
Induction heating
Encyclopedia

Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
) by electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electric current across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. It underlies the operation of generators, transformers, induction motors, electric motors, synchronous motors, and solenoids....
, where eddy current
Eddy current
Eddy currents are electric currents induced in conductors when a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field; due to relative motion of the field source and conductor or due to variations of the field with time. This can cause a circulating flow of electrons, or current, within the body of...
s (also called Foucault currents) are generated within the metal and resistance leads to Joule heating
Joule heating
Joule heating, also known as ohmic heating and resistive heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor releases heat. It was first studied by James Prescott Joule in 1841. Joule immersed a length of wire in a fixed mass of water and measured the temperature...
of the metal. An induction heater
Induction heater
An induction heater is a key piece of equipment used in all forms of induction heating. Typically an induction heater operates at either medium frequency or radio frequency ranges. Three main components form the basis of a modern induction heater including the power unit , the work head and the...
(for any process) consists of an electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
, through which a high-frequency alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC) is passed. Heat may also be generated by magnetic hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
losses in materials that have significant relative permeability
Permeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
. The frequency of AC used depends on the object size, material type, coupling (between the work coil and the object to be heated) and the penetration depth.
Applications
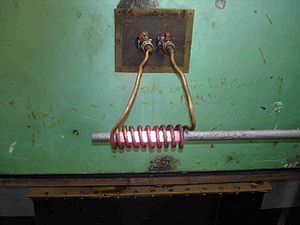
Brazing
Brazing is a metal-joining process whereby a filler metal is heated above and distributed between two or more close-fitting parts by capillary action. The filler metal is brought slightly above its melting temperature while protected by a suitable atmosphere, usually a flux...
and soldering and heating to fit. Iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and its alloys
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
respond best to induction heating, due to their ferromagnetic nature. Eddy currents can, however, be generated in any conductor, and magnetic hysteresis can occur in any magnetic material. Induction heating has been used to heat liquid conductors (such as molten metals) and also gaseous conductors (such as a gas plasma - see Induction plasma technology
Induction plasma technology
The 1960s were the incipient period of Thermal Plasma Technology, driven by the necessity of aerospace programs. Among the various methods of thermal plasma generation, induction plasma takes up an important role....
). Induction heating is often used to heat graphite crucibles (containing other materials) and is used extensively in the semiconductor industry for the heating of silicon and other semiconductors. Supply frequency (mains, 50/60 Hz) induction heating is used for many lower cost industrial applications as inverters are not required.
Induction furnace
An induction furnaceInduction furnace
An induction furnace is an electrical furnace in which the heat is applied by induction heating of metal. The advantage of the induction furnace is a clean, energy-efficient and well-controllable melting process compared to most other means of metal melting...
uses induction to heat metal to its melting point. Once molten, the high-frequency magnetic field can also be used to stir the hot metal, which is useful in ensuring that alloying additions
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
are fully mixed into the melt. Most induction furnaces consist of a tube of water-cooled copper rings surrounding a container of refractory
Refractory
A refractory material is one that retains its strength at high temperatures. ASTM C71 defines refractories as "non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, or as components of systems, that are exposed to environments above...
material. Induction furnaces are used in most modern foundries as a cleaner method of melting metals than a reverberatory furnace
Reverberatory furnace
A reverberatory furnace is a metallurgical or process furnace that isolates the material being processed from contact with the fuel, but not from contact with combustion gases...
or a cupola
Blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally iron.In a blast furnace, fuel and ore and flux are continuously supplied through the top of the furnace, while air is blown into the bottom of the chamber, so that the chemical reactions...
. Sizes range from a kilogram of capacity to a hundred tonnes capacity. Induction furnaces often emit a high-pitched whine or hum when they are running, depending on their operating frequency. Metals melted include iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
, and precious metal
Precious metal
A precious metal is a rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical element of high economic value.Chemically, the precious metals are less reactive than most elements, have high lustre, are softer or more ductile, and have higher melting points than other metals...
s. Because it is a clean and non-contact process it can be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere. Vacuum furnaces make use of induction heating for the production of specialty steels and other alloys that would oxidize if heated in the presence of air.
Induction welding
A similar, smaller-scale process is used for induction weldingInduction welding
Induction welding is a form of welding that uses electromagnetic induction to heat the workpiece. The welding apparatus contains an induction coil that is energised with a radio-frequency electric current. This generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field that acts on either an electrically...
. Plastics may also be welded by induction, if they are either doped with ferromagnetic ceramics (where magnetic hysteresis of the particles provides the heat required) or by metallic particles.
Seams of tubes can be welded this way. Currents induced in a tube run along the open seam and heat the edges resulting in a temperature high enough for welding. At this point the seam edges are forced together and the seam is welded. The RF current can also be conveyed to the tube by brushes, but the result is still the same — the current flows along the open seam, heating it.
Induction cooking
In induction cookingInduction cooker
An induction cooker uses induction heating for cooking. Unlike other forms of cooking, heat is generated directly in the pot or pan , as opposed to being generated in the stovetop by electrical coils or burning gas...
, an induction coil in the cook-top heats the iron base of cookware. Copper-bottomed pans, aluminium pans and other non-ferrous pans are generally unsuitable.
The heat induced in the base is transferred to the food via (metal surface) conduction
Heat conduction
In heat transfer, conduction is a mode of transfer of energy within and between bodies of matter, due to a temperature gradient. Conduction means collisional and diffusive transfer of kinetic energy of particles of ponderable matter . Conduction takes place in all forms of ponderable matter, viz....
. Benefits of induction cookers include efficiency, safety (the induction cook-top is not heated itself) and speed. Drawbacks include the fact that non-ferrous and other cookware such as glass and ceramic cannot be used on an induction cook-top. Both installed and portable induction cookers are available.
Induction brazing
Induction brazingInduction brazing
Induction brazing is when two or more materials are joined together by a filler metal that has a lower melting point than the base materials using induction heating...
is often used in higher production runs. It produces uniform results and is very repeatable.
Heating to fit
Induction heating is often used to heat an item causing it to expand prior to fitting or assembly. Bearings are routinely heated in this way using mains frequency (50/60 Hz) and a laminated steel transformer type core passing through the centre of the bearing.Heat treatment
Induction heating is often used in the heat treatmentHeat treatment
Heat treating is a group of industrial and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as glass...
of metal items.
The most common applications are induction hardening
Induction hardening
Induction hardening is a form of heat treatment in which a metal part is heated by induction heating and then quenched. The quenched metal undergoes a martensitic transformation, increasing the hardness and brittleness of the part...
of steel parts, induction soldering
Soldering
Soldering is a process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the workpiece...
/brazing
Brazing
Brazing is a metal-joining process whereby a filler metal is heated above and distributed between two or more close-fitting parts by capillary action. The filler metal is brought slightly above its melting temperature while protected by a suitable atmosphere, usually a flux...
as a means of joining metal components and induction annealing
Annealing (metallurgy)
Annealing, in metallurgy and materials science, is a heat treatment wherein a material is altered, causing changes in its properties such as strength and hardness. It is a process that produces conditions by heating to above the recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature, and...
to selectively soften a selected area of a steel part.
Induction heating can produce high power densities which allow short interaction times to reach the required temperature. This gives tight control of the heating pattern with the pattern following the applied magnetic field quite closely and allows reduced thermal distortion and damage.
This ability can be used in hardening to produce parts with varying properties. The most common hardening process is to produce a localised surface hardening of an area that needs wear-resistance, while retaining the toughness of the original structure as needed elsewhere. The depth of induction hardened patterns can be controlled through choice of induction-frequency, power-density and interaction time.
There are limits to the flexibility of the process - mainly arising from the need to produce dedicated inductors for many applications. This is quite expensive and requires the marshalling of high current-densities in small copper inductors, which can require specialized engineering and 'copper-fitting'.
Induction heating for Plastic processing
Induction heating is often used in the industrial applications of plastic process with injection and extrusion machines.The induction heating improves energy efficiency for injection and extrusion plastic processes.
- The heating is applied direct to the cylindrical barrel melting the plastic material without the heat transfer delay time that ordinary elements have, resulting in:
- faster machine start up
- the induction coil is powered within 1/4 the time heater band elements of the same amps do for the same amount of heat absorption, reducing energy consumption
- to replace a heater band element with an induction heating system 40% lower current inverter is used, thereby reducing maximum consumption capacity; even after the reduction in power capacity, the heating capacity is increased by 50%
- The increased heating capacity further reduces starting up time by 50%
- The barrel melting the plastic material is insulated with 15 mm ceramic insulation and in that way
- heat is not escaping to the environment and we have significant energy saving
- the induction coils are not getting heated up from the heat generated in the barrel so they operate in low temperature resulting in long life expectancy when ornery heater band elements if insulation is used there life expectancy is reduced dramatically
- The frequencies used start from 30 kHz and are reduced to 5 kHz as the barrel thickness increases
- The distance of the coil from the barrel surface is reduced as the diameter of the barrel increase
The technology cost of applying to industrial equipment as injection and extrusion machines is reduced as time goes on and inverter technology is advances
Details
The basic setup is an ACAlternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
power supply that provides electricity with low volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
age but very high current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
and high frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
. The workpiece to heat is placed inside an air coil driven by the power supply, usually in combination with a resonant tank capacitor to increase the reactive power. The alternating magnetic field induces eddy current
Eddy current
Eddy currents are electric currents induced in conductors when a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field; due to relative motion of the field source and conductor or due to variations of the field with time. This can cause a circulating flow of electrons, or current, within the body of...
s in the workpiece.
| Frequency (kHz) | Workpiece type |
|---|---|
| 5–30 | Thick materials |
| 100–400 | Small workpieces or shallow penetration |
| 480 | Microscopic pieces |
Magnetic materials improve the induction heat process because of hysteresis. In essence materials with high permeability
Permeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
(100–500) are easier to heat with induction heating. Hysteresis heating occurs below the Curie temperature
Curie point
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature , or Curie point, is the temperature at which a ferromagnetic or a ferrimagnetic material becomes paramagnetic on heating; the effect is reversible. A magnet will lose its magnetism if heated above the Curie temperature...
where materials lose their magnetic properties.
So high permeability and temperatures below Curie temperature in the workpiece is useful. Also temperature difference, mass, and specific heat influence the workpiece heating.
The energy transfer of induction heating is coupled to the distance between the coil and the workpiece. Energy losses occur through heat conduction
Heat conduction
In heat transfer, conduction is a mode of transfer of energy within and between bodies of matter, due to a temperature gradient. Conduction means collisional and diffusive transfer of kinetic energy of particles of ponderable matter . Conduction takes place in all forms of ponderable matter, viz....
from workpiece to fixture, natural convection
Convective heat transfer
Convective heat transfer, often referred to as convection, is the transfer of heat from one place to another by the movement of fluids. The presence of bulk motion of the fluid enhances the heat transfer between the solid surface and the fluid. Convection is usually the dominant form of heat...
, and thermal radiation
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation....
.
The induction coil is usually made of 3.175–4.7625 mm diameter copper tubing and fluid cooled. Diameter, shape, and number of turns influence the efficiency and field pattern.

