MOX fuel
Encyclopedia
Mixed oxide fuel, commonly referred to as MOX fuel, is nuclear fuel
that contains more than one oxide
of fissile
material. MOX fuel contains plutonium
blended with natural uranium
, reprocessed uranium
, or depleted uranium
. MOX fuel is an alternative to the low-enriched uranium (LEU) fuel used in the light water reactor
s that predominate nuclear power
generation. For example, a mixture of 7% plutonium and 93% uranium reacts similarly, although not identically, to LEU fuel.
One attraction of MOX fuel is that it is a way of utilizing surplus weapons-grade
plutonium, which would otherwise be stored as nuclear waste and might be stolen to make nuclear weapons. On the other hand, some fear that normalising the global commercial use of MOX fuel and the associated expansion of nuclear reprocessing
will increase, rather than reduce, the risk of nuclear proliferation
.
there is both fission
of uranium isotopes such as uranium-235
, and the formation of new, heavier isotopes due to neutron capture
, primarily by uranium-238
. Most of the fuel mass in a reactor is . This can become plutonium-239
and by successive neutron capture plutonium-240
, plutonium-241
, plutonium-242
and other transuranic or actinide
nuclides. and are fissile
, like . Small quantities of uranium-236
, neptunium-237 and plutonium-238
are formed similarly from .
Normally, with the fuel being changed every three years or so, most of the is "burned" in the reactor. It behaves like , with a slightly higher cross section
for fission, and its fission releases a similar amount of energy
. Typically about one percent of the spent fuel discharged from a reactor is plutonium, and some two thirds of the plutonium is . Worldwide, almost 100 tonnes of plutonium in spent fuel arises each year. A single recycling of plutonium increases the energy derived from the original uranium by some 12%, and if the is also recycled by re-enrichment, this becomes about 20%. With additional recycling the percentage of fissile (usually meaning odd-neutron number
nuclides) in the mix decreases and even-neutron number, neutron-absorbing nuclide increase, requiring the total plutonium and/or enriched uranium percentage to be increased. Today in thermal reactor
s plutonium is only recycled once as MOX fuel, and spent MOX fuel, with a high proportion of minor actinides
and even plutonium isotopes, is stored as waste.
Re-licensing precedes the introduction of MOX fuel into existing nuclear reactor
s. Often only a third to half of the fuel load is switched to MOX. The use of MOX does change the operating characteristics of a reactor, and the plant must be designed or adapted slightly to take it. More control rod
s are needed. For more than 50% MOX loading, significant changes are necessary and a reactor needs to be designed accordingly. The Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station
near Phoenix, Arizona
was designed for 100% MOX core compatibility but so far have always operated on fresh low enriched uranium. In theory the three Palo Verde reactors could use the MOX arising from seven conventionally fueled reactors each year and would no longer require fresh Uranium fuel.
According to Atomic Energy of Canada Limited
(AECL), CANDU reactor
s could use 100% MOX cores without physical modification. AECL reported to the United States National Academy of Sciences
committee on plutonium disposition that it has extensive experience in testing the use of MOX fuel containing from 0.5 to 3% plutonium.
 Reprocessing
Reprocessing
of commercial nuclear fuel to make MOX is done in the United Kingdom
and France
, and to a lesser extent in Russia
, India
and Japan
. China
plans to develop fast breeder reactors and reprocessing. Reprocessing of spent commercial-reactor nuclear fuel is not permitted in the United States due to nonproliferation considerations. All of these nations have long had nuclear weapons from military-focused research reactor
fuels except Japan.
The United States is building a MOX plant at the Savannah River Site
in South Carolina. The Tennessee Valley Authority and Duke Energy
are interested in using the reactor fuel from the conversion of weapons-grade plutonium.
Licensing and safety issues of using MOX fuel include:
About 30% of the plutonium originally loaded into MOX fuel is consumed by use in a thermal reactor. If one third of the core fuel load is MOX and two-thirds uranium fuel, there is zero net gain of plutonium in the spent fuel
.
All plutonium isotopes are either fissile or fertile, although plutonium-242
needs to absorb 3 neutrons before becoming fissile curium
-245; in thermal reactors isotopic degradation limits the plutonium recycle potential. About 1% of spent nuclear fuel
from current LWRs is plutonium, with approximate isotopic composition 52% , 24% , 15% , 6% and 2% when the fuel is first removed from the reactor.
for almost all of the actinides, including , fast reactors can use all of them for fuel. All actinides, including TRU or transuranium actinides can undergo neutron induced fission with unmoderated or fast neutrons. A fast reactor is more efficient for using plutonium and higher actinides as fuel. Depending on how the reactor is fueled it can either be used as a plutonium breeder
or burner.
These fast reactors are better suited for the transmutation
of other actinides than are thermal reactors. Because thermal reactors use slow or moderated neutrons, the actinides which are not fissionable with thermal neutrons tend to absorb the neutrons instead of fissioning. This leads to build up of heavier actinides and lowers the number of thermal neutrons available to continue the chain reaction.
plant.
, is equivalent to uranium oxide
fuel enriched to about 4.5% , assuming that the plutonium has about 60–65% . If weapons-grade plutonium were used (>90% ), only about 5% plutonium would be needed in the mix.
and plutonium nitrate in nitric acid
is converted by treatment with a base such as ammonia to form a mixture of ammonium diuranate
and plutonium hydroxide. This after heating in 5% hydrogen
in argon
will form a mixture of uranium dioxide
and plutonium dioxide
. The resulting powder can be converted using a base
into green pellets using a press
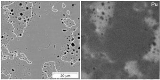
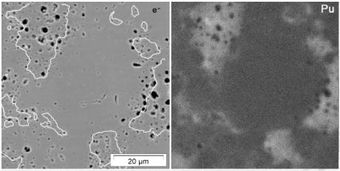
. The green pellet can then be sintered into mixed uranium and plutonium oxide pellet. While this second type of fuel is more homogenous on the microscopic scale (scanning electron microscope
) it is possible to see plutonium rich areas and plutonium poor areas. It can be helpful to think of the solid as being like a salami
(more than one solid material present in the pellet).
of short-lived isotope
s of plutonium. In particular, decays to americium
-241 which is a gamma ray
emitter, giving rise to a potential occupational health
hazard if the separated plutonium over five years old is used in a normal MOX plant. While is a gamma emitter most of the photon
s it emits are low in energy, so 1 mm of lead, or thick glass on a glovebox
will give the operators a great deal of protection to their torso
s. When working with large amounts of americium in a glovebox, the potential exists for a high dose of radiation to be delivered to the hands.
As a result old reactor-grade plutonium can be difficult to use in a MOX fuel plant, as the it contains decays with a short 14.1 year half-life into more radioactive which makes the fuel difficult to handle in a production plant. Within about 5 years typical reactor-grade plutonium would contain too much (about 3%). But it is possible to purify the plutonium bearing the americium by a chemical separation process. Even under the worst possible conditions the americium/plutonium mixture will never be as radioactive as a spent-fuel dissolution liquor, so it should be relatively straight forward to recover the plutonium by PUREX
or another aqueous reprocessing method.
Also, is fissile while the isotopes of plutonium
with even mass number
s are not (in general thermal neutrons will usually fission isotopes with an odd number of neutron
s, but rarely those with an even number), so decay of to leaves plutonium with a lower proportion of isotopes usable as fuel, and a higher proportion of isotopes that simply capture neutrons (though they may become fissile isotopes after one or more captures). The decay of to and subsequent removal of this uranium would have the opposite effect, but both has a longer halflife (87.7 years vs. 14.3) and is a smaller proportion of the spent nuclear fuel. , , and all have much longer halflives so that decay is negligible. ( has an even longer halflife, but is unlikely to be formed by successive neutron capture because quickly decays with a halflife of 5 hours giving .)
and curium
could be added to a U/Pu MOX fuel before it is loaded into a fast reactor. This is one means of transmutation. Work with curium is much harder than americium because curium is a neutron emitter, the MOX production line would need to be shielded with both lead
and water
to protect the workers.
Also, the neutron irradiation of curium generates the higher actinide
s, such as californium
, which increase the neutron
dose associated with the used nuclear fuel; this has the potential to pollute the fuel cycle with strong neutron emitters. As a result, it is likely that curium will be excluded from most MOX fuels.
and plutonium oxides has also been studied. According to a Norwegian study, "the coolant void reactivity
of the thorium-plutonium fuel is negative for plutonium contents up to 21%, whereas the transition lies at 16% for MOX fuel." The authors concluded, "Thorium-plutonium fuel seems to offer some advantages over MOX fuel with regards to control rod
and boron worths, CVR and plutonium consumption."
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
that contains more than one oxide
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
of fissile
Fissile
In nuclear engineering, a fissile material is one that is capable of sustaining a chain reaction of nuclear fission. By definition, fissile materials can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of any energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons...
material. MOX fuel contains plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
blended with natural uranium
Natural uranium
Natural uranium refers to refined uranium with the same isotopic ratio as found in nature. It contains 0.7 % uranium-235, 99.3 % uranium-238, and a trace of uranium-234 by weight. In terms of the amount of radioactivity, approximately 2.2 % comes from uranium-235, 48.6 % uranium-238, and 49.2 %...
, reprocessed uranium
Reprocessed uranium
Reprocessed uranium is the uranium recovered from nuclear reprocessing, as done commercially in France, the UK and Japan and by nuclear weapons states' military plutonium production programs. This uranium actually makes up the bulk of the material separated during reprocessing...
, or depleted uranium
Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope U-235 than natural uranium . Uses of DU take advantage of its very high density of 19.1 g/cm3...
. MOX fuel is an alternative to the low-enriched uranium (LEU) fuel used in the light water reactor
Light water reactor
The light water reactor is a type of thermal reactor that uses normal water as its coolant and neutron moderator. Thermal reactors are the most common type of nuclear reactor, and light water reactors are the most common type of thermal reactor...
s that predominate nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
generation. For example, a mixture of 7% plutonium and 93% uranium reacts similarly, although not identically, to LEU fuel.
One attraction of MOX fuel is that it is a way of utilizing surplus weapons-grade
Weapons-grade
A weapons-grade substance is one that is pure enough to be used to make a weapon or has properties that make it suitable for weapons use. Weapons-grade plutonium and uranium are the most common examples, but it may also be used to refer to chemical and biological weapons...
plutonium, which would otherwise be stored as nuclear waste and might be stolen to make nuclear weapons. On the other hand, some fear that normalising the global commercial use of MOX fuel and the associated expansion of nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing technology was developed to chemically separate and recover fissionable plutonium from irradiated nuclear fuel. Reprocessing serves multiple purposes, whose relative importance has changed over time. Originally reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing...
will increase, rather than reduce, the risk of nuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation is a term now used to describe the spread of nuclear weapons, fissile material, and weapons-applicable nuclear technology and information, to nations which are not recognized as "Nuclear Weapon States" by the Treaty on the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons, also known as the...
.
Overview
In every uranium-based nuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor core
A nuclear reactor core is the portion of a nuclear reactor containing the nuclear fuel components where the nuclear reactions take place.- Description :...
there is both fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
of uranium isotopes such as uranium-235
Uranium-235
- References :* .* DOE Fundamentals handbook: Nuclear Physics and Reactor theory , .* A piece of U-235 the size of a grain of rice can produce energy equal to that contained in three tons of coal or fourteen barrels of oil. -External links:* * * one of the earliest articles on U-235 for the...
, and the formation of new, heavier isotopes due to neutron capture
Neutron capture
Neutron capture is a kind of nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus collides with one or more neutrons and they merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, which are repelled...
, primarily by uranium-238
Uranium-238
Uranium-238 is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature. It is not fissile, but is a fertile material: it can capture a slow neutron and after two beta decays become fissile plutonium-239...
. Most of the fuel mass in a reactor is . This can become plutonium-239
Plutonium-239
Plutonium-239 is an isotope of plutonium. Plutonium-239 is the primary fissile isotope used for the production of nuclear weapons, although uranium-235 has also been used and is currently the secondary isotope. Plutonium-239 is also one of the three main isotopes demonstrated usable as fuel in...
and by successive neutron capture plutonium-240
Plutonium-240
Plutonium-240 is an isotope of the metal plutonium formed when plutonium-239 captures a neutron. About 62% to 73% of the time when Pu-239 captures a neutron it undergoes fission; the rest of the time it forms Pu-240. The longer a nuclear fuel element remains in a nuclear reactor the greater the...
, plutonium-241
Plutonium-241
Plutonium-241 is an isotope of plutonium formed when plutonium-240 captures a neutron. Like Pu-239 but unlike 240Pu, 241Pu is fissile, with a neutron absorption cross section about 1/3 greater than 239Pu, and a similar probability of fissioning on neutron absorption, around 73%. In the non-fission...
, plutonium-242
Plutonium-242
Pu-242 is one of the isotopes of plutonium, the second longest-lived, with a half-life of 373,300 years.242Pu's halflife is about 15 times as long as Pu-239's halflife; therefore it is 1/15 as radioactive and not one of the larger contributors to nuclear waste radioactivity.242Pu's gamma ray...
and other transuranic or actinide
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
nuclides. and are fissile
Fissile
In nuclear engineering, a fissile material is one that is capable of sustaining a chain reaction of nuclear fission. By definition, fissile materials can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of any energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons...
, like . Small quantities of uranium-236
Uranium-236
- See also :* Depleted uranium* Uranium market* Nuclear reprocessing* United States Enrichment Corporation* Nuclear fuel cycle* Nuclear power-External links:* *...
, neptunium-237 and plutonium-238
Plutonium-238
-External links:**...
are formed similarly from .
Normally, with the fuel being changed every three years or so, most of the is "burned" in the reactor. It behaves like , with a slightly higher cross section
Nuclear cross section
The nuclear cross section of a nucleus is used to characterize the probability that a nuclear reaction will occur. The concept of a nuclear cross section can be quantified physically in terms of "characteristic area" where a larger area means a larger probability of interaction...
for fission, and its fission releases a similar amount of energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
. Typically about one percent of the spent fuel discharged from a reactor is plutonium, and some two thirds of the plutonium is . Worldwide, almost 100 tonnes of plutonium in spent fuel arises each year. A single recycling of plutonium increases the energy derived from the original uranium by some 12%, and if the is also recycled by re-enrichment, this becomes about 20%. With additional recycling the percentage of fissile (usually meaning odd-neutron number
Neutron number
The neutron number, symbol N, is the number of neutrons in a nuclide.Atomic number plus neutron number equals mass number: Z+N=A....
nuclides) in the mix decreases and even-neutron number, neutron-absorbing nuclide increase, requiring the total plutonium and/or enriched uranium percentage to be increased. Today in thermal reactor
Thermal reactor
A thermal reactor is a nuclear reactor that uses slow or thermal neutrons. Most power reactors are of this type. These type of reactors use a neutron moderator to slow neutrons until they approach the average kinetic energy of the surrounding particles, that is, to reduce the speed of the neutrons...
s plutonium is only recycled once as MOX fuel, and spent MOX fuel, with a high proportion of minor actinides
Minor actinides
The minor actinides are the actinide elements in used nuclear fuel other than uranium and plutonium, which are termed the major actinides. The minor actinides include neptunium, americium, curium, berkelium, californium, einsteinium, and fermium...
and even plutonium isotopes, is stored as waste.
Re-licensing precedes the introduction of MOX fuel into existing nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
s. Often only a third to half of the fuel load is switched to MOX. The use of MOX does change the operating characteristics of a reactor, and the plant must be designed or adapted slightly to take it. More control rod
Control rod
A control rod is a rod made of chemical elements capable of absorbing many neutrons without fissioning themselves. They are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of uranium and plutonium...
s are needed. For more than 50% MOX loading, significant changes are necessary and a reactor needs to be designed accordingly. The Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station
Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station
The Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station is a nuclear power plant located in Wintersburg, Arizona, about 45 miles west of central Phoenix. It is the largest nuclear generation facility in the United States, averaging over 3.3 gigawatts of electrical power production in 2008 to serve...
near Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix is the capital, and largest city, of the U.S. state of Arizona, as well as the sixth most populated city in the United States. Phoenix is home to 1,445,632 people according to the official 2010 U.S. Census Bureau data...
was designed for 100% MOX core compatibility but so far have always operated on fresh low enriched uranium. In theory the three Palo Verde reactors could use the MOX arising from seven conventionally fueled reactors each year and would no longer require fresh Uranium fuel.
According to Atomic Energy of Canada Limited
Atomic Energy of Canada Limited
Atomic Energy of Canada Limited or AECL is a Canadian federal Crown corporation and Canada's largest nuclear science and technology laboratory...
(AECL), CANDU reactor
CANDU reactor
The CANDU reactor is a Canadian-invented, pressurized heavy water reactor. The acronym refers to its deuterium-oxide moderator and its use of uranium fuel...
s could use 100% MOX cores without physical modification. AECL reported to the United States National Academy of Sciences
United States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences is a corporation in the United States whose members serve pro bono as "advisers to the nation on science, engineering, and medicine." As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and...
committee on plutonium disposition that it has extensive experience in testing the use of MOX fuel containing from 0.5 to 3% plutonium.
Current applications

Nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing technology was developed to chemically separate and recover fissionable plutonium from irradiated nuclear fuel. Reprocessing serves multiple purposes, whose relative importance has changed over time. Originally reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing...
of commercial nuclear fuel to make MOX is done in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, and to a lesser extent in Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
plans to develop fast breeder reactors and reprocessing. Reprocessing of spent commercial-reactor nuclear fuel is not permitted in the United States due to nonproliferation considerations. All of these nations have long had nuclear weapons from military-focused research reactor
Research reactor
Research reactors are nuclear reactors that serve primarily as a neutron source. They are also called non-power reactors, in contrast to power reactors that are used for electricity production, heat generation, or maritime propulsion.-Purpose:...
fuels except Japan.
The United States is building a MOX plant at the Savannah River Site
Savannah River Site
The Savannah River Site is a nuclear reservation in the United States in the state of South Carolina, located on land in Aiken, Allendale and Barnwell Counties adjacent to the Savannah River, southeast of Augusta, Georgia. The site was built during the 1950s to refine nuclear materials for...
in South Carolina. The Tennessee Valley Authority and Duke Energy
Duke Energy
Duke Energy , headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, is an energy company with assets in the United States, Canada and Latin America.-Overview:...
are interested in using the reactor fuel from the conversion of weapons-grade plutonium.
Thermal reactors
About 30 thermal reactors in Europe (Belgium, Switzerland, Germany and France) are using MOX and a further 20 have been licensed to do so. Most reactors use it as about one third of their core, but some will accept up to 50% MOX assemblies. In France, EDF aims to have all its 900 MWe series of reactors running with at least one-third MOX. Japan aimed to have one third of its reactors using MOX by 2010, and has approved construction of a new reactor with a complete fuel loading of MOX. Of the total nuclear fuel used today, MOX provides 2%.Licensing and safety issues of using MOX fuel include:
- As plutonium isotopes absorb more neutrons than uranium fuels, reactor control systems may need modification.
- MOX fuel tends to run hotter because of lower thermal conductivity, which may be an issue in some reactor designs.
- Fission gas release in MOX fuel assemblies may limit the maximum burn-up time of MOX fuel.
About 30% of the plutonium originally loaded into MOX fuel is consumed by use in a thermal reactor. If one third of the core fuel load is MOX and two-thirds uranium fuel, there is zero net gain of plutonium in the spent fuel
Spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor...
.
All plutonium isotopes are either fissile or fertile, although plutonium-242
Plutonium-242
Pu-242 is one of the isotopes of plutonium, the second longest-lived, with a half-life of 373,300 years.242Pu's halflife is about 15 times as long as Pu-239's halflife; therefore it is 1/15 as radioactive and not one of the larger contributors to nuclear waste radioactivity.242Pu's gamma ray...
needs to absorb 3 neutrons before becoming fissile curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
-245; in thermal reactors isotopic degradation limits the plutonium recycle potential. About 1% of spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor...
from current LWRs is plutonium, with approximate isotopic composition 52% , 24% , 15% , 6% and 2% when the fuel is first removed from the reactor.
Fast reactors
Because the fission to capture ratio of neutron cross-section with high energy or fast neutrons changes to favour fissionNuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
for almost all of the actinides, including , fast reactors can use all of them for fuel. All actinides, including TRU or transuranium actinides can undergo neutron induced fission with unmoderated or fast neutrons. A fast reactor is more efficient for using plutonium and higher actinides as fuel. Depending on how the reactor is fueled it can either be used as a plutonium breeder
Breeder reactor
A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor capable of generating more fissile material than it consumes because its neutron economy is high enough to breed fissile from fertile material like uranium-238 or thorium-232. Breeders were at first considered superior because of their superior fuel economy...
or burner.
These fast reactors are better suited for the transmutation
Nuclear transmutation
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or isotope into another. In other words, atoms of one element can be changed into atoms of other element by 'transmutation'...
of other actinides than are thermal reactors. Because thermal reactors use slow or moderated neutrons, the actinides which are not fissionable with thermal neutrons tend to absorb the neutrons instead of fissioning. This leads to build up of heavier actinides and lowers the number of thermal neutrons available to continue the chain reaction.
Fabrication
The first step is separating the plutonium from the remaining uranium (about 96% of the spent fuel) and the fission products with other wastes (together about 3%). This is undertaken at a nuclear reprocessingNuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing technology was developed to chemically separate and recover fissionable plutonium from irradiated nuclear fuel. Reprocessing serves multiple purposes, whose relative importance has changed over time. Originally reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing...
plant.
Dry mixing
MOX fuel can be made by grinding together uranium oxide (UO2) and plutonium oxide (PuO2) before the mixed oxide is pressed into pellets, but this process has the disadvantage of forming lots of radioactive dust. MOX fuel, consisting of 7% plutonium mixed with depleted uraniumDepleted uranium
Depleted uranium is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope U-235 than natural uranium . Uses of DU take advantage of its very high density of 19.1 g/cm3...
, is equivalent to uranium oxide
Uranium oxide
Uranium oxide is an oxide of the element uranium.The metal uranium forms several oxides:* Uranium dioxide or uranium oxide * Uranium trioxide or uranium oxide...
fuel enriched to about 4.5% , assuming that the plutonium has about 60–65% . If weapons-grade plutonium were used (>90% ), only about 5% plutonium would be needed in the mix.
Coprecipitation
A mixture of uranyl nitrateUranyl nitrate
Uranyl nitrate is a water soluble yellow uranium salt. The yellow-green crystals of uranium nitrate hexahydrate are triboluminescent.Uranyl nitrate can be prepared by reaction of uranium salts with nitric acid...
and plutonium nitrate in nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
is converted by treatment with a base such as ammonia to form a mixture of ammonium diuranate
Ammonium diuranate
Ammonium diuranate or ' , is one of the intermediate chemical forms of uranium produced during yellowcake production. The name 'yellowcake' originally given to this bright yellow substance, now applies to mixtures of uranium oxides which are actually hardly ever yellow...
and plutonium hydroxide. This after heating in 5% hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
in argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
will form a mixture of uranium dioxide
Uranium dioxide
Uranium dioxide or uranium oxide , also known as urania or uranous oxide, is an oxide of uranium, and is a black, radioactive, crystalline powder that naturally occurs in the mineral uraninite. It is used in nuclear fuel rods in nuclear reactors. A mixture of uranium and plutonium dioxides is used...
and plutonium dioxide
Plutonium dioxide
Plutonium oxide is the chemical compound with the formula PuO2. This high melting point solid is a principal compound of plutonium. It can vary in color from yellow to olive green, depending on the particle size, temperature and method of production....
. The resulting powder can be converted using a base
Binder (material)
-See also:*Adhesive or Glue*Cement*Paint...
into green pellets using a press
Machine press
A machine press, commonly shortened to press, is a machine tool that changes the shape of a workpiece.-Servomechanism:A servomechanism press, also known as a servo press or a electro press, is a press driven by an AC servo motor. The torque produced is converted to a linear force via a ball screw....
. The green pellet can then be sintered into mixed uranium and plutonium oxide pellet. While this second type of fuel is more homogenous on the microscopic scale (scanning electron microscope
Scanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope is a type of electron microscope that images a sample by scanning it with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern...
) it is possible to see plutonium rich areas and plutonium poor areas. It can be helpful to think of the solid as being like a salami
Salami
Salami is cured sausage, fermented and air-dried meat, originating from one of a variety of animals. Historically, salami has been popular among Southern European peasants because it can be stored at room temperature for periods of up to 10 years, supplementing a possibly meager or inconsistent...
(more than one solid material present in the pellet).
Americium content
Plutonium from reprocessed fuel is usually fabricated into MOX as soon as possible to avoid problems with the decayRadioactive decay
Radioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles . The emission is spontaneous, in that the atom decays without any physical interaction with another particle from outside the atom...
of short-lived isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
s of plutonium. In particular, decays to americium
Americium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
-241 which is a gamma ray
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
emitter, giving rise to a potential occupational health
Occupational safety and health
Occupational safety and health is a cross-disciplinary area concerned with protecting the safety, health and welfare of people engaged in work or employment. The goal of all occupational safety and health programs is to foster a safe work environment...
hazard if the separated plutonium over five years old is used in a normal MOX plant. While is a gamma emitter most of the photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s it emits are low in energy, so 1 mm of lead, or thick glass on a glovebox
Glovebox
A glovebox is a sealed container that is designed to allow one to manipulate objects where a separate atmosphere is desired. Built into the sides of the glovebox are gloves arranged in such a way that the user can place their hands into the gloves and perform tasks inside the box without breaking...
will give the operators a great deal of protection to their torso
Torso
Trunk or torso is an anatomical term for the central part of the many animal bodies from which extend the neck and limbs. The trunk includes the thorax and abdomen.-Major organs:...
s. When working with large amounts of americium in a glovebox, the potential exists for a high dose of radiation to be delivered to the hands.
As a result old reactor-grade plutonium can be difficult to use in a MOX fuel plant, as the it contains decays with a short 14.1 year half-life into more radioactive which makes the fuel difficult to handle in a production plant. Within about 5 years typical reactor-grade plutonium would contain too much (about 3%). But it is possible to purify the plutonium bearing the americium by a chemical separation process. Even under the worst possible conditions the americium/plutonium mixture will never be as radioactive as a spent-fuel dissolution liquor, so it should be relatively straight forward to recover the plutonium by PUREX
PUREX
PUREX is an acronym standing for Plutonium - URanium EXtraction — de facto standard aqueous nuclear reprocessing method for the recovery of uranium and plutonium from used nuclear fuel. It is based on liquid-liquid extraction ion-exchange.The PUREX process was invented by Herbert H. Anderson and...
or another aqueous reprocessing method.
Also, is fissile while the isotopes of plutonium
Isotopes of plutonium
Plutonium is an artificial element, except for trace quantities of primordial 244Pu, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. It was synthesized long before being found in nature, the first isotope synthesized being 238Pu in 1940....
with even mass number
Mass number
The mass number , also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. Because protons and neutrons both are baryons, the mass number A is identical with the baryon number B as of the nucleus as of the whole atom or ion...
s are not (in general thermal neutrons will usually fission isotopes with an odd number of neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s, but rarely those with an even number), so decay of to leaves plutonium with a lower proportion of isotopes usable as fuel, and a higher proportion of isotopes that simply capture neutrons (though they may become fissile isotopes after one or more captures). The decay of to and subsequent removal of this uranium would have the opposite effect, but both has a longer halflife (87.7 years vs. 14.3) and is a smaller proportion of the spent nuclear fuel. , , and all have much longer halflives so that decay is negligible. ( has an even longer halflife, but is unlikely to be formed by successive neutron capture because quickly decays with a halflife of 5 hours giving .)
Curium content
It is possible that both americiumAmericium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
and curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
could be added to a U/Pu MOX fuel before it is loaded into a fast reactor. This is one means of transmutation. Work with curium is much harder than americium because curium is a neutron emitter, the MOX production line would need to be shielded with both lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
and water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
to protect the workers.
Also, the neutron irradiation of curium generates the higher actinide
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
s, such as californium
Californium
Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the...
, which increase the neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
dose associated with the used nuclear fuel; this has the potential to pollute the fuel cycle with strong neutron emitters. As a result, it is likely that curium will be excluded from most MOX fuels.
Thorium MOX
MOX fuel containing thoriumThorium
Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder....
and plutonium oxides has also been studied. According to a Norwegian study, "the coolant void reactivity
Void coefficient
In nuclear engineering, the void coefficient is a number that can be used to estimate how much the reactivity of a nuclear reactor changes as voids form in the reactor moderator or coolant...
of the thorium-plutonium fuel is negative for plutonium contents up to 21%, whereas the transition lies at 16% for MOX fuel." The authors concluded, "Thorium-plutonium fuel seems to offer some advantages over MOX fuel with regards to control rod
Control rod
A control rod is a rod made of chemical elements capable of absorbing many neutrons without fissioning themselves. They are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of uranium and plutonium...
and boron worths, CVR and plutonium consumption."
See also
- Nuclear fuel cycleNuclear fuel cycleThe nuclear fuel cycle, also called nuclear fuel chain, is the progression of nuclear fuel through a series of differing stages. It consists of steps in the front end, which are the preparation of the fuel, steps in the service period in which the fuel is used during reactor operation, and steps in...
- Nuclear breeder reactor
- Spent nuclear fuel shipping caskSpent nuclear fuel shipping caskSpent nuclear fuel shipping casks are used to transport spent nuclear fuel used in nuclear power plants and research reactors to disposal sites such as the nuclear reprocessing center at COGEMA La Hague site...
- Nuclear powerNuclear powerNuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
- Nuclear fissionNuclear fissionIn nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
- Nuclear power plantNuclear power plantA nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is one or more nuclear reactors. As in a conventional thermal power station the heat is used to generate steam which drives a steam turbine connected to a generator which produces electricity.Nuclear power plants are usually...
- Hanford SiteHanford SiteThe Hanford Site is a mostly decommissioned nuclear production complex on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, operated by the United States federal government. The site has been known by many names, including Hanford Works, Hanford Engineer Works or HEW, Hanford Nuclear Reservation...

