
Chelicerata
Encyclopedia
The subphylum Chelicerata constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum (or superphylum) Arthropod
a, and includes horseshoe crab
s, scorpion
s, spider
s and mite
s. They originated as marine animals, possibly in the Cambrian
period, but the first confirmed chelicerate fossil
s, eurypterid
s, date from in the Late Ordovician
period.
The surviving marine species include the four species of Xiphosura
ns (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of Pycnogonida (sea spiders), if the latter are chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species.
Like all arthropod
s, chelicerates have segmented
bodies with jointed limbs, all covered in a cuticle
made of chitin
and protein
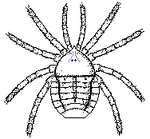
s. The chelicerate bauplan consists of two tagmata, the cephalothorax
and the abdomen
, except that mites have lost a visible division between these sections. The chelicerae
, which give the group its name, are the only appendage
s that appear before the mouth. In most sub-groups they are modest pincers used in feeding. However, spiders' chelicerae form fangs which in most species are used to inject venom
into their prey. The group has the open circulatory system typical of the arthropods, in which a tube-like heart pumps blood through the hemocoel, which is the major body cavity. Marine chelicerates have gills, while the air-breathing forms generally have both book lung
s and tracheae
. In general the ganglia of living chelicerates' central nervous system
s fuse into large masses in the cephalothorax, but there are wide variations and this fusion is very limited in the Mesothelae
, which are regarded as the oldest and most primitive group of spiders. Most chelicerates rely on modified bristles for touch and for information about vibrations, air currents, and chemical changes in their environment. The most active hunting spiders also have very acute eyesight.
Chelicerates were originally predators, but the group has diversified to use all the major feeding strategies: predation, parasitism
, herbivory, scavenging
and eating decaying organic matter. Although harvestmen can digest solid food, the guts of most modern chelicerates are too narrow for this, and they generally liquidize their food by grinding it with their chelicerae and pedipalps and flooding it with digestive enzyme
s. To conserve water, air-breathing chelicerates excrete waste as solids that are removed from their blood by Malpighian tubules, structures which also evolved independently
in insect
s. While the marine horseshoe crabs rely on external fertilization
, air-breathing chelicerates use internal but usually indirect fertilization. Predatory species generally use elaborate courtship
rituals to prevent males from being eaten before they can mate. Most lay eggs that hatch as what look like miniature adults, but all scorpions and a few species of mites keep the eggs inside their bodies until the young emerge. In most chelicerate species the young have to fend for themselves, but in scorpions and some species of spider the females protect and feed their young.
The evolution
ary origins of chelicerates from the early arthropods have been debated for decades. Although there is considerable agreement about the relationships between most chelicerate sub-groups, the inclusion of the Pycnogonida in this taxon has recently been questioned (see below), and the exact position of scorpions is still controversial, though they were long considered the most primitive (basal) of the arachnids.
Although the venom of a few spider and scorpion species can be very dangerous to humans, medical researchers are investigating the use of these venoms for the treatment of disorders ranging from cancer
to erectile dysfunction
. The medical industry also uses the blood of horseshoe crabs as a test for the presence of contaminant bacteria
. Genetic engineers have experimented with modifying goats' milk and plants' leaves to produce spider silk
. Mites can cause allergies in humans, transmit several diseases to humans and their livestock
, and are serious agricultural pests.
s as they have: segmented
bodies with jointed limbs, all covered in a cuticle
made of chitin
and protein
s; heads that are composed of several segments that fuse during the development of the embryo
; a much reduced coelom
; a hemocoel through which the blood
circulates, driven by a tube-like heart. Chelicerates' bodies consist of two tagmata, sets of segments that serve similar functions: the foremost one, called the cephalothorax
or prosoma, is a complete fusion of the segments that in an insect
would form two separate tagmata, the head and thorax
; the rear tagma is called the abdomen
or opisthosoma
. However in the Acari (mites and ticks) there is no visible division between these sections.
The cephalothorax
is formed in the embryo by fusion of the acron
, which carries the eyes, with segments two to seven, which all have paired appendages, while segment one is lost during the embryo's development. Segment two has a pair of chelicerae, small appendages that often form pincer
s, segment three has a pair of pedipalp
s that in most sub-groups perform sensory functions, while the remaining four cephalothorax
segments have pairs of legs. In primitive forms the acron has a pair of compound eyes on the sides and four pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes") in the middle. The mouth is between segments two and three.
The abdomen consists of twelve or fewer segments which originally formed two groups, a "preabdomen" or "mesoma" of seven segments and a "postabdomen" or "metasoma" of five, terminating with a telson
or spike. The abdominal appendages of modern chelicerates are missing or heavily modified – for example in spider
s the remaining appendages form spinnerets that extrude silk
, while those of horseshoe crab
s (Xiphosura) form gill
s.
Like all arthropods, chelicerates' bodies and appendages are covered with a tough cuticle
made mainly of chitin and proteins which are chemically hardened. Since this cannot stretch, the animals have to molt in order to grow, in other words they grow new but still soft cuticles and then cast off the old one and wait for the new one to harden. Until the new cuticle has hardened the animals are defenseless and almost immobilized.
s from segment three, behind the mouth.
The chelicerae ("claw horns") that give the sub-phylum its name normally consist of three sections, and the claw is formed by the third section and a rigid extension of the second. However spiders' have only two sections, and the second forms a fang that folds away behind the first when not in use. The relative sizes of chelicerae vary widely: those of some eurypterid
s formed large claws that extended ahead of the body, while scorpion
s' are tiny pincers that are used in feeding and project only slightly in front of the head.
In most chelicerates the pedipalps are relatively small and are used as sensors. However those of male spiders have bulbous tips that act as syringe
s to inject sperm
into the females' reproductive openings when mating, while scorpions' form large claws used for capturing prey.
restricted to small areas round the reproductive and excretory systems. The main body cavity is a hemocoel that runs most of the length of the body and through which blood flows, driven by a tubular heart that collects blood from the rear and pumps it forward. Although arteries direct the blood to specific parts of the body, they have open ends rather than joining directly to vein
s, and chelicerates therefore have open circulatory system
s as is typical for arthropods.
s, which deliver oxygen and remove waste gases via the blood, and tracheae
, which do the same without using the blood as a transport system. The living horseshoe crab
s are aquatic and have book gills that lie in a horizontal plane. For a long time it was assumed that the extinct eurypterid
s had gills, but the fossil evidence was ambiguous. However a fossil of the 45 millimetres (1.8 in) long eurypterid Onychopterella
, from the Late Ordovician
period, has what appear to be three pairs of vertically oriented book gills whose internal structure is very similar to that of scorpions' book lungs.
s and almost all spider
s are predators that "pre-process" food in preoral cavities formed by the chelicerae and the bases of the pedipalp
s. However one predominantly vegetarian spider species is known, and many supplement their diets with nectar and pollen
. Many of the Acari (ticks and mites) are blood-sucking parasites, but there are many predatory, vegetarian and scavenger
sub-groups. All the Acari have a retractable feeding assembly that consists of the chelicerae, pedipalps and parts of the exoskeleton
, and which forms a preoral cavity for pre-processing food.
Harvestmen are among the minority of living chelicerates that can take solid food, and the group includes predators, vegetarians and scavengers. Horseshoe crab
s are also capable of processing solid food, and use a distinctive feeding system. Claws at the tips of their legs grab small invertebrates and pass them to a food groove that runs from between the rearmost legs to the mouth, which is on the underside of the head and faces slightly backwards. The bases of the legs form toothed gnathobases that both grind the food and push it towards the mouth. This is how the earliest arthropod
s are thought to have fed.
ous wastes to ammonia
and dump it via their gills, and excrete other wastes as feces
via the anus
. They also have nephridia ("little kidneys"), which extract other wastes for excretion as urine
. Ammonia is so toxic that it must be diluted rapidly with large quantities of water. Most terrestrial chelicerates cannot afford to use so much water and therefore convert nitrogenous wastes to other chemicals which can be excreted as dry matter. Extraction is done by various combinations of nephridia and Malpighian tubules. The tubules filter wastes out of the blood and dump them into the hindgut as solids, a system that has evolved independently
in insect
s and several groups of arachnid
s.
Chelicerate nervous systems are based on the standard arthropod model of a pair of nerve cord
s, each with a ganglion
per segment, and a brain formed by fusion of the ganglia just behind the mouth with those ahead of it. However since chelicerates lose the first segment, which bears antenna
e in other arthropods, chelicerate brains include only one pair of pre-oral ganglia instead of two. There is a notable but variable trend towards fusion of other ganglia into the brain. The brains of horseshoe crabs include all the ganglia of the cephalothorax plus those of the first two abdominal segments, while the other abdominal segments retain separate pairs of ganglia. In most living arachnid
s, except scorpion
s if they are true arachnids, all the ganglia, including those which would normally be in the abdomen, are fused into a single mass in the cephalothorax and there are no ganglia in the abdomen. However in the Mesothelae
, which are regarded as the most primitive living spiders, the ganglia of the abdomen and the rear part of the cephalothorax remain unfused, and in scorpions the ganglia of the cephalothorax are fused but the abdomen retains separate pairs of ganglia.
s would block out information about the outside world, except that they are penetrated by many sensors or connections from sensors to the nervous system. In fact spiders and other arthropods have modified their cuticles into elaborate arrays of sensors. Various touch and vibration sensors, mostly bristles called seta
e, respond to different levels of force, from strong contact to very weak air currents. Chemical sensors provide equivalents of taste
and smell
, often by means of setae.
Living chelicerates have both compound eyes, mounted on the sides of the head, and pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes"), mounted in the middle. The eyes of horseshoe crab
s can detect movement but not form images. At the other extreme, jumping spider
s have a very wide field of vision, and their main eyes are ten times as acute as those of dragonflies
.
 Horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
s, which are aquatic, use external fertilization
, in other words the sperm
and ova
meet outside the parents' bodies. Their trilobite
-like larva
e look rather like miniature adults as they have full sets of appendages and eyes, but initially they have only two pairs of book-gills and gain three more pairs as they molt.
Being air-breathing animals, the living arachnid
s use internal fertilization
, which is direct in some species, in other words the males' genitalia make contact with the females'. However in most species fertilization is indirect. Male spiders use their pedipalp
s as syringe
s to "inject" sperm into the females' reproductive openings, but most arachnids produce spermatophore
s (packages of sperm) which the females take into their bodies. Courtship
rituals are common, especially in the most powerful predators, where males risk being eaten before mating. Most arachnids lay eggs, but all scorpions and a few mite
s keep the eggs inside their bodies until they hatch and offspring rather like miniature adults emerge.
Levels of parental care for the young range from zero to prolonged. Scorpions carry their young on their backs until the first molt, and in a few semi-social species the young remain with their mother. Some spiders care for their young, for example a wolf spider
's brood cling to rough bristles on the mother's back, and females of some species respond to the "begging" behavior of their young by giving them their prey, provided it is no longer struggling, or even regurgitate
food.
record because, like all arthropod
s, their exoskeleton
s are organic
and hence their fossils are rare except in a few lagerstätte
n where conditions were exceptionally suited to preserving fairly soft tissues. The Burgess shale
animals Sanctacaris
and Sidneyia
from about have been classified as chelicerates, the former because of its pattern of tagmosis (how the segments are grouped, especially in the head) and the latter because its appendages resemble those of the Xiphosura
(horseshoe crabs). However cladistic analyses that consider wider ranges of characteristics place neither as chelicerates. There is debate about whether Fuxianhuia
from earlier in the Cambrian
period, about , was a chelicerate. Another Cambrian fossil, Kodymirus
, was originally classified as an aglaspid but may have been a eurypterid
and therefore a chelicerate. If any of these was closely related to chelicerates, there is a gap of at least 43 million years in the record between true chelicerates and their nearest not-quite chelicerate relatives.
 Until recently the earliest known xiphosura
Until recently the earliest known xiphosura
n fossil dated from the Late Llandovery stage of the Silurian
, but in 2008 an older specimen was reported from about in the Late Ordovician
. Eurypterids have left few good fossils and the earliest confirmed eurypterids appear in the Late Ordovician
period a little over .
The oldest known arachnid
is the trigonotarbid Palaeotarbus jerami, from about in the Silurian
period, and had a triangular cephalothorax
and segmented abdomen, as well as eight legs and a pair of pedipalp
s.
Attercopus
fimbriunguis, from in the Devonian
period, bears the earliest known silk-producing spigots, and was therefore hailed as a spider, but it lacked spinnerets and hence was not a true spider. Several Carboniferous
spiders were members of the Mesothelae
, a primitive group now represented only by the Liphistiidae
.
The Late Silurian
Proscorpius has been classified as a scorpion, but differed significantly from modern scorpions: it appears wholly aquatic since it had gill
s rather than book lung
s or trachea
e; its mouth was completely under its head and almost between the first pair of legs, as in the extinct eurypterid
s and living horseshoe crab
s. Fossils of terrestrial scorpions with book lung
s have been found in Early Devonian
rocks from about .
s; and myriapods, which includes centipede
s and millipede
s) than these other groups are to each other. Recent research since 2001, using both molecular phylogenetics (the application of cladistic analysis to biochemistry
, especially to organisms' DNA
and RNA
) and detailed examination of how various arthropods' nervous system
s develop in the embryo
s, suggests that chelicerates are most closely related to myriapods, while hexapods and crustaceans are each other's closest relatives. However these results are derived from analyzing only living arthropods, and including extinct ones such as trilobite
s causes a swing back to the "traditional" view, placing trilobites as the sister-group of the Tracheata (hexapods plus myriapods) and chelicerates as least closely related to the other groups.
Arachnida (spider
s, scorpion
s, mite
s, etc.), Xiphosura
(horseshoe crab
s) and Eurypterida (sea scorpion
s, extinct). The extinct Chasmataspida
may be a sub-group within Eurypterida. The Pycnogonida (sea spider
s) were traditionally classified as chelicerates, but some features suggest they may be representatives of the earliest arthropods from which the well-known groups such as chelicerates evolved.
However the structure of "family tree" relationships within the Chelicerata has been controversial ever since the late 19th century. An attempt in 2002 to combine analysis of RNA
features of modern chelicerates and anatomical features of modern and fossil ones produced credible results for many lower-level groups, but its results for the high-level relationships between major sub-groups of chelicerates were unstable, in other words minor changes in the inputs caused significant changes in the outputs of the computer program used (POY). An analysis in 2007 using only anatomical features produced the cladogram
on the right, but also noted that many uncertainties remain.
The position of scorpions is particularly controversial. Some early fossils such as the Late Silurian
Proscorpius have been classified by paleontologists as scorpions, but described as wholly aquatic as they had gill
s rather than book lung
s or trachea
e. Their mouths are also completely under their heads and almost between the first pair of legs, as in the extinct eurypterid
s and living horseshoe crab
s. This presents a difficult choice: classify Proscorpius and other aquatic fossils as something other than scorpions, despite the similarities; accept that "scorpions" are not monophyletic but consist of separate aquatic and terrestrial groups; or treat scorpions as more closely related to eurypterids and possibly horseshoe crabs than to spiders and other arachnid
s, so that either scorpions are not arachnids or "arachnids" are not monophyletic.
are marine animals that breathe dissolved oxygen
, the vast majority of living species are air-breathers, although a few spider species build "diving bell
" webs that enable them to live under water. Like their ancestors, most living chelicerates are carnivores, mainly on small invertebrate
s. However many species feed as parasites, vegetarians, scavenger
s and detritivore
s.
_lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg) In the past, Native American
In the past, Native American
s ate the flesh of horseshoe crabs, and used the tail spines as spear tips and the shells to bail water out of their canoes. More recent attempts to use horseshoe crabs as food for livestock
were abandoned when it was found that this gave the meat a bad taste. The blood of horseshoe crabs contains a clotting agent Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
which is now used to test that antibiotics and kidney machines are free of dangerous bacteria
, and to detect spinal meningitis and some cancer
s.
Cooked tarantula
spiders are considered a delicacy in Cambodia
, and by the Piaroa
Indians of southern Venezuela. Spider venom
s may be a less polluting alternative to conventional pesticide
s as they are deadly to insects but the great majority are harmless to vertebrate
s. Possible medical uses for spider venoms are being investigated, for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia, Alzheimer's disease
, stroke
s, and erectile dysfunction
. Because spider silk is both light and very strong, attempts are being made to produce it in goats' milk and in the leaves of plants, by means of genetic engineering
.
There were about 100 reliably reported deaths from spider bites in the 20th century, compared with 1,500 from jellyfish
stings.
Scorpion stings are thought to be a significant danger in less-developed countries, for example they cause about 1,000 deaths per year in Mexico
but only one every few years in the USA. Most of these incidents are caused by accidental human "invasions" of scorpion's nests. However medical uses of scorpion venom are being investigated for treatment of brain cancers and bone diseases.
Tick
s are parasitic, and some transmit micro-organisms and parasites that can cause diseases in humans, while the saliva of a few species can directly cause tick paralysis
if they are not removed within a day or two.
A few of the closely related mites also infest humans, some causing intense itching by their bites and others by burrowing into the skin. Species that normally infest other animals such as rodent
s may infest humans if their normal hosts are eliminated. Three species of mite are a threat to honey bee
s and one of these, Varroa destructor
, has become the largest single problem faced by beekeeper
s worldwide. Mites cause several forms of allergic diseases, including hay fever
, asthma
and eczema
, and they aggravate atopic dermatitis
. Mites are also significant crop pests, although predatory mites may be useful in controlling some of these.
Arthropod
An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton , a segmented body, and jointed appendages. Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda , and include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others...
a, and includes horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s, scorpion
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
s, spider
Spider
Spiders are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, and chelicerae with fangs that inject venom. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all other groups of organisms...
s and mite
Mite
Mites, along with ticks, are small arthropods belonging to the subclass Acari and the class Arachnida. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of ticks and mites is called acarology.-Diversity and systematics:...
s. They originated as marine animals, possibly in the Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
period, but the first confirmed chelicerate fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s, eurypterid
Eurypterid
Eurypterids are an extinct group of arthropods related to arachnids which include the largest known arthropods that ever lived. They are members of the extinct order Eurypterida ; which is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order in terms of species...
s, date from in the Late Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
period.
The surviving marine species include the four species of Xiphosura
Xiphosura
Xiphosura is an order of marine chelicerates which includes a large number of extinct lineages and only four recent species in the family Limulidae, which include the horseshoe crabs...
ns (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of Pycnogonida (sea spiders), if the latter are chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species.
Like all arthropod
Arthropod
An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton , a segmented body, and jointed appendages. Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda , and include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others...
s, chelicerates have segmented
Segmentation (biology)
Segmentation in biology refers to either a type of gastrointestinal motility or the division of some animal and plant body plans into a series of repetitive segments. This article will focus on the segmentation of animal body plans, specifically using the examples of the phyla Arthropoda,...
bodies with jointed limbs, all covered in a cuticle
Cuticle
A cuticle , or cuticula, is a term used for any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticles" are non-homologous; differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition...
made of chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
and protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. The chelicerate bauplan consists of two tagmata, the cephalothorax
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. The word cephalothorax is derived from the Greek words for head and thorax...
and the abdomen
Abdomen
In vertebrates such as mammals the abdomen constitutes the part of the body between the thorax and pelvis. The region enclosed by the abdomen is termed the abdominal cavity...
, except that mites have lost a visible division between these sections. The chelicerae
Chelicerae
The chelicerae are mouthparts of the Chelicerata, an arthropod subphylum that includes arachnids, Merostomata , and Pycnogonida . Chelicerae are pointed appendages which are used to grasp food, and are found in place of the chewing mandibles most other arthropods have...
, which give the group its name, are the only appendage
Appendage
In invertebrate biology, an appendage is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body . It is a general term that covers any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment...
s that appear before the mouth. In most sub-groups they are modest pincers used in feeding. However, spiders' chelicerae form fangs which in most species are used to inject venom
Venom
Venom is the general term referring to any variety of toxins used by certain types of animals that inject it into their victims by the means of a bite or a sting...
into their prey. The group has the open circulatory system typical of the arthropods, in which a tube-like heart pumps blood through the hemocoel, which is the major body cavity. Marine chelicerates have gills, while the air-breathing forms generally have both book lung
Book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange and is found in arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is found inside a ventral abdominal cavity and connects with the surroundings through a small opening. Book lungs are not related to the lungs...
s and tracheae
Invertebrate trachea
The invertebrate trachea refers to the open respiratory system composed of spiracles, tracheae, and tracheoles that terrestrial arthropods have to transport metabolic gases to and from tissues....
. In general the ganglia of living chelicerates' central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
s fuse into large masses in the cephalothorax, but there are wide variations and this fusion is very limited in the Mesothelae
Mesothelae
The Mesothelae are a suborder of spiders that includes the extinct families Arthrolycosidae and Arthromygalidae and the only extant family Liphistiidae....
, which are regarded as the oldest and most primitive group of spiders. Most chelicerates rely on modified bristles for touch and for information about vibrations, air currents, and chemical changes in their environment. The most active hunting spiders also have very acute eyesight.
Chelicerates were originally predators, but the group has diversified to use all the major feeding strategies: predation, parasitism
Parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. Traditionally parasite referred to organisms with lifestages that needed more than one host . These are now called macroparasites...
, herbivory, scavenging
Scavenger
Scavenging is both a carnivorous and herbivorous feeding behavior in which individual scavengers search out dead animal and dead plant biomass on which to feed. The eating of carrion from the same species is referred to as cannibalism. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by...
and eating decaying organic matter. Although harvestmen can digest solid food, the guts of most modern chelicerates are too narrow for this, and they generally liquidize their food by grinding it with their chelicerae and pedipalps and flooding it with digestive enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s. To conserve water, air-breathing chelicerates excrete waste as solids that are removed from their blood by Malpighian tubules, structures which also evolved independently
Convergent evolution
Convergent evolution describes the acquisition of the same biological trait in unrelated lineages.The wing is a classic example of convergent evolution in action. Although their last common ancestor did not have wings, both birds and bats do, and are capable of powered flight. The wings are...
in insect
Insect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
s. While the marine horseshoe crabs rely on external fertilization
External fertilization
External fertilization is a form of fertilization in which a sperm cell is united with an egg cell external to the bodies of the reproducing individuals. In contrast, internal fertilization takes place inside the female after insemination through copulation....
, air-breathing chelicerates use internal but usually indirect fertilization. Predatory species generally use elaborate courtship
Courtship
Courtship is the period in a couple's relationship which precedes their engagement and marriage, or establishment of an agreed relationship of a more enduring kind. In courtship, a couple get to know each other and decide if there will be an engagement or other such agreement...
rituals to prevent males from being eaten before they can mate. Most lay eggs that hatch as what look like miniature adults, but all scorpions and a few species of mites keep the eggs inside their bodies until the young emerge. In most chelicerate species the young have to fend for themselves, but in scorpions and some species of spider the females protect and feed their young.
The evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
ary origins of chelicerates from the early arthropods have been debated for decades. Although there is considerable agreement about the relationships between most chelicerate sub-groups, the inclusion of the Pycnogonida in this taxon has recently been questioned (see below), and the exact position of scorpions is still controversial, though they were long considered the most primitive (basal) of the arachnids.
Although the venom of a few spider and scorpion species can be very dangerous to humans, medical researchers are investigating the use of these venoms for the treatment of disorders ranging from cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
to erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to develop or maintain an erection of the penis during sexual performance....
. The medical industry also uses the blood of horseshoe crabs as a test for the presence of contaminant bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. Genetic engineers have experimented with modifying goats' milk and plants' leaves to produce spider silk
Spider silk
Spider silk is a protein fiber spun by spiders. Spiders use their silk to make webs or other structures, which function as nets to catch other animals, or as nests or cocoons for protection for their offspring...
. Mites can cause allergies in humans, transmit several diseases to humans and their livestock
Livestock
Livestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
, and are serious agricultural pests.
Description
Segmentation and cuticle
The Chelicerata are arthropodArthropod
An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton , a segmented body, and jointed appendages. Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda , and include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others...
s as they have: segmented
Segmentation (biology)
Segmentation in biology refers to either a type of gastrointestinal motility or the division of some animal and plant body plans into a series of repetitive segments. This article will focus on the segmentation of animal body plans, specifically using the examples of the phyla Arthropoda,...
bodies with jointed limbs, all covered in a cuticle
Cuticle
A cuticle , or cuticula, is a term used for any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticles" are non-homologous; differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition...
made of chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
and protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s; heads that are composed of several segments that fuse during the development of the embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
; a much reduced coelom
Coelom
The coelom is a fluid-filled cavity formed within the mesoderm. Coeloms developed in triploblasts but were subsequently lost in several lineages. Loss of coelom is correlated with reduction in body size...
; a hemocoel through which the blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
circulates, driven by a tube-like heart. Chelicerates' bodies consist of two tagmata, sets of segments that serve similar functions: the foremost one, called the cephalothorax
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. The word cephalothorax is derived from the Greek words for head and thorax...
or prosoma, is a complete fusion of the segments that in an insect
Insect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
would form two separate tagmata, the head and thorax
Thorax
The thorax is a division of an animal's body that lies between the head and the abdomen.-In tetrapods:...
; the rear tagma is called the abdomen
Abdomen
In vertebrates such as mammals the abdomen constitutes the part of the body between the thorax and pelvis. The region enclosed by the abdomen is termed the abdominal cavity...
or opisthosoma
Opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma . It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata...
. However in the Acari (mites and ticks) there is no visible division between these sections.
The cephalothorax
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. The word cephalothorax is derived from the Greek words for head and thorax...
is formed in the embryo by fusion of the acron
Prostomium
Prostomium is the first body segment in annelid worms. It is in front of the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. It sometimes bears antennae and eyes. It often functions like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding...
, which carries the eyes, with segments two to seven, which all have paired appendages, while segment one is lost during the embryo's development. Segment two has a pair of chelicerae, small appendages that often form pincer
Pincer
Pincer may refer to:*Pincer *Pincer , part of an animal*Pincer ligand, a terdentate, often planar molecule that tightly binds a variety of metal ions.*Pingas...
s, segment three has a pair of pedipalp
Pedipalp
Pedipalps , are the second pair of appendages of the prosoma in the subphylum Chelicerata. They are traditionally thought to be homologous with mandibles in Crustacea and insects, although more recent studies Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi), are the second pair of appendages of the...
s that in most sub-groups perform sensory functions, while the remaining four cephalothorax
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. The word cephalothorax is derived from the Greek words for head and thorax...
segments have pairs of legs. In primitive forms the acron has a pair of compound eyes on the sides and four pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes") in the middle. The mouth is between segments two and three.
The abdomen consists of twelve or fewer segments which originally formed two groups, a "preabdomen" or "mesoma" of seven segments and a "postabdomen" or "metasoma" of five, terminating with a telson
Telson
The telson is the last division of the body of a crustacean. It is not considered a true segment because it does not arise in the embryo from teloblast areas as do real segments. It never carries any appendages, but a forked "tail" called the caudal furca is often present. Together with the...
or spike. The abdominal appendages of modern chelicerates are missing or heavily modified – for example in spider
Spider
Spiders are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, and chelicerae with fangs that inject venom. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all other groups of organisms...
s the remaining appendages form spinnerets that extrude silk
Spider silk
Spider silk is a protein fiber spun by spiders. Spiders use their silk to make webs or other structures, which function as nets to catch other animals, or as nests or cocoons for protection for their offspring...
, while those of horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s (Xiphosura) form gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
s.
Like all arthropods, chelicerates' bodies and appendages are covered with a tough cuticle
Cuticle
A cuticle , or cuticula, is a term used for any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticles" are non-homologous; differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition...
made mainly of chitin and proteins which are chemically hardened. Since this cannot stretch, the animals have to molt in order to grow, in other words they grow new but still soft cuticles and then cast off the old one and wait for the new one to harden. Until the new cuticle has hardened the animals are defenseless and almost immobilized.
 |
 |
Chelicerae and pedipalps
These appendages vary widely in form and function and the only consistent difference between them is their position: chelicerae arise from segment two, ahead of the mouth, and pedipalpPedipalp
Pedipalps , are the second pair of appendages of the prosoma in the subphylum Chelicerata. They are traditionally thought to be homologous with mandibles in Crustacea and insects, although more recent studies Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi), are the second pair of appendages of the...
s from segment three, behind the mouth.
The chelicerae ("claw horns") that give the sub-phylum its name normally consist of three sections, and the claw is formed by the third section and a rigid extension of the second. However spiders' have only two sections, and the second forms a fang that folds away behind the first when not in use. The relative sizes of chelicerae vary widely: those of some eurypterid
Eurypterid
Eurypterids are an extinct group of arthropods related to arachnids which include the largest known arthropods that ever lived. They are members of the extinct order Eurypterida ; which is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order in terms of species...
s formed large claws that extended ahead of the body, while scorpion
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
s' are tiny pincers that are used in feeding and project only slightly in front of the head.
In most chelicerates the pedipalps are relatively small and are used as sensors. However those of male spiders have bulbous tips that act as syringe
Syringe
A syringe is a simple pump consisting of a plunger that fits tightly in a tube. The plunger can be pulled and pushed along inside a cylindrical tube , allowing the syringe to take in and expel a liquid or gas through an orifice at the open end of the tube...
s to inject sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
into the females' reproductive openings when mating, while scorpions' form large claws used for capturing prey.
Body cavities and circulatory systems
As in all arthropods, the chelicerate body has a very small coelomCoelom
The coelom is a fluid-filled cavity formed within the mesoderm. Coeloms developed in triploblasts but were subsequently lost in several lineages. Loss of coelom is correlated with reduction in body size...
restricted to small areas round the reproductive and excretory systems. The main body cavity is a hemocoel that runs most of the length of the body and through which blood flows, driven by a tubular heart that collects blood from the rear and pumps it forward. Although arteries direct the blood to specific parts of the body, they have open ends rather than joining directly to vein
Vein
In the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
s, and chelicerates therefore have open circulatory system
Circulatory system
The circulatory system is an organ system that passes nutrients , gases, hormones, blood cells, etc...
s as is typical for arthropods.
Respiratory systems
These depend on individual sub-groups' environments. Modern terrestrial chelicerates generally have both book lungBook lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange and is found in arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is found inside a ventral abdominal cavity and connects with the surroundings through a small opening. Book lungs are not related to the lungs...
s, which deliver oxygen and remove waste gases via the blood, and tracheae
Invertebrate trachea
The invertebrate trachea refers to the open respiratory system composed of spiracles, tracheae, and tracheoles that terrestrial arthropods have to transport metabolic gases to and from tissues....
, which do the same without using the blood as a transport system. The living horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s are aquatic and have book gills that lie in a horizontal plane. For a long time it was assumed that the extinct eurypterid
Eurypterid
Eurypterids are an extinct group of arthropods related to arachnids which include the largest known arthropods that ever lived. They are members of the extinct order Eurypterida ; which is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order in terms of species...
s had gills, but the fossil evidence was ambiguous. However a fossil of the 45 millimetres (1.8 in) long eurypterid Onychopterella
Onychopterella
Onychopterella is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid in the Family Eurypteridae.- Description :Eurypteridae, which lived from the Ordovician to the Late Carboniferous period, were characterized by small to large exoskeletons with inconspicuous semilunar scales or curved ridges. The telson, was...
, from the Late Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
period, has what appear to be three pairs of vertically oriented book gills whose internal structure is very similar to that of scorpions' book lungs.
Feeding and digestion
The guts of most modern chelicerates are too narrow to take solid food. All scorpionScorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
s and almost all spider
Spider
Spiders are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, and chelicerae with fangs that inject venom. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all other groups of organisms...
s are predators that "pre-process" food in preoral cavities formed by the chelicerae and the bases of the pedipalp
Pedipalp
Pedipalps , are the second pair of appendages of the prosoma in the subphylum Chelicerata. They are traditionally thought to be homologous with mandibles in Crustacea and insects, although more recent studies Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi), are the second pair of appendages of the...
s. However one predominantly vegetarian spider species is known, and many supplement their diets with nectar and pollen
Pollen
Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
. Many of the Acari (ticks and mites) are blood-sucking parasites, but there are many predatory, vegetarian and scavenger
Scavenger
Scavenging is both a carnivorous and herbivorous feeding behavior in which individual scavengers search out dead animal and dead plant biomass on which to feed. The eating of carrion from the same species is referred to as cannibalism. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by...
sub-groups. All the Acari have a retractable feeding assembly that consists of the chelicerae, pedipalps and parts of the exoskeleton
Exoskeleton
An exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton of, for example, a human. In popular usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of exoskeleton animals include insects such as grasshoppers...
, and which forms a preoral cavity for pre-processing food.
Harvestmen are among the minority of living chelicerates that can take solid food, and the group includes predators, vegetarians and scavengers. Horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s are also capable of processing solid food, and use a distinctive feeding system. Claws at the tips of their legs grab small invertebrates and pass them to a food groove that runs from between the rearmost legs to the mouth, which is on the underside of the head and faces slightly backwards. The bases of the legs form toothed gnathobases that both grind the food and push it towards the mouth. This is how the earliest arthropod
Arthropod
An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton , a segmented body, and jointed appendages. Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda , and include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others...
s are thought to have fed.
Excretion
Horseshoe crabs convert nitrogenNitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
ous wastes to ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
and dump it via their gills, and excrete other wastes as feces
Feces
Feces, faeces, or fæces is a waste product from an animal's digestive tract expelled through the anus or cloaca during defecation.-Etymology:...
via the anus
Anus
The anus is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, unwanted semi-solid matter produced during digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, may be one or more of: matter which the animal cannot digest,...
. They also have nephridia ("little kidneys"), which extract other wastes for excretion as urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
. Ammonia is so toxic that it must be diluted rapidly with large quantities of water. Most terrestrial chelicerates cannot afford to use so much water and therefore convert nitrogenous wastes to other chemicals which can be excreted as dry matter. Extraction is done by various combinations of nephridia and Malpighian tubules. The tubules filter wastes out of the blood and dump them into the hindgut as solids, a system that has evolved independently
Convergent evolution
Convergent evolution describes the acquisition of the same biological trait in unrelated lineages.The wing is a classic example of convergent evolution in action. Although their last common ancestor did not have wings, both birds and bats do, and are capable of powered flight. The wings are...
in insect
Insect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
s and several groups of arachnid
Arachnid
Arachnids are a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals in the subphylum Chelicerata. All arachnids have eight legs, although in some species the front pair may convert to a sensory function. The term is derived from the Greek words , meaning "spider".Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial...
s.
Nervous system
| Cephalothorax ganglia fused into brain | Abdominal ganglia fused into brain | |
|---|---|---|
| Horseshoe crabs | All | First two segments only |
| Scorpion Scorpion Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger... s |
All | None |
| Mesothelae Mesothelae The Mesothelae are a suborder of spiders that includes the extinct families Arthrolycosidae and Arthromygalidae and the only extant family Liphistiidae.... |
First two pairs only | None |
| Other arachnid Arachnid Arachnids are a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals in the subphylum Chelicerata. All arachnids have eight legs, although in some species the front pair may convert to a sensory function. The term is derived from the Greek words , meaning "spider".Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial... s |
All | All |
Chelicerate nervous systems are based on the standard arthropod model of a pair of nerve cord
Nerve cord
Nerve cord may refer to the following structures:* in invertebrates, it refers to the ventral nerve cord, whereas* in chordates, it stands for the dorsal nerve cord....
s, each with a ganglion
Ganglion
In anatomy, a ganglion is a biological tissue mass, most commonly a mass of nerve cell bodies. Cells found in a ganglion are called ganglion cells, though this term is also sometimes used to refer specifically to retinal ganglion cells....
per segment, and a brain formed by fusion of the ganglia just behind the mouth with those ahead of it. However since chelicerates lose the first segment, which bears antenna
Antenna (biology)
Antennae in biology have historically been paired appendages used for sensing in arthropods. More recently, the term has also been applied to cilium structures present in most cell types of eukaryotes....
e in other arthropods, chelicerate brains include only one pair of pre-oral ganglia instead of two. There is a notable but variable trend towards fusion of other ganglia into the brain. The brains of horseshoe crabs include all the ganglia of the cephalothorax plus those of the first two abdominal segments, while the other abdominal segments retain separate pairs of ganglia. In most living arachnid
Arachnid
Arachnids are a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals in the subphylum Chelicerata. All arachnids have eight legs, although in some species the front pair may convert to a sensory function. The term is derived from the Greek words , meaning "spider".Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial...
s, except scorpion
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
s if they are true arachnids, all the ganglia, including those which would normally be in the abdomen, are fused into a single mass in the cephalothorax and there are no ganglia in the abdomen. However in the Mesothelae
Mesothelae
The Mesothelae are a suborder of spiders that includes the extinct families Arthrolycosidae and Arthromygalidae and the only extant family Liphistiidae....
, which are regarded as the most primitive living spiders, the ganglia of the abdomen and the rear part of the cephalothorax remain unfused, and in scorpions the ganglia of the cephalothorax are fused but the abdomen retains separate pairs of ganglia.
Senses
As with other arthropods, chelicerates' cuticleCuticle
A cuticle , or cuticula, is a term used for any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticles" are non-homologous; differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition...
s would block out information about the outside world, except that they are penetrated by many sensors or connections from sensors to the nervous system. In fact spiders and other arthropods have modified their cuticles into elaborate arrays of sensors. Various touch and vibration sensors, mostly bristles called seta
Seta
Seta is a biological term derived from the Latin word for "bristle". It refers to a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.-Animal setae:In zoology, most "setae" occur in invertebrates....
e, respond to different levels of force, from strong contact to very weak air currents. Chemical sensors provide equivalents of taste
Taste
Taste is one of the traditional five senses. It refers to the ability to detect the flavor of substances such as food, certain minerals, and poisons, etc....
and smell
Smell
Smell may refer to:* Olfaction, sense of smell, the ability of humans and other animals to perceive odors* Odor, the percept resultant from the sense of smell...
, often by means of setae.
Living chelicerates have both compound eyes, mounted on the sides of the head, and pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes"), mounted in the middle. The eyes of horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s can detect movement but not form images. At the other extreme, jumping spider
Jumping spider
The jumping spider family contains more than 500 described genera and about 5,000 described species, making it the largest family of spiders with about 13% of all species. Jumping spiders have some of the best vision among invertebrates and use it in courtship, hunting and navigation...
s have a very wide field of vision, and their main eyes are ten times as acute as those of dragonflies
Dragonfly
A dragonfly is a winged insect belonging to the order Odonata, the suborder Epiprocta or, in the strict sense, the infraorder Anisoptera . It is characterized by large multifaceted eyes, two pairs of strong transparent wings, and an elongated body...
.
Reproduction

Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s, which are aquatic, use external fertilization
External fertilization
External fertilization is a form of fertilization in which a sperm cell is united with an egg cell external to the bodies of the reproducing individuals. In contrast, internal fertilization takes place inside the female after insemination through copulation....
, in other words the sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
and ova
Ovum
An ovum is a haploid female reproductive cell or gamete. Both animals and embryophytes have ova. The term ovule is used for the young ovum of an animal, as well as the plant structure that carries the female gametophyte and egg cell and develops into a seed after fertilization...
meet outside the parents' bodies. Their trilobite
Trilobite
Trilobites are a well-known fossil group of extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period , and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic era before...
-like larva
Larva
A larva is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle...
e look rather like miniature adults as they have full sets of appendages and eyes, but initially they have only two pairs of book-gills and gain three more pairs as they molt.
Being air-breathing animals, the living arachnid
Arachnid
Arachnids are a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals in the subphylum Chelicerata. All arachnids have eight legs, although in some species the front pair may convert to a sensory function. The term is derived from the Greek words , meaning "spider".Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial...
s use internal fertilization
Internal fertilization
In mammals, internal fertilization is done through copulation, which involves the insertion of the penis into the vagina. Some other higher vertebrate animals reproduce internally, but their fertilization is cloacal.The union of spermatozoa of the parent organism. At some point, the growing egg or...
, which is direct in some species, in other words the males' genitalia make contact with the females'. However in most species fertilization is indirect. Male spiders use their pedipalp
Pedipalp
Pedipalps , are the second pair of appendages of the prosoma in the subphylum Chelicerata. They are traditionally thought to be homologous with mandibles in Crustacea and insects, although more recent studies Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi), are the second pair of appendages of the...
s as syringe
Syringe
A syringe is a simple pump consisting of a plunger that fits tightly in a tube. The plunger can be pulled and pushed along inside a cylindrical tube , allowing the syringe to take in and expel a liquid or gas through an orifice at the open end of the tube...
s to "inject" sperm into the females' reproductive openings, but most arachnids produce spermatophore
Spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass created by males of various animal species, containing spermatozoa and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during copulation...
s (packages of sperm) which the females take into their bodies. Courtship
Courtship
Courtship is the period in a couple's relationship which precedes their engagement and marriage, or establishment of an agreed relationship of a more enduring kind. In courtship, a couple get to know each other and decide if there will be an engagement or other such agreement...
rituals are common, especially in the most powerful predators, where males risk being eaten before mating. Most arachnids lay eggs, but all scorpions and a few mite
Mite
Mites, along with ticks, are small arthropods belonging to the subclass Acari and the class Arachnida. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of ticks and mites is called acarology.-Diversity and systematics:...
s keep the eggs inside their bodies until they hatch and offspring rather like miniature adults emerge.
Levels of parental care for the young range from zero to prolonged. Scorpions carry their young on their backs until the first molt, and in a few semi-social species the young remain with their mother. Some spiders care for their young, for example a wolf spider
Wolf spider
Wolf spiders are members of the family Lycosidae, from the Ancient Greek word "" meaning "wolf". They are robust and agile hunters with good eyesight. They live mostly solitary lives and hunt alone. Some are opportunistic hunters pouncing upon prey as they find it or even chasing it over short...
's brood cling to rough bristles on the mother's back, and females of some species respond to the "begging" behavior of their young by giving them their prey, provided it is no longer struggling, or even regurgitate
Regurgitation (digestion)
Regurgitation is the expulsion of material from the mouth, pharynx, or esophagus, usually characterized by the presence of undigested food or blood.Regurgitation is used by a number of species to feed their young...
food.
Fossil record
There are large gaps in the chelicerates' fossilFossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
record because, like all arthropod
Arthropod
An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton , a segmented body, and jointed appendages. Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda , and include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others...
s, their exoskeleton
Exoskeleton
An exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton of, for example, a human. In popular usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of exoskeleton animals include insects such as grasshoppers...
s are organic
Organic matter
Organic matter is matter that has come from a once-living organism; is capable of decay, or the product of decay; or is composed of organic compounds...
and hence their fossils are rare except in a few lagerstätte
Lagerstätte
A Lagerstätte is a sedimentary deposit that exhibits extraordinary fossil richness or completeness.Palaeontologists distinguish two kinds....
n where conditions were exceptionally suited to preserving fairly soft tissues. The Burgess shale
Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale Formation, located in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, is one of the world's most celebrated fossil fields, and the best of its kind. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils...
animals Sanctacaris
Sanctacaris
Sanctacaris is a Middle Cambrian arthropod from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. It was most famously regarded as a primitive chelicerate, a group which includes spiders and scorpions, although subsequent phylogenetic studies have not always supported this conclusion; it is best accommodated...
and Sidneyia
Sidneyia
Sidneyia is an extinct arthropod known from fossils found in the Cambrian-age Burgess Shale formation of British Columbia. -General description:...
from about have been classified as chelicerates, the former because of its pattern of tagmosis (how the segments are grouped, especially in the head) and the latter because its appendages resemble those of the Xiphosura
Xiphosura
Xiphosura is an order of marine chelicerates which includes a large number of extinct lineages and only four recent species in the family Limulidae, which include the horseshoe crabs...
(horseshoe crabs). However cladistic analyses that consider wider ranges of characteristics place neither as chelicerates. There is debate about whether Fuxianhuia
Fuxianhuia
Fuxianhuia protensa is a Lower Cambrian fossil arthropod known from the Chengjiang Fauna in China. Its purportedly primitive features have led to its playing a pivotal role in discussions about the euarthropod stem group...
from earlier in the Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
period, about , was a chelicerate. Another Cambrian fossil, Kodymirus
Kodymirus
Kodymirus is a problematic genus of Cambrian arthropod, known from the Czech republic, which bears some resemblance to the eurypterids, aglaspidids and chelicerates...
, was originally classified as an aglaspid but may have been a eurypterid
Eurypterid
Eurypterids are an extinct group of arthropods related to arachnids which include the largest known arthropods that ever lived. They are members of the extinct order Eurypterida ; which is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order in terms of species...
and therefore a chelicerate. If any of these was closely related to chelicerates, there is a gap of at least 43 million years in the record between true chelicerates and their nearest not-quite chelicerate relatives.

Xiphosura
Xiphosura is an order of marine chelicerates which includes a large number of extinct lineages and only four recent species in the family Limulidae, which include the horseshoe crabs...
n fossil dated from the Late Llandovery stage of the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
, but in 2008 an older specimen was reported from about in the Late Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
. Eurypterids have left few good fossils and the earliest confirmed eurypterids appear in the Late Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
period a little over .
The oldest known arachnid
Arachnid
Arachnids are a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals in the subphylum Chelicerata. All arachnids have eight legs, although in some species the front pair may convert to a sensory function. The term is derived from the Greek words , meaning "spider".Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial...
is the trigonotarbid Palaeotarbus jerami, from about in the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
period, and had a triangular cephalothorax
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. The word cephalothorax is derived from the Greek words for head and thorax...
and segmented abdomen, as well as eight legs and a pair of pedipalp
Pedipalp
Pedipalps , are the second pair of appendages of the prosoma in the subphylum Chelicerata. They are traditionally thought to be homologous with mandibles in Crustacea and insects, although more recent studies Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi), are the second pair of appendages of the...
s.
Attercopus
Attercopus
Previously interpreted as the world's oldest spider, Attercopus fimbriunguis belongs to an extinct order of arachnids named Uraraneida; thought to be close to the origins of spiders...
fimbriunguis, from in the Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
period, bears the earliest known silk-producing spigots, and was therefore hailed as a spider, but it lacked spinnerets and hence was not a true spider. Several Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
spiders were members of the Mesothelae
Mesothelae
The Mesothelae are a suborder of spiders that includes the extinct families Arthrolycosidae and Arthromygalidae and the only extant family Liphistiidae....
, a primitive group now represented only by the Liphistiidae
Liphistiidae
The spider family Liphistiidae comprises 5 genera and 85 species from Southeast Asia, China, and Japan. They are among the most basal living spiders, belonging to the suborder Mesothelae...
.
The Late Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
Proscorpius has been classified as a scorpion, but differed significantly from modern scorpions: it appears wholly aquatic since it had gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
s rather than book lung
Book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange and is found in arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is found inside a ventral abdominal cavity and connects with the surroundings through a small opening. Book lungs are not related to the lungs...
s or trachea
Invertebrate trachea
The invertebrate trachea refers to the open respiratory system composed of spiracles, tracheae, and tracheoles that terrestrial arthropods have to transport metabolic gases to and from tissues....
e; its mouth was completely under its head and almost between the first pair of legs, as in the extinct eurypterid
Eurypterid
Eurypterids are an extinct group of arthropods related to arachnids which include the largest known arthropods that ever lived. They are members of the extinct order Eurypterida ; which is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order in terms of species...
s and living horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s. Fossils of terrestrial scorpions with book lung
Book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange and is found in arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is found inside a ventral abdominal cavity and connects with the surroundings through a small opening. Book lungs are not related to the lungs...
s have been found in Early Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
rocks from about .
Relationships with other arthropods
The "traditional" view of the arthropod "family tree" shows chelicerates as less closely related to the other major living groups (crustaceans; hexapods, which includes insectInsect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
s; and myriapods, which includes centipede
Centipede
Centipedes are arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda of the subphylum Myriapoda. They are elongated metameric animals with one pair of legs per body segment. Despite the name, centipedes can have a varying number of legs from under 20 to over 300. Centipedes have an odd number of pairs of...
s and millipede
Millipede
Millipedes are arthropods that have two pairs of legs per segment . Each segment that has two pairs of legs is a result of two single segments fused together as one...
s) than these other groups are to each other. Recent research since 2001, using both molecular phylogenetics (the application of cladistic analysis to biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
, especially to organisms' DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
and RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
) and detailed examination of how various arthropods' nervous system
Nervous system
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
s develop in the embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
s, suggests that chelicerates are most closely related to myriapods, while hexapods and crustaceans are each other's closest relatives. However these results are derived from analyzing only living arthropods, and including extinct ones such as trilobite
Trilobite
Trilobites are a well-known fossil group of extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period , and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic era before...
s causes a swing back to the "traditional" view, placing trilobites as the sister-group of the Tracheata (hexapods plus myriapods) and chelicerates as least closely related to the other groups.
Major sub-groups
It is generally agreed that the Chelicerata contain the classesClass (biology)
In biological classification, class is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order...
Arachnida (spider
Spider
Spiders are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, and chelicerae with fangs that inject venom. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all other groups of organisms...
s, scorpion
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
s, mite
Mite
Mites, along with ticks, are small arthropods belonging to the subclass Acari and the class Arachnida. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of ticks and mites is called acarology.-Diversity and systematics:...
s, etc.), Xiphosura
Xiphosura
Xiphosura is an order of marine chelicerates which includes a large number of extinct lineages and only four recent species in the family Limulidae, which include the horseshoe crabs...
(horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s) and Eurypterida (sea scorpion
Sea Scorpion
Sea Scorpion may refer to:* Eurypterids, members of the extinct class Eurypterida* some members of the Cottidae family of fish including the Long-spined Sea Scorpion and Short-spined Sea Scorpion...
s, extinct). The extinct Chasmataspida
Chasmataspida
Chasmataspidida are a rare, extinct group of chelicerate arthropods. They are probably related to either horseshoe crabs and/or sea scorpions...
may be a sub-group within Eurypterida. The Pycnogonida (sea spider
Sea spider
Sea spiders, also called Pantopoda or pycnogonids, are marine arthropods of class Pycnogonida. They are cosmopolitan, found especially in the Mediterranean and Caribbean Seas, as well as the Arctic and Antarctic Oceans. There are over 1300 known species, ranging in size from to over in some deep...
s) were traditionally classified as chelicerates, but some features suggest they may be representatives of the earliest arthropods from which the well-known groups such as chelicerates evolved.
However the structure of "family tree" relationships within the Chelicerata has been controversial ever since the late 19th century. An attempt in 2002 to combine analysis of RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
features of modern chelicerates and anatomical features of modern and fossil ones produced credible results for many lower-level groups, but its results for the high-level relationships between major sub-groups of chelicerates were unstable, in other words minor changes in the inputs caused significant changes in the outputs of the computer program used (POY). An analysis in 2007 using only anatomical features produced the cladogram
Cladogram
A cladogram is a diagram used in cladistics which shows ancestral relations between organisms, to represent the evolutionary tree of life. Although traditionally such cladograms were generated largely on the basis of morphological characters, DNA and RNA sequencing data and computational...
on the right, but also noted that many uncertainties remain.
The position of scorpions is particularly controversial. Some early fossils such as the Late Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
Proscorpius have been classified by paleontologists as scorpions, but described as wholly aquatic as they had gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
s rather than book lung
Book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange and is found in arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is found inside a ventral abdominal cavity and connects with the surroundings through a small opening. Book lungs are not related to the lungs...
s or trachea
Invertebrate trachea
The invertebrate trachea refers to the open respiratory system composed of spiracles, tracheae, and tracheoles that terrestrial arthropods have to transport metabolic gases to and from tissues....
e. Their mouths are also completely under their heads and almost between the first pair of legs, as in the extinct eurypterid
Eurypterid
Eurypterids are an extinct group of arthropods related to arachnids which include the largest known arthropods that ever lived. They are members of the extinct order Eurypterida ; which is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order in terms of species...
s and living horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crab
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, is a marine chelicerate arthropod. Despite its name, it is more closely related to spiders, ticks, and scorpions than to crabs. Horseshoe crabs are most commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the northern Atlantic coast of North America...
s. This presents a difficult choice: classify Proscorpius and other aquatic fossils as something other than scorpions, despite the similarities; accept that "scorpions" are not monophyletic but consist of separate aquatic and terrestrial groups; or treat scorpions as more closely related to eurypterids and possibly horseshoe crabs than to spiders and other arachnid
Arachnid
Arachnids are a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals in the subphylum Chelicerata. All arachnids have eight legs, although in some species the front pair may convert to a sensory function. The term is derived from the Greek words , meaning "spider".Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial...
s, so that either scorpions are not arachnids or "arachnids" are not monophyletic.
Diversity
Although well behind the insects, chelicerates are one of the most diverse groups of animals, with over 77,000 living species that have been described in scientific publications. Some estimates suggest that there may be 130,000 undescribed species of spider and nearly 500,000 undescribed species of mites and ticks. While the earliest chelicerates and the living Pycnogonida (if they are chelicerates) and XiphosuraXiphosura
Xiphosura is an order of marine chelicerates which includes a large number of extinct lineages and only four recent species in the family Limulidae, which include the horseshoe crabs...
are marine animals that breathe dissolved oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, the vast majority of living species are air-breathers, although a few spider species build "diving bell
Diving bell
A diving bell is a rigid chamber used to transport divers to depth in the ocean. The most common types are the wet bell and the closed bell....
" webs that enable them to live under water. Like their ancestors, most living chelicerates are carnivores, mainly on small invertebrate
Invertebrate
An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. The group includes 97% of all animal species – all animals except those in the chordate subphylum Vertebrata .Invertebrates form a paraphyletic group...
s. However many species feed as parasites, vegetarians, scavenger
Scavenger
Scavenging is both a carnivorous and herbivorous feeding behavior in which individual scavengers search out dead animal and dead plant biomass on which to feed. The eating of carrion from the same species is referred to as cannibalism. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by...
s and detritivore
Detritivore
Detritivores, also known as detritophages or detritus feeders or detritus eaters or saprophages, are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus . By doing so, they contribute to decomposition and the nutrient cycles...
s.
| Diversity of living chelicerates | ||
| Group | Described species | Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Pycnogonida (sea-spiders) | 500 | Carnivorous |
| Xiphosura Xiphosura Xiphosura is an order of marine chelicerates which includes a large number of extinct lineages and only four recent species in the family Limulidae, which include the horseshoe crabs... (horseshoe crabs) |
4 | Carnivorous |
| Araneae (spiders) | 34,000 | Carnivorous; 1 vegetarian |
| Acari (mites and ticks) | 32,000 | Carnivorous, parasitic, vegetarian, detritivore Detritivore Detritivores, also known as detritophages or detritus feeders or detritus eaters or saprophages, are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus . By doing so, they contribute to decomposition and the nutrient cycles... |
| Opiliones Opiliones Opiliones are an order of arachnids commonly known as harvestmen. , over 6,400 species of harvestmen have been discovered worldwide, although the real number of extant species may exceed 10,000. The order Opiliones can be divided into four suborders: Cyphophthalmi, Eupnoi, Dyspnoi and Laniatores... (harvestmen) |
5,000 | Carnivorous, vegetarian, detritivore |
| Pseudoscorpiones (false scorpions) | 3,200 | Carnivorous |
| Scorpiones (scorpions) | 1,400 | Carnivorous |
| Solifugae Solifugae Solifugae are an order of Arachnida, known as camel spiders, wind scorpions and sun spiders or solifuges, comprising more than 1,000 described species in about 153 genera... (sunspiders) |
900 | Carnivorous, omnivorous |
| Schizomida (small whipscorpions) | 180 | |
| Amblypygi (whipspiders) | 100 | |
| Uropygi (Thelyphonida – whipscorpions) | 90 | Carnivorous |
| Palpigradi (micro whipscorpions) | 60 | |
| Ricinulei Ricinulei The Order Ricinulei is a group of arachnids known as hooded tickspiders. In older works they are sometimes referred to as Podogona., 60 extant species of ricinuleids have been described worldwide, all in the single family Ricinoididae. They occur today in west-central Africa and the Neotropical... |
60 |
Interaction with humans
_lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg)
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
s ate the flesh of horseshoe crabs, and used the tail spines as spear tips and the shells to bail water out of their canoes. More recent attempts to use horseshoe crabs as food for livestock
Livestock
Livestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
were abandoned when it was found that this gave the meat a bad taste. The blood of horseshoe crabs contains a clotting agent Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
Limulus amebocyte lysate is an aqueous extract of blood cells from the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. LAL reacts with bacterial endotoxin or lipopolysaccharide , which is a membrane component of Gram negative bacteria...
which is now used to test that antibiotics and kidney machines are free of dangerous bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, and to detect spinal meningitis and some cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
s.
Cooked tarantula
Tarantula
Tarantulas comprise a group of often hairy and often very large arachnids belonging to the family Theraphosidae, of which approximately 900 species have been identified. Some members of the same Suborder may also be called "tarantulas" in the common parlance. This article will restrict itself to...
spiders are considered a delicacy in Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
, and by the Piaroa
Piaroa
The Piaroa are an indigenous American ethnic group living along the banks of the Orinoco River and its tributaries in present day Venezuela, and in a few scattered locations elsewhere in Venezuela and in Colombia...
Indians of southern Venezuela. Spider venom
Venom
Venom is the general term referring to any variety of toxins used by certain types of animals that inject it into their victims by the means of a bite or a sting...
s may be a less polluting alternative to conventional pesticide
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling or mitigating any pest.A pesticide may be a chemical unicycle, biological agent , antimicrobial, disinfectant or device used against any pest...
s as they are deadly to insects but the great majority are harmless to vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s. Possible medical uses for spider venoms are being investigated, for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia, Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
, stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
s, and erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to develop or maintain an erection of the penis during sexual performance....
. Because spider silk is both light and very strong, attempts are being made to produce it in goats' milk and in the leaves of plants, by means of genetic engineering
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA or synthetic genes into the organism of interest...
.
There were about 100 reliably reported deaths from spider bites in the 20th century, compared with 1,500 from jellyfish
Jellyfish
Jellyfish are free-swimming members of the phylum Cnidaria. Medusa is another word for jellyfish, and refers to any free-swimming jellyfish stages in the phylum Cnidaria...
stings.
Scorpion stings are thought to be a significant danger in less-developed countries, for example they cause about 1,000 deaths per year in Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
but only one every few years in the USA. Most of these incidents are caused by accidental human "invasions" of scorpion's nests. However medical uses of scorpion venom are being investigated for treatment of brain cancers and bone diseases.
Tick
Tick
Ticks are small arachnids in the order Ixodida, along with mites, constitute the subclass Acarina. Ticks are ectoparasites , living by hematophagy on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians...
s are parasitic, and some transmit micro-organisms and parasites that can cause diseases in humans, while the saliva of a few species can directly cause tick paralysis
Tick paralysis
Tick paralysis is the only tick-borne disease that is not caused by an infectious organism. The illness is caused by a neurotoxin produced in the tick's salivary gland. After prolonged attachment, the engorged tick transmits the toxin to its host...
if they are not removed within a day or two.
A few of the closely related mites also infest humans, some causing intense itching by their bites and others by burrowing into the skin. Species that normally infest other animals such as rodent
Rodent
Rodentia is an order of mammals also known as rodents, characterised by two continuously growing incisors in the upper and lower jaws which must be kept short by gnawing....
s may infest humans if their normal hosts are eliminated. Three species of mite are a threat to honey bee
Honey bee
Honey bees are a subset of bees in the genus Apis, primarily distinguished by the production and storage of honey and the construction of perennial, colonial nests out of wax. Honey bees are the only extant members of the tribe Apini, all in the genus Apis...
s and one of these, Varroa destructor
Varroa destructor
Varroa destructor is an external parasitic mite that attacks honey bees Apis cerana and Apis mellifera. The disease caused by the mites is called varroatosis....
, has become the largest single problem faced by beekeeper
Beekeeper
A beekeeper is a person who keeps honey bees for the purposes of securing commodities such as honey, beeswax, pollen, royal jelly; pollinating fruits and vegetables; raising queens and bees for sale to other farmers; and/or for purposes satisfying natural scientific curiosity...
s worldwide. Mites cause several forms of allergic diseases, including hay fever
Hay Fever
Hay Fever is a comic play written by Noël Coward in 1924 and first produced in 1925 with Marie Tempest as the first Judith Bliss. Laura Hope Crews played the role in New York...
, asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
and eczema
Eczema
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the epidermis . In England, an estimated 5.7 million or about one in every nine people have been diagnosed with the disease by a clinician at some point in their lives.The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions...
, and they aggravate atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory, chronically relapsing, non-contagious and pruritic skin disorder...
. Mites are also significant crop pests, although predatory mites may be useful in controlling some of these.

