.gif)
Capacitor (component)
Encyclopedia
Practical capacitors are often classified according to the material used as the dielectric, with the dielectrics divided into two broad categories: bulk insulators and metal-oxide films (so-called electrolytic capacitors).
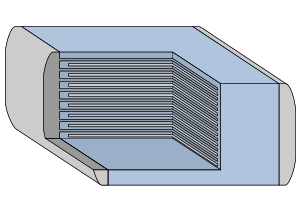 Capacitor
Capacitor
s have thin conducting plates (usually made of metal), separated by a layer of dielectric
, then stacked or rolled to form a compact device.
Many types of capacitors are available commercially, with capacitance ranging from the picofarad, microfarad range to more than a farad, and voltage ratings up to hundreds of kilovolts. In general, the higher the capacitance and voltage rating, the larger the physical size of the capacitor and the higher the cost. Tolerances in capacitance value for discrete capacitors are usually specified as a percentage of the nominal value. Tolerances ranging from 50% (electrolytic types) to less than 1% are commonly available.
Another figure of merit for capacitors is stability with respect to time and temperature, sometimes called drift. Variable capacitors are generally less stable than fixed types.
The electrodes need round edges to avoid field electron emission. Air has a low breakdown voltage, so any air inside a capacitor - especially at plate edges - will reduce the voltage rating. Even closed air bubbles in the insulator or between the insulator and the electrode lead to gas discharge, particularly in AC
or high frequency
applications. Groups of identically constructed capacitor elements are often connected in series for operation at higher voltage. High voltage capacitors need large, smooth, and round terminals to prevent corona discharge
.
|
|
|
|- align = "center"
|
|
|
|- align = "center"
|
|
|
|- align = "center"
|
|
|
|- align = "center"
| Capacitor
| Polarized
Capacitor
| Variable
Capacitor


s that change their capacitance as a function of the applied reverse bias voltage.
Variable capacitance is also used in sensors for physical quantities, including microphones, pressure and hygro sensors.
For a particular dielectric, the breakdown voltage is proportional to the thickness of the dielectric.
If a manufacturer makes a new capacitor with the same dielectric as some old capacitor, but with half the thickness of the dielectric, the new capacitor has half the breakdown voltage of the old capacitor.
Because the plates are closer together, the manufacturer can put twice the parallel-plate area inside the new capacitor and still fit it in the same volume (capacitor size) as the old capacitor.
Since the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is given by:
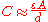
this new capacitor has 4 times the capacitance as the old capacitor.
Since the energy stored in a capacitor is given by: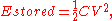
this new capacitor has the same maximum energy density as the old capacitor.
The energy density
depends only on the dielectric.
Making a few thick layers of dielectric (which can support a high voltage, but results in a low capacitance), or making many very thin layers of dielectric (which results in a low breakdown voltage, but a higher capacitance) has no effect on the energy density.
(dielectric loss). The lower the Q, the lossier the capacitor. Aluminum electrolytic types have typically low Q factors. High Q capacitors tend to exhibit low DC leakage currents. Tan-delta is the tangent of the phase angle between voltage and current in the capacitor. This angle is sometimes called the loss angle. It is related to the power factor which is zero for an ideal capacitor.
that is used to describe the resistive parts of the impedance of certain electronic components. The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors and inductors tends to assume they are ideal or "perfect" devices, contributing only capacitance or inductance to the circuit. However, all (non-superconducting) physical devices are constructed of materials with nonzero electrical resistance, which means that all real-world components contain some resistance in addition to their other properties. A low ESR capacitor typically has an ESR of 0.01 Ω. Low values are preferred for high-current, pulse applications.
Low ESR capacitors have the capability to deliver huge currents into short circuits, which can be dangerous.
For capacitors, ESR takes into account the internal lead and plate resistances and other factors. An easy way to deal with these inherent resistances in circuit analysis is to express each real capacitor as a combination of an ideal component and a small resistor in series, the resistor having a value equal to the resistance of the physical device.
high-speed logic circuits from the power supply. The decoupling capacitor supplies transient
current to the chip. Without decouplers, the IC demands current faster than the connection to the power supply can supply it, as parts of the circuit rapidly switch on and off. Large capacitors tend to have much higher ESL than small ones. As a result, electronics will frequently use multiple bypass capacitors—a small (100 nF) capacitor rated for high frequencies and a large electrolytic rated for lower frequencies, and occasionally, an intermediate value capacitor.
Non-polarised capacitors also suffer from aging, changing their values slightly over long periods of time.
In high voltage DC applications, accumulated capacitor stress due to in-rush currents at circuit power-up can be minimized with a pre-charge
circuit.
or soakage, and it effectively creates a hysteresis
or memory effect in capacitors.
The percentage of the original voltage restored depends upon the dielectric and is a non-linear function of original voltage.
In many applications of capacitors dielectric absorption is not a problem but in some applications, such as long-time-constant
integrator
s, sample-and-hold circuits, switched-capacitor analog-to-digital converter
s, and very low-distortion filter
s, it is important that the capacitor does not recover a residual charge after full discharge, and capacitors with low absorption are specified. For safety, high-voltage capacitors are often stored with their terminals short circuited.
Some dielectrics have very low dielectric absorption, e.g., polystyrene, polypropylene, NPO ceramic, and Teflon. Others, in particular those used in electrolytic
and supercapacitor
s, tend to have high absorption.
applications.
'leakage'; this ultimately limits how long capacitors can store charge. Before modern low-leakage dielectrics were developed this was a major source of problems in some applications (long time-constant timers, sample-and-holds, etc.).
In the late 1960s a standardized set of geometrically increasing preferred values
was introduced. According to the number of values per decade, these were called the E3, E6, E12, etc. series
In many applications capacitors need not be specified to tight tolerance (they often need only to exceed a certain value); this is particularly true for electrolytic capacitors, which are often used for filtering
and bypassing. Consequently capacitors, particularly electrolytics, often have a tolerance range of ±20% and need to be available only within E6 (or E3) series values.
Other types of capacitors, e.g. ceramic, can be manufactured to tighter tolerances and are available in E12 or closer-spaced values (e.g. 47 pF, 56 pF, 68 pF).
Since the establishment of the SI
in 1960, the range of prefixes used to specify capacitor values has expanded to include everything from pico- to kilo-, which is the range of commercially available capacitors. In some regions, however, certain prefixes can be less common than others; notably, in North America, use of millifarad and nanofarad is uncommon.
, tolerance, working voltage and polarity (if relevant). For most types of capacitor, numerical markings are used, whereas some capacitors, especially older types, use colour coding.
Smaller capacitors use a shorthand notation, to display all the relevant information in the limited space. The most commonly used format is: XYZ J/K/M VOLTS V, where XYZ represents the capacitance (calculated as XY×10Z pF), the letters J, K or M indicate the tolerance (±5%, ±10% and ±20% respectively) and VOLTS V represents the working voltage.
Polarised capacitors, for which one electrode must always be positive relative to the other, have clear polarity markings, usually a stripe or a "-" sign on the side of the negative electrode. Also, the negative lead is usually shorter.
Examples:
An electrolytic capacitor might be marked with the following information: 47µF 160V 105°C
A capacitor with the following text on its body: 105K 330V
has a capacitance of 10×105 pF = 1 µF (±10%) with a working voltage of 330 V.
A capacitor with the following text: 473M 100V
has a capacitance of 47×103 pF = 47 nF (±20%) with a working voltage of 100 V.
s.
*Or ±0.5 pF, whichever is greater.
Capacitor construction

Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s have thin conducting plates (usually made of metal), separated by a layer of dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
, then stacked or rolled to form a compact device.
Many types of capacitors are available commercially, with capacitance ranging from the picofarad, microfarad range to more than a farad, and voltage ratings up to hundreds of kilovolts. In general, the higher the capacitance and voltage rating, the larger the physical size of the capacitor and the higher the cost. Tolerances in capacitance value for discrete capacitors are usually specified as a percentage of the nominal value. Tolerances ranging from 50% (electrolytic types) to less than 1% are commonly available.
Another figure of merit for capacitors is stability with respect to time and temperature, sometimes called drift. Variable capacitors are generally less stable than fixed types.
The electrodes need round edges to avoid field electron emission. Air has a low breakdown voltage, so any air inside a capacitor - especially at plate edges - will reduce the voltage rating. Even closed air bubbles in the insulator or between the insulator and the electrode lead to gas discharge, particularly in AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
or high frequency
High frequency
High frequency radio frequencies are between 3 and 30 MHz. Also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decameters . Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted Medium-frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Very high frequency...
applications. Groups of identically constructed capacitor elements are often connected in series for operation at higher voltage. High voltage capacitors need large, smooth, and round terminals to prevent corona discharge
Corona discharge
In electricity, a corona discharge is an electrical discharge brought on by the ionization of a fluid surrounding a conductor that is electrically energized...
.
Types of dielectric
|- align = "center"|
|
|
|- align = "center"
|
|
|
|- align = "center"
|
|
|
|- align = "center"
|
|
|
|- align = "center"
| Capacitor
| Polarized
Capacitor
| Variable
Capacitor
- Air-gap: air-gap capacitors have a low dielectric loss. Large-valued, tunable capacitors that can be used for resonating HF antennas can be made this way.
- CeramicCeramic capacitorIn electronics, a ceramic capacitor is a capacitor constructed of alternating layers of metal and ceramic, with the ceramic material acting as the dielectric. The temperature coefficient depends on whether the dielectric is Class 1 or Class 2...
: the main differences between ceramic dielectric types are the temperature coefficient of capacitance, and the dielectric loss. C0G and NP0 (negative-positive-zero, i.e. ±0) dielectrics have the lowest losses, and are used in filters, as timing elements, and for balancing crystal oscillatorCrystal oscillatorA crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal of piezoelectric material to create an electrical signal with a very precise frequency...
s. Ceramic capacitors tend to have low inductance because of their small size. NP0 refers to the shape of the capacitor's temperature coefficient graph (how much the capacitance changes with temperature). NP0 means that the graph is flat and the device is not affected by temperature changes.- C0G or NP0: typically 1 pF to 100 nF, 5%. High tolerance and good temperature performance. Larger and more expensive.
- X7R: typically 100 pF to 22 µF, 10%. Good for non-critical coupling, timing applications. Subject to microphonicsMicrophonicsMicrophonics describes the phenomenon where certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal...
. Temperature up to 125°C - X8R: typically 100 pF to 10 µF, 25-100v, 5-10%. Good for high temperature up to 150°C
- Z5U or 2E6: typically 1 nF to 10 µF, 20%. Good for bypass, coupling applications. Low price and small size. Subject to microphonicsMicrophonicsMicrophonics describes the phenomenon where certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal...
. - Ceramic chip: 1% accurate, values up to about 1 µF, typically made from Lead zirconate titanateLead zirconate titanateLead zirconate titanate , also called PZT, is a ceramic perovskite material that shows a marked piezoelectric effect. PZT-based compounds are composed of the chemical elements lead and zirconium and the chemical compound titanate which are combined under extremely high temperatures. A filter is...
(PZT) ferroelectric ceramic
- Gimmick: these capacitors are made by twisting together 2 pieces of insulated wire. Values usually range from 3 pF to 15 pF. Usually used in homemade VHF circuits for oscillation feedback.
- Trimmer: these capacitors have a rotating plate (which can be rotated to change the capacitance) separated from a fixed plate by a dielectric medium. Typically values range from 5 pF to 60 pF.
- Glass: used to form extremely stable, reliable capacitors.
- Paper: common in antique radio equipment, paper dielectric and aluminum foil layers rolled into a cylinder and sealed with wax. Low values up to a few μF, working voltage up to several hundred volts, oil-impregnated bathtub types to 5 kV used for motor starting and high-voltage power supplies, and up to 25 kV for large oil-impregnated energy discharge types.
- PolycarbonatePolycarbonatePolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
: good for filters, low temperature coefficient, good aging, expensive. - PolyesterPolyesterPolyester is a category of polymers which contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Although there are many polyesters, the term "polyester" as a specific material most commonly refers to polyethylene terephthalate...
, (PET filmPET film (biaxially oriented)BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties and electrical insulation.A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other...
): (from about 1 nF to 10 μF) signal capacitors, integrators. - PolystyrenePolystyrenePolystyrene ) also known as Thermocole, abbreviated following ISO Standard PS, is an aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon that is manufactured from petroleum by the chemical industry...
: (usually in the picofarad range) stable signal capacitors. - PolypropylenePolypropylenePolypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes...
: low-loss, high voltage, resistant to breakdown, signal capacitors. - PTFE or Teflon: higher performing and more expensive than other plastic dielectrics.
- Silver micaSilver mica capacitorSilver mica capacitors are high precision, stability and reliability capacitors. They are available in small values, and are mostly used at high frequencies.-Clamped Mica capacitors:...
: These are fast and stable for HF and low VHF RF circuits, but expensive. - Electrolytic capacitorElectrolytic capacitorAn electrolytic capacitor is a type of capacitor that uses an electrolyte, an ionic conducting liquid, as one of its plates, to achieve a larger capacitance per unit volume than other types. They are often referred to in electronics usage simply as "electrolytics"...
s have a larger capacitance per unit volume than other types, making them valuable in relatively high-current and low-frequency electrical circuitsElectrical networkAn electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
, e.g. in power-supply filters or as coupling capacitors in audio amplifiers. High-capacity electrolytics, also known as supercapacitors or ultracapacitors, have applications similar to those of rechargeable batteries, e.g. in electrically powered vehicles. - Printed circuit boardPrinted circuit boardA printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
: metal conductive areas in different layers of a multi-layer printed circuit board can act as a highly stable capacitor. It is common industry practice to fill unused areas of one PCB layer with the ground conductor and another layer with the power conductor, forming a large distributed capacitor between the layers, or to make power traces broader than signal traces. - In integrated circuits, small capacitors can be formed through appropriate patterns of metallization on an isolating substrate.
- VacuumVacuumIn everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
: vacuum variable capacitorVacuum variable capacitorA vacuum variable capacitor uses a high vacuum as the dielectric instead of air or other insulating material. This allows for a higher voltage rating and/or capacitance value using a smaller total volume. In addition to the higher voltage rating a vacuum dielectric greatly reduces the chance of...
s are generally expensive, housed in a glass or ceramic body, typically rated for 5-30 kV. Typically used in high power RFRadio frequencyRadio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
transmitters because the dielectric has virtually no loss and is self-healing. May be fixed or adjustable.
Fixed capacitor comparisons
| Capacitor type | Dielectric Dielectric A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric... used | Features/applications | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper Capacitors | Paper Paper Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets.... or oil Oil An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils.... -impregnated paper |
Impregnated paper was extensively used for older capacitors, using wax, oil, or epoxy as an impregnant. Oil-Kraft paper capacitors are still used in certain high voltage High voltage The term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements... applications. Has mostly been replaced by plastic Plastic A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs... film capacitors. |
Large size. Also, paper is highly hygroscopic, absorbing moisture Moisture Humidity is the amount of moisture the air can hold before it rains. Moisture refers to the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts... from the atmosphere Earth's atmosphere The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night... despite plastic enclosures and impregnates. Absorbed moisture degrades performance by increasing dielectric losses (power factor Power factor The power factor of an AC electric power system is defined as the ratio of the real power flowing to the load over the apparent power in the circuit, and is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1 . Real power is the capacity of the circuit for performing work in a particular time... ) and decreasing insulation Electrical insulation thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation... resistance. |
| Metal Metal A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light... ized Paper Capacitors |
Paper | Comparatively smaller in size than paper-foil capacitors | Suitable only for lower current applications. Has been largely superseded by metalized film capacitors |
| PET film PET film (biaxially oriented) BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties and electrical insulation.A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other... Capacitor |
Polyester film | Smaller in size when compared to paper or polypropylene capacitors of comparable specifications. May use plates of foil, metalized film, or a combination. PET film PET film (biaxially oriented) BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties and electrical insulation.A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other... capacitors have almost completely replaced paper capacitors for most DC Direct current Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through... electronic applications. Operating voltages up to 60,000 V DC and operating temperature Operating temperature An operating temperature is the temperature at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the... s up to 125 °C. Low moisture absorption. |
Temperature stability is poorer than paper capacitors. Usable at low (AC Alternating current In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction.... power) frequencies, but inappropriate for RF Radio frequency Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals... applications due to excessive dielectric heating. |
| Kapton Kapton Kapton is a polyimide film developed by DuPont which can remain stable in a wide range of temperatures, from -273 to +400 °C... Capacitor |
Kapton polyimide Polyimide Polyimide is a polymer of imide monomers. The structure of imide is as shown. Polyimides have been in mass production since 1955... film |
Similar to PET film, but significantly higher operating temperature (up to 250 °C). Polyimides have the highest dielectric strength of any known dielectric. | Higher cost than PET. Temperature stability is poorer than paper capacitors. Usable at low (AC Alternating current In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction.... power) frequencies, but inappropriate for RF applications due to excessive dielectric heating. |
| Polystyrene Capacitor | Polystyrene Polystyrene Polystyrene ) also known as Thermocole, abbreviated following ISO Standard PS, is an aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon that is manufactured from petroleum by the chemical industry... |
Excellent general purpose plastic film capacitor. Excellent stability, low moisture pick-up and a slightly negative temperature coefficient Temperature coefficient The temperature coefficient is the relative change of a physical property when the temperature is changed by 1 K.In the following formula, let R be the physical property to be measured and T be the temperature at which the property is measured. T0 is the reference temperature, and ΔT is the... that can be used to match the positive temperature co-efficient of other components. Ideal for low power RF and precision analog applications |
Maximum operating temperature is limited to about +85 °C. Comparatively bigger in size. |
| Polycarbonate Plastic Film Capacitor | Polycarbonate Polycarbonate PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%... |
Superior insulation Electrical insulation thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation... resistance Electrical resistance The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical... , dissipation Dissipation In physics, dissipation embodies the concept of a dynamical system where important mechanical models, such as waves or oscillations, lose energy over time, typically from friction or turbulence. The lost energy converts into heat, which raises the temperature of the system. Such systems are called... factor, and dielectric absorption versus polystyrene capacitors. Moisture pick-up is less, with about ±80 ppm temperature coefficient. Can use full operating voltage across entire temperature range (−55 °C to 125 °C) |
Maximum operating temperature limited to about 125 °C. |
| Polypropylene Plastic Film Capacitors | Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes... |
Extremely low dissipation factor, higher dielectric strength than polycarbonate and polyester films, low moisture absorption, and high insulation resistance. May use plates of foil, metalized film, or a combination. Film is compatible with self-healing technology to improve reliability. Usable in high frequency applications and high frequency high power applications such as induction heating Induction heating Induction heating is the process of heating an electrically conducting object by electromagnetic induction, where eddy currents are generated within the metal and resistance leads to Joule heating of the metal... (often combined with water-cooling) due to very low dielectric losses. Larger value and higher voltage types from 1 to 100 μF at up to 440 V AC are used as run capacitors in some types of single phase electric motors. |
More susceptible to damage from transient over-voltages or voltage reversals than oil-impregnated Kraft paper for pulsed power Pulsed power Pulsed power is the term used to describe the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it very quickly thus increasing the instantaneous power.-Overview:... energy discharge applications. |
| Polysulphone Plastic Film Capacitors | Polysulfone Polysulfone Polysulfone describes a family of thermoplastic polymers. These polymers are known for their toughness and stability at high temperatures. They contain the subunit aryl-SO2-aryl, the defining feature of which is the sulfone group. Polysulfones were introduced in 1965 by Union Carbide... |
Similar to polycarbonate. Can withstand full voltage at comparatively higher temperatures. Moisture pick-up is typically 0.2%, limiting its stability. | Very limited availability and higher cost |
| PTFE Fluorocarbon (TEFLON) Film Capacitors | Polytetra- fluoroethylene Polytetrafluoroethylene Polytetrafluoroethylene is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that finds numerous applications. PTFE is most well known by the DuPont brand name Teflon.... |
Lowest loss solid dielectric. Operating temperatures up to 250 °C, extremely high insulation resistance, and good stability. Used in stringent, mission-critical applications | Large size (due to low dielectric constant), and higher cost than other film capacitors. |
| Polyamide Plastic Film Capacitors | Polyamide Polyamide A polyamide is a polymer containing monomers of amides joined by peptide bonds. They can occur both naturally and artificially, examples being proteins, such as wool and silk, and can be made artificially through step-growth polymerization or solid-phase synthesis, examples being nylons, aramids,... |
Operating temperatures of up to 200 °C. High insulation resistance, good stability and low dissipation factor. | Large size and high cost. |
| Metalized Plastic Film Capacitors | Polyester Polyester Polyester is a category of polymers which contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Although there are many polyesters, the term "polyester" as a specific material most commonly refers to polyethylene terephthalate... or Polycarbonate Polycarbonate PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%... |
Reliable and significantly smaller in size. Thin metalization can be used to advantage by making capacitors "self healing". | Thin plates limit maximum current carrying capability. |
| Stacked Plate Mica Capacitors | Mica Mica The mica group of sheet silicate minerals includes several closely related materials having highly perfect basal cleavage. All are monoclinic, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in chemical composition... |
Advantages of mica capacitors Silver mica capacitor Silver mica capacitors are high precision, stability and reliability capacitors. They are available in small values, and are mostly used at high frequencies.-Clamped Mica capacitors:... arise from the fact that the dielectric material (mica) is inert Inert -Chemistry:In chemistry, the term inert is used to describe a substance that is not chemically reactive.The noble gases were previously known as inert gases because of their perceived lack of participation in any chemical reactions... . It does not change physically or chemically with age and it has good temperature stability. Very resistant to corona Corona discharge In electricity, a corona discharge is an electrical discharge brought on by the ionization of a fluid surrounding a conductor that is electrically energized... damage |
Unless properly sealed, susceptible to moisture pick-up which will increase the power factor and decrease insulation resistance. Higher cost due to scarcity of high grade dielectric material and manually-intensive assembly. |
| Metalized Mica or Silver Mica Capacitors | Mica | Silver mica capacitor Silver mica capacitor Silver mica capacitors are high precision, stability and reliability capacitors. They are available in small values, and are mostly used at high frequencies.-Clamped Mica capacitors:... s have the above mentioned advantages. In addition, they have much reduced moisture infiltration. |
Higher cost |
| Glass Capacitors | Glass Glass Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives... |
Similar to Mica Capacitors Silver mica capacitor Silver mica capacitors are high precision, stability and reliability capacitors. They are available in small values, and are mostly used at high frequencies.-Clamped Mica capacitors:... . Stability and frequency characteristics are better than silver mica capacitor Silver mica capacitor Silver mica capacitors are high precision, stability and reliability capacitors. They are available in small values, and are mostly used at high frequencies.-Clamped Mica capacitors:... s. Ultra-reliable, ultra-stable, and resistant to nuclear radiation. |
High cost. |
| Class-I Temperature Compensating Type Ceramic Capacitors | Mixture of complex Titanate Titanate In chemistry, titanate usually refers to inorganic compounds composed of titanium oxides. In some cases, the term is used more generally for any titanium-containing anion, e.g. [TiCl6]2- and [Ti7]2-. This article focuses on the oxides.... compound Chemical compound A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together... s |
Low cost and small size, excellent high frequency Frequency Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency... characteristics and good reliability. Predictable linear Linear In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f... capacitance Capacitance In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor... change with operating temperature. Available in voltages up to 15,000 volts |
Capacitance changes with change in applied voltage, with frequency and with aging effects. |
| Class-II High dielectric strength Type Ceramic Capacitors | Barium titanate Barium titanate Barium titanate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula BaTiO3. Barium titanate is a white powder and transparent as larger crystals... based dielectrics |
Smaller than Class-I type due to higher dielectric strength of ceramics used. Available in voltages up to 50,000 volts. | Not as stable as Class-I type with respect to temperature, and capacitance changes significantly with applied voltage. |
| Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors Electrolytic capacitor An electrolytic capacitor is a type of capacitor that uses an electrolyte, an ionic conducting liquid, as one of its plates, to achieve a larger capacitance per unit volume than other types. They are often referred to in electronics usage simply as "electrolytics"... |
Aluminum oxide | Very large capacitance to volume ratio, inexpensive, polarized. Primary applications are as smoothing and reservoir capacitors in power supplies. | Dielectric leakage is high, large internal resistance and inductance Inductance In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit... limits high frequency performance, poor low temperature stability and loose tolerances. May vent or burst open when overloaded and/or overheated. Limited to about 500 volts. |
| Lithium Ion Capacitors Lithium ion capacitor A lithium-ion capacitor is a hybrid type of capacitor. Activated carbon is used as cathode. The anode of the LIC consists of carbon material which is pre-doped with lithium ion... |
Lithium Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... ion |
The lithium ion capacitors have a higher power density as compared to batteries and LIC’s are safer in use than LIB’s in which thermal runaway reactions may occur. Compared to an electric double-layer capacitor (EDLC), the LIC has a higher output voltage. They both have similar power densities, but energy density of an LIC is much higher. | New technology. |
| Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitors Tantalum capacitor The tantalum capacitor is a highly reliable type of electrolytic capacitor, available in both solid-bodied and separately encased forms. The encased "wet" variant is not used often in modern designs... |
Tantalum oxide | Large capacitance to volume ratio, smaller size, good stability, wide operating temperature range, long reliable operating life. Extensively used in miniaturized equipment and computers. Available in both polarized and unpolarized varieties. Solid Solid Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a... tantalum capacitors have much better characteristics than their wet counterparts. |
Higher cost than aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Voltage limited to about 50 volts. Explodes quite violently when voltage rating, current rating, or slew rates are exceeded, or when a polarized version is subjected to reverse voltage. |
| Electrolytic double-layer capacitors (EDLC) Supercapacitor Supercapacitor An electric double-layer capacitor , also known as supercapacitor, supercondenser, electrochemical double layer capacitor, or ultracapacitor, is an electrochemical capacitor with relatively high energy density. Their energy density is typically hundreds of times greater than conventional... s |
Thin Electrolyte Electrolyte In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible.... layer and Activated Carbon Activated carbon Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced... |
Extremely large capacitance to volume ratio, small size, low ESR. Available in hundreds, or thousands, of farads. A relatively new capacitor technology. Often used to temporarily provide power to equipment during battery replacement. Can rapidly absorb and deliver larger currents than batteries during charging and discharging, making them valuable for hybrid vehicle Hybrid vehicle A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:... s. Polarized, low operating voltage (volts per capacitor cell). Groups of cells are stacked to provide higher overall operating voltage. |
Relatively high cost. |
| Alternating current oil-filled Capacitors | Oil Oil An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils.... -impregnated paper |
Usually PET or polypropylene film dielectric. Primarily designed to provide very large capacitance for industrial AC Alternating current In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction.... applications to withstand large currents and high peak voltages at power line Electric power transmission Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers... frequencies. The applications include AC motor Electric motor An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force... starting and running, phase Phase (waves) Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:... splitting, power factor Power factor The power factor of an AC electric power system is defined as the ratio of the real power flowing to the load over the apparent power in the circuit, and is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1 . Real power is the capacity of the circuit for performing work in a particular time... correction, voltage regulation Regulation Regulation is administrative legislation that constitutes or constrains rights and allocates responsibilities. It can be distinguished from primary legislation on the one hand and judge-made law on the other... , control equipment, etc.. |
Limited to low frequency applications due to high dielectric losses at higher frequencies. |
| Direct current oil-filled capacitors | Paper or Paper-polyester film combination | Primarily designed for DC applications such as filter Electronic filter Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both... ing, bypass Bypass (telecommunications) In telecommunications, the term bypass has these meanings:# The use of any telecommunications facilities or services that circumvents those of the local exchange common carrier.... ing, coupling Coupling (electronics) In electronics and telecommunication, coupling is the desirable or undesirable transfer of energy from one medium, such as a metallic wire or an optical fiber, to another medium, including fortuitous transfer.... , arc suppression Arc suppression Arc suppression is a method of attempting to reduce to near elimination the luminous discharge of electrical current , between two electrodes, through a gas... , voltage doubling, etc... |
Operating voltage rating must be derated as per the curve supplied by the manufacturer if the DC contains ripple. Physically larger than polymer dielectric counterparts. |
| Energy Storage Capacitors | Kraft Kraft process The kraft process describes a technology for conversion of wood into wood pulp consisting of almost pure cellulose fibers... capacitor paper impregnated with electrical grade castor oil Castor oil Castor oil is a vegetable oil obtained from the castor bean . Castor oil is a colorless to very pale yellow liquid with mild or no odor or taste. Its boiling point is and its density is 961 kg/m3... or similar high dielectric constant fluid, with extended foil plates |
Designed specifically for intermittent duty, high current discharge applications. More tolerant of voltage reversal than many polymer dielectrics. Typical applications include pulsed power Pulsed power Pulsed power is the term used to describe the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it very quickly thus increasing the instantaneous power.-Overview:... , electromagnetic forming Electromagnetic forming Electromagnetic forming is a type of high velocity, cold forming process for electrically conductive metals, most commonly copper and aluminium. The workpiece is reshaped by high intensity pulsed magnetic fields that induce a current in the workpiece and a corresponding repulsive magnetic field,... , pulsed laser Laser A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation... s, Marx generator Marx generator A Marx generator is an electrical circuit first described by Erwin Otto Marx in 1924. Its purpose is to generate a high-voltage pulse. Marx generators are often used to simulate the effects of lightning on power line gear and aviation equipment.... s, and pulsed welders Welding Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes... . |
Physically large and heavy. Significantly lower energy density than polymer dielectric systems. Not self-healing. Device may fail catastrophically due to high stored energy. |
| Niobium Oxide Capacitors | Niobium oxide Niobium oxide Niobium oxide may refer to:* Niobium monoxide , NbO* Niobium dioxide , NbO2* Niobium pentoxide , Nb2O5In addition to the above, other distinct oxides exist... is used in capacitors where a layer of Nb2O5 is formed around NbO grains as the dielectric. |
. | . |
| Vacuum Capacitors | Vacuum Vacuum In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in... capacitors use highly evacuated glass or ceramic chamber with concentric cylindrical electrodes. |
Extremely low loss. Used for high voltage High voltage The term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements... high power RF Radio frequency Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals... applications, such as transmitters and induction heating where even a small amount of dielectric loss would cause excessive heating. Can be self-healing if arc-over Electric arc An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on... current is limited. |
Very high cost, fragile, physically large, and relatively low capacitance. |


Variable capacitors
Variable capacitors may have their capacitance intentionally and repeatedly changed over the life of the device. They include capacitors that use a mechanical construction to change the distance between the plates, or the amount of plate surface area which overlaps, and variable capacitance diodeVaricap
In electronics, a varicap diode, varactor diode, variable capacitance diode, variable reactance diode or tuning diode is a type of diode which has a variable capacitance that is a function of the voltage impressed on its terminals....
s that change their capacitance as a function of the applied reverse bias voltage.
Variable capacitance is also used in sensors for physical quantities, including microphones, pressure and hygro sensors.
Breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of the dielectric limits the power density of capacitors.For a particular dielectric, the breakdown voltage is proportional to the thickness of the dielectric.
If a manufacturer makes a new capacitor with the same dielectric as some old capacitor, but with half the thickness of the dielectric, the new capacitor has half the breakdown voltage of the old capacitor.
Because the plates are closer together, the manufacturer can put twice the parallel-plate area inside the new capacitor and still fit it in the same volume (capacitor size) as the old capacitor.
Since the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is given by:
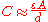
this new capacitor has 4 times the capacitance as the old capacitor.
Since the energy stored in a capacitor is given by:
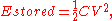
this new capacitor has the same maximum energy density as the old capacitor.
The energy density
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
depends only on the dielectric.
Making a few thick layers of dielectric (which can support a high voltage, but results in a low capacitance), or making many very thin layers of dielectric (which results in a low breakdown voltage, but a higher capacitance) has no effect on the energy density.
Q factor, dissipation and tan-delta
Capacitors have Q (quality) factor (and the inverse, dissipation factor, D or tan-delta) which relates capacitance at a certain frequency to the combined losses due to dielectric leakage and series internal resistance (also known as ESR) dissipation factorDissipation factor
In physics, the dissipation factor is a measure of loss-rate of energy of a mode of oscillation in a dissipative system. It is the reciprocal of Quality factor, which represents the quality of oscillation....
(dielectric loss). The lower the Q, the lossier the capacitor. Aluminum electrolytic types have typically low Q factors. High Q capacitors tend to exhibit low DC leakage currents. Tan-delta is the tangent of the phase angle between voltage and current in the capacitor. This angle is sometimes called the loss angle. It is related to the power factor which is zero for an ideal capacitor.
Equivalent series resistance (ESR)
This is an effective resistanceElectrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
that is used to describe the resistive parts of the impedance of certain electronic components. The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors and inductors tends to assume they are ideal or "perfect" devices, contributing only capacitance or inductance to the circuit. However, all (non-superconducting) physical devices are constructed of materials with nonzero electrical resistance, which means that all real-world components contain some resistance in addition to their other properties. A low ESR capacitor typically has an ESR of 0.01 Ω. Low values are preferred for high-current, pulse applications.
Low ESR capacitors have the capability to deliver huge currents into short circuits, which can be dangerous.
For capacitors, ESR takes into account the internal lead and plate resistances and other factors. An easy way to deal with these inherent resistances in circuit analysis is to express each real capacitor as a combination of an ideal component and a small resistor in series, the resistor having a value equal to the resistance of the physical device.
Equivalent series inductance (ESL)
ESL in signal capacitors is mainly caused by the leads used to connect the plates to the outside world and the series interconnects used to join sets of plates together internally. For any real-world capacitor, there is a frequency above DC at which it ceases to behave as a pure capacitance. This is called the (first) resonant frequency. This is critically important with decouplingDecoupling
The term "decoupling" is used in many different contexts.-Economic growth without environmental damage:In economic and environmental fields, decoupling is becoming increasingly used in the context of economic production and environmental quality. When used in this way, it refers to the ability of...
high-speed logic circuits from the power supply. The decoupling capacitor supplies transient
Transient (oscillation)
A transient event is a short-lived burst of energy in a system caused by a sudden change of state.The source of the transient energy may be an internal event or a nearby event...
current to the chip. Without decouplers, the IC demands current faster than the connection to the power supply can supply it, as parts of the circuit rapidly switch on and off. Large capacitors tend to have much higher ESL than small ones. As a result, electronics will frequently use multiple bypass capacitors—a small (100 nF) capacitor rated for high frequencies and a large electrolytic rated for lower frequencies, and occasionally, an intermediate value capacitor.
Maximum voltage and current
Important properties of capacitors are the maximum working voltage (potential, measured in volts) and the amount of energy lost in the dielectric. For high-power or high-speed capacitors, the maximum ripple current, peak current, fault current, and percent voltage reversal are further considerations. Typically the voltage is 66% of the rated voltage. A voltage higher than that, usually reduces the life expectancy depending on manufacturer. The time for a voltage to discharge is 6 time constants.Temperature dependence
Another major non-ideality is temperature coefficient (change in capacitance with temperature) which is usually quoted in parts per million (ppm) per degree Celsius.Aging
When refurbishing old (especially audio) equipment, it is a good idea to replace all of the electrolyte-based capacitors. After long storage, the electrolyte and dielectric layer within electrolytic capacitors may deteriorate; before powering up equipment with old electrolytics, it may be useful to apply low voltage to allow the capacitors to reform before applying full voltage. Deteriorating capacitors are a frequent cause of hum in aging audio equipment.Non-polarised capacitors also suffer from aging, changing their values slightly over long periods of time.
In high voltage DC applications, accumulated capacitor stress due to in-rush currents at circuit power-up can be minimized with a pre-charge
Pre-charge
Pre-charge of the powerline voltages in a high voltage DC application is a preliminary mode which current-limits the power source such that a controlled rise time of the system voltage during power up is achieved....
circuit.
Dielectric absorption (soakage)
Some types of dielectrics, when they have been holding a voltage for a long time, maintain a "memory" of that voltage: after they have been quickly fully discharged and left without an applied voltage, a voltage will gradually be established which is some fraction of the original voltage. For some dielectrics 10% or more of the original voltage may reappear. This phenomenon of unwanted charge storage is called dielectric absorptionDielectric absorption
Dielectric absorption is the name given to the effect by which a capacitor that has been charged for a long time discharges only incompletely when briefly discharged. Although an ideal capacitor would remain at zero volts after being discharged, real capacitors will develop a small voltage, a...
or soakage, and it effectively creates a hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
or memory effect in capacitors.
The percentage of the original voltage restored depends upon the dielectric and is a non-linear function of original voltage.
In many applications of capacitors dielectric absorption is not a problem but in some applications, such as long-time-constant
Time constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter \tau , is the risetime characterizing the response to a time-varying input of a first-order, linear time-invariant system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a system that can be modeled by a single first order...
integrator
Integrator
An integrator is a device to perform the mathematical operation known as integration, a fundamental operation in calculus.The integration function is often part of engineering, physics, mechanical, chemical and scientific calculations....
s, sample-and-hold circuits, switched-capacitor analog-to-digital converter
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
s, and very low-distortion filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
s, it is important that the capacitor does not recover a residual charge after full discharge, and capacitors with low absorption are specified. For safety, high-voltage capacitors are often stored with their terminals short circuited.
Some dielectrics have very low dielectric absorption, e.g., polystyrene, polypropylene, NPO ceramic, and Teflon. Others, in particular those used in electrolytic
Electrolytic capacitor
An electrolytic capacitor is a type of capacitor that uses an electrolyte, an ionic conducting liquid, as one of its plates, to achieve a larger capacitance per unit volume than other types. They are often referred to in electronics usage simply as "electrolytics"...
and supercapacitor
Supercapacitor
An electric double-layer capacitor , also known as supercapacitor, supercondenser, electrochemical double layer capacitor, or ultracapacitor, is an electrochemical capacitor with relatively high energy density. Their energy density is typically hundreds of times greater than conventional...
s, tend to have high absorption.
Voltage non-linearities
Capacitors may also change capacitance with applied voltage. This effect is more prevalent in high k ceramic and some high voltage capacitors. This is a small source of non-linearity in low-distortion filters and other analogAnalogue electronics
Analogue electronics are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal...
applications.
Leakage
The resistance between the terminals of a capacitor is never truly infinite, leading to some level of d.c.Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
'leakage'; this ultimately limits how long capacitors can store charge. Before modern low-leakage dielectrics were developed this was a major source of problems in some applications (long time-constant timers, sample-and-holds, etc.).
Standard values
Before 1960 electronic components values were not standardised. The more common, but not the only, values for capacitors were 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 5.0, 6.0, and 8.0 as base numbers multiplied by some negative or positive power of ten. Values in the nanofarad range and above were stated in microfarads (often incorrectly abbreviated as mF or mfd); lower values were stated in micro-microfarads (µµF, now called picofarads, pF).In the late 1960s a standardized set of geometrically increasing preferred values
Preferred number
In industrial design, preferred numbers are standard guidelines for choosing exact product dimensions within a given set of constraints....
was introduced. According to the number of values per decade, these were called the E3, E6, E12, etc. series
| Series | Values | |||||||||||
| E3 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 4.7 | |||||||||
| E6 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 4.7 | 6.8 | ||||||
| E12 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 4.7 | 5.6 | 6.8 | 8.2 |
In many applications capacitors need not be specified to tight tolerance (they often need only to exceed a certain value); this is particularly true for electrolytic capacitors, which are often used for filtering
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
and bypassing. Consequently capacitors, particularly electrolytics, often have a tolerance range of ±20% and need to be available only within E6 (or E3) series values.
Other types of capacitors, e.g. ceramic, can be manufactured to tighter tolerances and are available in E12 or closer-spaced values (e.g. 47 pF, 56 pF, 68 pF).
Since the establishment of the SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
in 1960, the range of prefixes used to specify capacitor values has expanded to include everything from pico- to kilo-, which is the range of commercially available capacitors. In some regions, however, certain prefixes can be less common than others; notably, in North America, use of millifarad and nanofarad is uncommon.
Capacitor markings
Capacitors, like most other electronic components, have markings in their bodies to indicate their electrical characteristics, in particular capacitanceCapacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
, tolerance, working voltage and polarity (if relevant). For most types of capacitor, numerical markings are used, whereas some capacitors, especially older types, use colour coding.
Numerical markings
On capacitors that are large enough (e.g. electrolytic capacitors) the capacity and working voltage are printed on the body without encoding. Sometimes the markings also include the maximum working temperature, manufacturer's name and other information.Smaller capacitors use a shorthand notation, to display all the relevant information in the limited space. The most commonly used format is: XYZ J/K/M VOLTS V, where XYZ represents the capacitance (calculated as XY×10Z pF), the letters J, K or M indicate the tolerance (±5%, ±10% and ±20% respectively) and VOLTS V represents the working voltage.
Polarised capacitors, for which one electrode must always be positive relative to the other, have clear polarity markings, usually a stripe or a "-" sign on the side of the negative electrode. Also, the negative lead is usually shorter.
Examples:
An electrolytic capacitor might be marked with the following information: 47µF 160V 105°C
A capacitor with the following text on its body: 105K 330V
has a capacitance of 10×105 pF = 1 µF (±10%) with a working voltage of 330 V.
A capacitor with the following text: 473M 100V
has a capacitance of 47×103 pF = 47 nF (±20%) with a working voltage of 100 V.
Colour coding
Capacitors may be marked with 3 or more coloured bands or dots. 3-colour coding encodes most significant digit, second most significant digit, and multiplier. Additional bands have meanings which may vary from one type to another. Low-tolerance capacitors may begin with the first 3 (rather than 2) digits of the value. It is usually, but not always, possible to work out what scheme is used by the particular colours used. Cylindrical capacitors marked with bands may look like resistorResistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
s.
| Colour | Significant digits | Multiplier | Capacitance tolerance | Characteristic | DC working voltage | Operating temperature | EIA/vibration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | 1 | ±20% | — | — | −55 °C to +70 °C | 10 to 55 Hz | |
| Brown | 1 | 10 | ±1% | B | 100 | — | — | |
| Red | 2 | 100 | ±2% | C | — | −55 °C to +85 °C | — | |
| Orange | 3 | 1,000 | — | D | 300 | — | — | |
| Yellow | 4 | 10,000 | — | E | — | −55 °C to +125°C | 10 to 2000 Hz | |
| Green | 5 | — | ±0.5% | F | 500 | — | — | |
| Blue | 6 | — | — | — | — | −55 °C to +150 °C | — | |
| Violet | 7 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Grey | 8 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| White | 9 | — | — | — | — | — | EIA Electronic Industries Alliance The Electronic Industries Alliance was a standards and trade organization composed as an alliance of trade associations for electronics manufacturers in the United States. They developed standards to ensure the equipment of different manufacturers was compatible and interchangeable... |
|
| Gold | — | — | ±5%* | — | 1000 | — | — | |
| Silver | — | — | ±10% | — | — | — | — | |
See also
- Capacitor plagueCapacitor plagueThe capacitor plague was a problem with a large number of premature failures of aluminium electrolytic capacitors with non solid or liquid electrolyte of certain brands especially from Taiwan manufacturers . The first flawed capacitors were seen in 1999, but most of the affected capacitors failed...
(premature failure of certain incorrectly formulated electrolytic capacitors) - SupercapacitorSupercapacitorAn electric double-layer capacitor , also known as supercapacitor, supercondenser, electrochemical double layer capacitor, or ultracapacitor, is an electrochemical capacitor with relatively high energy density. Their energy density is typically hundreds of times greater than conventional...
- Electronic devices and circuitsCircuit designThe process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems all the way down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit...
- Electronic color codeElectronic color codeThe electronic color code is used to indicate the values or ratings of electronic components, very commonly for resistors, but also for capacitors, inductors, and others...
- InductorInductorAn inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
External links
- Spark Museum (von Kleist and Musschenbroek)
- Biography of von Kleist
- Modeling Dielectric Absorption in Capacitors
- A different view of all this capacitor stuff

