
Minor actinides
Encyclopedia
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
elements in used nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
other than uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
and plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
, which are termed the major actinides
Major actinides
Major actinides is a term used in the nuclear power industry that refers to the plutonium and uranium present in used nuclear fuel, as opposed to the minor actinides neptunium, americium, curium, berkelium, and californium....
. The minor actinides include neptunium
Neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a...
, americium
Americium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
, curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
, berkelium
Berkelium
Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949...
, californium
Californium
Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the...
, einsteinium
Einsteinium
Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein...
, and fermium
Fermium
Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,...
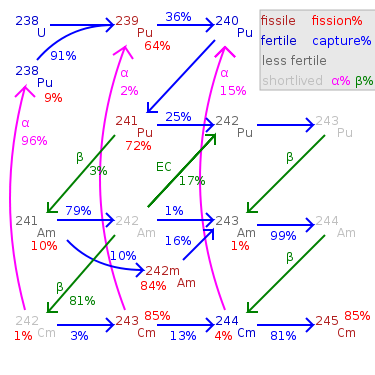
. The most important isotopes in spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor...
are neptunium-237, americium-241, americium-243, curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
-242 through -248, and californium
Californium
Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the...
-249 through -252.
Plutonium and the minor actinide
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
s will be responsible for the bulk of the radiotoxicity and heat generation of used nuclear fuel in the medium term (300 to 20,000 years in the future
Future
The future is the indefinite time period after the present. Its arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics. Due to the nature of the reality and the unavoidability of the future, everything that currently exists and will exist is temporary and will come...
). There are no fission products with halflife in this range.
The plutonium from a power reactor tends to have a greater amount of Pu-241 than the plutonium generated by the lower burnup
Burnup
In nuclear power technology, burnup is a measure of how much energy is extracted from a primary nuclear fuel source...
operations designed to create weapons-grade plutonium. Because the reactor-grade plutonium contains so much Pu-241 the presence of americium-241 makes the plutonium less suitable for making an atom bomb. The ingrowth of americium
Americium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
in plutonium is one of the methods for identifying the origin of an unknown sample of plutonium and the time since it was last separated chemically from the americium.
Americium is commonly used in industry as both an alpha particle
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
and low photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
energy gamma radiation source. For instance it is used in many smoke detectors. Americium can be formed by neutron capture of Pu-239 and Pu-240 forming Pu-241 which then decays by beta decay to Am-241. In general, as the energy of the neutrons increases, the ratio of the fission cross section to the neutron capture cross section changes in favour of fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
. Hence if MOX
Mox
MOX might be a name or acronym for:*Malaysian Oxygen Berhad - A Malaysian company that is specializes in providing total gas solutions.*Mixed Oxide Fuel, from nuclear reprocessing*An alien race in the TimeSplitters 2 video game, the Mox...
is used in a thermal reactor
Thermal reactor
A thermal reactor is a nuclear reactor that uses slow or thermal neutrons. Most power reactors are of this type. These type of reactors use a neutron moderator to slow neutrons until they approach the average kinetic energy of the surrounding particles, that is, to reduce the speed of the neutrons...
such as a boiling water reactor
Boiling water reactor
The boiling water reactor is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuclear reactor after the pressurized water reactor , also a type of light water nuclear reactor...
(BWR) or pressurized water reactor
Pressurized water reactor
Pressurized water reactors constitute a large majority of all western nuclear power plants and are one of three types of light water reactor , the other types being boiling water reactors and supercritical water reactors...
(PWR) then more americium can be expected in the used fuel than that from a fast neutron reactor
Fast neutron reactor
A fast neutron reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons...
.
Some of them have been found in fallout
Nuclear fallout
Fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and shock wave have passed. It commonly refers to the radioactive dust and ash created when a nuclear weapon explodes...
from bomb tests. See Actinides in the environment
Actinides in the environment
Actinides in the environment refer to the sources, environmental behaviour and effects of actinides in Earth's environment. Environmental radioactivity is not limited solely to actinides; non-actinides such as radon and radium are of note....
for details of the actinides in the environment.
| Isotope | Fraction | DLWR | Dfast Fast neutron reactor A fast neutron reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons... | Dsuperthermal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Np-237 | 0.0539 | 1.12 | ||
| Pu-238 | 0.0364 | 0.17 | ||
| Pu-239 | 0.451 | |||
| Pu-240 | 0.206 | 0.44 | ||
| 0.14 | ||||
| Pu-241 | 0.121 | |||
| Pu-242 | 0.0813 | 1.76 | ||
| 1.12 | ||||
| Am-241 | 0.0242 | 1.12 | ||
| Am-242m | 0.000088 | 0.15 | ||
| Am-243 | 0.0179 | 0.82 | ||
| 0.21 | ||||
| Cm-243 | 0.00011 | |||
| Cm-244 | 0.00765 | |||
| Cm-245 | 0.000638 | |||
| Weighted sum | ||||

