Sub-replacement fertility
Encyclopedia
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate
(TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the previous one in a given area. In developed countries sub-replacement fertility is any rate below approximately 2.1 children born per woman, but the threshold can be as high as 3.4 in some developing countries because of higher mortality rates
. Taken globally, the total fertility rate at replacement was 2.33 children per woman in 2003. This can be "translated" as 2 children per woman to replace the parents, as well as a third to make up for infertile women and men, those who do not wish to have children, the higher probability of boys
being born, and early mortality prior to the end of their fertile life.
Replacement level fertility in terms of the net reproduction rate
(NRR) is exactly one, because the NRR takes both mortality rates and sex ratios at birth into account.
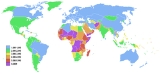
 Today about 42% of the world population lives in nations with sub-replacement fertility. Nonetheless most of these countries still have growing populations due to immigration
Today about 42% of the world population lives in nations with sub-replacement fertility. Nonetheless most of these countries still have growing populations due to immigration
, population momentum
and increase of the life expectancy
. This includes most nations of Europe
, Canada
, Australia
, Russia
, Iran
, Tunisia
, China
, Japan
, and many others. The countries or areas that have the lowest fertility are Hong Kong
, Macau
, Singapore
, Taiwan
, Ukraine
and Lithuania
. Only a few countries have low enough or sustained sub-replacement fertility (sometimes combined with other population factors like emigration
) to have population decline
, such as Japan
, Germany
, Lithuania
, and Ukraine
.
 There have been a number of explanations for the general decline in fertility rates in much of the world, and the true explanation is almost certainly a combination of different factors.
There have been a number of explanations for the general decline in fertility rates in much of the world, and the true explanation is almost certainly a combination of different factors.
and human development
are related to this phenomenon (see the Demographic-economic paradox
). High costs of living and job insecurity can make it difficult for young people to marry and start families.
around the world is considered by some a central cause. In recent times, residents of urban areas tend to have fewer children than people in rural areas,. The need for extra labour from children on farms does not apply to urban-dwellers. Cities tend to have higher property prices, making a large family more expensive, especially in those societies where each child is now expected to have his own bedroom, rather than sharing with siblings as was the case until recently. Rural areas also tend to be more conservative with less contraception
and abortion
than urban areas.
.
The other way around, the same review also stated that government support of assisted reproductive technology
is beneficial for families, but its effect on total fertility rate in Europe is extremely small.
Other social changes both separate and related to feminism also have played a role. Bearing children is regarded as less of a social duty than it once was in many societies. Women's social status increasingly correlates with their work or behaviour as consumers rather than from their role as mothers. Indeed having a large family is often socially deprecated, being associated with lower status groups.
and Iran
) have launched programs to reduce fertility rates and curb population growth. (See One-child policy
in China and Family planning in Iran
.)
Specifically, if the age of childbearing increases – but assuming that the total number of births over a life cycle remains unchanged – then while this increase is happening, the measured TFR is lower (the births happen in a later year), but when the age of childbearing stops increasing the TFR increase, due to these births catching up. For illustration, if in the past women always had 1 child at the age of 20 (TFR of 1), but suddenly in the year 2000 all women born in 1980 or later postponed having children until age 30, there would suddenly be no births for 10 years (TFR of 0), and then 10 years later (2010) it would suddenly jump back up (TFR of 1) (assuming flat population structure, no deaths, etc.), even though the life cycle TFR was always 1.
Thus, period TFR reflects not only life cycle TFR, but also timing effects, and these effects are conflated in a simple period TFR number. Life cycle TFR is unambiguous, and strict measure of life cycle fertility are not affected by this effect (e.g., counting the average children that have been born to all women who cease child-bearing in a given year (via menopause, sterilization, death, etc.)), but are lagging statistics because they require women to cease child-bearing before they are counted. Thus, adjusted measures of TFR – period TFR, adjusted for timing – are proposed instead to give a more accurate measure of life cycle fertility, without needing to wait until women have definitively ceased bearing children.
Thus, if age of childbearing is increasing and life cycle fertility is decreasing, period TFR will initially overstate the decline, and then may have a spurious increase even if life cycle fertility is actually still declining. This is computed to be the case in Spain in the period 1980–2002, for instance.
John Bongaarts and Griffith Feeney have suggested that this tempo effect is driving the decline of measured fertility rate in the developed world. Taking tempo changes into account, adjusted birth rates for a number of European countries are higher than the conventional TFR. A particularly strong example is the Czech Republic in the period 1992–2002, which witnessed a steady rise in childbearing age, hence the period TFR dropped sharply, overstating the decline in life cycle fertility.
: recently high fertility rates produce a disproportionately young population, and younger populations have higher birth rates. This is why some nations with sub-replacement fertility still have a growing population, because a relatively large fraction of their population are still of child-bearing age. But if the fertility trend is sustained (and not compensated by immigration
), it results in population ageing
and population decline
. This is forecast for most of the countries of Europe
and East Asia
.
Current estimates expect the world's total fertility rate to fall below replacement levels by 2050,
although population momentum will continue to increase global population for several generations beyond that. The promise of eventual population decline helps reduce concerns of overpopulation
, but many believe the Earth's carrying capacity
has already been exceeded and that even a stable population would not be sustainable
.
Sub-replacement fertility can also change social relations in a society. Fewer children, combined with lower infant mortality
has also made the death of children a far greater tragedy in the modern world than it was just fifty years ago. Having many families with only one or two children also reduces greatly the number of sibling
s, aunts and uncles.
Population aging poses an economic cost on societies, as the number of elderly retirees rises in relation to the number of young workers. This has been raised as a political issue in France
, Germany
, and the United States
, where many people have advocated policy changes to encourage higher fertility and immigration rates. In France, payments to couples to have children have increased birthrate.
Attempts to increase the fertility rate among working women bring difficult political dilemmas: how far to alter traditional working practices so that women who are juggling work and child-raising responsibilities are not disadvantaged in their careers compared with men (for example, by legislating for compulsory paternity leave, flexible working and/or limiting total weekly working hours for men as well as women) and above all the question of whether the problem of sub-replacement fertility is so serious that unmarried women should also now be encouraged to have more children.
Giving women paid maternity leave can have the unintended negative consequence of dissuading employers from hiring women because they may fear having to pay a pregnant woman wages for a job she isn't doing. This may increase the gender-wage gap, the income disparity between men and women in the labor force. This disincentive can be ameliorated by giving parental leave to both men and women.
Germany’s family minister Ursula von der Leyen
has stated that the slight increase in Germany
, Italy
, and other European countries with low fertility might be the first small steps to an eventual recovery. Although the increase will so far not counter an expected population decline it will however slow it down. European analysts hope, with the help of government incentives and large-scale change towards family-friendly policies, to stall the population decline and reverse it by around 2030, expecting that most of Europe will have a slight natural increase by then. C. D. Howe Institute
, for example, tries to demonstrate that immigration can not be used to effectively counter population ageing
.
' rates have remained stable and even slightly increased. This is largely due to the high fertility rate among communities such as Hispanics, but it is also because the fertility rate among non-Hispanic whites
in the US, after falling to about 1.6 in the 1970s and early 1980s, had increased and is now around 1.9, or slightly below replacement level, rather than collapsing to the 1.3-1.5 level common in Europe.
New England
has a rate similar to most Western European countries, while the South, Midwest, and border states have fertility rates considerably higher than replacement. States where The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has a strong presence, most notably Utah
, also have higher-than-replacement fertility rates, especially among the LDS population. Heaton and Goodman (1985) found that LDS women average about one child more than women in other religious groups.
, which recorded a TFR of over 2.00 in 2008, Australia
, where the birth rate rose from 1.73 in 2001 to 1.93 in 2007 and New Zealand
, where the TFR was 2.2 in 2008. A few developed countries have never had sub-replacement fertility for reasons that are unique to the particular country. One example of that is Israel, where the growing Arab and religious Jewish populations (mostly Haredim) have high fertility rates, and the aliyah
of Jews from the diaspora
also contributes to Israel's population growth.
Economic dynamics:
Total Fertility Rate
The total fertility rate of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates through her lifetime, and she...
(TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the previous one in a given area. In developed countries sub-replacement fertility is any rate below approximately 2.1 children born per woman, but the threshold can be as high as 3.4 in some developing countries because of higher mortality rates
Mortality rate
Mortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
. Taken globally, the total fertility rate at replacement was 2.33 children per woman in 2003. This can be "translated" as 2 children per woman to replace the parents, as well as a third to make up for infertile women and men, those who do not wish to have children, the higher probability of boys
Sex ratio
Sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population. The primary sex ratio is the ratio at the time of conception, secondary sex ratio is the ratio at time of birth, and tertiary sex ratio is the ratio of mature organisms....
being born, and early mortality prior to the end of their fertile life.
Replacement level fertility in terms of the net reproduction rate
Net reproduction rate
The net reproduction rate is the average number of daughters that would be born to a female if she passed through her lifetime conforming to the age-specific fertility and mortality rates of a given year. This rate is similar to the gross reproduction rate but takes into account that some females...
(NRR) is exactly one, because the NRR takes both mortality rates and sex ratios at birth into account.

Immigration
Immigration is the act of foreigners passing or coming into a country for the purpose of permanent residence...
, population momentum
Population momentum
Population momentum refers to population growth at the national level which would occur even if levels of childbearing immediately declined to replacement level. For countries with above-replacement fertility , population momentum represents natural increase to the population...
and increase of the life expectancy
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
. This includes most nations of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
, Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
, China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, Japan
Aging of Japan
The ageing of Japan outweighs all other nations with the highest proportion of elderly citizens, 21% over the age of 65. In 1989, only 11.6% of the population was 65 years or older, but projections were that 25.6% would be in that age category by 2030...
, and many others. The countries or areas that have the lowest fertility are Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
, Macau
Macau
Macau , also spelled Macao , is, along with Hong Kong, one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China...
, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
. Only a few countries have low enough or sustained sub-replacement fertility (sometimes combined with other population factors like emigration
Emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving one's country or region to settle in another. It is the same as immigration but from the perspective of the country of origin. Human movement before the establishment of political boundaries or within one state is termed migration. There are many reasons why people...
) to have population decline
Population decline
Population decline can refer to the decline in population of any organism, but this article refers to population decline in humans. It is a term usually used to describe any great reduction in a human population...
, such as Japan
Aging of Japan
The ageing of Japan outweighs all other nations with the highest proportion of elderly citizens, 21% over the age of 65. In 1989, only 11.6% of the population was 65 years or older, but projections were that 25.6% would be in that age category by 2030...
, Germany
Demographics of Germany
The Demographics of Germany were determined also by a series of full Census in Germany, with the most recent held in 1987. Since reunification, German authorities rely on a micro census....
, Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
.
Causes

Economic development
The growth of wealthGross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
and human development
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
are related to this phenomenon (see the Demographic-economic paradox
Demographic-economic paradox
The demographic-economic paradox is the inverse correlation found between wealth and fertility within and between nations. The higher the degree of education and GDP per capita of a human population, subpopulation or social stratum, the fewer children are born in any industrialized country...
). High costs of living and job insecurity can make it difficult for young people to marry and start families.
Urbanization
The increase of urbanizationUrbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
around the world is considered by some a central cause. In recent times, residents of urban areas tend to have fewer children than people in rural areas,. The need for extra labour from children on farms does not apply to urban-dwellers. Cities tend to have higher property prices, making a large family more expensive, especially in those societies where each child is now expected to have his own bedroom, rather than sharing with siblings as was the case until recently. Rural areas also tend to be more conservative with less contraception
Contraception
Contraception is the prevention of the fusion of gametes during or after sexual activity. The term contraception is a contraction of contra, which means against, and the word conception, meaning fertilization...
and abortion
Abortion
Abortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from the uterus of a fetus or embryo prior to viability. An abortion can occur spontaneously, in which case it is usually called a miscarriage, or it can be purposely induced...
than urban areas.
Contraception
Changes in contraception are also an important cause, and one that has seen dramatic changes in the last few generations. Legalization, and widespread acceptance, of contraception in the developed world is a large factor in decreased fertility levels. A systematic review, however, came to the result that European fertility rates do not seem to be decreased significantly by availability of contraceptionContraception
Contraception is the prevention of the fusion of gametes during or after sexual activity. The term contraception is a contraction of contra, which means against, and the word conception, meaning fertilization...
.
The other way around, the same review also stated that government support of assisted reproductive technology
Assisted reproductive technology
Assisted reproductive technology is a general term referring to methods used to achieve pregnancy by artificial or partially artificial means. It is reproductive technology used primarily in infertility treatments. Some forms of ART are also used in fertile couples for genetic reasons...
is beneficial for families, but its effect on total fertility rate in Europe is extremely small.
Female social role
Growing female participation in the work force has led to many women delaying or deciding against having children, or to not have as many. A longer pursuit of education also delays marriages. Greater access to contraception and abortion, and greater proclivity of women to use them, also has reduced rates.Other social changes both separate and related to feminism also have played a role. Bearing children is regarded as less of a social duty than it once was in many societies. Women's social status increasingly correlates with their work or behaviour as consumers rather than from their role as mothers. Indeed having a large family is often socially deprecated, being associated with lower status groups.
Government policies
Some governments (e.g. those of ChinaChina
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
and Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
) have launched programs to reduce fertility rates and curb population growth. (See One-child policy
One-child policy
The one-child policy refers to the one-child limitation applying to a minority of families in the population control policy of the People's Republic of China . The Chinese government refers to it under the official translation of family planning policy...
in China and Family planning in Iran
Family planning in Iran
The Republic of Iran has a comprehensive and effective program of family planning. While Iran's population grew at a rate of more than 3%/year between 1956 and 1986, the growth rate began to decline in the late 1980s and early 1990s after the government initiated a major population control program...
.)
Religiosity
Religiousness have been found to have virtually no causal relationship to fertility rates.Tempo effect
In the conventionally reported measure of TFR, the period TFR (based on the level of fertility or number of births in a given year), there is a statistical effect called the tempo effect which makes it a misleading measure of overall (life cycle) fertility.Specifically, if the age of childbearing increases – but assuming that the total number of births over a life cycle remains unchanged – then while this increase is happening, the measured TFR is lower (the births happen in a later year), but when the age of childbearing stops increasing the TFR increase, due to these births catching up. For illustration, if in the past women always had 1 child at the age of 20 (TFR of 1), but suddenly in the year 2000 all women born in 1980 or later postponed having children until age 30, there would suddenly be no births for 10 years (TFR of 0), and then 10 years later (2010) it would suddenly jump back up (TFR of 1) (assuming flat population structure, no deaths, etc.), even though the life cycle TFR was always 1.
Thus, period TFR reflects not only life cycle TFR, but also timing effects, and these effects are conflated in a simple period TFR number. Life cycle TFR is unambiguous, and strict measure of life cycle fertility are not affected by this effect (e.g., counting the average children that have been born to all women who cease child-bearing in a given year (via menopause, sterilization, death, etc.)), but are lagging statistics because they require women to cease child-bearing before they are counted. Thus, adjusted measures of TFR – period TFR, adjusted for timing – are proposed instead to give a more accurate measure of life cycle fertility, without needing to wait until women have definitively ceased bearing children.
Thus, if age of childbearing is increasing and life cycle fertility is decreasing, period TFR will initially overstate the decline, and then may have a spurious increase even if life cycle fertility is actually still declining. This is computed to be the case in Spain in the period 1980–2002, for instance.
John Bongaarts and Griffith Feeney have suggested that this tempo effect is driving the decline of measured fertility rate in the developed world. Taking tempo changes into account, adjusted birth rates for a number of European countries are higher than the conventional TFR. A particularly strong example is the Czech Republic in the period 1992–2002, which witnessed a steady rise in childbearing age, hence the period TFR dropped sharply, overstating the decline in life cycle fertility.
Partnership instability
Another explanation for falling fertility could be a reduction in the frequency of sex in populations with low birth rates. For example, according to a survey published by the Japanese Family Planning Association in March 2007, a record 39.7 per cent of Japanese citizens aged 16–49 had not had sex for more than a month.http://www.ctv.ca/servlet/ArticleNews/story/CTVNews/20070314/japan_sex_070314/20070314?hub=Health A study came to the result that instability of modern partnerships is a major cause of European sub-replacement fertility.Effects
Sub-replacement fertility do not immediately translate into a population decline because of population momentumPopulation momentum
Population momentum refers to population growth at the national level which would occur even if levels of childbearing immediately declined to replacement level. For countries with above-replacement fertility , population momentum represents natural increase to the population...
: recently high fertility rates produce a disproportionately young population, and younger populations have higher birth rates. This is why some nations with sub-replacement fertility still have a growing population, because a relatively large fraction of their population are still of child-bearing age. But if the fertility trend is sustained (and not compensated by immigration
Immigration
Immigration is the act of foreigners passing or coming into a country for the purpose of permanent residence...
), it results in population ageing
Population ageing
Population ageing or population aging occurs when the median age of a country or region rises. This happens because of rising life expectancy or declining birth rates. Excepting 18 countries termed 'demographic outliers' by the UN) this process is taking place in every country and region across...
and population decline
Population decline
Population decline can refer to the decline in population of any organism, but this article refers to population decline in humans. It is a term usually used to describe any great reduction in a human population...
. This is forecast for most of the countries of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
.
Current estimates expect the world's total fertility rate to fall below replacement levels by 2050,
although population momentum will continue to increase global population for several generations beyond that. The promise of eventual population decline helps reduce concerns of overpopulation
Overpopulation
Overpopulation is a condition where an organism's numbers exceed the carrying capacity of its habitat. The term often refers to the relationship between the human population and its environment, the Earth...
, but many believe the Earth's carrying capacity
Carrying capacity
The carrying capacity of a biological species in an environment is the maximum population size of the species that the environment can sustain indefinitely, given the food, habitat, water and other necessities available in the environment...
has already been exceeded and that even a stable population would not be sustainable
Sustainability
Sustainability is the capacity to endure. For humans, sustainability is the long-term maintenance of well being, which has environmental, economic, and social dimensions, and encompasses the concept of union, an interdependent relationship and mutual responsible position with all living and non...
.
Sub-replacement fertility can also change social relations in a society. Fewer children, combined with lower infant mortality
Infant mortality
Infant mortality is defined as the number of infant deaths per 1000 live births. Traditionally, the most common cause worldwide was dehydration from diarrhea. However, the spreading information about Oral Re-hydration Solution to mothers around the world has decreased the rate of children dying...
has also made the death of children a far greater tragedy in the modern world than it was just fifty years ago. Having many families with only one or two children also reduces greatly the number of sibling
Sibling
Siblings are people who share at least one parent. A male sibling is called a brother; and a female sibling is called a sister. In most societies throughout the world, siblings usually grow up together and spend a good deal of their childhood socializing with one another...
s, aunts and uncles.
Population aging poses an economic cost on societies, as the number of elderly retirees rises in relation to the number of young workers. This has been raised as a political issue in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, where many people have advocated policy changes to encourage higher fertility and immigration rates. In France, payments to couples to have children have increased birthrate.
Forecast
Some European governments, fearful of a future pensions crisis, have developed natalist policies to attempt to encourage more women to have children. Measures include increasing tax allowances for working parents, improving child-care provision, reducing working hours/weekend working in female-dominated professions such as healthcare and a stricter enforcement of anti-discrimination measures to prevent professional women's promotion prospects being hindered when they take time off work to care for children. Over recent years, the fertility rate has increased to around 2.0 in France and 1.8 in Britain and some other northern European countries, but the role of population policies in these trends is debated.Attempts to increase the fertility rate among working women bring difficult political dilemmas: how far to alter traditional working practices so that women who are juggling work and child-raising responsibilities are not disadvantaged in their careers compared with men (for example, by legislating for compulsory paternity leave, flexible working and/or limiting total weekly working hours for men as well as women) and above all the question of whether the problem of sub-replacement fertility is so serious that unmarried women should also now be encouraged to have more children.
Giving women paid maternity leave can have the unintended negative consequence of dissuading employers from hiring women because they may fear having to pay a pregnant woman wages for a job she isn't doing. This may increase the gender-wage gap, the income disparity between men and women in the labor force. This disincentive can be ameliorated by giving parental leave to both men and women.
Germany’s family minister Ursula von der Leyen
Ursula von der Leyen
Ursula Gertrud von der Leyen is a German politician of the conservative Christian Democratic Union.Since 30 November 2009, she has served as the Federal Minister of Labour and Social Affairs in the Second Cabinet Merkel. In the First Cabinet Merkel , she served as Federal Minister of Family...
has stated that the slight increase in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, and other European countries with low fertility might be the first small steps to an eventual recovery. Although the increase will so far not counter an expected population decline it will however slow it down. European analysts hope, with the help of government incentives and large-scale change towards family-friendly policies, to stall the population decline and reverse it by around 2030, expecting that most of Europe will have a slight natural increase by then. C. D. Howe Institute
C. D. Howe Institute
The C.D. Howe Institute is a Canadian public policy think tank based in downtown Toronto, Ontario. Founded in 1958, the Institute publishes research and hosts conferences on a wide variety of issues in Canadian economic and social policy...
, for example, tries to demonstrate that immigration can not be used to effectively counter population ageing
Population ageing
Population ageing or population aging occurs when the median age of a country or region rises. This happens because of rising life expectancy or declining birth rates. Excepting 18 countries termed 'demographic outliers' by the UN) this process is taking place in every country and region across...
.
United States
While almost all of the developed world, and many other nations, have seen plummeting fertility rates over the last twenty years, the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
' rates have remained stable and even slightly increased. This is largely due to the high fertility rate among communities such as Hispanics, but it is also because the fertility rate among non-Hispanic whites
Non-Hispanic Whites
Non-Hispanic Whites or White, Not Hispanic or Latino are people in the United States, as defined by the Census Bureau, who are of the White race and are not of Hispanic or Latino origin/ethnicity. Hence the designation is exclusive in the sense that it defines who is not included as opposed to who is...
in the US, after falling to about 1.6 in the 1970s and early 1980s, had increased and is now around 1.9, or slightly below replacement level, rather than collapsing to the 1.3-1.5 level common in Europe.
New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
has a rate similar to most Western European countries, while the South, Midwest, and border states have fertility rates considerably higher than replacement. States where The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has a strong presence, most notably Utah
Utah
Utah is a state in the Western United States. It was the 45th state to join the Union, on January 4, 1896. Approximately 80% of Utah's 2,763,885 people live along the Wasatch Front, centering on Salt Lake City. This leaves vast expanses of the state nearly uninhabited, making the population the...
, also have higher-than-replacement fertility rates, especially among the LDS population. Heaton and Goodman (1985) found that LDS women average about one child more than women in other religious groups.
Other developed countries
Some other developed countries are also experiencing an increase in their birth rate, including FranceFrance
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, which recorded a TFR of over 2.00 in 2008, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, where the birth rate rose from 1.73 in 2001 to 1.93 in 2007 and New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, where the TFR was 2.2 in 2008. A few developed countries have never had sub-replacement fertility for reasons that are unique to the particular country. One example of that is Israel, where the growing Arab and religious Jewish populations (mostly Haredim) have high fertility rates, and the aliyah
Aliyah
Aliyah is the immigration of Jews to the Land of Israel . It is a basic tenet of Zionist ideology. The opposite action, emigration from Israel, is referred to as yerida . The return to the Holy Land has been a Jewish aspiration since the Babylonian exile...
of Jews from the diaspora
Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora is the English term used to describe the Galut גלות , or 'exile', of the Jews from the region of the Kingdom of Judah and Roman Iudaea and later emigration from wider Eretz Israel....
also contributes to Israel's population growth.
See also
- DemographyDemographyDemography is the statistical study of human population. It can be a very general science that can be applied to any kind of dynamic human population, that is, one that changes over time or space...
- Fertility and intelligenceFertility and intelligenceFertility and intelligence research investigates the relationship between fertility and intelligence. Demographic studies have indicated that in humans, fertility and intelligence tend to be inversely correlated, that is to say, the more intelligent, as measured by IQ tests, exhibit a lower total...
- List of countries and territories by fertility rate
- Natalistic politics, countering sub-replacement fertility
- Population declinePopulation declinePopulation decline can refer to the decline in population of any organism, but this article refers to population decline in humans. It is a term usually used to describe any great reduction in a human population...
- Population stabilization
Economic dynamics:
- Demographic-economic paradoxDemographic-economic paradoxThe demographic-economic paradox is the inverse correlation found between wealth and fertility within and between nations. The higher the degree of education and GDP per capita of a human population, subpopulation or social stratum, the fewer children are born in any industrialized country...
- Dependency ratioDependency ratioIn economics and geography the dependency ratio is an age-population ratio of those typically not in the labor force and those typically in the labor force...
- Economic collapseEconomic collapseThere is no precise definition of an economic collapse. While some might consider a a severe, prolonged depression with high bankruptcy rates and high unemployment an economic collapse, others would additionally look for a breakdown in normal commerce, such as hyperinfalation, or even a sharp...
- Pensions crisisPensions crisisThe pensions crisis is a predicted difficulty in paying for corporate, state and federal pensions in the U.S. and Europe, due to a difference between pension obligations and the resources set aside to fund them. Shifting demographics are causing a lower ratio of workers per retiree, while retirees...

