Mixe languages
Encyclopedia
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
. According to a 1995 classification, there are seven of them (including one that is extinct). The four that are spoken in Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
are commonly called Mixe while their two relatives spoken in Veracruz
Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave , is one of the 31 states that, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided in 212 municipalities and its capital city is...
are commonly called "Popoluca
Popoluca
Popoluca is a Nahuatl term for various indigenous peoples of southeastern Veracruz and Oaxaca. Many of them speak languages of the Mixe–Zoque family...
", but sometimes also Mixe (these are "Oluta Popoluca
Oluta Popoluca
Oluta Popoluca also called Olutec is a moribund Mixe–Zoquean language of the Mixean branch spoken by a few elderly people in the town of Oluta in Southern Veracruz, Mexico....
" or "Olutec Mixe" and "Sayula Popoluca
Sayula Popoluca
Sayula Popoluca, also called Sayultec, is a Mixe language spoken by around 4,000 indigenous people in and around the town of Sayula de Alemán in the southern part of the state of Veracruz, Mexico. The language has been extensively studied by Lawrence E...
" or "Sayultec Mixe"). This article is about the Oaxaca Mixe languages, which their speakers call Ayuujk, Ayüük or Ayuhk.
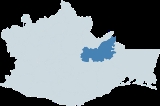
Oaxaca Mixe languages are spoken in the Sierra Mixe of eastern Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
by around 188,000 indigenous Mixe
Mixe
The Mixe or Mije is an indigenous group inhabiting the eastern highlands of the Mexican state of Oaxaca. They speak the Mixe languages which are classified in the Mixe–Zoque family, and are more culturally conservative than other indigenous groups of the region, maintaining their language to this...
people. These four languages are: North Highland Mixe, spoken around Totontepec; South Highland Mixe, spoken around Santa María Tlahuitoltepec
Santa María Tlahuitoltepec
Santa María Tlahuitoltepec is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of km².It is part of the Sierra Mixe district within the Sierra Norte de Oaxaca Region.-References:...
, Ayutla
San Pedro y San Pablo Ayutla
San Pedro y San Pablo Ayutla is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico.It is part of the Sierra Mixe district within the Sierra Norte de Oaxaca Region....
and Tamazulapan); Midland Mixe, spoken around Juquila and Zacatepec
Zacatepec
Zacatepec is a Mexican football team based in Zacatepec, Morelos. They are nicknamed Cañeros . Their colors are white and green . Their uniform color is a white shirt with a big green line in the middle and white shorts and socks. Their greatest achievements were in the 1950s when Zacatepec won two...
; and Lowland Mixe, spoken in San Juan Guichicovi
San Juan Guichicovi
San Juan Guichicovi is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico.It is part of the Juchitán District in the west of the Istmo de Tehuantepec region.The town was founded on 15 March 1825: Guichicovi means "New Town" in Zapotec.-Environment:...
(this language is also known as "Isthmus Mixe").
Phonology of Mixe
Mixe phonologyPhonology
Phonology is, broadly speaking, the subdiscipline of linguistics concerned with the sounds of language. That is, it is the systematic use of sound to encode meaning in any spoken human language, or the field of linguistics studying this use...
is complicated and little documented. There is a palatalized series of all consonant phonemes (as in Russian, Polish, or Gaelic) and possibly a fortis/lenis
Fortis and lenis
In linguistics, fortis and lenis are terms generally used to refer to groups of consonants that are produced with greater and lesser energy, respectively, such as in energy applied, articulation, etc....
distinction in the stop series, the recognition of which however is obscured by a tendency of allophonic voicing of consonants in voiced environments. Syllable nuclei are notoriously complex in Mixe, varying in length and phonation. Most descriptions report three contrastive vowel length
Vowel length
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived duration of a vowel sound. Often the chroneme, or the "longness", acts like a consonant, and may etymologically be one, such as in Australian English. While not distinctive in most dialects of English, vowel length is an important phonemic factor in...
s. There are multiple values of phonation, one being the typical one (what some phoneticians call "modal voicing"). The other types of phonation have been variously termed checked vowels
Checked and free vowels
In phonetics and phonology, checked vowels are those that usually must be followed by a consonant in a stressed syllable, while free vowels are those that may stand in a stressed open syllable with no following consonant.-Usage:...
, creaky voice
Creaky voice
In linguistics, creaky voice , is a special kind of phonation in which the arytenoid cartilages in the larynx are drawn together; as a result, the vocal folds are compressed rather tightly, becoming relatively slack and compact...
, vowels and breathy voice
Breathy voice
Breathy voice is a phonation in which the vocal cords vibrate, as they do in normal voicing, but are held further apart, so that a larger volume of air escapes between them. This produces an audible noise...
vowels. Some Mixe variants are vowel innovative and some, notably North Highland Mixe, have complicated umlaut
I-mutation
I-mutation is an important type of sound change, more precisely a category of regressive metaphony, in which a back vowel is fronted, and/or a front vowel is raised, if the following syllable contains /i/, /ī/ or /j/ I-mutation (also known as umlaut, front mutation, i-umlaut, i/j-mutation or...
systems raising vowel qualities in certain phonological environments.
The Verb
The morphosyntactic alignmentMorphosyntactic alignment
In linguistics, morphosyntactic alignment is the system used to distinguish between the arguments of transitive verbs and those of intransitive verbs...
of Mixe is ergative and it also has an obviative
Obviative
Obviate third person person is a grammatical person marking that distinguishes a non-salient third person referent from a more salient third person referent in a given discourse context...
system which serves to distinguish between verb participants in reference to its direct–inverse system. The Mixe verb
Verb
A verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action , or a state of being . In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive...
is complex and inflects for many categories and also shows a lot of derivational morphology
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the identification, analysis and description, in a language, of the structure of morphemes and other linguistic units, such as words, affixes, parts of speech, intonation/stress, or implied context...
. One of the parameters of verb inflection is whether a verb occurs in an independent or dependent clause; this distinction is marked by both differential affixation and stem ablaut. Unlike Sayultec Mixe (spoken in the neighboring state of Veracruz), Mixe languages of Oaxaca only mark one argument on the verb: either the object or the subject of the verb depending on whether the verb is in the direct or inverse form. Mixe shows a wide variety of possibilities for noun incorporation
Incorporation (linguistics)
Incorporation is a phenomenon by which a word, usually a verb, forms a kind of compound with, for instance, its direct object or adverbial modifier, while retaining its original syntactic function....
.
The Noun
The Mixe noun does not normally inflect, except that human nouns inflect for plural. Noun compounding is a very productive process, and the profuse derivational morphology allows for creation of new nouns both from verbs and other nouns.Syntax
Mixe languages are have SOV constituent order, prepositions and genitives precede the noun. But relative clauses follow the noun.Text example of Mixe
The example below is from Lowland Mixe.| Orthography: |
| Pronunciation: [ pwes haduʔn ʔidaː ʲ-ʔɨjoːb hɨjaʔaj ʔidaː ʔaldeano mɨːd ʲ-toʔoʃʲɨʰk ʲtɨɡoˑjʲ jɨ mɨkuʔu ] |
| Gloss: Well there this 3p-poor person this ranch-hand with 3p.poss-woman 3p-CAUS/PAS-lose-DEP the devil |
| Translation : "Well that's how this poor person, this ranch hand with his wife, made the devil lose" |
Mixe
Mixe-language programming is carried by the CDINational Commission for the Development of Indigenous Peoples
The National Commission for the Development of Indigenous Peoples is a decentralized agency of the Mexican Federal Public Administration. It was founded in 2003 as a replacement for the National Indigenist Institute . It has its headquarters in Mexico City and, since 15 December 2006, has been...
's radio station XEGLO, based in Guelatao de Juárez, Oaxaca.

