian" has come...
. At the time of the Peloponnesian war
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War, 431 to 404 BC, was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases...
only the north part of this wall remained, and this portion was still called the Pelasgic Wall; while the south part which had been rebuilt by Cimon, was called the Cimonian Wall. On the west end of the Acropolis, where access is alone practicable, were the magnificent Propylaea
Propylaea
A Propylaea, Propylea or Propylaia is any monumental gateway based on the original Propylaea that serves as the entrance to the Acropolis in Athens...
, "the Entrances," built by Pericles
Pericles
Pericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
, before the right wing of which was the small Temple of Athena Nike. The summit of the Acropolis was covered with temples, statues of bronze and marble, and various other works of art. Of the temples, the grandest was the Parthenon
Parthenon
The Parthenon is a temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their virgin patron. Its construction began in 447 BC when the Athenian Empire was at the height of its power. It was completed in 438 BC, although...
, sacred to the "Virgin" goddess Athena
Athena
In Greek mythology, Athena, Athenê, or Athene , also referred to as Pallas Athena/Athene , is the goddess of wisdom, courage, inspiration, civilization, warfare, strength, strategy, the arts, crafts, justice, and skill. Minerva, Athena's Roman incarnation, embodies similar attributes. Athena is...
; and north of the Parthenon was the magnificent Erechtheion, containing three separate temples, one to Athena Polias, or the "Protectress of the State," the Erechtheion proper, or sanctuary of Erechtheus
Erechtheus
Erechtheus in Greek mythology was the name of an archaic king of Athens, the re-founder of the polis and a double at Athens for Poseidon, as "Poseidon Erechtheus"...
, and the Pandroseion
Pandroseion
The Pandroseion was a sanctuary dedicated to Pandrosus, one of the daughters of Cecrops I, the first king of AtticaGreece, located on the Acropolis of Athens...
, or sanctuary of Pandrosos, the daughter of Cecrops. Between the Parthenon and Erechtheion was the colossal Statue of Athena Promachos
Athena Promachos
The Athena Promachos was a colossal bronze statue of Athena sculpted by Pheidias, which stood between the Propylaea and the Parthenon on the Acropolis of Athens. Athena was the goddess of wisdom and warriors and the protectress of Athens...
, or the "Fighter in the Front," whose helmet and spear was the first object on the Acropolis visible from the sea.

Lower city
The lower city was built in the plain round the Acropolis, but this plain also contained several hills, especially in the southwest part. On the west side the walls embraced the Hill of the Nymphs and the PnyxPnyx
The Pnyx is a hill in central Athens, the capital of Greece. It is located less than west of the Acropolis and 1.6 km south-west of the centre of modern Athens, Syntagma Square.-The site:...
, and to the southeast they ran along beside the Ilissos
Ilissos
The Ilissos or Ilissus is a river in Athens, Greece. Originally a tributary of the Kifissos River, it is now largely channeled underground.-Ancient Athens:...
.
Gates
There were many gates, among the more important there were:- On the West side: Dipylon, the most frequented gate of the city, leading from the inner Kerameikos to the outer Kerameikos, and to the AcademyPlatonic AcademyThe Academy was founded by Plato in ca. 387 BC in Athens. Aristotle studied there for twenty years before founding his own school, the Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenistic period as a skeptical school, until coming to an end after the death of Philo of Larissa in 83 BC...
. The Sacred Gate, where the sacred road to Eleusis began. The Knight's Gate, probably between the Hill of the Nymphs and the PnyxPnyxThe Pnyx is a hill in central Athens, the capital of Greece. It is located less than west of the Acropolis and 1.6 km south-west of the centre of modern Athens, Syntagma Square.-The site:...
. The Piraean Gate, between the Pnyx and the Mouseion, leading to the carriage road between the Long Walls to the Piraeus. The Melitian Gate, so called because it led to the demeDemeIn Ancient Greece, a deme or demos was a subdivision of Attica, the region of Greece surrounding Athens. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in...
Melite, within the city. - On the South side: The Gate of the Dead in the neighbourhood of the Mouseion. The Itonian Gate, near the Ilissos, where the road to Phalerum began.
- On the East side: The Gate of Diochares, leading to the LyceumLyceumThe lyceum is a category of educational institution defined within the education system of many countries, mainly in Europe. The definition varies between countries; usually it is a type of secondary school.-History:...
. The Diomean Gate, leading to CynosargesCynosargesCynosarges was a public gymnasium located just outside the walls of Ancient Athens on the southern bank of the Ilissos river.Its name derives from Cynos-argos and means white or swift dog...
and the deme Diomea. - On the North side: The Acharnian Gate, leading to the deme Acharnai.
Districts
- The Inner Kerameikos, or "Potter's Quarter," in the west of the city, extending north as far as the Dipylon gate, by which it was separated from the outer Kerameikos; the Kerameikos contained the AgoraAncient Agora of AthensThe Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and is bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Colonus Agoraeus.-History:The agora in Athens had private housing, until it...
, or "market-place," the only one in the city, lying northwest of the Acropolis, and north of the AreopagusAreopagusThe Areopagus or Areios Pagos is the "Rock of Ares", north-west of the Acropolis, which in classical times functioned as the high Court of Appeal for criminal and civil cases in Athens. Ares was supposed to have been tried here by the gods for the murder of Poseidon's son Alirrothios .The origin...
. - The demeDemeIn Ancient Greece, a deme or demos was a subdivision of Attica, the region of Greece surrounding Athens. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in...
Melite, in the west of the city, south of the inner Kerameikos. - The deme Skambonidai, in the northern part of the city, east of the inner Kerameikos.
- The Kollytos, in the southern part of the city, south and southwest of the Acropolis.
- Koele, a district in the southwest of the city.
- Limnai, a district east of Milete and Kollytos, between the Acropolis and the Ilissos.
- Diomea, a district in the east of the city, near the gate of the same name and the CynosargesCynosargesCynosarges was a public gymnasium located just outside the walls of Ancient Athens on the southern bank of the Ilissos river.Its name derives from Cynos-argos and means white or swift dog...
. - Agrai, a district south of Diomea.
Hills
- The AreopagusAreopagusThe Areopagus or Areios Pagos is the "Rock of Ares", north-west of the Acropolis, which in classical times functioned as the high Court of Appeal for criminal and civil cases in Athens. Ares was supposed to have been tried here by the gods for the murder of Poseidon's son Alirrothios .The origin...
, the "Hill of AresAresAres is the Greek god of war. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. In Greek literature, he often represents the physical or violent aspect of war, in contrast to the armored Athena, whose functions as a goddess of intelligence include military strategy and...
," west of the Acropolis, which gave its name to the celebrated council that held its sittings there, was accessible on the south side by a flight of steps cut out of the rock. - The Hill of the Nymphs, northwest of the Areopagus.
- The PnyxPnyxThe Pnyx is a hill in central Athens, the capital of Greece. It is located less than west of the Acropolis and 1.6 km south-west of the centre of modern Athens, Syntagma Square.-The site:...
, a semicircular hill, southwest of the Areopagus, where the ekklesiaEcclesia (ancient Athens)The ecclesia or ekklesia was the principal assembly of the democracy of ancient Athens during its "Golden Age" . It was the popular assembly, opened to all male citizens over the age of 30 with 2 years of military service by Solon in 594 BC meaning that all classes of citizens in Athens were able...
(assemblies) of the people were held in earlier times, for afterwards the people usually met in the Theatre of DionysusTheatre of DionysusThe Theatre of Dionysus is a major open-air theatre and one of the earliest preserved in Athens. It was used for festivals in honor of the god Dionysus...
. - The Mouseion, "the Hill of the Muses," south of the Pnyx and the Areopagus.
Streets
Among the more important streets, there were:- The Piraean Street, which led from the Piraean gate to the AgoraAncient Agora of AthensThe Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and is bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Colonus Agoraeus.-History:The agora in Athens had private housing, until it...
. - The Panathenaic Way, which led from the Dipylon gate to the AcropolisAcropolis of AthensThe Acropolis of Athens or Citadel of Athens is the best known acropolis in the world. Although there are many other acropoleis in Greece, the significance of the Acropolis of Athens is such that it is commonly known as The Acropolis without qualification...
via the AgoraAncient Agora of AthensThe Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and is bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Colonus Agoraeus.-History:The agora in Athens had private housing, until it...
, along which a solemn procession was made during the Panathenaic Festival. - The Street of the Tripods, on the east side of the Acropolis.
Public buildings

- Temples. Of these the most important was the Olympieion, or Temple of Olympian Zeus, southeast of the Acropolis, near the Ilissos and the fountain Callirrhoë, which was long unfinished, and was first completed by HadrianHadrianHadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
. The Temple of HephaestusTemple of HephaestusThe Temple of Hephaestus, also known as the Hephaisteion or earlier as the Theseion, is the best-preserved ancient Greek temple; it remains standing largely as built. It is a Doric peripteral temple, and is located at the north-west side of the Agora of Athens, on top of the Agoraios Kolonos hill....
, located to the west of the AgoraAncient Agora of AthensThe Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and is bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Colonus Agoraeus.-History:The agora in Athens had private housing, until it...
. The Temple of AresTemple of AresThe Temple of Ares was a building located in the northern part of the Ancient Agora of Athens. The Temple was identified as such by Pausanias but the ruins present today indicate a complex history...
, to the north of the Agora. MetroonMetroonMetroon was the name given to a building dedicated to the mother goddess, Cybele, Rhea, or Demeter, in Ancient Greece.- Agora, Athens :...
, or temple of the mother of the gods, on the west side of the Agora. Besides these, there was a vast number of other temples in all parts of the city. - The BouleuterionBouleuterionA bouleuterion was a building which housed the council of citizens in Ancient Greece. There are several extant remains of Bouleuterions around Greece and former Greek territories of ancient times....
(Senate House), at the west side of the Agora. - The TholosPrytaneionA Prytaneion was seat of the Prytaneis , and so the seat of government in ancient Greece. The term is used to describe any of a range of ancient structures where officials met but the term is also used to refer to the building where the officials and winners of the Olympic games met at Olympia...
, a round building close to the Bouleuterion, built c. 470 BC470 BCYear 470 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Mamercus...
by Cimon, which served as the PrytaneionPrytaneionA Prytaneion was seat of the Prytaneis , and so the seat of government in ancient Greece. The term is used to describe any of a range of ancient structures where officials met but the term is also used to refer to the building where the officials and winners of the Olympic games met at Olympia...
, in which the PrytaneisPrytaneisThe Prytaneis were the executives of the boule of ancient Athens. The term is probably of pre-Greek origin ....
took their meals and offered their sacrifices. - StoaStoaStoa in Ancient Greek architecture; covered walkways or porticos, commonly for public usage. Early stoae were open at the entrance with columns, usually of the Doric order, lining the side of the building; they created a safe, enveloping, protective atmosphere.Later examples were built as two...
e, or Colonnades, supported by pillars, and used as places of resort in the heat of the day, of which there were several in Athens. In the AgoraAncient Agora of AthensThe Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and is bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Colonus Agoraeus.-History:The agora in Athens had private housing, until it...
there were: the Stoa BasileiosStoa BasileiosBasileios Stoa , also Basilike Stoa , both meaning Royal Stoa, was a stoa constructed in Ancient Athens in the 5th century BC. It was located in the northwest corner of the Athenian Agora.The Royal Stoa was the headquarters of the King Archon and of the Areios Pagos council Basileios Stoa , also...
, the court of the King-ArchonArchon of AthensThis is a list of the eponymous archons of Athens.-Background:The archon was the chief magistrate in many Greek cities, but in Athens there was a council of archons which comprised a form of executive government...
, on the west side of the Agora; the Stoa EleutheriosStoa of ZeusThe Stoa of Zeus at Athens, was a two-aisled stoa located in the northwest corner of the Ancient Agora of Athens. It was built circa 425 BC–410 BC for religious purposes in dedication to Zeus by the Eleutherios : a cult founded after the Persian War...
, or Colonnade of Zeus Eleutherios, on the west side of the Agora; the Stoa PoikileStoa PoikileThe Stoa Poikile or Painted Porch, originally called the Porch of Peisianax , was erected during the 5th century BC and was located on the north side of the Ancient Agora of Athens. The Stoa was the location from which Zeno of Citium taught Stoicism...
, so called because it was adorned with fresco painting of the Battle of MarathonBattle of MarathonThe Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. It was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate...
by PolygnotusPolygnotusPolygnotus was an ancient Greek painter from the middle of the 5th century BC, son and pupil of Aglaophon. He was a native of Thasos, but was adopted by the Athenians, and admitted to their citizenship....
, on the north side of the Agora.

- Theatres. The Theatre of DionysusTheatre of DionysusThe Theatre of Dionysus is a major open-air theatre and one of the earliest preserved in Athens. It was used for festivals in honor of the god Dionysus...
, on the southeast slope of the Acropolis, was the great theatre of the state. Besides this there were OdeonOdeon (building)Odeon is the name for several ancient Greek and Roman buildings built for singing exercises, musical shows and poetry competitions. They were generally small in size, especially compared with a full-size ancient Greek theatre....
s, for contests in vocal and instrumental music, an ancient one near the fountain Callirrhoë, and a second built by PericlesPericlesPericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
, close to the theatre of Dionysius, on the southeast slope of the Acropolis. The large odeon surviving today, the Odeon of Herodes AtticusOdeon of Herodes AtticusThe Odeon of Herodes Atticus is a stone theatre structure located on the south slope of the Acropolis of Athens. It was built in 161 AD by Herodes Atticus in memory of his wife, Aspasia Annia Regilla...
was built in Roman times. - Panathenaic Stadium, south of the Ilissos, in the district Agrai, where the athletic portion of the Panathenaic GamesPanathenaic GamesThe Panathenaic Games were held every four years in Athens in Ancient Greece since 566 BC. They continued into the third century AD. These Games incorporated religious festival, ceremony , athletic competitions, and cultural events hosted within a stadium.-Religious festival:The games were part of...
were held.
Suburbs
- The Outer Kerameikos, northwest of the city, was the finest suburb of Athens; here were buried the Athenians who had fallen in war, and at the further end of it was the AcademyPlatonic AcademyThe Academy was founded by Plato in ca. 387 BC in Athens. Aristotle studied there for twenty years before founding his own school, the Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenistic period as a skeptical school, until coming to an end after the death of Philo of Larissa in 83 BC...
, 6 stadia from the city. - CynosargesCynosargesCynosarges was a public gymnasium located just outside the walls of Ancient Athens on the southern bank of the Ilissos river.Its name derives from Cynos-argos and means white or swift dog...
, east of the city, across the Ilissos, reached from the Diomea gate, a gymnasiumGymnasium (ancient Greece)The gymnasium in ancient Greece functioned as a training facility for competitors in public games. It was also a place for socializing and engaging in intellectual pursuits. The name comes from the Ancient Greek term gymnós meaning "naked". Athletes competed in the nude, a practice said to...
sacred to HeraclesHeraclesHeracles ,born Alcaeus or Alcides , was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, foster son of Amphitryon and great-grandson of Perseus...
, where the Cynic AntisthenesAntisthenesAntisthenes was a Greek philosopher and a pupil of Socrates. Antisthenes first learned rhetoric under Gorgias before becoming an ardent disciple of Socrates. He adopted and developed the ethical side of Socrates' teachings, advocating an ascetic life lived in accordance with virtue. Later writers...
taught. - LyceumLyceumThe lyceum is a category of educational institution defined within the education system of many countries, mainly in Europe. The definition varies between countries; usually it is a type of secondary school.-History:...
, east of the city, a gymnasium sacred to Apollo LyceusApolloApollo is one of the most important and complex of the Olympian deities in Greek and Roman mythology...
, where AristotleAristotleAristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
taught.
Culture

Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BCE and continued through the Hellenistic period, at which point Ancient Greece was incorporated in the Roman Empire...
) and the arts (see Greek theatre). Some of the most important figures of Western cultural and intellectual history lived in Athens during this period: the dramatists Aeschylus
Aeschylus
Aeschylus was the first of the three ancient Greek tragedians whose work has survived, the others being Sophocles and Euripides, and is often described as the father of tragedy. His name derives from the Greek word aiskhos , meaning "shame"...
, Aristophanes
Aristophanes
Aristophanes , son of Philippus, of the deme Cydathenaus, was a comic playwright of ancient Athens. Eleven of his forty plays survive virtually complete...
, Euripides
Euripides
Euripides was one of the three great tragedians of classical Athens, the other two being Aeschylus and Sophocles. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him but according to the Suda it was ninety-two at most...
and Sophocles
Sophocles
Sophocles is one of three ancient Greek tragedians whose plays have survived. His first plays were written later than those of Aeschylus, and earlier than or contemporary with those of Euripides...
, the philosophers Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
, Plato
Plato
Plato , was a Classical Greek philosopher, mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the...
and Socrates
Socrates
Socrates was a classical Greek Athenian philosopher. Credited as one of the founders of Western philosophy, he is an enigmatic figure known chiefly through the accounts of later classical writers, especially the writings of his students Plato and Xenophon, and the plays of his contemporary ...
, the historians Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
, Thucydides
Thucydides
Thucydides was a Greek historian and author from Alimos. His History of the Peloponnesian War recounts the 5th century BC war between Sparta and Athens to the year 411 BC...
and Xenophon
Xenophon
Xenophon , son of Gryllus, of the deme Erchia of Athens, also known as Xenophon of Athens, was a Greek historian, soldier, mercenary, philosopher and a contemporary and admirer of Socrates...
, the poet Simonides
Simonides of Ceos
Simonides of Ceos was a Greek lyric poet, born at Ioulis on Kea. The scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria included him in the canonical list of nine lyric poets, along with Bacchylides and Pindar...
and the sculptor Phidias
Phidias
Phidias or the great Pheidias , was a Greek sculptor, painter and architect, who lived in the 5th century BC, and is commonly regarded as one of the greatest of all sculptors of Classical Greece: Phidias' Statue of Zeus at Olympia was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World...
. The leading statesman of this period was Pericles
Pericles
Pericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
, who used the tribute paid by the members of the Delian League to build the Parthenon
Parthenon
The Parthenon is a temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their virgin patron. Its construction began in 447 BC when the Athenian Empire was at the height of its power. It was completed in 438 BC, although...
and other great monuments of classical Athens. The city became, in Pericles's words, "the school of Hellas [Greece]."
See also
- Archon of AthensArchon of AthensThis is a list of the eponymous archons of Athens.-Background:The archon was the chief magistrate in many Greek cities, but in Athens there was a council of archons which comprised a form of executive government...
- Delian leagueDelian LeagueThe Delian League, founded in circa 477 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, members numbering between 150 to 173, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Greco–Persian Wars...
- AtticaAtticaAttica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
- Attic GreekAttic GreekAttic Greek is the prestige dialect of Ancient Greek that was spoken in Attica, which includes Athens. Of the ancient dialects, it is the most similar to later Greek, and is the standard form of the language studied in courses of "Ancient Greek". It is sometimes included in Ionic.- Origin and range...
- Acropolis of AthensAcropolis of AthensThe Acropolis of Athens or Citadel of Athens is the best known acropolis in the world. Although there are many other acropoleis in Greece, the significance of the Acropolis of Athens is such that it is commonly known as The Acropolis without qualification...
- Ancient Agora of AthensAncient Agora of AthensThe Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and is bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Colonus Agoraeus.-History:The agora in Athens had private housing, until it...
- Academy of Plato
- Ecclesia (ancient Athens)Ecclesia (ancient Athens)The ecclesia or ekklesia was the principal assembly of the democracy of ancient Athens during its "Golden Age" . It was the popular assembly, opened to all male citizens over the age of 30 with 2 years of military service by Solon in 594 BC meaning that all classes of citizens in Athens were able...
- Athenian democracyAthenian democracyAthenian democracy developed in the Greek city-state of Athens, comprising the central city-state of Athens and the surrounding territory of Attica, around 508 BC. Athens is one of the first known democracies. Other Greek cities set up democracies, and even though most followed an Athenian model,...
- Classical GreeceClassical GreeceClassical Greece was a 200 year period in Greek culture lasting from the 5th through 4th centuries BC. This classical period had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire and greatly influenced the foundation of Western civilizations. Much of modern Western politics, artistic thought, such as...

