
Temperature coefficient
Encyclopedia
The temperature coefficient is the relative change of a physical property when the temperature
is changed by 1 K
.
In the following formula, let R be the physical property to be measured and T be the temperature at which the property is measured. T0 is the reference temperature, and ΔT is the difference between T and T0. Finally, α is the (linear) temperature coefficient. Given these definitions, the physical property is: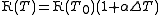
Here α has the dimension
s of an inverse temperature (1/K or K−1).
This equation is linear
with respect to temperature. For quantities that vary polynomial
ly or logarithm
ically with temperature, it may be possible to calculate a temperature coefficient that is a useful approximation for a certain range of temperatures. For quantities that vary exponentially
with temperature, such as the rate of a chemical reaction
, any temperature coefficient would be valid only over a very small temperature range.
Different temperature coefficients are specified for various applications, including nuclear, electrical and magnetic.
of a material rises with increasing temperature, typically in a defined temperature range. For most materials, the thermal conductivity will decrease with increasing temperature.
Materials with a negative temperature coefficient have been used in floor heating since 1971. The negative temperature coefficient avoids excessive local heating beneath carpets, bean bag
chairs, mattress
es etc., which can damage wooden floors
, and may infrequently cause fires.
Most ceramic
s exhibit NTC behaviour, which is governed by an Arrhenius equation
over a wide range of temperatures:
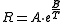
where R is resistance, A and B are constants, and T is absolute temperature (K).
The constant B is related to the energies required to form and move the charge carrier
s responsible for electrical conduction – hence, as the value of B decreases, the material becomes insulating. Practical and commercial NTC resistor
s aim to combine modest resistance with a value of B that provides good sensitivity to temperature. Such is the importance of the B constant value, that it is possible to characterize NTC thermistor
s using the B parameter equation: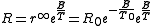
where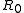 is resistance at temperature
is resistance at temperature 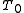 .
.
Therefore, many materials that produce acceptable values of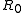 include materials that have been alloyed or possess variable cation valence states and thus contain a high natural defect center concentration. The value of B strongly depends on the energy required to dissociate the charge carriers that are used for the electrical conduction from these defect centers.
include materials that have been alloyed or possess variable cation valence states and thus contain a high natural defect center concentration. The value of B strongly depends on the energy required to dissociate the charge carriers that are used for the electrical conduction from these defect centers.
s and traveling-wave tubes (TWTs), need to have constant field over a wide temperature range
. The reversible temperature coefficient (RTC) of Br is defined as: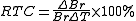
To address these requirements, temperature compensated magnets were developed in the late 1970s. For conventional SmCo magnets, Br decreases as temperature increases. Conversely, for GdCo magnets, Br increases as temperature increases within certain temperature ranges. By combining samarium
and gadolinium
in the alloy, the temperature coefficient can be reduced to nearly zero.
and thus of electronic devices (wire
s, resistors) has to be taken into account when constructing devices and circuits
. The temperature dependence of conductors
is to a great degree linear and can be described by the approximation below.

where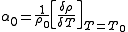
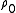 just corresponds to the specific resistance temperature coefficient at a specified reference value (normally T = 0 °C)
just corresponds to the specific resistance temperature coefficient at a specified reference value (normally T = 0 °C)
That of a semiconductor
is however exponential:
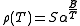
where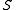 is defined as the cross sectional area and
is defined as the cross sectional area and  and
and 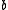 are coefficients determining the shape of the function and the value of resistivity at a given temperature.
are coefficients determining the shape of the function and the value of resistivity at a given temperature.
For both, is referred to as the resistance temperature coefficient.
is referred to as the resistance temperature coefficient.
This property is used in devices such as thermistors.
The coefficient of thermal expansion is often used to develop thermometers. Here lengths of materials can express temperature. The coefficient is also used for several types of thermostats.
of elastic materials varies with temperature, typically decreasing with higher temperature.
, the temperature coefficient of reactivity is a measure of the change in reactivity (resulting in a change in power), brought about by a change in temperature of the reactor components or the reactor coolant. This may be defined as
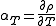
Where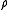 is reactivity and T is temperature. The relationship shows that
is reactivity and T is temperature. The relationship shows that  is the value of the partial differential of reactivity with respect to temperature and is referred to as the "temperature coefficient of reactivity". As a result, the temperature feedback provided by
is the value of the partial differential of reactivity with respect to temperature and is referred to as the "temperature coefficient of reactivity". As a result, the temperature feedback provided by  has an intuitive application to passive nuclear safety
has an intuitive application to passive nuclear safety
. A negative is broadly cited as important for reactor safety, but wide temperature variations across real reactors (as opposed to a theoretical homogeneous reactor) limit the usability of a single metric as a marker of reactor safety.
is broadly cited as important for reactor safety, but wide temperature variations across real reactors (as opposed to a theoretical homogeneous reactor) limit the usability of a single metric as a marker of reactor safety.
In water moderated nuclear reactors, the bulk of reactivity changes with respect to temperature are brought about by changes in the temperature of the water. However each element of the core has a specific temperature coefficient of reactivity (e.g. the fuel or cladding). The mechanisms which drive fuel temperature coefficients of reactivity are different than water temperature coefficients. While water expands as temperature increases, causing longer neutron travel times during moderation
, fuel material will not expand appreciably. Changes in reactivity in fuel due to temperature stem from a phenomenon known as doppler broadening
, where resonance absorption of fast neutrons in fuel filler material prevents those neutrons from thermalizing (slowing down).
parts is sometimes specified as ppm/°C
. This specifies the percentage (expressed in parts per million) that its electrical characteristics will deviate when taken to a temperature above or below the operating temperature.
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
is changed by 1 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
.
In the following formula, let R be the physical property to be measured and T be the temperature at which the property is measured. T0 is the reference temperature, and ΔT is the difference between T and T0. Finally, α is the (linear) temperature coefficient. Given these definitions, the physical property is:
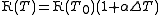
Here α has the dimension
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
s of an inverse temperature (1/K or K−1).
This equation is linear
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
with respect to temperature. For quantities that vary polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
ly or logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
ically with temperature, it may be possible to calculate a temperature coefficient that is a useful approximation for a certain range of temperatures. For quantities that vary exponentially
Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
with temperature, such as the rate of a chemical reaction
Arrhenius equation
The Arrhenius equation is a simple, but remarkably accurate, formula for the temperature dependence of the reaction rate constant, and therefore, rate of a chemical reaction. The equation was first proposed by the Dutch chemist J. H. van 't Hoff in 1884; five years later in 1889, the Swedish...
, any temperature coefficient would be valid only over a very small temperature range.
Different temperature coefficients are specified for various applications, including nuclear, electrical and magnetic.
Negative temperature coefficient
A negative temperature coefficient (NTC) occurs when the thermal conductivityThermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
of a material rises with increasing temperature, typically in a defined temperature range. For most materials, the thermal conductivity will decrease with increasing temperature.
Materials with a negative temperature coefficient have been used in floor heating since 1971. The negative temperature coefficient avoids excessive local heating beneath carpets, bean bag
Bean bag
A bean bag is a sealed bag containing dried beans, PVC pellets or expanded polystyrene, with various applications.-Games:...
chairs, mattress
Mattress
A mattress is a manufactured product to sleep or lie on, consisting of resilient materials and covered with an outer fabric or ticking. In the developed world it is typically part of a bed set and is placed upon a foundation....
es etc., which can damage wooden floors
Wood flooring
Wood flooring is any product manufactured from timber that is designed for use as flooring, either structural or aesthetic. Bamboo flooring is often considered a wood floor, although it is made from a grass rather than a timber....
, and may infrequently cause fires.
Most ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
s exhibit NTC behaviour, which is governed by an Arrhenius equation
Arrhenius equation
The Arrhenius equation is a simple, but remarkably accurate, formula for the temperature dependence of the reaction rate constant, and therefore, rate of a chemical reaction. The equation was first proposed by the Dutch chemist J. H. van 't Hoff in 1884; five years later in 1889, the Swedish...
over a wide range of temperatures:
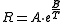
where R is resistance, A and B are constants, and T is absolute temperature (K).
The constant B is related to the energies required to form and move the charge carrier
Charge carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a free particle carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric currents in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons and ions...
s responsible for electrical conduction – hence, as the value of B decreases, the material becomes insulating. Practical and commercial NTC resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
s aim to combine modest resistance with a value of B that provides good sensitivity to temperature. Such is the importance of the B constant value, that it is possible to characterize NTC thermistor
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a portmanteau of thermal and resistor...
s using the B parameter equation:
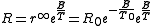
where
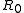 is resistance at temperature
is resistance at temperature 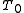 .
.Therefore, many materials that produce acceptable values of
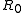 include materials that have been alloyed or possess variable cation valence states and thus contain a high natural defect center concentration. The value of B strongly depends on the energy required to dissociate the charge carriers that are used for the electrical conduction from these defect centers.
include materials that have been alloyed or possess variable cation valence states and thus contain a high natural defect center concentration. The value of B strongly depends on the energy required to dissociate the charge carriers that are used for the electrical conduction from these defect centers.Reversible temperature coefficient
Residual magnetic flux density or Br changes with temperature and it is one of the important characteristics of magnet performance. Some applications, such as interial gyroscopeGyroscope
A gyroscope is a device for measuring or maintaining orientation, based on the principles of angular momentum. In essence, a mechanical gyroscope is a spinning wheel or disk whose axle is free to take any orientation...
s and traveling-wave tubes (TWTs), need to have constant field over a wide temperature range
Temperature range
Atmospheric temperature range is the numerical difference between the minimum and maximum values of temperature observed in a given location....
. The reversible temperature coefficient (RTC) of Br is defined as:
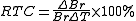
To address these requirements, temperature compensated magnets were developed in the late 1970s. For conventional SmCo magnets, Br decreases as temperature increases. Conversely, for GdCo magnets, Br increases as temperature increases within certain temperature ranges. By combining samarium
Samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with the symbol Sm, atomic number 62 and atomic weight 150.36. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually assumes the oxidation state +3...
and gadolinium
Gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with...
in the alloy, the temperature coefficient can be reduced to nearly zero.
Temperature coefficient of electrical resistance
The temperature dependence of electrical resistanceElectrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
and thus of electronic devices (wire
Wire
A wire is a single, usually cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads and to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Standard sizes are determined by various...
s, resistors) has to be taken into account when constructing devices and circuits
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
. The temperature dependence of conductors
Electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is a material which contains movable electric charges. In metallic conductors such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons...
is to a great degree linear and can be described by the approximation below.

where
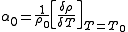
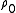 just corresponds to the specific resistance temperature coefficient at a specified reference value (normally T = 0 °C)
just corresponds to the specific resistance temperature coefficient at a specified reference value (normally T = 0 °C)That of a semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
is however exponential:
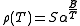
where
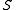 is defined as the cross sectional area and
is defined as the cross sectional area and  and
and 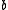 are coefficients determining the shape of the function and the value of resistivity at a given temperature.
are coefficients determining the shape of the function and the value of resistivity at a given temperature.For both,
 is referred to as the resistance temperature coefficient.
is referred to as the resistance temperature coefficient.This property is used in devices such as thermistors.
Positive temperature coefficient of resistance
A positive temperature coefficient (PTC) refers to materials that experience an increase in electrical resistance when their temperature is raised. Materials which have useful engineering applications usually show a relatively rapid increase with temperature, i.e. a higher coefficient. The higher the coefficient, the greater an increase in electrical resistance for a given temperature increase.Coefficient of thermal expansion
The physical dimensions of matter can be affected by temperature. The coefficient of thermal expansion for a given sample of matter can be used to approximate its change in volume given a change in temperature. A similar coefficient, the linear thermal expansion coefficient, is also often used to measure the change of length of an object in one-dimension.The coefficient of thermal expansion is often used to develop thermometers. Here lengths of materials can express temperature. The coefficient is also used for several types of thermostats.
Temperature coefficient of elasticity
The elastic modulusElastic modulus
An elastic modulus, or modulus of elasticity, is the mathematical description of an object or substance's tendency to be deformed elastically when a force is applied to it...
of elastic materials varies with temperature, typically decreasing with higher temperature.
Temperature coefficient of reactivity
In nuclear engineeringNuclear engineering
Nuclear engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the application of the breakdown as well as the fusion of atomic nuclei and/or the application of other sub-atomic physics, based on the principles of nuclear physics...
, the temperature coefficient of reactivity is a measure of the change in reactivity (resulting in a change in power), brought about by a change in temperature of the reactor components or the reactor coolant. This may be defined as
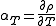
Where
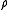 is reactivity and T is temperature. The relationship shows that
is reactivity and T is temperature. The relationship shows that  is the value of the partial differential of reactivity with respect to temperature and is referred to as the "temperature coefficient of reactivity". As a result, the temperature feedback provided by
is the value of the partial differential of reactivity with respect to temperature and is referred to as the "temperature coefficient of reactivity". As a result, the temperature feedback provided by  has an intuitive application to passive nuclear safety
has an intuitive application to passive nuclear safetyPassive nuclear safety
Passive nuclear safety is a safety feature of a nuclear reactor that does not require operator actions or electronic feedback in order to shut down safely in the event of a particular type of emergency...
. A negative
 is broadly cited as important for reactor safety, but wide temperature variations across real reactors (as opposed to a theoretical homogeneous reactor) limit the usability of a single metric as a marker of reactor safety.
is broadly cited as important for reactor safety, but wide temperature variations across real reactors (as opposed to a theoretical homogeneous reactor) limit the usability of a single metric as a marker of reactor safety.In water moderated nuclear reactors, the bulk of reactivity changes with respect to temperature are brought about by changes in the temperature of the water. However each element of the core has a specific temperature coefficient of reactivity (e.g. the fuel or cladding). The mechanisms which drive fuel temperature coefficients of reactivity are different than water temperature coefficients. While water expands as temperature increases, causing longer neutron travel times during moderation
Neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, thereby turning them into thermal neutrons capable of sustaining a nuclear chain reaction involving uranium-235....
, fuel material will not expand appreciably. Changes in reactivity in fuel due to temperature stem from a phenomenon known as doppler broadening
Doppler broadening
In atomic physics, Doppler broadening is the broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atoms or molecules. Different velocities of the emitting particles result in different shifts, the cumulative effect of which is the line broadening.The...
, where resonance absorption of fast neutrons in fuel filler material prevents those neutrons from thermalizing (slowing down).
Units
The thermal coefficient of electrical circuitElectrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
parts is sometimes specified as ppm/°C
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
. This specifies the percentage (expressed in parts per million) that its electrical characteristics will deviate when taken to a temperature above or below the operating temperature.

