
Plutonium-242
Encyclopedia
Pu-242 is one of the isotopes of plutonium
, the second longest-lived, with a half-life
of 373,300 years.
242Pu's halflife is about 15 times as long as Pu-239's halflife; therefore it is 1/15 as radioactive and not one of the larger contributors to nuclear waste radioactivity.
242Pu's gamma ray
emissions are also weaker than those of the other isotopes.
It is not fissile
(though it is fissionable by fast neutrons) and its neutron capture
cross section
is also low.
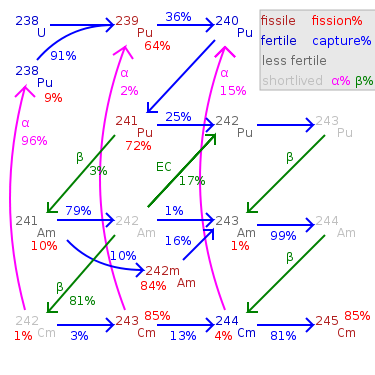 Pu-242 is produced by successive neutron capture
Pu-242 is produced by successive neutron capture
on Pu-239, Pu-240, and Pu-241. The odd-mass isotopes 239Pu and 241Pu have about a 3/4 chance of undergoing fission
on capture of a thermal neutron and about a 1/4 chance of retaining the neutron
and becoming the following isotope. The proportion of 242Pu is low at low burnup
but increases nonlinearly.
Pu-242 has a particularly low cross section
for thermal neutron capture; and it takes four neutron absorptions to become another fissile
isotope (either curium
-245 or Pu-241) and undergo fission
. Even then, there is a chance either of those two fissile isotopes will fail to fission but instead absorb the fourth neutron, becoming curium-246 (on the way to even heavier actinide
s like californium
, which is a neutron emitter by spontaneous fission and difficult to handle) or becoming 242Pu again; so the mean number of neutrons absorbed before fission is even higher than 4. Therefore Pu-242 is particularly unsuited to recycling in a thermal reactor
and would be better used in a fast reactor where it can be fissioned directly. However, 242Pu's low cross section means that relatively little of it will be transmuted during one cycle in a thermal reactor.
Isotopes of plutonium
Plutonium is an artificial element, except for trace quantities of primordial 244Pu, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. It was synthesized long before being found in nature, the first isotope synthesized being 238Pu in 1940....
, the second longest-lived, with a half-life
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
of 373,300 years.
242Pu's halflife is about 15 times as long as Pu-239's halflife; therefore it is 1/15 as radioactive and not one of the larger contributors to nuclear waste radioactivity.
242Pu's gamma ray
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
emissions are also weaker than those of the other isotopes.
It is not fissile
Fissile
In nuclear engineering, a fissile material is one that is capable of sustaining a chain reaction of nuclear fission. By definition, fissile materials can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of any energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons...
(though it is fissionable by fast neutrons) and its neutron capture
Neutron capture
Neutron capture is a kind of nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus collides with one or more neutrons and they merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, which are repelled...
cross section
Neutron cross-section
In nuclear and particle physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power...
is also low.
In the nuclear fuel cycle

Neutron capture
Neutron capture is a kind of nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus collides with one or more neutrons and they merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, which are repelled...
on Pu-239, Pu-240, and Pu-241. The odd-mass isotopes 239Pu and 241Pu have about a 3/4 chance of undergoing fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
on capture of a thermal neutron and about a 1/4 chance of retaining the neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
and becoming the following isotope. The proportion of 242Pu is low at low burnup
Burnup
In nuclear power technology, burnup is a measure of how much energy is extracted from a primary nuclear fuel source...
but increases nonlinearly.
Pu-242 has a particularly low cross section
Neutron cross-section
In nuclear and particle physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power...
for thermal neutron capture; and it takes four neutron absorptions to become another fissile
Fissile
In nuclear engineering, a fissile material is one that is capable of sustaining a chain reaction of nuclear fission. By definition, fissile materials can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of any energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons...
isotope (either curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
-245 or Pu-241) and undergo fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
. Even then, there is a chance either of those two fissile isotopes will fail to fission but instead absorb the fourth neutron, becoming curium-246 (on the way to even heavier actinide
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
s like californium
Californium
Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the...
, which is a neutron emitter by spontaneous fission and difficult to handle) or becoming 242Pu again; so the mean number of neutrons absorbed before fission is even higher than 4. Therefore Pu-242 is particularly unsuited to recycling in a thermal reactor
Thermal reactor
A thermal reactor is a nuclear reactor that uses slow or thermal neutrons. Most power reactors are of this type. These type of reactors use a neutron moderator to slow neutrons until they approach the average kinetic energy of the surrounding particles, that is, to reduce the speed of the neutrons...
and would be better used in a fast reactor where it can be fissioned directly. However, 242Pu's low cross section means that relatively little of it will be transmuted during one cycle in a thermal reactor.

