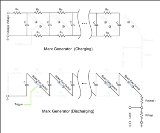
Marx generator
Encyclopedia

Erwin Otto Marx
Erwin Otto Marx was a German electrical engineer who invented the Marx generator, a device for producing high voltage electrical pulses.He worked as an engineering scientist in Braunschweig from 1918 to 1950 where he performed research and development for electrical power distribution via long...
in 1924. Its purpose is to generate a high-voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
pulse. Marx generators are often used to simulate the effects of lightning on power line gear
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
and aviation equipment.
A bank of 36 Marx generators is used by Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia National Laboratories
The Sandia National Laboratories, managed and operated by the Sandia Corporation , are two major United States Department of Energy research and development national laboratories....
to generate X-rays in their Z Machine
Z machine
The Z machine is the largest X-ray generator in the world and is designed to test materials in conditions of extreme temperature and pressure. Operated by Sandia National Laboratories, it gathers data to aid in computer modeling of nuclear weapons...
.
Principle
A number of capacitors are charged in parallel to a given voltage, V, and then connected in series by spark gapSpark gap
A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the voltage difference between the conductors exceeds the gap's breakdown voltage, a spark forms,...
switches, ideally producing a voltage of V multiplied by the number, n, of capacitors (or stages). Due to various practical constraints, the output voltage is somewhat less than n×V.
Optimization
Proper performance depends upon selection of capacitorCapacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
and the timing of the discharge. Switching times can be improved by doping of the electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s with radioactive isotopes caesium
Caesium
Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature...
137 or nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
63, and by orienting the spark gaps so that ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
light from a firing spark gap switch illuminates the remaining open spark gaps. Insulation of the high voltages produced is often accomplished by immersing the Marx generator in transformer oil
Transformer oil
Transformer oil or insulating oil is usually a highly-refined mineral oil that is stable at high temperatures and has excellent electrical insulating properties. It is used in oil-filled transformers, some types of high voltage capacitors, fluorescent lamp ballasts, and some types of high voltage...
or a high pressure electronegative gas such as sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
Note that the less resistance there is between the capacitor and the charging power supply, the faster it will charge. Thus, in this design, those closer to the power supply will charge quicker than those farther away. If the generator is allowed to charge long enough, all capacitors will attain the same voltage.
In the ideal case, the closing of the switch closest to the charging power supply applies a voltage 2V to the second switch. This switch will then close, applying a voltage 3V to the third switch. This switch will then close, resulting in a cascade down the generator that produces nV at the generator output (again, only in the ideal case).
The first switch may be allowed to spontaneously break down (sometimes called a self break) during charging if the absolute timing of the output pulse is unimportant. However, it is usually intentionally triggered once all the capacitors in the Marx bank have reached full charge, either by reducing the gap distance, by pulsing an additional trigger electrode (such as a Trigatron
Trigatron
A trigatron is a type of triggerable spark gap switch designed for high current and high voltage, . It has very simple construction and in many cases is the lowest cost high energy switching option. It may operate in open air, it may be sealed, or it may be filled with a dielectric gas other than air...
), by ionising the air in the gap using a pulsed laser, or by reducing the air pressure within the gap.
The charging resistors, Rc, need to be properly sized for both charging and discharging. They are sometimes replaced with inductors
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
for improved efficiency and faster charging. In many generators the resistors are made from plastic or glass tubing filled with dilute copper sulfate solution. These liquid resistors overcome many of the problems experienced by more-conventional solid resistive materials, which have a tendency to lower their resistance over time under high voltage conditions.
Short pulses
The Marx generator is also used to generate short high-power pulses for Pockels cells, driving a TEA laserTEA laser
A TEA laser is a transversely-excited atmospheric-pressure laser.-Invention:The CO2 TEA laser was invented in the late 1960s by Dr Jacques Beaulieu working at the Defence Research Establishment, Valcartier, in Quebec, Canada...
, ignition of the conventional explosive of a nuclear weapon, and radar pulses.
Shortness is relative, as the switching time of even high-speed versions is not less than 1 ns, and thus many low-power electronic devices are faster. In the design of high-speed circuits, electrodynamics is important, and the Marx generator supports this insofar as it uses short thick leads between its components, but the design is nevertheless essentially an electrostatic one. (In electrodynamic terms, when the first stage breaks down it creates a spherical electromagnetic wave whose electric field vector is opposed to the static high voltage. This moving electromagnetic field has the wrong orientation to trigger the next stage, and may even reach the load; such noise in front of the edge is undesirable in many switching applications. If the generator is inside a tube of (say) 1 m diameter, it requires around 10 wave reflections for the field to settle to static conditions, which restricts pulse leading edge width to 30 ns or more. Smaller devices are of course faster.) When the first gap breaks down, pure electrostatic theory predicts that the voltage across all stages rises. However, stages are coupled capacitively to ground and serially to each other, and thus each stage encounters a voltage rise that is increasingly weaker the further the stage is from the switching one; the adjacent stage to the switching one therefore encounters the largest voltage rise, and thus switches in turn. As more stages switch, the voltage rise to the remainder increases, which speeds up their operation. Thus a voltage rise fed into the first stage becomes amplified and steepened at the same time.
The speed of a switch is determined by the speed of the charge carriers, which gets higher with higher voltage, and by the current available to charge the inevitable parasitic capacity. In solid-state avalanche devices, a high voltage automatically leads to high current. Because the high voltage is applied only for a short time, solid-state switches will not heat up excessively. As compensation for the higher voltages encountered, the later stages have to carry lower charge too. Stage cooling and capacitor recharging also go well together.
Stage variants
Avalanche diodeAvalanche diode
In electronics, an avalanche diode is a diode that is designed to go through avalanche breakdown at a specified reverse bias voltage. The junction of an avalanche diode is designed to prevent current concentration at hot spots, so that the diode is undamaged by the breakdown...
s can replace the spark gap for stage voltages less than 500 volts. The charge carriers easily leave the electrodes, so no extra ionisation is needed and jitter is low. The diodes also have a longer lifetime than spark gaps.
A speedy switching device is an NPN avalanche transistor
Avalanche transistor
An avalanche transistor is a bipolar junction transistor designed for operation in the region of its collector-current/collector-to-emitter voltage characteristics beyond the collector to emitter breakdown voltage, called avalanche breakdown region ...
fitted with a coil between base and emitter. The transistor is initially switched off and about 300 volts exists across its collector-base junction. This voltage is high enough that a charge carrier in this region can create more carriers by impact ionisation, but the probability is too low to form a proper avalanche; instead a somewhat noisy leakage current flows. When the preceding stage switches, the emitter-base junction is pushed into forward bias and the collector-base junction enters full avalanche mode, so charge carriers injected into the collector-base region multiply in a chain reaction. Once the Marx generator has completely fired, voltages everywhere drop, each switch avalanche stops, its matched coil puts its base-emitter junction into reverse bias, and the low static field allows remaining charge carriers to drain out of its collector-base junction.
Applications
One application is so-called boxcarBoxcar function
In mathematics, a boxcar function is any function which is zero over the entirereal line except for a single interval where it is equal to a constant, A; it is a simple step function...
switching of a Pockels cell. Four Marx generators are used, each of the two electrodes of the Pockels cell being connected to a positive pulse generator and a negative pulse generator. Two generators of opposite polarity, one on each electrode, are first fired to charge the Pockels cell into one polarity. This will also partly charge the other two generators but not trigger them, because they have been only partly charged beforehand. Leakage through the Marx resistors needs to be compensated by a small bias current through the generator. At the trailing edge of the boxcar, the two other generators are fired to "reverse" the cell.
Marx generators are used to provide high-voltage pulses for the testing of insulation of electrical apparatus such as large power transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s, or insulators used for supporting power transmission lines. Voltages applied may exceed 2 million volts for high-voltage apparatus.
See also
- Cockcroft-Walton generatorCockcroft-Walton generatorThe Cockcroft–Walton generator, or multiplier, is an electric circuit which generates a high DC voltage from a low voltage AC or pulsing DC input...
- a similar circuit which has the same "ladder" structure. CW generator produces a constant DC. - Explosively pumped flux compression generatorExplosively pumped flux compression generatorAn explosively pumped flux compression generator is a device used to generate a high-power electromagnetic pulse by compressing magnetic flux using high explosive....
- A solution to the opposite problem of creating huge currents at lower voltages. - TransformerTransformerA transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
- An inductive circuit that is analogous to using mechanical gears to increase torque or speed. Can convert AC from one voltage and current, to another. Any increase in voltage will result in a reduction in current. The opposite is also true.
Further reading
- M. Obara, "Strip-Line Multichannel-Surface-Spark-Gap-Type Marx Generator for Fast Discharge Lasers", IEEE Conference Record of the 1980 Fourteenth Pulse Power Modulator Symposium, USA, Jun. 3-5, 1980, pp. 201–208.
- G. Bauer, "A low-impedance high-voltage nanosecond pulser", Journal of Scientific Instruments, London, GB, Jun. 1, 1968, vol. 1, pp. 688–689.
- Graham et al., "Compact 400 kV Marx Generator With Common Switch Housing", Pulsed Power Conference, 11th Annual Digest of Technical Papers 1997, vol. 2, pp. 1519–1523.
- S.M. Turnbull, "Development of a High Voltage, High PRF PFN Marx Generator", Conference Record of the 1998 23rd Int'l Power Modulation Symposium, pp. 213–16.
- R. Ness, et al. "Compact, Megavolt, Rep-Rated Marx Generators", IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 38, No. 4, 1991, pp. 803–809.
- Shkaruba et al., "Arkad'ev-Mark Generator with Capacitive Coupling", Instrum Exp Tech May-Jun. 1985, vol. 28, No. 3 part 2, May 1985, pp. 625–628, XP002080293.
- I. C. Sumerville, "A Simple Compact 1 MV, 4 kJ Marx", Proceedings of the Pulsed Power Conference, Monterey, California, Jun. 11-24, 1989, No. conf. 7, Jun. 11, 1989, pp. 744–746, XP000138799.
External links
- "Marx Generator". ecse.rpi.edu. (ed. explains the Febetron 2020 pulser experimented within the RPIRensselaer Polytechnic InstituteStephen Van Rensselaer established the Rensselaer School on November 5, 1824 with a letter to the Rev. Dr. Samuel Blatchford, in which van Rensselaer asked Blatchford to serve as the first president. Within the letter he set down several orders of business. He appointed Amos Eaton as the school's...
Plasma Dynamics Laboratory) - Jochen Kronjaeger, ""Marx generator". Jochen's High Voltage Page, 2003.
- Jim Lux, "Marx Generators", High Voltage Experimenter's Handbook, 3 May 1998.
- "The 'Quick & Dirty' Marx generator". Mike's Electric Stuff, May 2003.
- Abandoned Marx generator complex in Russia

