
Chiapa de Corzo, Chiapas
Encyclopedia
Chiapa de Corzo is a small city and (municipality
) situated in the west-central part of the Mexican
state of Chiapas
. Located in the Grijalva River
valley of the Chiapas highlands
, Chiapa de Corzo lies some 15 km (9.3 mi) to the east of the state capital, Tuxtla Gutiérrez
. Chiapa has been occupied since at least 1400 BCE, with a major archeological site which reached it height between 700 BCE and 200 CE. It is important because the earliest inscribed date, the earliest form of hieroglyphic writing and the earliest Mesoamerica
n tomb burial have all been found here. Chiapa is also the site of the first Spanish city founded in Chiapas in 1528. However, because of the climate, most Spanish would move into the mountains to found what is now known as San Cristóbal de las Casas
. Chiapa would be left to the indigenous and to the Dominican
friars and called Chiapa de los Indios (with San Cristobal known as Chiapa de los Españoles). The current name was created to honor Liberal
politician Angel Albino Corzo.
and has one of the main docks along this waterway. The town is laid out in Spanish style, centered on a very large plaza which the municipality claims is larger than the Zocalo
, or main plaza of Mexico City
. (sec.
This plaza has a number of important features. The largest and best known is the La Pila fountain. This was constructed in 1562 in Moorish
style, made of brick in the form of a diamond. The structure is attributed to Dominican brother Rodrigo de León. It measures fifty two meters in circumference and twelve meters in height. It has eight arches and a cylindrical tower which occasionally functioned as a watchtower. Another important feature is the La Pochota kapok
tree. According to tradition, the Spanish town was founded around this tree. The last feature is a clock tower which was constructed in the 1950s. The town’s main structures are centered on this plaza, including the municipal palace and the former home of Liberal governor Angel Albino Corzo, for whom the town is partially named. One side of the plaza is taken by the “portales” a series of arches initially built in the 18th century, which contain a number of businesses. Unlike many towns, the main church does not face this plaza. It is set back from it about a block.
The Santo Domingo church and former monastery is the largest structure in the town, set on a small hill overlooking the river.(sectorchiapas) It is locally known as the “Iglesia Grande” or Big Church. The structure was built in the second half of the 16th century and attributed to Pedro de Barrientos and Juan Alonso. The church is one of the best preserved from the 16th century in Chiapas. It has three naves, a coffered ceiling and cupolas above the presbytery and intersection. It is based on the Moorish churches of the Seville region in Spain, but it also has Gothic
, Renaissance
and Neoclassical
influences. Its main bell tower has the largest bells in the country. The main altar of the church is only about two decades old and made of cedar
, designed in Puebla
. The entire piece is supposed to be gilded but so far only a small area in the upper part has had this treatment. The gold used here is 24 karat from Italy and measures two meters by eighty centimeters. The work cost 150,000 pesos
, which was collected through raffles and donations for the project. To finish the work, another half a million pesos is needed. Other images in the church include an image of the Virgin of Guadalupe, Saint Joseph
, the Archangel Michael, Saint Dominic
and Saint Sebastian . The church complex is partially maintained by the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (INAH) .
To the side of the Big Church is the former Dominican monastery. This structure has been restored to house exhibition halls, including those associated with the Museo de la Laca
(Lacquer Museum) . The most important craft in the municipality is the working of wood, often with these pieces glazed in lacquer. One item is the masks used for traditional dances such as Parachicos. Another is the popular musical instrument the marimba
. Lacquer is used on wooden items and other things such as gourds. It is decorative, often with intricate designs. This craft is locally called “laca.”
Other important churches in the town include the Calvario and the San Sebastian. The Calvario Church is from the 17th century. It was remodeled in Gothic Revival architecture
at the beginning of the 19th century. Its interior conserves a wooden relief which was part of the Santo Domingo Church. San Sebastian is a church in ruins located on the San Gregorio hill. It was constructed in the 17th century when the city was at its height. It had three naves separated by archways. However, only its apse
and facade remain with elements of Moorish, Renaissance and Baroque elements.
The municipality Chiapa de Corzo is the local governing authority for 83 other communities, all of which are considered rural for a total territory of 906.7km2. These communities include Julián Grajales, Las Flechas, Salvador Urbina, El Palmar San Gabriel, Caleció Narcia, Ignacio Allende, Venustiano Carranza and Nicolás Bravo. ) Twenty three percent of the municipality’s land is communally owned in ejido
s with the rest either privately owned or parkland. The municipality borders the municipalities of Soyaló
, Osumacinta
, Tuxtla Gutiérrez
, Suchiapa
, Villaflores
, Zinacantán
, Ixtapa
, Acala
and Villa Corzo
. The municipality has 233.55 km of principal roadways, divided among rural roads managed by SCT, the Comisión Estatal de Campinos, the Secretaría de Obras Públicas, Desarrollo Rural, Defensa Nacional and the Comisión Nacional del Agua.
Throughout the municipality, festivals, music and cuisine are similar. The Festival of the Señor de El Calvario is a social and religious event which occurs on 7 October. It honors an image of Christ with masses, popular dances, fireworks and amusement rides along with cultural and sporting events. The Fiesta Grande is celebrated from 15 to 23 January and it is the most important for the year. The marimba
is the most often heard instrument at festivals and parties. The main dishes include stews with potatoes and squash seeds, pork with rice and tamales. Cochito is pork cooked in an adobo
sauce. It is popular throughout the state but important in Chiapa de Corzo for the Comida Grande which is served during the Festival of San Sebastian in January. Another is a beef dish where the meat is dried then fried then served with a sauce made from squash seeds, green tomatoes and achiote
. Typical sweets are also made with squash seeds. A typical cold drink is pozol
.
Historically, the dominant indigenous ethnicity has been the Zoques and there are still Zoque communities in the municipality. As of 2005, there were 2,899 people who spoke an indigenous language, out of a total of over 60,000. Most of the municipality’s population is young with 64% under the age of thirty and the average age of twenty one. The rate of population growth is just over three percent, which is above the state average of 2.06%. The population of the municipality is expected to double within twenty three years. Over 48% of the population lives in the city proper and the rest live in the 276 rural communities. Population density is at 67 inhabitants per square kilometers, below the regional average of 75/km2 but above the state average of 52. The average woman has 2.89 children which is below the state average of 3.47. Over 76% of the population is Catholic with about 13percent belonging to a Protestant or other Christian group. Illiteracy as of 2000 was at just under twenty percent, down from just under twenty five percent in 1990. Of those over 15 years of age, just under 25% have not completed primary school, about 17% with primary completed and over 35% having education above the primary level.
According to Consejo Nacional de Población (CONAPO) the municipality has a high rate of socioeconomic marginalization, despite the fact that it is between the two least marginalized municipalities in the state, Tuxtla Gutiérrez and San Cristóbal. As of 2005, there were 16,327 residences. Just over 84% of homes are owned by their residents, with an average occupancy of 4.62 people per home, which is about state average. Over 28% of homes have dirt floors and about 64% have cement. About 62% of homes have cinderblock walls, and roofs are either made of tile (about 40%) and or a slab of concrete (about 30%). About 95% of homes have electricity, over 70% have running water and over 77% have sewerage, all above state average.
Over 35% of the municipality’s working population is in agriculture. Of these, about a third do not receive any salary for their work. Principle crops include corn, peanuts, sorghum
, cotton, bananas, mango
s, melons, jocote (Spondias purpurea), chard
, lettuce and onions. Livestock includes cattle, pigs and domestic fowl as well as beekeeping. Fishing is limited to species such as mojarra
and catfish
. Just over 20% of the population is dedicated to industry, construction and transportation. The main industry is the Nestlé
plant. There are also plants that manufacture plywood
and bricks. There is also some handcraft workshops. Over 41% of the population is dedicated to commerce, services and tourism. One of the main tourist attractions for the municipality is the Sumidero Canyon
, with the municipal docks on the Grijalva River mostly serving tour boats into the National Park up to the La Angostura Dam. Most commerce is small stores and commercial centers for local needs and some for tourism. Services include hotels, auto repair and professional services. There are three hotels with seventy nine rooms.
and Saint Sebastian. The festival has been included in UNESCO's
Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists on November 16, 2010, listed as "Parachicos in the traditional January feast of Chiapa de Corzo". Since then, the event has experienced a surge in interest, making the Dance of the Parachicos the highlight. However, this has not assured the survival of the event or of the Parachicos dancers. There are fewer dancers than in the past, and many of the younger generation are not interested in the time it takes to carve a traditional mask from wood then lacquer it.
The Fiesta Grande de Enero is a celebration which joins a number of events which all happen in the month of January. Originally, these were the feast days of patron saints and other figures, including a Christ figure called the Our Lord of Esquipulas, Anthony the Great and Saint Sebastian. Since then, it has developed to include other events and overall it is meant to give thanks for what has been received over the past year. On 8 January, the Fiesta Grande is announced and the first of the dances, by dancers called “Chuntas,” is performed. The feast day of the Our Lord of Esquipulas is on January 15, who is honored where he is kept at the Señor de Milagros Church. On 16 January the festival of Saint Sebastian is announced. 17 January is dedicated to San Antonio Abad with a parade of Parachicos. On 18 January, the Parachicos visit the graves of deceased patrons. On 19 January the festival of Saint Sebastian is announced. The 20th is dedicated to this saint as well, with activities starting early and foods such as pepita con tasajo to the public. On the 21 of January a naval battle takes place on the Grijalva River, which consists of a spectacle using thousands of fireworks. This tradition began in 1599, when Pedro de Barrientos, vicar
of the Santo Domingo Church, encouraged the development of fireworks making. He came up with the naval battle idea as a diversion and over time it became a way to fascinate visitors. Today, the battle is a recreation of the Battle of Puerto Arturo which occurred on 21 January 1906, by a group of local firework makers. On 22 January, there is a parade with floats. This day is marked with confetti
and mariachi
s along with various types of dancers. The last day, the 23rd is marked by a parade of dancers. Then there is a mass. During these last hours, the drums and flutes play a melancholy tune as the fireworks ends and the streets quiet. The Parachicos cry during their mass as the festival ends. The traditional food during this time is pork with rice and pepita con tasajo.
Although the Parachicos are the best known and recognized of the dancers, there are actually three types. All refer back to a story that takes place in the colonial era. According to legend, Doña María de Angula was a rich Spanish woman who traveled in search of a cure for a mysterious paralytic illness suffered by her son, which no doctor could cure. When she arrived here, she was directed to a curandero
, or local healer called a namandiyuguá. After examining the boy, he instructed his mother to bathe him in the waters of a small lake called Cumbujuya, after which he was miraculously cured. To distract and amuse the boy, a local group disguised themselves as Spaniards with masks and began to dance showing “para el chico” which means “for the boy.” According to one version of the story, this is what cured the child. The tradition of these dancers began in 1711, leading the Spanish to called the event “para el chico”, which eventually evolved into Parachicos.
The term is also used to refer to the best known of the dancers of the Fiesta Grande. The Parachicos dress in a mask, a helmet or wig made of ixtle, a Saltillo style sarape. The mask is carved of wood and decorated with lacquer to mimic a Spanish face. Originally the masks had beards, but over time they evolved and many have an almost childlike look. The ixtle head covering is supposed to mimic blonde hair. The dancers carry a type of maraca made of metal called chinchin to make noise along with the taping of their boot heels. These carry a guitar and/or whip (the latter used by encomenderos in the colonial period) . The dancers use the whips to lightly tap children, youths, old men and even some women. These dancers appear a number of times during the days of the Fiesta Grande. These processions visit the various churches on their path, which are decorated with branches, on which are hung breads, sweets, fruits and plastic decorations.
Accompanying the Parachicos or dancing on their own is another type of dancer called “chuntas.” These are men dressed as women as the word chunta means maid or servant. These figures represent the “servants” of Doña María. Most of the men dress in shirts and long skirts. The two types of dancers appear on several occasions during the days of the festival dancing and marching to pipes, drums and other instruments. The dance reenancts the search for relief from a pain and suffering, including hunger. The dancers distribute food and small gifts for this reason. The route is lined by spectators who hope to receive some of the gifts that the dancers distribute.
The “patron” of the dances and processions has been the Nigenda family for about seventy years, whose house at 10 Alvaro Obregon Avenue becomes the meeting point for the dancers during the festival. At the back of the patio of this house, there is an altar which the portraits of two deceased members of the family Atilano Negenda and Arsenio Nigenda. The latter ceded the charge of the dance to the current patron, Guadalupe Rubicel Gomez Nigenda in 1999. The Parachicos dress in their costumes at the patron’s house, then they pray as a group. First the musicians exit playing flutes, drums and whistles. At a signal, the hundreds of Parachicos begin dancing and shouting. At the end of the parade is the patron, Rubisel Nigenda, who is accompanying by a “Chulita” a young woman who does not wear a mask, but rather an old fashioned traditional Chiapan dress, with a long skirt, embroidered shirt and roses. She represents the women of Chiapas. They are followed by people carrying flags representing various saints. In the middle of these is the flag of the city’s patron saint and “king” of the festival, Saint Sebastian.
, also called the Grande de Chiapa and the Santo Domingo. Streams include El Chiquito, Majular, Nandaburé and Nandalumí. The climate is hot and relatively humid with most rain falling from July to November. The annual average temperature in the city is 26C with an annual rainfall of 990mm.
The natural vegetation of the area is lowland rainforest with pine-oak forests in the extreme north. However, much of these forests have been overexploited with the loss of wildlife. Wildlife includes river crocodile
s, coral snake
s, heloderma
, iguana
s, opossums and skunk
s. Part of the Sumidero Canyon National Park is in the municipality. The El Chorreadero is a state park located in the municipality centered on the waterfall of the same name. It has an area of 100 hectares with lowland rainforest and secondary vegetation. The Grijalva River extends twenty three km from the city to the Chicoasén Dam, formally known as the Ing. Manuel Moreno Torres, one of the largest in Latin America. Boats touring the canyon leave from the Cahuaré Docks.
of Mesoamerica
n history. The immediate area of the municipality was settled around 1200 BCE by a group of people related to the Olmec
culture, who are thought to have been speakers of an early Mixe–Zoquean language. However, the exact relationship between Chiapa de Corzo and the Olmec world has not been definitively established. By 900 or 800 BCE, the village, now archeological site, show a strong relationship with the Olmec center of La Venta
, but it is unknown is Chiapa was ruled by La Venta or not. However, much the settlement shared many features with La Venta, including a ceremonial pond and pottery styles as well as using the same sources for materials such as obsidian
and andesite
.
The Chiapa site is important because it shows a Mixe–Zoque–Olmec culture which eventually split from the Olmec. The development of the ancient city has been divided into a number of phases. The earliest and most important are the Escalera or Chiapa III (700-500BCE) and Francesa or Chiapa IV (500BCE to 100CE) phase. Olmec influence is strongest in the Escalera phase when it became a planned town with formal plazas and monumental buildings. However, contacts with Mayan areas is evident as well. However, even during this phase, there are significant differences in architecture and pottery which suggest a distinct Zoque identity from the Mixe–Zoque/Olmec cultural base. The distinction grew in the Francesca period as monumental structures were enlarged and pottery was almost all locally made. There is also evidence of participation in long distance trade networks, and the first examples of hieroglyphic writing appear. The earliest Long Count inscription in Mesoamerica
derives from this phase, with a date of 36 BCE appearing on Stela 2. At its height, was an independent city on major trade routes. It may have been a major influence for the later Maya civilization as the pyramids in Chiapa are very similar to the E group pyramids found in most of Mesoamerica. The following Horcones phase and Istmo phase to 400 CE show more elaborate tomb construction and craft specialization. By the end of these phases, however, craft activity diminishes and long distance ties contracted even though tombs remain elaborate. The final centuries are associated with the Jiquipilas phase around 400 CE. It is not known what brought down the civilization, but the city became gradually abandoned and appears to have become a pilgrimage site, perhaps by Zoque who had been conquered by the Chiapa people .
Whether the Chiapa actually conquered the Zoque city or whether it had fallen before their arrival, the newcomers decided to occupy the adjacent floodplain of the Grijalva River, where the modern town is, and leave the old ruins untouched. By the early 16th century, this town had become a local power center called Napinaica. The Chiapa people were distinct from others in Chiapas in size, nudity, and fierceness which impressed the Spanish who noted it in their writings. These people were fiercely opposed to Spanish intrusion and were a major obstacle to the first efforts by the conquistadors to dominate. However, in 1528, Diego de Mazariegos succeeded in breaking this resistance by enlisting the help of neighboring peoples who were enemies of the Chiapa. The last Chiapa leader, named Sanguieme, tried to help his people escape the domination of the Spanish but, according to historian Jean de Vos, he was captured and burned alive in a hammock
strung between two kapok
trees, with a hundred of his followers hung from trees near the river.
After the conquest, the town was refounded with the name of Villa Real de Chiapa by a large kapok tree called La Pochota as the first European city in Chiapas. However, the hot climate of the area did not entice many Spanish to stay. Most instead went to the northeast into the cooler mountains to found another city, today San Cristobal. The mountain city would be founded as Chiapa de los Españoles, while Villa Real de Chiapa would become known Chiapa de los Indios, left to the indigenous and monks there to evangelize them. Despite this, the city would remain one of the most important for the first 200 years of colonization. While it was an encomienda
at first, it became a dependency of the Spanish Crown in 1552, changing its name to Pueblo de la Real Corona de Chiapa de Indios. The developers of the area were Dominican friars, who followed the ideals of Bartolomé de las Casas
in neighboring San Cristobal. They worked to protect the indigenous against the abuses of the Spanish colonizers, allowing them to gain the trust of the local people and convert them to Christianity. They also taught the local indigenous crafts such as European pottery methods, fireworks making and rope making. The Dominicans also built many of the landmarks of the town such as the La Pila fountain. This protection and the very high percentage of indigenous population in the colonial period allowed for many indigenous names to survive to the present day. Along with surnames such as Grajales, Castellanos, Marino Hernández, there is Nandayapa, Tawa, Nuriulú, Nampulá and Nangusé among others.
In 1849, the city was declared the seat of its district. The town was officially declared a city in 1851. “de Corzo” was added to the name in 1881 in honor of Liberal
politician Angel Albino Corzo. In 1863, there was a battle between the French and the Liberals
, with the latter led by Salvador Urbina.
Between 1970 and 1979, the construction of the Chicoasén Dam caused tremblers in the area. One of these toppled the large bell in the main church.
The main highway that connects the city with San Cristóbal was built in 2000. During this same year, the first non PRI municipal president was elected, from the National Action Party
.
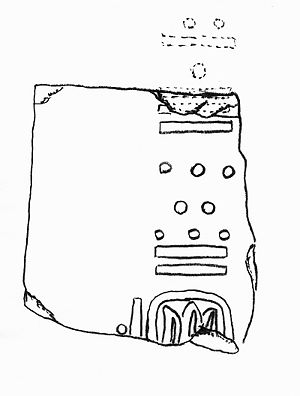 While there is evidence of human occupation in the region from at least the Archaic period
While there is evidence of human occupation in the region from at least the Archaic period
the main archeological site for the area is near the modern town of Chiapa de Corzo. It was one of the largest settlements in early Mesoamerica occupied from 1200 BCE to 600 CE. This site had been occupied from at least 1400 BCE until sometime in the late Classic period. The site reached its height between 700 BCE to 200 CE, when it was a large settlement along major trade routes.
The site is important for a number of reasons. First, while it was definitely inhabited by Mixe
-Zoque
speakers, it has strong ties to the Olmec
s, but it is not known what exactly theses ties were. Some theories state that the population was genetically related to the Olmecs, while others suppose that they were dominated by the Olmecs initially but then eventually broke away. There have been significant finds here such as the oldest Mesoamerican Long Count calendar
with the date of 36 BCE on a monument, as well as a pottery shard with the oldest instance of writing system
yet discovered.
A recent discovery has been the oldest pre Hispanic tomb, dated to between 700 and 500 BCE. It was found in a previously excavated 20-meter-tall pyramid, but in the very center. The occupant is richly attired with more than twenty axes found as offerings, placed in the cardinal directions. The culture is considered to be Olmec although more exact dating needs to be done. The offerings show Olmec influence, such as depictions of wide eyes and lips, but other typical Olmec decorations such as earspools
and breastplates are missing. In addition to the axes, there are also more than three thousand pieces made of jade
, river pearls, obsidian
and amber
, from areas as far away as Guatemala
and the Valley of Mexico
, showing trade networks. The face was covered in a seashell with eye and mouth openings, the earliest example of a funeral mask. The burial shows that many elements of Mesoamerican burials are older than previously thought.
The archeological site lies just outside the urban sprawl of modern Chiapa de Corzo, but the city is growing over it and many areas known to contains ruins underground are encroached upon by modern homes and businesses. The discovery of the ancient tomb has prompted the Mexican government to buy more lands and extend the site by 7,200 square meters to one and a half hectares. Part of the site has been open to tourism since late 2009.
Municipalities of Mexico
Municipalities are the second-level administrative division in Mexico . There are 2,438 municipalities in Mexico, making the average municipality population 45,616...
) situated in the west-central part of the Mexican
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
state of Chiapas
Chiapas
Chiapas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas is one of the 31 states that, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 118 municipalities and its capital city is Tuxtla Gutierrez. Other important cites in Chiapas include San Cristóbal de las...
. Located in the Grijalva River
Grijalva River
Grijalva River, formerly known as Tabasco River. is a 480 km long river in southeastern Mexico. It is named after Juan de Grijalva who visited the area in 1518. The river rises in Chiapas highlands and flows from Chiapas to the state of Tabasco through the Sumidero Canyon into the Bay of...
valley of the Chiapas highlands
Chiapas highlands
The region of the Chiapas Highlands is located in Chiapas, the southern-most state of Mexico.Many pre-Columbian Maya civilization sites are located in these highlands....
, Chiapa de Corzo lies some 15 km (9.3 mi) to the east of the state capital, Tuxtla Gutiérrez
Tuxtla Gutiérrez
Tuxtla Gutiérrez is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Chiapas. It is considered to be the state’s most modern city, with most of its public buildings dating from the 20th century. One exception to this is the San Marcos Cathedral which began as a Dominican parish church built in...
. Chiapa has been occupied since at least 1400 BCE, with a major archeological site which reached it height between 700 BCE and 200 CE. It is important because the earliest inscribed date, the earliest form of hieroglyphic writing and the earliest Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
n tomb burial have all been found here. Chiapa is also the site of the first Spanish city founded in Chiapas in 1528. However, because of the climate, most Spanish would move into the mountains to found what is now known as San Cristóbal de las Casas
San Cristóbal de las Casas
San Cristóbal de las Casas also known as it's native Tsotsil name, Jovel is a city and municipality located in the Central Highlands region of the Mexican state of Chiapas...
. Chiapa would be left to the indigenous and to the Dominican
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers , after the 15th century more commonly known as the Dominican Order or Dominicans, is a Catholic religious order founded by Saint Dominic and approved by Pope Honorius III on 22 December 1216 in France...
friars and called Chiapa de los Indios (with San Cristobal known as Chiapa de los Españoles). The current name was created to honor Liberal
Reform War
The Reform War in Mexico is one of the episodes of the long struggle between Liberal and Conservative forces that dominated the country’s history in the 19th century. The Liberals wanted a federalist government, limiting traditional Catholic Church and military influence in the country...
politician Angel Albino Corzo.
Town and municipality
The town/municipality is located about fifteen km from the state capital of Tuxtla Gutiérrez and connected to the city of San Cristóbal de las Casas via Federal Highway 190 also known as the Panamerican Highway . The town is located along the Grijalva RiverGrijalva River
Grijalva River, formerly known as Tabasco River. is a 480 km long river in southeastern Mexico. It is named after Juan de Grijalva who visited the area in 1518. The river rises in Chiapas highlands and flows from Chiapas to the state of Tabasco through the Sumidero Canyon into the Bay of...
and has one of the main docks along this waterway. The town is laid out in Spanish style, centered on a very large plaza which the municipality claims is larger than the Zocalo
Zócalo
The Zócalo is the main plaza or square in the heart of the historic center of Mexico City. The plaza used to be known simply as the "Main Square" or "Arms Square," and today its formal name is Plaza de la Constitución...
, or main plaza of Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
. (sec.
This plaza has a number of important features. The largest and best known is the La Pila fountain. This was constructed in 1562 in Moorish
Moorish architecture
Moorish architecture is the western term used to describe the articulated Berber-Islamic architecture of North Africa and Al-Andalus.-Characteristic elements:...
style, made of brick in the form of a diamond. The structure is attributed to Dominican brother Rodrigo de León. It measures fifty two meters in circumference and twelve meters in height. It has eight arches and a cylindrical tower which occasionally functioned as a watchtower. Another important feature is the La Pochota kapok
Kapok
Ceiba pentandra is a tropical tree of the order Malvales and the family Malvaceae , native to Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean, northern South America, and to tropical west Africa...
tree. According to tradition, the Spanish town was founded around this tree. The last feature is a clock tower which was constructed in the 1950s. The town’s main structures are centered on this plaza, including the municipal palace and the former home of Liberal governor Angel Albino Corzo, for whom the town is partially named. One side of the plaza is taken by the “portales” a series of arches initially built in the 18th century, which contain a number of businesses. Unlike many towns, the main church does not face this plaza. It is set back from it about a block.
The Santo Domingo church and former monastery is the largest structure in the town, set on a small hill overlooking the river.(sectorchiapas) It is locally known as the “Iglesia Grande” or Big Church. The structure was built in the second half of the 16th century and attributed to Pedro de Barrientos and Juan Alonso. The church is one of the best preserved from the 16th century in Chiapas. It has three naves, a coffered ceiling and cupolas above the presbytery and intersection. It is based on the Moorish churches of the Seville region in Spain, but it also has Gothic
Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished during the high and late medieval period. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture....
, Renaissance
Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture is the architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 17th centuries in different regions of Europe, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance...
and Neoclassical
Neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture was an architectural style produced by the neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century, manifested both in its details as a reaction against the Rococo style of naturalistic ornament, and in its architectural formulas as an outgrowth of some classicizing...
influences. Its main bell tower has the largest bells in the country. The main altar of the church is only about two decades old and made of cedar
Cedar wood
Cedar wood comes from several different trees that grow in different parts of the world, and may have different uses.* California incense-cedar, from Calocedrus decurrens, is the primary type of wood used for making pencils...
, designed in Puebla
Puebla
Puebla officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 217 municipalities and its capital city is Puebla....
. The entire piece is supposed to be gilded but so far only a small area in the upper part has had this treatment. The gold used here is 24 karat from Italy and measures two meters by eighty centimeters. The work cost 150,000 pesos
Mexican peso
The peso is the currency of Mexico. Modern peso and dollar currencies have a common origin in the 15th–19th century Spanish dollar, most continuing to use its sign, "$". The Mexican peso is the 12th most traded currency in the world, the third most traded in the Americas, and by far the most...
, which was collected through raffles and donations for the project. To finish the work, another half a million pesos is needed. Other images in the church include an image of the Virgin of Guadalupe, Saint Joseph
Saint Joseph
Saint Joseph is a figure in the Gospels, the husband of the Virgin Mary and the earthly father of Jesus Christ ....
, the Archangel Michael, Saint Dominic
Saint Dominic
Saint Dominic , also known as Dominic of Osma, often called Dominic de Guzmán and Domingo Félix de Guzmán was the founder of the Friars Preachers, popularly called the Dominicans or Order of Preachers , a Catholic religious order...
and Saint Sebastian . The church complex is partially maintained by the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (INAH) .
To the side of the Big Church is the former Dominican monastery. This structure has been restored to house exhibition halls, including those associated with the Museo de la Laca
Museo de la Laca and the Santo Domingo monastery
The former monastery of Santo Domingo/Museo de la Laca is located in the city of Chiapa de Corzo, Chiapas, Mexico. The monastery with its church was built in the 16th century, with the monastery secularized later. The church retains its original function...
(Lacquer Museum) . The most important craft in the municipality is the working of wood, often with these pieces glazed in lacquer. One item is the masks used for traditional dances such as Parachicos. Another is the popular musical instrument the marimba
Marimba
The marimba is a musical instrument in the percussion family. It consists of a set of wooden keys or bars with resonators. The bars are struck with mallets to produce musical tones. The keys are arranged as those of a piano, with the accidentals raised vertically and overlapping the natural keys ...
. Lacquer is used on wooden items and other things such as gourds. It is decorative, often with intricate designs. This craft is locally called “laca.”
Other important churches in the town include the Calvario and the San Sebastian. The Calvario Church is from the 17th century. It was remodeled in Gothic Revival architecture
Gothic Revival architecture
The Gothic Revival is an architectural movement that began in the 1740s in England...
at the beginning of the 19th century. Its interior conserves a wooden relief which was part of the Santo Domingo Church. San Sebastian is a church in ruins located on the San Gregorio hill. It was constructed in the 17th century when the city was at its height. It had three naves separated by archways. However, only its apse
Apse
In architecture, the apse is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome...
and facade remain with elements of Moorish, Renaissance and Baroque elements.
The municipality Chiapa de Corzo is the local governing authority for 83 other communities, all of which are considered rural for a total territory of 906.7km2. These communities include Julián Grajales, Las Flechas, Salvador Urbina, El Palmar San Gabriel, Caleció Narcia, Ignacio Allende, Venustiano Carranza and Nicolás Bravo. ) Twenty three percent of the municipality’s land is communally owned in ejido
Ejido
The ejido system is a process whereby the government promotes the use of communal land shared by the people of the community. This use of community land was a common practice during the time of Aztec rule in Mexico...
s with the rest either privately owned or parkland. The municipality borders the municipalities of Soyaló
Soyaló
Soyaló is a town and one of the 119 Municipalities of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.As of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 7,767. It covers an area of 178.9 km²....
, Osumacinta
Osumacinta
Osumacinta is a town and one of the 119 Municipalities of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.As of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 3,132. It covers an area of 221.1 km²....
, Tuxtla Gutiérrez
Tuxtla Gutiérrez
Tuxtla Gutiérrez is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Chiapas. It is considered to be the state’s most modern city, with most of its public buildings dating from the 20th century. One exception to this is the San Marcos Cathedral which began as a Dominican parish church built in...
, Suchiapa
Suchiapa
Suchiapa is a town and one of the 119 Municipalities of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.As of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 15,890. It covers an area of 355.2 km²....
, Villaflores
Villaflores, Chiapas
Villaflores is a town and municipio in the state of Chiapas, southern Mexico, and the name of its largest settlement and seat of the municipal government. Situated in the Sierra Madre de Chiapas range, the municipality has an area of approximately 1232km² at an average elevation of 540m above mean...
, Zinacantán
Zinacantan
San Lorenzo Zinacantán is a municipio in the southern part of the Central Chiapas highlands in the Mexican state of Chiapas. About 98% of its population are Tzotzil Maya, an indigenous people with linguistic and cultural ties to other highland Maya peoples.Zinacantán literally means "land of bats"...
, Ixtapa
Ixtapa, Chiapas
Ixtapa is a town and one of the 119 municipalities of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.As of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 18,533. It covers an area of 313 km²....
, Acala
Acala, Chiapas
Acala is a town and one of the 119 Municipalities of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.As of 2005, the town itself has a population of 12,686 with 24,800 in the municipality.It covers an area of 295.6 km²....
and Villa Corzo
Villa Corzo
Villa Corzo is a town and one of the 119 municipalities of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.The only urban area is the Villa Corzo City ....
. The municipality has 233.55 km of principal roadways, divided among rural roads managed by SCT, the Comisión Estatal de Campinos, the Secretaría de Obras Públicas, Desarrollo Rural, Defensa Nacional and the Comisión Nacional del Agua.
Throughout the municipality, festivals, music and cuisine are similar. The Festival of the Señor de El Calvario is a social and religious event which occurs on 7 October. It honors an image of Christ with masses, popular dances, fireworks and amusement rides along with cultural and sporting events. The Fiesta Grande is celebrated from 15 to 23 January and it is the most important for the year. The marimba
Marimba
The marimba is a musical instrument in the percussion family. It consists of a set of wooden keys or bars with resonators. The bars are struck with mallets to produce musical tones. The keys are arranged as those of a piano, with the accidentals raised vertically and overlapping the natural keys ...
is the most often heard instrument at festivals and parties. The main dishes include stews with potatoes and squash seeds, pork with rice and tamales. Cochito is pork cooked in an adobo
Adobo
Adobo is the immersion of raw food into a preparation, in the form of a stock , of different components, including paprika , oregano, salt, garlic, and vinegar — mixed according to the place of origin and the food with which it is intended to be used—primarily to preserve and enhance the flavor of...
sauce. It is popular throughout the state but important in Chiapa de Corzo for the Comida Grande which is served during the Festival of San Sebastian in January. Another is a beef dish where the meat is dried then fried then served with a sauce made from squash seeds, green tomatoes and achiote
Achiote
Achiote is a shrub or small tree from the tropical region of the Americas. The name derives from the Nahuatl word for the shrub, achiotl. It is also known as Aploppas, and its original Tupi name urucu. It is cultivated there and in Southeast Asia, where it was introduced by the Spanish in the...
. Typical sweets are also made with squash seeds. A typical cold drink is pozol
Pozol
Pozol is a name for both the fermented corn dough and the drink made from it, which has its origins in Pre-Columbian Mexico. To the drink, other ingredients besides corn dough and water, such as cocoa, may be added...
.
Historically, the dominant indigenous ethnicity has been the Zoques and there are still Zoque communities in the municipality. As of 2005, there were 2,899 people who spoke an indigenous language, out of a total of over 60,000. Most of the municipality’s population is young with 64% under the age of thirty and the average age of twenty one. The rate of population growth is just over three percent, which is above the state average of 2.06%. The population of the municipality is expected to double within twenty three years. Over 48% of the population lives in the city proper and the rest live in the 276 rural communities. Population density is at 67 inhabitants per square kilometers, below the regional average of 75/km2 but above the state average of 52. The average woman has 2.89 children which is below the state average of 3.47. Over 76% of the population is Catholic with about 13percent belonging to a Protestant or other Christian group. Illiteracy as of 2000 was at just under twenty percent, down from just under twenty five percent in 1990. Of those over 15 years of age, just under 25% have not completed primary school, about 17% with primary completed and over 35% having education above the primary level.
According to Consejo Nacional de Población (CONAPO) the municipality has a high rate of socioeconomic marginalization, despite the fact that it is between the two least marginalized municipalities in the state, Tuxtla Gutiérrez and San Cristóbal. As of 2005, there were 16,327 residences. Just over 84% of homes are owned by their residents, with an average occupancy of 4.62 people per home, which is about state average. Over 28% of homes have dirt floors and about 64% have cement. About 62% of homes have cinderblock walls, and roofs are either made of tile (about 40%) and or a slab of concrete (about 30%). About 95% of homes have electricity, over 70% have running water and over 77% have sewerage, all above state average.
Over 35% of the municipality’s working population is in agriculture. Of these, about a third do not receive any salary for their work. Principle crops include corn, peanuts, sorghum
Sorghum
Sorghum is a genus of numerous species of grasses, one of which is raised for grain and many of which are used as fodder plants either cultivated or as part of pasture. The plants are cultivated in warmer climates worldwide. Species are native to tropical and subtropical regions of all continents...
, cotton, bananas, mango
Mango
The mango is a fleshy stone fruit belonging to the genus Mangifera, consisting of numerous tropical fruiting trees in the flowering plant family Anacardiaceae. The mango is native to India from where it spread all over the world. It is also the most cultivated fruit of the tropical world. While...
s, melons, jocote (Spondias purpurea), chard
Chard
Chard , is a leafy green vegetable often used in Mediterranean cooking. While the leaves are always green, chard stalks vary in color. Chard has been bred to have highly nutrious leaves at the expense of the root...
, lettuce and onions. Livestock includes cattle, pigs and domestic fowl as well as beekeeping. Fishing is limited to species such as mojarra
Mojarra
The mojarras are a family, Gerreidae, of fishes in the order Perciformes. It has seven genera.Mojarras are a common prey and bait fish in many parts of the Caribbean including the South American Coast and Caribbean islands. These species tend to be difficult to identify in the field and often...
and catfish
Catfish
Catfishes are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the heaviest and longest, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia and the second longest, the wels catfish of Eurasia, to detritivores...
. Just over 20% of the population is dedicated to industry, construction and transportation. The main industry is the Nestlé
Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. is the world's largest food and nutrition company. Founded and headquartered in Vevey, Switzerland, Nestlé originated in a 1905 merger of the Anglo-Swiss Milk Company, established in 1867 by brothers George Page and Charles Page, and Farine Lactée Henri Nestlé, founded in 1866 by Henri...
plant. There are also plants that manufacture plywood
Plywood
Plywood is a type of manufactured timber made from thin sheets of wood veneer. It is one of the most widely used wood products. It is flexible, inexpensive, workable, re-usable, and can usually be locally manufactured...
and bricks. There is also some handcraft workshops. Over 41% of the population is dedicated to commerce, services and tourism. One of the main tourist attractions for the municipality is the Sumidero Canyon
Sumidero Canyon
Sumidero Canyon is a narrow and deep canyon surrounded by a national park located just north of the city of Tuxtla Gutiérrez in the Mexican state of Chiapas. The canyon’s creation began around the same time as the Grand Canyon in the U.S. state of Arizona, by a crack in the area’s crust and...
, with the municipal docks on the Grijalva River mostly serving tour boats into the National Park up to the La Angostura Dam. Most commerce is small stores and commercial centers for local needs and some for tourism. Services include hotels, auto repair and professional services. There are three hotels with seventy nine rooms.
The Fiesta Grande de Enero
The Fiesta Grande de Enero (Great January Feast) takes place from 4 to 23 January every year in Chiapa de Corzo, to honor local patron saints Our Lord of Esquipulas, Anthony the GreatAnthony the Great
Anthony the Great or Antony the Great , , also known as Saint Anthony, Anthony the Abbot, Anthony of Egypt, Anthony of the Desert, Anthony the Anchorite, Abba Antonius , and Father of All Monks, was a Christian saint from Egypt, a prominent leader among the Desert Fathers...
and Saint Sebastian. The festival has been included in UNESCO's
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists on November 16, 2010, listed as "Parachicos in the traditional January feast of Chiapa de Corzo". Since then, the event has experienced a surge in interest, making the Dance of the Parachicos the highlight. However, this has not assured the survival of the event or of the Parachicos dancers. There are fewer dancers than in the past, and many of the younger generation are not interested in the time it takes to carve a traditional mask from wood then lacquer it.
The Fiesta Grande de Enero is a celebration which joins a number of events which all happen in the month of January. Originally, these were the feast days of patron saints and other figures, including a Christ figure called the Our Lord of Esquipulas, Anthony the Great and Saint Sebastian. Since then, it has developed to include other events and overall it is meant to give thanks for what has been received over the past year. On 8 January, the Fiesta Grande is announced and the first of the dances, by dancers called “Chuntas,” is performed. The feast day of the Our Lord of Esquipulas is on January 15, who is honored where he is kept at the Señor de Milagros Church. On 16 January the festival of Saint Sebastian is announced. 17 January is dedicated to San Antonio Abad with a parade of Parachicos. On 18 January, the Parachicos visit the graves of deceased patrons. On 19 January the festival of Saint Sebastian is announced. The 20th is dedicated to this saint as well, with activities starting early and foods such as pepita con tasajo to the public. On the 21 of January a naval battle takes place on the Grijalva River, which consists of a spectacle using thousands of fireworks. This tradition began in 1599, when Pedro de Barrientos, vicar
Vicar
In the broadest sense, a vicar is a representative, deputy or substitute; anyone acting "in the person of" or agent for a superior . In this sense, the title is comparable to lieutenant...
of the Santo Domingo Church, encouraged the development of fireworks making. He came up with the naval battle idea as a diversion and over time it became a way to fascinate visitors. Today, the battle is a recreation of the Battle of Puerto Arturo which occurred on 21 January 1906, by a group of local firework makers. On 22 January, there is a parade with floats. This day is marked with confetti
Confetti
Confetti is a multitude of pieces of paper, mylar or metallic material which is usually thrown at parades and celebrations, especially weddings . Confetti is made in a variety of colors, and commercially available confetti is available in imaginative shapes...
and mariachi
Mariachi
Mariachi is a genre of music that originated in the State of Jalisco, in Mexico. It is an integration of stringed instruments highly influenced by the cultural impacts of the historical development of Western Mexico. Throughout the history of mariachi, musicians have experimented with brass, wind,...
s along with various types of dancers. The last day, the 23rd is marked by a parade of dancers. Then there is a mass. During these last hours, the drums and flutes play a melancholy tune as the fireworks ends and the streets quiet. The Parachicos cry during their mass as the festival ends. The traditional food during this time is pork with rice and pepita con tasajo.
Although the Parachicos are the best known and recognized of the dancers, there are actually three types. All refer back to a story that takes place in the colonial era. According to legend, Doña María de Angula was a rich Spanish woman who traveled in search of a cure for a mysterious paralytic illness suffered by her son, which no doctor could cure. When she arrived here, she was directed to a curandero
Curandero
A curandero or curandeiro is a traditional folk healer or shaman in Latin America, who is dedicated to curing physical or spiritual illnesses. The role of a curandero or curandera can also incorporate the roles of psychiatrist along with that of doctor and healer. Many curanderos use Catholic...
, or local healer called a namandiyuguá. After examining the boy, he instructed his mother to bathe him in the waters of a small lake called Cumbujuya, after which he was miraculously cured. To distract and amuse the boy, a local group disguised themselves as Spaniards with masks and began to dance showing “para el chico” which means “for the boy.” According to one version of the story, this is what cured the child. The tradition of these dancers began in 1711, leading the Spanish to called the event “para el chico”, which eventually evolved into Parachicos.
The term is also used to refer to the best known of the dancers of the Fiesta Grande. The Parachicos dress in a mask, a helmet or wig made of ixtle, a Saltillo style sarape. The mask is carved of wood and decorated with lacquer to mimic a Spanish face. Originally the masks had beards, but over time they evolved and many have an almost childlike look. The ixtle head covering is supposed to mimic blonde hair. The dancers carry a type of maraca made of metal called chinchin to make noise along with the taping of their boot heels. These carry a guitar and/or whip (the latter used by encomenderos in the colonial period) . The dancers use the whips to lightly tap children, youths, old men and even some women. These dancers appear a number of times during the days of the Fiesta Grande. These processions visit the various churches on their path, which are decorated with branches, on which are hung breads, sweets, fruits and plastic decorations.
Accompanying the Parachicos or dancing on their own is another type of dancer called “chuntas.” These are men dressed as women as the word chunta means maid or servant. These figures represent the “servants” of Doña María. Most of the men dress in shirts and long skirts. The two types of dancers appear on several occasions during the days of the festival dancing and marching to pipes, drums and other instruments. The dance reenancts the search for relief from a pain and suffering, including hunger. The dancers distribute food and small gifts for this reason. The route is lined by spectators who hope to receive some of the gifts that the dancers distribute.
The “patron” of the dances and processions has been the Nigenda family for about seventy years, whose house at 10 Alvaro Obregon Avenue becomes the meeting point for the dancers during the festival. At the back of the patio of this house, there is an altar which the portraits of two deceased members of the family Atilano Negenda and Arsenio Nigenda. The latter ceded the charge of the dance to the current patron, Guadalupe Rubicel Gomez Nigenda in 1999. The Parachicos dress in their costumes at the patron’s house, then they pray as a group. First the musicians exit playing flutes, drums and whistles. At a signal, the hundreds of Parachicos begin dancing and shouting. At the end of the parade is the patron, Rubisel Nigenda, who is accompanying by a “Chulita” a young woman who does not wear a mask, but rather an old fashioned traditional Chiapan dress, with a long skirt, embroidered shirt and roses. She represents the women of Chiapas. They are followed by people carrying flags representing various saints. In the middle of these is the flag of the city’s patron saint and “king” of the festival, Saint Sebastian.
Environment
The municipality consists of rolling hills which alternate with flat areas, mostly along rivers and streams. Most of the territory is in the Central Valley region but in the northwest, it transitions into the Central Highlands. The main rivers include the GrijalvaGrijalva River
Grijalva River, formerly known as Tabasco River. is a 480 km long river in southeastern Mexico. It is named after Juan de Grijalva who visited the area in 1518. The river rises in Chiapas highlands and flows from Chiapas to the state of Tabasco through the Sumidero Canyon into the Bay of...
, also called the Grande de Chiapa and the Santo Domingo. Streams include El Chiquito, Majular, Nandaburé and Nandalumí. The climate is hot and relatively humid with most rain falling from July to November. The annual average temperature in the city is 26C with an annual rainfall of 990mm.
The natural vegetation of the area is lowland rainforest with pine-oak forests in the extreme north. However, much of these forests have been overexploited with the loss of wildlife. Wildlife includes river crocodile
Crocodile
A crocodile is any species belonging to the family Crocodylidae . The term can also be used more loosely to include all extant members of the order Crocodilia: i.e...
s, coral snake
Coral snake
The coral snakes are a large group of elapid snakes that can be subdivided into two distinct groups, Old World coral snakes and New World coral snakes...
s, heloderma
Heloderma
Heloderma, the only genus of the family Helodermatidae, consists of venomous lizards native to the southwestern United States, Mexico and as far south as Guatemala. It includes two separate species, with six subspecies...
, iguana
Iguana
Iguana is a herbivorous genus of lizard native to tropical areas of Central America and the Caribbean. The genus was first described in 1768 by Austrian naturalist Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in his book Specimen Medicum, Exhibens Synopsin Reptilium Emendatam cum Experimentis circa Venena...
s, opossums and skunk
Skunk
Skunks are mammals best known for their ability to secrete a liquid with a strong, foul odor. General appearance varies from species to species, from black-and-white to brown or cream colored. Skunks belong to the family Mephitidae and to the order Carnivora...
s. Part of the Sumidero Canyon National Park is in the municipality. The El Chorreadero is a state park located in the municipality centered on the waterfall of the same name. It has an area of 100 hectares with lowland rainforest and secondary vegetation. The Grijalva River extends twenty three km from the city to the Chicoasén Dam, formally known as the Ing. Manuel Moreno Torres, one of the largest in Latin America. Boats touring the canyon leave from the Cahuaré Docks.
History
The region has been inhabited at least since the Archaic periodMesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
n history. The immediate area of the municipality was settled around 1200 BCE by a group of people related to the Olmec
Olmec
The Olmec were the first major Pre-Columbian civilization in Mexico. They lived in the tropical lowlands of south-central Mexico, in the modern-day states of Veracruz and Tabasco....
culture, who are thought to have been speakers of an early Mixe–Zoquean language. However, the exact relationship between Chiapa de Corzo and the Olmec world has not been definitively established. By 900 or 800 BCE, the village, now archeological site, show a strong relationship with the Olmec center of La Venta
La Venta
La Venta is a pre-Columbian archaeological site of the Olmec civilization located in the present-day Mexican state of Tabasco. Some of the artifacts have been moved to the museum "Parque - Museo de La Venta", which is in Villahermosa, the capital of Tabasco....
, but it is unknown is Chiapa was ruled by La Venta or not. However, much the settlement shared many features with La Venta, including a ceremonial pond and pottery styles as well as using the same sources for materials such as obsidian
Obsidian
Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed as an extrusive igneous rock.It is produced when felsic lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimum crystal growth...
and andesite
Andesite
Andesite is an extrusive igneous, volcanic rock, of intermediate composition, with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between basalt and dacite. The mineral assemblage is typically dominated by plagioclase plus pyroxene and/or hornblende. Magnetite,...
.
The Chiapa site is important because it shows a Mixe–Zoque–Olmec culture which eventually split from the Olmec. The development of the ancient city has been divided into a number of phases. The earliest and most important are the Escalera or Chiapa III (700-500BCE) and Francesa or Chiapa IV (500BCE to 100CE) phase. Olmec influence is strongest in the Escalera phase when it became a planned town with formal plazas and monumental buildings. However, contacts with Mayan areas is evident as well. However, even during this phase, there are significant differences in architecture and pottery which suggest a distinct Zoque identity from the Mixe–Zoque/Olmec cultural base. The distinction grew in the Francesca period as monumental structures were enlarged and pottery was almost all locally made. There is also evidence of participation in long distance trade networks, and the first examples of hieroglyphic writing appear. The earliest Long Count inscription in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
derives from this phase, with a date of 36 BCE appearing on Stela 2. At its height, was an independent city on major trade routes. It may have been a major influence for the later Maya civilization as the pyramids in Chiapa are very similar to the E group pyramids found in most of Mesoamerica. The following Horcones phase and Istmo phase to 400 CE show more elaborate tomb construction and craft specialization. By the end of these phases, however, craft activity diminishes and long distance ties contracted even though tombs remain elaborate. The final centuries are associated with the Jiquipilas phase around 400 CE. It is not known what brought down the civilization, but the city became gradually abandoned and appears to have become a pilgrimage site, perhaps by Zoque who had been conquered by the Chiapa people .
Whether the Chiapa actually conquered the Zoque city or whether it had fallen before their arrival, the newcomers decided to occupy the adjacent floodplain of the Grijalva River, where the modern town is, and leave the old ruins untouched. By the early 16th century, this town had become a local power center called Napinaica. The Chiapa people were distinct from others in Chiapas in size, nudity, and fierceness which impressed the Spanish who noted it in their writings. These people were fiercely opposed to Spanish intrusion and were a major obstacle to the first efforts by the conquistadors to dominate. However, in 1528, Diego de Mazariegos succeeded in breaking this resistance by enlisting the help of neighboring peoples who were enemies of the Chiapa. The last Chiapa leader, named Sanguieme, tried to help his people escape the domination of the Spanish but, according to historian Jean de Vos, he was captured and burned alive in a hammock
Hammock
A hammock is a sling made of fabric, rope, or netting, suspended between two points, used for swinging, sleeping, or resting. It normally consists of one or more cloth panels, or a woven network of twine or thin rope stretched with ropes between two firm anchor points such as trees or posts....
strung between two kapok
Kapok
Ceiba pentandra is a tropical tree of the order Malvales and the family Malvaceae , native to Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean, northern South America, and to tropical west Africa...
trees, with a hundred of his followers hung from trees near the river.
After the conquest, the town was refounded with the name of Villa Real de Chiapa by a large kapok tree called La Pochota as the first European city in Chiapas. However, the hot climate of the area did not entice many Spanish to stay. Most instead went to the northeast into the cooler mountains to found another city, today San Cristobal. The mountain city would be founded as Chiapa de los Españoles, while Villa Real de Chiapa would become known Chiapa de los Indios, left to the indigenous and monks there to evangelize them. Despite this, the city would remain one of the most important for the first 200 years of colonization. While it was an encomienda
Encomienda
The encomienda was a system that was employed mainly by the Spanish crown during the colonization of the Americas to regulate Native American labor....
at first, it became a dependency of the Spanish Crown in 1552, changing its name to Pueblo de la Real Corona de Chiapa de Indios. The developers of the area were Dominican friars, who followed the ideals of Bartolomé de las Casas
Bartolomé de Las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas O.P. was a 16th-century Spanish historian, social reformer and Dominican friar. He became the first resident Bishop of Chiapas, and the first officially appointed "Protector of the Indians"...
in neighboring San Cristobal. They worked to protect the indigenous against the abuses of the Spanish colonizers, allowing them to gain the trust of the local people and convert them to Christianity. They also taught the local indigenous crafts such as European pottery methods, fireworks making and rope making. The Dominicans also built many of the landmarks of the town such as the La Pila fountain. This protection and the very high percentage of indigenous population in the colonial period allowed for many indigenous names to survive to the present day. Along with surnames such as Grajales, Castellanos, Marino Hernández, there is Nandayapa, Tawa, Nuriulú, Nampulá and Nangusé among others.
In 1849, the city was declared the seat of its district. The town was officially declared a city in 1851. “de Corzo” was added to the name in 1881 in honor of Liberal
Reform War
The Reform War in Mexico is one of the episodes of the long struggle between Liberal and Conservative forces that dominated the country’s history in the 19th century. The Liberals wanted a federalist government, limiting traditional Catholic Church and military influence in the country...
politician Angel Albino Corzo. In 1863, there was a battle between the French and the Liberals
French intervention in Mexico
The French intervention in Mexico , also known as The Maximilian Affair, War of the French Intervention, and The Franco-Mexican War, was an invasion of Mexico by an expeditionary force sent by the Second French Empire, supported in the beginning by the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of Spain...
, with the latter led by Salvador Urbina.
Between 1970 and 1979, the construction of the Chicoasén Dam caused tremblers in the area. One of these toppled the large bell in the main church.
The main highway that connects the city with San Cristóbal was built in 2000. During this same year, the first non PRI municipal president was elected, from the National Action Party
National Action Party
National Action Party may mean:*National Action Party *National Action Party *National Action Party *National Action Party...
.
Archeology

Mesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
the main archeological site for the area is near the modern town of Chiapa de Corzo. It was one of the largest settlements in early Mesoamerica occupied from 1200 BCE to 600 CE. This site had been occupied from at least 1400 BCE until sometime in the late Classic period. The site reached its height between 700 BCE to 200 CE, when it was a large settlement along major trade routes.
The site is important for a number of reasons. First, while it was definitely inhabited by Mixe
Mixe languages
The Mixe languages are languages of the Mixean branch of the Mixe–Zoquean language family indigenous to southern Mexico. According to a 1995 classification, there are seven of them...
-Zoque
Zoque languages
The Zoque languages are languages of the Zoquean branch of the Mixe–Zoquean language family indigenous to southern Mexico.The Zoque languages are spoken in the in northern Chiapas and far eastern Chiapas around Chimalapa, and in Ayapa Tabasco altogether by around 88,000 indigenous Zoque people...
speakers, it has strong ties to the Olmec
Olmec
The Olmec were the first major Pre-Columbian civilization in Mexico. They lived in the tropical lowlands of south-central Mexico, in the modern-day states of Veracruz and Tabasco....
s, but it is not known what exactly theses ties were. Some theories state that the population was genetically related to the Olmecs, while others suppose that they were dominated by the Olmecs initially but then eventually broke away. There have been significant finds here such as the oldest Mesoamerican Long Count calendar
Mesoamerican Long Count calendar
The Mesoamerican Long Count calendar is a non-repeating, vigesimal and base-18 calendar used by several Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya. For this reason, it is sometimes known as the Maya Long Count calendar...
with the date of 36 BCE on a monument, as well as a pottery shard with the oldest instance of writing system
Mesoamerican writing systems
Mesoamerica, like India, Mesopotamia, China, and Egypt, is one of the few places in the world where writing has developed independently. Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are logosyllabic, combining the use of logograms with a syllabary, and they are often called hieroglyphic scripts...
yet discovered.
A recent discovery has been the oldest pre Hispanic tomb, dated to between 700 and 500 BCE. It was found in a previously excavated 20-meter-tall pyramid, but in the very center. The occupant is richly attired with more than twenty axes found as offerings, placed in the cardinal directions. The culture is considered to be Olmec although more exact dating needs to be done. The offerings show Olmec influence, such as depictions of wide eyes and lips, but other typical Olmec decorations such as earspools
Plug (jewellery)
A plug , in the context of body modification, is a short, cylindrical piece of jewellery commonly worn in larger-gauge body piercings. Because of their size—which is often substantially thicker than a standard wire earring—plugs can be made out of almost any material...
and breastplates are missing. In addition to the axes, there are also more than three thousand pieces made of jade
Jade
Jade is an ornamental stone.The term jade is applied to two different metamorphic rocks that are made up of different silicate minerals:...
, river pearls, obsidian
Obsidian
Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed as an extrusive igneous rock.It is produced when felsic lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimum crystal growth...
and amber
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin , which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents...
, from areas as far away as Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
and the Valley of Mexico
Valley of Mexico
The Valley of Mexico is a highlands plateau in central Mexico roughly coterminous with the present-day Distrito Federal and the eastern half of the State of Mexico. Surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, the Valley of Mexico was a centre for several pre-Columbian civilizations, including...
, showing trade networks. The face was covered in a seashell with eye and mouth openings, the earliest example of a funeral mask. The burial shows that many elements of Mesoamerican burials are older than previously thought.
The archeological site lies just outside the urban sprawl of modern Chiapa de Corzo, but the city is growing over it and many areas known to contains ruins underground are encroached upon by modern homes and businesses. The discovery of the ancient tomb has prompted the Mexican government to buy more lands and extend the site by 7,200 square meters to one and a half hectares. Part of the site has been open to tourism since late 2009.

