
Territorial evolution of Canada
Encyclopedia
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
was created in 1867 when three colonies of British North America
British North America
British North America is a historical term. It consisted of the colonies and territories of the British Empire in continental North America after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of American independence in 1783.At the start of the Revolutionary War in 1775 the British...
were united. One of these colonies split into two new provinces, three other colonies joined later. The new federation continued as a British colonial possession, gradually evolving into an independent nation several decades later.
Before being part of British North America, the provinces that made up the new Dominion of Canada were part of the colonies
Former colonies and territories in Canada
Former colonies, territories, boundaries, and claims in Canada prior to the current classification of provinces and territories. In North America, ethnographers commonly classify Aboriginals into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits and by related linguistic dialects...
of Canada
Canada, New France
Canada was the name of the French colony that once stretched along the St. Lawrence River; the other colonies of New France were Acadia, Louisiana and Newfoundland. Canada, the most developed colony of New France, was divided into three districts, each with its own government: Quebec,...
and Acadia
Acadia
Acadia was the name given to lands in a portion of the French colonial empire of New France, in northeastern North America that included parts of eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces, and modern-day Maine. At the end of the 16th century, France claimed territory stretching as far south as...
in New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
, which were gradually ceded to Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
and the United Kingdom after defeat in several wars. The French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
influence lived on, as the French language
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
was common in the initial provinces of Canada, and remains one of the two official languages of the country.
The central expanse of Canada was originally settled by the Hudson's Bay Company
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
of the Kingdom of England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
, which had a royal monopoly over trade in the region; Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America, consisting of the Hudson Bay drainage basin that was nominally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company for 200 years from 1670 to 1870, although numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the...
was named after the company's first director, Prince Rupert of the Rhine
Prince Rupert of the Rhine
Rupert, Count Palatine of the Rhine, Duke of Bavaria, 1st Duke of Cumberland, 1st Earl of Holderness , commonly called Prince Rupert of the Rhine, KG, FRS was a noted soldier, admiral, scientist, sportsman, colonial governor and amateur artist during the 17th century...
. The North West Company
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what was to become Western Canada...
later moved into a large portion of the region, and competition and minor hostilities between the two companies forced their merger. What was to become Colony of British Columbia
Colony of British Columbia
The Colony of British Columbia was a crown colony in British North America from 1858 until 1866. At its creation, it physically constituted approximately half the present day Canadian province of British Columbia, since it did not include the Colony of Vancouver Island, the vast and still largely...
was claimed as part of New Spain
New Spain
New Spain, formally called the Viceroyalty of New Spain , was a viceroyalty of the Spanish colonial empire, comprising primarily territories in what was known then as 'América Septentrional' or North America. Its capital was Mexico City, formerly Tenochtitlan, capital of the Aztec Empire...
and Russian America, until 1793 and 1825 respectively, and was for a time shared with the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
as what was known to Americans as the Oregon Country
Oregon Country
The Oregon Country was a predominantly American term referring to a disputed ownership region of the Pacific Northwest of North America. The region was occupied by British and French Canadian fur traders from before 1810, and American settlers from the mid-1830s, with its coastal areas north from...
, until in 1846 the border was extended west from the Rockies to the Pacific along the 49th parallel north
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
.
Since it was formed, Canada's external borders have changed seven times, and it has grown from four provinces to ten provinces and three territories
Provinces and territories of Canada
The provinces and territories of Canada combine to make up the world's second-largest country by area. There are ten provinces and three territories...
. It has only lost significant territory in the small border dispute with the Dominion of Newfoundland
Dominion of Newfoundland
The Dominion of Newfoundland was a British Dominion from 1907 to 1949 . The Dominion of Newfoundland was situated in northeastern North America along the Atlantic coast and comprised the island of Newfoundland and Labrador on the continental mainland...
over Labrador
Labrador
Labrador is the distinct, northerly region of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It comprises the mainland portion of the province, separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle...
, which joined Canada some time later.
Timeline
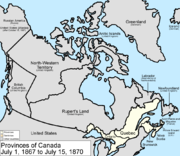
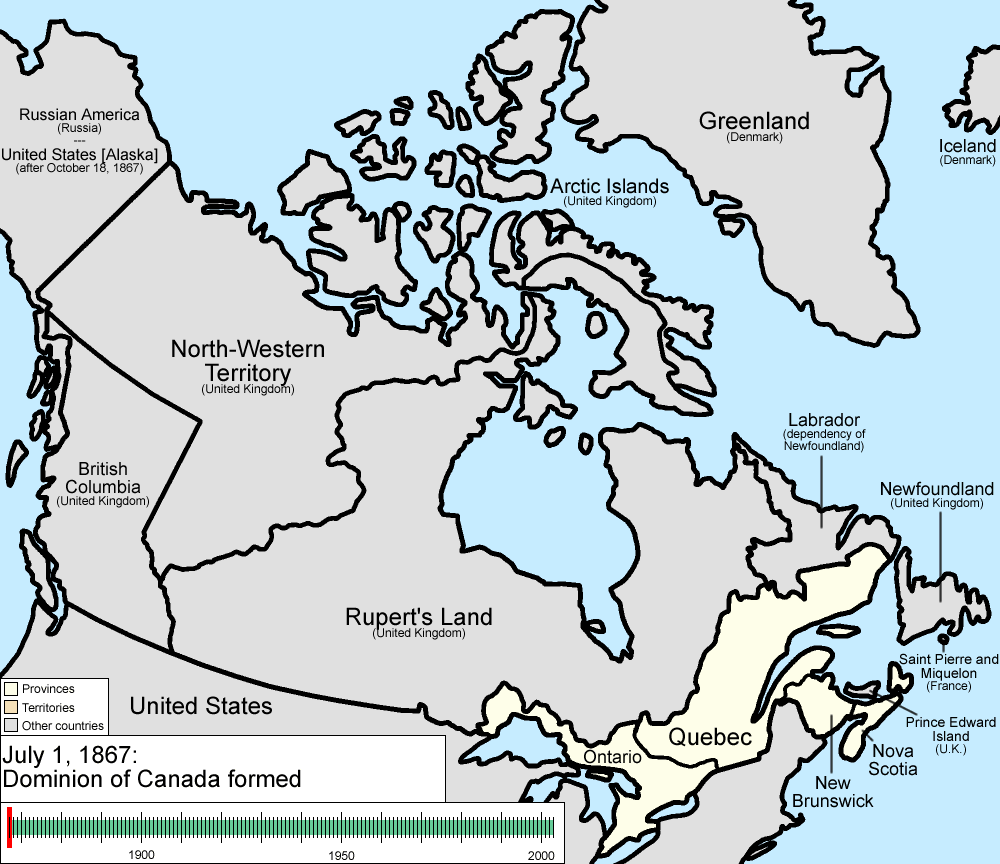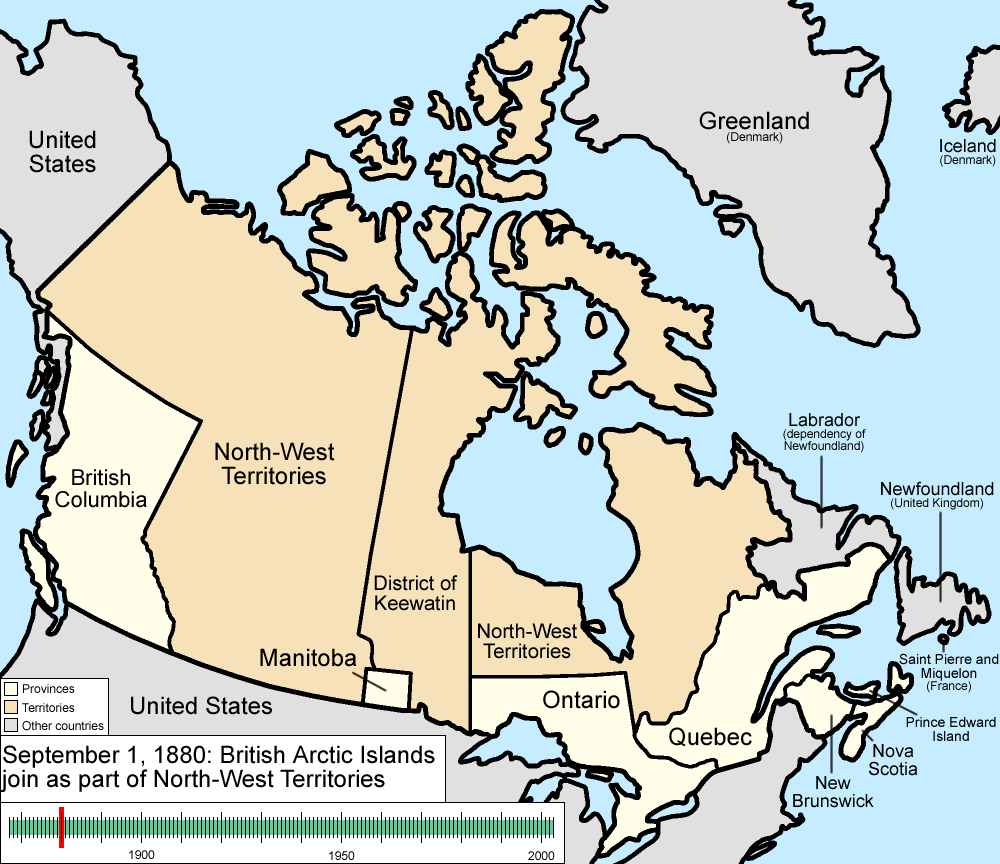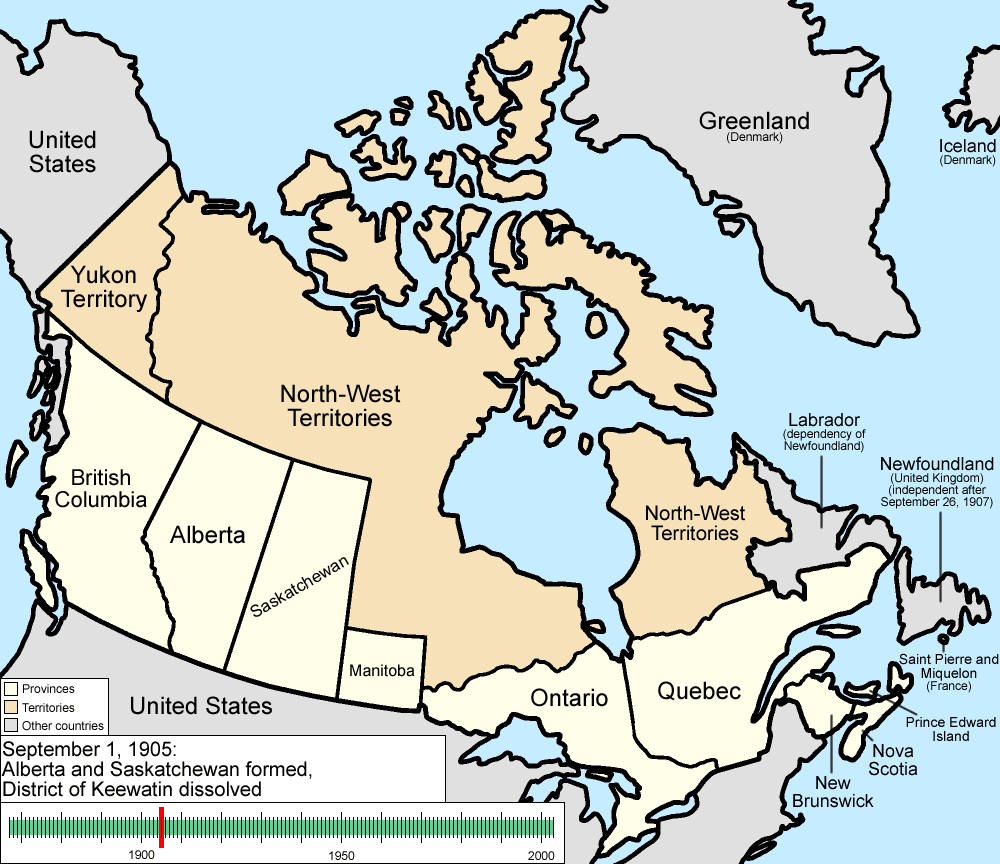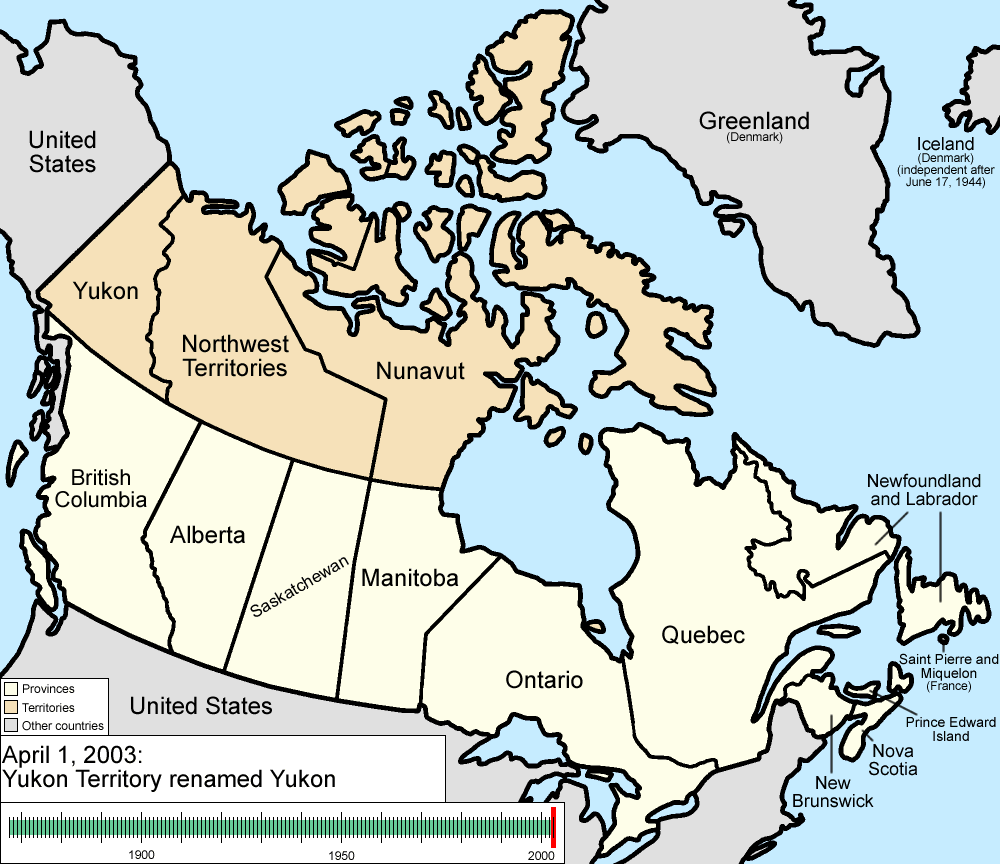
July 1, 1867
The Dominion of Canada was formed from three provincesCanadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation was the process by which the federal Dominion of Canada was formed on July 1, 1867. On that day, three British colonies were formed into four Canadian provinces...
of British North America
British North America
British North America is a historical term. It consisted of the colonies and territories of the British Empire in continental North America after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of American independence in 1783.At the start of the Revolutionary War in 1775 the British...
: the Province of Canada
Province of Canada
The Province of Canada, United Province of Canada, or the United Canadas was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of...
, which was split into the provinces of Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
and Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
, and the colonies of New Brunswick
New Brunswick
New Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the only province in the federation that is constitutionally bilingual . The provincial capital is Fredericton and Saint John is the most populous city. Greater Moncton is the largest Census Metropolitan Area...
and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
.

July 15, 1870
The United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
transferred most of its remaining land in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
to Canada, with Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America, consisting of the Hudson Bay drainage basin that was nominally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company for 200 years from 1670 to 1870, although numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the...
and the North-Western Territory
North-Western Territory
The North-Western Territory was a region of British North America until 1870. Named for where it lay in relation to Rupert's Land, the territory at its greatest extent covered what is now Yukon, mainland Northwest Territories, northwestern mainland Nunavut, northwestern Saskatchewan, northern...
becoming the North-West Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
. The Rupert's Land Act 1868 transferred the region to Canada as of 1869, but it was only consummated in 1870 when £300,000 were paid to the Hudson's Bay Company
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
. At this time, the Manitoba Act
Manitoba Act
The Manitoba Act, originally titled An Act to amend and continue the Act 32 and 33 Victoria, chapter 3; and to establish and provide for the Government of the Province of Manitoba, is an act of the Parliament of Canada that is defined by the Constitution Act, 1982 as forming a part of the...
took effect, and a small square of the newly acquired region surrounding the city of Winnipeg
Winnipeg
Winnipeg is the capital and largest city of Manitoba, Canada, and is the primary municipality of the Winnipeg Capital Region, with more than half of Manitoba's population. It is located near the longitudinal centre of North America, at the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine Rivers .The name...
was made the province of Manitoba
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
.
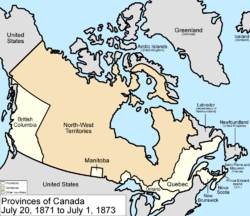
July 20, 1871
The BritishUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
colony
Colony of British Columbia
The Colony of British Columbia was a crown colony in British North America from 1858 until 1866. At its creation, it physically constituted approximately half the present day Canadian province of British Columbia, since it did not include the Colony of Vancouver Island, the vast and still largely...
of British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
joined Canada as the sixth province. British Columbia joined the Canadian confederation following The Great Confederation Debates in the spring of 1870 and the Confederation Negotiations of the following summer and winter.
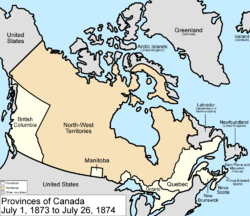
July 1, 1873
The British colony of Prince Edward IslandPrince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is a Canadian province consisting of an island of the same name, as well as other islands. The maritime province is the smallest in the nation in both land area and population...
joined Canada as the seventh province by an Act of Parliament (and, as part of the terms of union, was guaranteed a ferry
Ferry
A ferry is a form of transportation, usually a boat, but sometimes a ship, used to carry primarily passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo as well, across a body of water. Most ferries operate on regular, frequent, return services...
link, a term which was deleted upon completion of the Confederation Bridge
Confederation Bridge
The Confederation Bridge is a bridge spanning the Abegweit Passage of Northumberland Strait, linking Prince Edward Island with mainland New Brunswick, Canada. It was commonly referred to as the "Fixed Link" by residents of Prince Edward Island prior to its official naming. Construction took place...
in 1997).
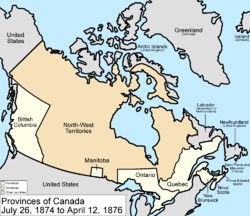
July 26, 1874
The borders of OntarioOntario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
were provisionally expanded north and west. When the Province of Canada was formed, its borders were not entirely clear, and Ontario claimed to eventually reach all the way to the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
and Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
. With Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America, consisting of the Hudson Bay drainage basin that was nominally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company for 200 years from 1670 to 1870, although numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the...
, Ontario was interested in clearly defining its borders, especially since some of the new areas it was interested in were rapidly growing. After the federal government asked Ontario to pay for construction in the new disputed area, the province asked for an elaboration on its limits, and its boundary was moved north to the 51st parallel north
51st parallel north
The 51st parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 51 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
.
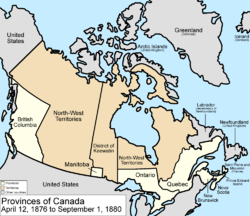
April 12, 1876
The District of KeewatinDistrict of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories.The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either kīwēhtin in Cree or giiwedin in Ojibwe—both of which mean north wind in their respective languages...
was created by the passage of the Keewatin Act on April 12, 1876 in a central separate strip from the North-West Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
, in order to provide government for the growing area north of Manitoba
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
and west of Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
.
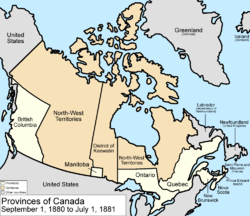
September 1, 1880
The United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
transferred its Arctic Islands
British Arctic Territories
British Arctic Territories were territories claimed by Britain in North America, consisting of the islands of what is now known in Canada as the High Arctic....
to Canada, and they were made part of the North-West Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
.
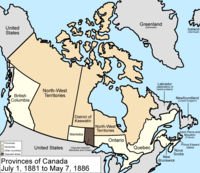
July 1, 1881
ManitobaManitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
's borders were expanded to a larger postage stamp province taking land easterly from the District of Keewatin
District of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories.The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either kīwēhtin in Cree or giiwedin in Ojibwe—both of which mean north wind in their respective languages...
to the western boundary of Ontario. Since the province's eastern border was defined as the "western boundary of Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
", the exact definition of which was still unclear, Ontario disputed a portion of the new region.
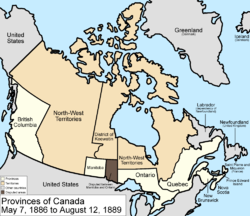
May 7, 1886
The southwestern border of the District of KeewatinDistrict of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories.The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either kīwēhtin in Cree or giiwedin in Ojibwe—both of which mean north wind in their respective languages...
was adjusted to conform to the boundaries of the new provisional districts of the North-West Territories created in 1882, returning some land to the North-West Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
. The provisional districts were, the District of Alberta
District of Alberta
The District of Alberta was one of four districts of the Northwest Territories created in 1882. It was styled the Alberta Provisional District to distinguish it from the District of Keewatin which had a more autonomous relationship from the NWT administration...
, the District of Athabasca
District of Athabasca
The District of Athabasca is a former district of Canada. Its northern boundary was the current southern boundary of the Northwest Territories and extended south to 55° north latitude. The westernmost part is now part of Alberta and most of the eastern part is now in Saskatchewan. The very...
, District of Assiniboia and the District of Saskatchewan
District of Saskatchewan
The District of Saskatchewan was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories. Much of the area was incorporated into the province of Saskatchewan. The western part became part of Alberta, and the eastern part is now part of Manitoba. Its capital was Prince Albert...
, which all remained administrative areas of the North-West Territories unlike the District of Keewatin
District of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories.The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either kīwēhtin in Cree or giiwedin in Ojibwe—both of which mean north wind in their respective languages...
.
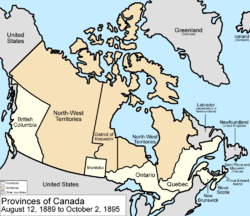
August 12, 1889
The dispute between ManitobaManitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
and Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
ended as Ontario's borders were finalized in accordance with the Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889, which extended the province west to the Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods is a lake occupying parts of the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Manitoba and the U.S. state of Minnesota. It separates a small land area of Minnesota from the rest of the United States. The Northwest Angle and the town of Angle Township can only be reached from the rest of...
and north to the Albany River
Albany River
The Albany River is a river in Northern Ontario, Canada, which flows northeast from Lake St. Joseph in Northwestern Ontario and empties into James Bay. It is long to the head of the Cat River, tying it with the Severn River for the title of longest river in Ontario...
.
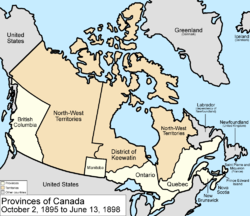
October 2, 1895
Keewatin covered the portion of the North-West Territories north of ManitobaManitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
on the mainland, and all islands within Hudson, James, and Ungava Bays. The portion between the District of Keewatin
District of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories.The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either kīwēhtin in Cree or giiwedin in Ojibwe—both of which mean north wind in their respective languages...
, Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, and Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
was not in a district, and was assigned to the District of Keewatin by an Order of Council. Four additional provisional districts of the North-West Territories were formed, the District of Yukon, the District of Ungava
District of Ungava
The District of Ungava was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories from 1895 to 1912. It covered the northern portion of what is today Quebec, the interior of Labrador and the offshore islands to the west and north, which are now part of the Nunavut.The continental...
, the District of Mackenzie
District of Mackenzie
The District of Mackenzie was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories. The district consisted of the portion of the Northwest Territories directly north of British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan on Canada's mainland....
, and the District of Franklin
District of Franklin
The District of Franklin was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories. The district consisted of the Canadian high Arctic Islands, notably Ellesmere Island, Baffin Island, and Victoria Island...
.
1897
The borders of the District of KeewatinDistrict of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories.The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either kīwēhtin in Cree or giiwedin in Ojibwe—both of which mean north wind in their respective languages...
were adjusted. Southampton Island
Southampton Island
Southampton Island is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of the island is stated as by Statistics Canada . It is the 34th largest...
, Coats Island
Coats Island
Coats Island lies at the northern end of Hudson Bay in the Kivalliq Region of Nunavut. At in size, it is the 107th largest island in the world, and Canada's 24th largest island....
, Mansel Island
Mansel Island
Mansel Island , a member of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an uninhabited island in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut. It is located in Hudson Bay off of Quebec's Ungava Peninsula. At in size, it is the 159th largest island in the world, and Canada's 28th largest island...
, Akimiski Island
Akimiski Island
Akimiski Island is the largest island in James Bay , Canada, which is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the territory of Nunavut. It has an area of , making it the 163rd largest island in the world, and Canada's 29th largest island. Akimiski Island is only from the province of Ontario...
, and other islands were transferred to Keewatin.
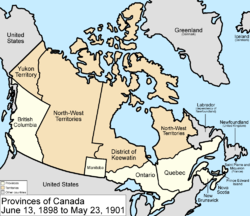
June 13, 1898
Yukon Territory was created from the District of Yukon in the northwestern part of the North-West TerritoriesNorthwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
, and the Quebec Boundary Extension Act, 1898
Quebec Boundary Extension Act, 1898
The Quebec Boundary Extension Act of 1898 was an act of the Parliament of Canada that expanded the territory of the province of Quebec. The province's northern boundary was set along the eastern shore of James Bay to the mouth of the Eastmain River, north along the river, then due east to the...
expanded the borders of Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
north to the Eastmain River
Eastmain River
The Eastmain River is a river in northwestern Quebec which rises in north central Quebec and flows 800 km west to drain into James Bay. 'East Main' is an old name for the east side of James Bay. This river drains an area of 46,400 km²...
.
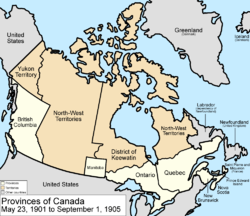
May 23, 1901
The eastern border of Yukon Territory was adjusted to the Peel RiverPeel River (Canada)
The Peel River is a tributary of the Mackenzie River in the Yukon and Northwest Territories in Canada. Its source is in the Ogilvie Mountains in the central Yukon at the confluence of the Ogilvie River and Blackstone River...
, so that the borders would not cross a watershed, and also to include some more islands.
October 20, 1903
The Alaska boundary disputeAlaska Boundary Dispute
The Alaska boundary dispute was a territorial dispute between the United States and Canada . It was resolved by arbitration in 1903. The dispute had been going on between the Russian and British Empires since 1821, and was inherited by the United States as a consequence of the Alaska Purchase in...
is resolved primarily in the favor of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.
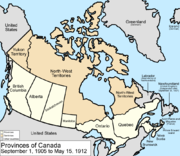
September 1, 1905
The provinces of AlbertaAlberta
Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which has an area of . Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota....
were created from the North-West Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
. Saskatchewan's western border and Alberta's eastern border run concurrent with the 4th meridian or the 110°W longitude. Saskatchewan's eastern border is not a meridian, but instead follows a staircase-shaped Dominion Land Survey
Dominion Land Survey
The Dominion Land Survey is the method used to divide most of Western Canada into one-square-mile sections for agricultural and other purposes. It is based on the layout of the Public Land Survey System used in the United States, but has several differences...
range line. Alberta's southern and northern borders are the same as Saskatchewan's: the southern border is the Canada – United States border or the 49th parallel
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
and the northern border is the 60th parallel
60th parallel north
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
. Alberta's western border runs along peaks of the Rocky Mountain ridge then extends north to the 60th parallel.
1906
The Northwest Territories Act was passed 1906, significantly removing the hyphen from the name of the territory.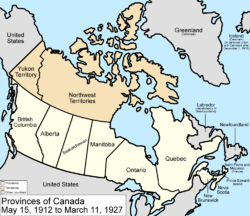
May 15, 1912
ManitobaManitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
, Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, and Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
were all expanded into their present-day boundaries. The Northwest Territories is now only situated north of the 60th parallel
60th parallel north
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
(except Hudson Bay and James Bay islands) with three districts, Keewatin, Mackenzie and Franklin.
1915
Brock IslandBrock Island
Brock Island is one of the uninhabited islands of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago located in the Northwest Territories, Canada. Located at 77°51'N 114°27'W, it measures in size and lies close to Mackenzie King Island. The first known sighting of the island was by Vilhjalmur Stefansson in...
, Borden Island
Borden Island
Borden Island is an uninhabited, low-lying island in the Queen Elizabeth Islands of northern Canada. With an area of in size, it is the 172nd largest island in the world, and Canada's 30th largest island...
, and Mackenzie King Island
Mackenzie King Island
Mackenzie King Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in northern Canada. It lies north of Melville Island and south of Borden Island, and like them is divided. Most of the island is in Northwest Territories, while its easternmost portion lies in Nunavut...
are discovered and added to the Northwest Territories.
1925
The boundaries of the Northwest Territories expand, and they now extend north to the North PoleNorth Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
.
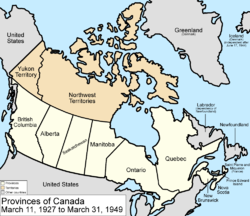
March 11, 1927
A BritishUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Privy Council of 1927 decided the issue of the border between Labrador
Labrador
Labrador is the distinct, northerly region of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It comprises the mainland portion of the province, separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle...
and Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
in Labrador's favour, transferring a small portion of land from Canada to the Dominion of Newfoundland
Dominion of Newfoundland
The Dominion of Newfoundland was a British Dominion from 1907 to 1949 . The Dominion of Newfoundland was situated in northeastern North America along the Atlantic coast and comprised the island of Newfoundland and Labrador on the continental mainland...
.
November 11, 1930
Sverdrup IslandsSverdrup Islands
The Sverdrup Islands is an archipelago of the northern Queen Elizabeth Islands, in Nunavut, Canada. The islands are situated in the Arctic Ocean, west of Ellesmere Island from 77° to 81° North and 85° to 106° West.- History :...
are ceded to Canada by Norway, in exchange for British recognition of Norway's soveriegnty over Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen Island is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and part of the Kingdom of Norway. It is long and 373 km2 in area, partly covered by glaciers . It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by an isthmus wide...
1948
Air Force IslandAir Force Island
Air Force Island is an uninhabited island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located along the southwestern coast of Baffin Island and measures in size....
, Prince Charles Island
Prince Charles Island
Prince Charles Island is a large, low-lying island with an area of , making it the world's 78th largest island and the 19th largest island in Canada. It is located in Foxe Basin, off the west coast of Baffin Island, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. Despite the island's size, it wasn't...
, and Foley Island
Foley Island
Foley Island is a low-lying Canadian arctic island located in Nunavut, Canada. It is along the southern coast of Baffin Island in the Foxe Basin and measures in area....
are discovered and added to Northwest Territories.
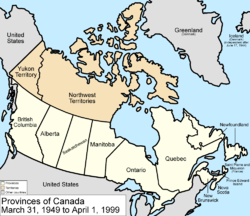
March 31, 1949
The Dominion of NewfoundlandDominion of Newfoundland
The Dominion of Newfoundland was a British Dominion from 1907 to 1949 . The Dominion of Newfoundland was situated in northeastern North America along the Atlantic coast and comprised the island of Newfoundland and Labrador on the continental mainland...
and its dependency of Labrador
Labrador
Labrador is the distinct, northerly region of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It comprises the mainland portion of the province, separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle...
joined as the tenth province
Provinces and territories of Canada
The provinces and territories of Canada combine to make up the world's second-largest country by area. There are ten provinces and three territories...
, named Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it incorporates the island of Newfoundland and mainland Labrador with a combined area of . As of April 2011, the province's estimated population is 508,400...
as proclaimed by the British North America Act 1949.
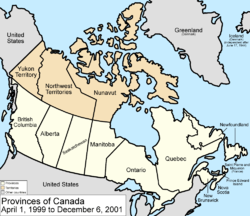
April 1, 1999
The territory of NunavutNunavut
Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993...
was created from the Northwest Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
. The provisional districts are no longer administrative areas of the Northwest Territories.
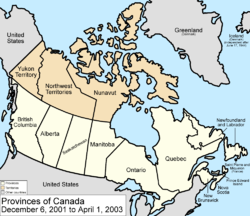
December 6, 2001
The province of Newfoundland was renamed Newfoundland and LabradorNewfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it incorporates the island of Newfoundland and mainland Labrador with a combined area of . As of April 2011, the province's estimated population is 508,400...
by the Constitution Amendment 2001 (Newfoundland and Labrador).

See also
- Former colonies and territories in CanadaFormer colonies and territories in CanadaFormer colonies, territories, boundaries, and claims in Canada prior to the current classification of provinces and territories. In North America, ethnographers commonly classify Aboriginals into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits and by related linguistic dialects...
- List of areas disputed by Canada and the United States
- Northwest Passage international waters dispute
- Territorial claims in the ArcticTerritorial claims in the ArcticUnder international law, no country currently owns the North Pole or the region of the Arctic Ocean surrounding it. The five surrounding Arctic states, Russia, the United States, Canada, Norway and Denmark , are limited to an exclusive economic zone of adjacent to their coasts.Upon ratification...
- Territorial evolution of North America since 1763

