
Linezolid
Encyclopedia
Linezolid (icon ) is a synthetic antibiotic
used for the treatment of serious infection
s caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant
to several other antibiotics. A member of the oxazolidinone
class of drugs, linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci
, vancomycin-resistant enterococci
(VRE), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
(MRSA). The main indications
of linezolid are infections of the skin
and soft tissue
s and pneumonia
(particularly hospital-acquired pneumonia
), although off-label use
for a variety of other infections is becoming popular. Linezolid is marketed by Pfizer
under the trade names Zyvox (in the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and several other countries), Zyvoxid (in Europe), and Zyvoxam (in Canada and Mexico). Generics are also available in India, such as Linospan (Cipla
).
Discovered in the 1990s and first approved for use in 2000, linezolid was the first commercially available 1,3-oxazolidinone antibiotic. , it is the only marketed oxazolidinone, although others are in development. As a protein synthesis inhibitor
, it stops the growth of bacteria by disrupting their production of proteins
. Although many antibiotics work this way, the exact mechanism of action
of linezolid appears to be unique to the oxazolidinone class. Bacterial resistance to linezolid has remained very low since it was first detected in 1999, although it may be increasing.
When administered for short periods, linezolid is a relatively safe drug; it can be used in patients of all ages and in people with liver disease
or poor kidney function
. Common adverse effect
s of short-term use include headache
, diarrhea
, and nausea
. Long-term use, however, has been associated with serious adverse effects; linezolid can cause bone marrow suppression
and low platelet counts
, particularly when used for more than two weeks. If used for longer periods still, it may cause peripheral neuropathy
(which can be irreversible), optic nerve damage
, and lactic acidosis
(a buildup of lactic acid
in the body), all most likely due to mitochondrial toxicity
.
Linezolid is quite expensive, as a course of treatment (20 tablets 600 mg) can cost between one and two thousand U.S. dollars; nonetheless, it appears to be more cost-effective than comparable antibiotics, mostly because of the possibility of switching from intravenous
to oral administration
as soon as patients are stable enough, without the need for dose adjustments.
of linezolid is the treatment of severe infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant
to other antibiotics; it should not be used against bacteria that are sensitive to drugs with a narrower spectrum of activity, such as penicillin
s and cephalosporin
s. In both the popular press and the scientific literature, linezolid has been called a "reserve antibiotic"—one that should be used sparingly so that it will remain effective as a drug of last resort
against potentially intractable infections.
In the United States, the indications for linezolid use approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) are: vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus infection, with or without bacterial invasion of the bloodstream
; hospital- and community-acquired pneumonia
caused by S. aureus or S. pneumoniae; complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) caused by susceptible bacteria, including diabetic foot
infection, unless complicated by osteomyelitis
(infection of the bone and bone marrow); and uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infections caused by S. pyogenes or S. aureus. The manufacturer advises against the use of linezolid for community-acquired pneumonia or uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infections caused by MRSA. In the United Kingdom, pneumonia and cSSSIs are the only indications noted in the product labeling.
Linezolid appears to be as safe and effective for use in children and newborns as it is in adults.
of randomized controlled trials found linezolid to be more effective than glycopeptide antibiotics (such as vancomycin and teicoplanin
) and beta-lactam antibiotic
s in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) caused by Gram-positive bacteria, and smaller studies appear to confirm its superiority over teicoplanin in the treatment of all serious Gram-positive infections.
In the treatment of diabetic foot infections, linezolid appears to be cheaper and more effective than vancomycin. In a 2004 open-label study, it was as effective as ampicillin/sulbactam
and co-amoxiclav
, and far superior in patients with foot ulcers and no osteomyelitis
, but with significantly higher rates of adverse effects. A 2008 meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials, however, found that linezolid treatment failed as often as other antibiotics, regardless of whether patients had osteomyelitis.
Some authors have recommended that combinations of cheaper or more cost-effective drugs (such as co-trimoxazole
with rifampicin
or clindamycin
) be tried before linezolid in the treatment of SSTIs when susceptibility of the causative organism allows it.
and the Infectious Diseases Society of America
recommend that linezolid be reserved for cases in which MRSA has been confirmed as the causative organism, or when MRSA infection is suspected based on the clinical presentation. The guidelines of the British Thoracic Society
do not recommend it as first-line treatment, but rather as an alternative to vancomycin. Linezolid is also an acceptable second-line treatment for community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia when penicillin resistance is present.
U.S. guidelines recommend either linezolid or vancomycin as the first-line treatment for hospital-acquired (nosocomial) MRSA pneumonia. Some studies have suggested that linezolid is better than vancomycin against nosocomial pneumonia, particularly ventilator-associated pneumonia
caused by MRSA, perhaps because the penetration of linezolid into bronchial fluids is much higher than that of vancomycin. Several issues in study design have been raised, however, calling into question results that suggest the superiority of linezolid. Regardless, linezolid's advantages include its high bioavailability
(because it allows easy switching to oral therapy), and the fact that poor kidney function is not an obstacle to use (whereas achieving the correct dosage of vancomycin in patients with renal insufficiency
is very difficult).
—should be treated with bactericidal antibiotics, not bacteriostatic ones. Nevertheless, preclinical studies were conducted to assess the efficacy of linezolid for these infections, and the drug has been used successfully to treat them in clinical practice. Linezolid appears to be a reasonable therapeutic option for infective endocarditis caused by multi-resistant Gram-positive bacteria, despite a lack of high-quality evidence to support this use. Results in the treatment of enterococcal endocarditis have varied, with some cases treated successfully and others not responding to therapy. Low- to medium-quality evidence is also mounting for its use in bone and joint infections, including chronic osteomyelitis, although adverse effects are a significant concern when long-term use is necessary.
In combination with other drugs, linezolid has been used to treat tuberculosis
. The optimal dose for this purpose has not been established. In adults, daily and twice-daily dosing have been used to good effect. Many months of treatment are often required, and the rate of adverse effects is high regardless of dosage. There is not enough reliable evidence of efficacy and safety to support this indication as a routine use.
Linezolid has been studied as an alternative to vancomycin in the treatment of febrile neutropenia
in cancer patients when Gram-positive infection is suspected. It is also one of few antibiotics that diffuse into the vitreous humor, and may therefore be effective in treating endophthalmitis
(inflammation of the inner linings and cavities of the eye) caused by susceptible bacteria. Again, there is little evidence for its use in this setting, as infectious endophthalmitis is treated widely and effectively with vancomycin injected directly into the eye
.
caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, linezolid was found to penetrate well into cerebrospinal fluid
, but its effectiveness was inferior to that of other antibiotics. There does not appear to be enough high-quality evidence to support the routine use of linezolid to treat bacterial meningitis. Nonetheless, it has been used successfully in many cases of central nervous system
infection—including meningitis—caused by susceptible bacteria, and has also been suggested as a reasonable choice for this indication when treatment options are limited or when other antibiotics have failed. The guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend linezolid as the first-line drug of choice for VRE meningitis, and as an alternative to vancomycin for MRSA meningitis. Linezolid appears superior to vancomycin in treating community-acquired MRSA infections of the central nervous system, although very few cases of such infections have been published (as of 2009).
, open-label
, phase III clinical trial comparing linezolid to vancomycin in the treatment of catheter-related bloodstream infections. Patients treated with vancomycin could be switched to oxacillin
or dicloxacillin
if the bacteria that caused their infection was found to be susceptible, and patients in both groups (linezolid and vancomycin) could receive specific treatment against Gram-negative bacteria if necessary. The study itself was published in January 2009.
Linezolid was associated with significant
ly greater mortality than the comparator antibiotics. When data from all participants were pooled, the study found that 21.5% of those given linezolid died, compared to 16% of those not receiving it. The difference was found to be due to the inferiority of linezolid in the treatment of Gram-negative infections alone or mixed Gram-negative/Gram-positive infections. In participants whose infection was due to Gram-positive bacteria alone, linezolid was as safe and effective as vancomycin. In light of these results, the FDA issued an alert reminding healthcare professionals that linezolid is not approved for the treatment of catheter-related infections or infections caused by Gram-negative organisms, and that more appropriate therapy should be instituted whenever a Gram-negative infection is confirmed or suspected.
of linezolid use (those occurring in more than 1% of people taking linezolid) include diarrhea (reported by 3–11% of clinical trial participants), headache (1–11%), nausea (3–10%), vomiting (1–4%), rash (2%), constipation (2%), altered taste perception (1–2%), and discoloration of the tongue (0.2–1%). Fungal infections such as thrush
and vaginal candidiasis
may also occur as linezolid suppresses normal bacterial flora and opens a niche for fungi (so-called antibiotic candidiasis
). Less common (and potentially more serious) adverse effects include allergic reactions, pancreatitis
, and elevated transaminases
, which may be a sign of liver damage. Unlike some antibiotics, such as erythromycin
and the quinolone
s, linezolid has no effect on the QT interval
, a measure of cardiac electrical conduction. Adverse effects in children are similar to those that occur in adults.
Like nearly all antibiotics, linezolid has been associated with Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea
(CDAD) and pseudomembranous colitis
, although the latter is uncommon, occurring in about one in two thousand patients in clinical trials. C. difficile appears to be susceptible to linezolid in vitro, and linezolid was even considered as a possible treatment for CDAD.
, linezolid is a "black triangle drug
" in the United Kingdom, meaning that it is under intensive postmarketing surveillance
by the Commission on Human Medicines
of the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
.
, characterized particularly by thrombocytopenia
(low platelet count), may occur during linezolid treatment; it appears to be the only adverse effect that occurs significantly
more frequently with linezolid than with glycopeptides or beta-lactams. It is uncommon in patients who receive the drug for 14 days or fewer, but occurs much more frequently in patients who receive longer courses or who have renal failure. A 2004 case report
suggested that pyridoxine
(a form of vitamin B6
) could reverse the anemia and thrombocytopenia caused by linezolid, but a later, larger study found no protective effect.
Long-term use of linezolid has also been associated with peripheral neuropathy
and optic neuropathy
, which is most common after several months of treatment and may be irreversible., Although the mechanism of injury is still poorly understood, mitochondrial toxicity
has been proposed as a cause; linezolid is toxic to mitochondria, probably because of the similarity between mitochondrial and bacterial ribosome
s. Lactic acidosis
, a potentially life-threatening buildup of lactic acid
in the body, may also occur due to mitochondrial toxicity. Because of these long-term effects, the manufacturer recommends weekly complete blood count
s during linezolid therapy to monitor for possible bone marrow suppression, and recommends that treatment last no more than 28 days. A more extensive monitoring protocol for early detection of toxicity in seriously ill patients receiving linezolid has been developed and proposed by a team of researchers in Melbourne, Australia. The protocol includes twice-weekly blood tests and liver function tests
; measurement of serum lactate
levels, for early detection of lactic acidosis; a review of all medications taken by the patient, interrupting the use of those that may interact
with linezolid; and periodic eye and neurological exams in patients set to receive linezolid for longer than four weeks.
The adverse effects of long-term linezolid therapy were first identified during postmarketing surveillance. Bone marrow suppression was not identified during Phase III trials, in which treatment did not exceed 21 days. Although some participants of early trials did experience thrombocytopenia, it was found to be reversible and did not occur significantly more frequently than in controls (participants not taking linezolid). There have also been postmarketing reports of seizure
s, and, , a single case each of Bell's palsy
(paralysis of the facial nerve
) and kidney toxicity
.
(MAOI), and should not be used concomitantly with other MAOIs, large amounts of tyramine
-rich foods (such as pork, aged cheeses, alcoholic beverages, or smoked and pickled foods), or serotonergic
drugs. There have been postmarketing reports
of serotonin syndrome
when linezolid was given with or soon after the discontinuation of serotonergic drugs, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
s such as paroxetine
and sertraline
. It may also enhance the blood pressure-increasing effects of sympathomimetic drugs such as pseudoephedrine
or phenylpropanolamine
. It should also not be given in combination with pethidine
(meperidine) under any circumstance due to the risk of serotonin syndrome
.
Linezolid does not inhibit
or induce
the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, which is responsible for the metabolism of many commonly used drugs, and therefore does not have any CYP-related interactions.
The FDA has received reports of serious central nervous system (CNS) reactions when the drug linezolid (Zyvox) is given to patients taking psychiatric medications that work through the serotonin system of the brain.
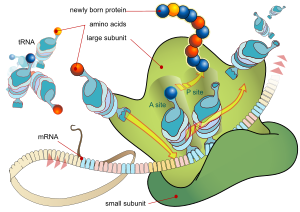 The oxazolidinones are protein synthesis inhibitor
The oxazolidinones are protein synthesis inhibitor
s: they stop the growth and reproduction of bacteria by disrupting translation
of messenger RNA
(mRNA) into protein
s in the ribosome
. Although its mechanism of action is not fully understood, linezolid appears to work on the first step of protein synthesis, initiation, unlike most other protein synthesis inhibitors, which inhibit elongation.
It does so by preventing the formation of the initiation complex, composed of the 30S
and 50S
subunits of the ribosome, tRNA
, and mRNA. Linezolid binds to the 23S
portion of the 50S subunit (the center of peptidyl transferase
activity), close to the binding site
s of chloramphenicol
, lincomycin
, and other antibiotics. Due to this unique mechanism of action, cross-resistance
between linezolid and other protein synthesis inhibitors is highly infrequent or nonexistent.
In 2008, the crystal structure
of linezolid bound to the 50S subunit of a ribosome from the archaea
n Haloarcula marismortui was elucidated by a team of scientists from Yale University
and deposited in the Protein Data Bank
. Another team in 2008 determined the structure of linezolid bound to a 50S subunit of Deinococcus radiodurans
. The authors proposed a refined model for the mechanism of action of oxazolidinones, finding that linezolid occupies the A site of the 50S ribosomal subunit, inducing a conformational change
that prevents tRNA from entering the site and ultimately forcing tRNA to separate from the ribosome.
of 0.55.
The oxazolidinone pharmacophore
—the chemical "template" essential for antimicrobial activity
—consists of a 1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
moiety
with an aryl
group at position 3 and an S-methyl group
, with another substituent
attached to it, at position 5 (the R-enantiomer
s of all oxazolidinones are devoid of antibiotic properties). In addition to this essential core, linezolid also contains several structural characteristics that improve its effectiveness and safety. An acetamide
substituent on the 5-methyl group is the best choice in terms of antibacterial efficacy, and is used in all of the more active oxazolidinones developed thus far; in fact, straying too far from an acetamide group at this position makes the drug lose its antimicrobial power, although weak to moderate activity is maintained when some isosteric
groups are used. A fluorine
atom at the 3′ position practically doubles in vitro and in vivo activity, and the electron-donating
nitrogen
atom in the morpholine
ring helps maintain high antibiotic potency and an acceptable safety profile.
The anticoagulant
rivaroxaban
(Xarelto) bears a striking structural similarity to linezolid; both drugs share the oxazolidinone pharmacophore, differing in only three areas (an extra ketone and chlorothiophene
, and missing the fluorine atom). However this similarity appears to carry no clinical significance.
drug: it does not occur in nature (unlike erythromycin and many other antibiotics) and was not developed by building upon a naturally occurring skeleton (unlike most beta-lactam
s, which are semisynthetic). Many approaches are available for oxazolidinone synthesis, and several routes for the synthesis of linezolid have been reported in the chemistry literature. Despite good yields
, the original method (developed by Upjohn for pilot plant
-scale production of linezolid and eperezolid) is lengthy, requires the use of expensive chemicals—such as palladium on carbon
and the highly sensitive reagents methanesulfonyl chloride
and n-butyllithium
—and needs low-temperature conditions. Much of the high cost of linezolid has been attributed to the expense of its synthesis. A somewhat more concise and cost-effective route better suited to large-scale production was patented by Upjohn in 1998.
Later syntheses have included an "atom-economical
" method starting from D-mannitol, developed by Indian pharmaceutical company Dr. Reddy's
and reported in 1999, and a route starting from (S)-glyceraldehyde acetonide (prepared from vitamin C
), developed by a team of researchers from Hunan Normal University
in Changsha, Hunan
, China. On June 25, 2008, during the 12th Annual Green Chemistry and Engineering Conference in New York, Pfizer reported the development of their "second-generation" synthesis of linezolid: a convergent
, green
synthesis starting from (S)-epichlorohydrin
, with higher yield and a 56% reduction in total waste.
(close to 100%) when given by mouth: the entire dose reaches the bloodstream, as if it had been given intravenously
. This means that people receiving intravenous linezolid may be switched to oral linezolid as soon as their condition allows it, whereas comparable antibiotics (such as vancomycin and quinupristin/dalfopristin) can only be given intravenously.
Taking linezolid with food somewhat slows its absorption, but the area under the curve is not affected.
Linezolid has low plasma protein binding
(approximately 31%, but highly variable) and an apparent volume of distribution
at steady state
of around 40–50 liters. Peak serum concentrations (Cmax) are reached one to two hours after administration of the drug. Linezolid is readily distributed to all tissues in the body apart from bone
matrix and white adipose tissue
. Notably, the concentration of linezolid in the epithelial lining fluid of the lower respiratory tract
is at least equal to, and often higher than, that achieved in serum (some authors have reported bronchial
fluid concentrations up to four times higher than serum concentrations), which may account for its efficacy
in treating pneumonia. Cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF) concentrations vary; peak CSF concentrations are lower than serum ones, due to slow diffusion across the blood-brain barrier
, and trough concentrations in the CSF are higher for the same reason. The average half-life is three hours in children, four hours in teenagers, and five hours in adults.
Linezolid is metabolized
in the liver
, by oxidation
of the morpholine
ring, without involvement of the cytochrome P450 system. This metabolic pathway leads to two major inactive metabolite
s (which each account for around 45% and 10% of an excreted dose at steady state), one minor metabolite, and several trace metabolites, none of which accounts for more than 1% of an excreted dose. Clearance
of linezolid varies with age and gender; it is fastest in children (which accounts for the shorter half-life), and appears to be 20% lower in women than in men.
, care should be taken to give linezolid after a session, because dialysis removes 30–40% of a dose from the body; no dosage adjustments are needed in people undergoing continuous hemofiltration
, although more frequent administration may be warranted in some cases. According to one study, linezolid may need to be given more frequently than normal in people with burn
s affecting more than 20% of body area
, due to increased nonrenal clearance of the drug.
Linezolid is in U.S. pregnancy category
C, meaning there have been no adequate studies of its safety when used by pregnant women, and although animal studies have shown mild toxicity to the fetus, the benefits of using the drug may outweigh its risks. It also passes into breast milk
, although the clinical significance of this (if any) is unknown.
—those whose cell wall
contains a thick layer of peptidoglycan
and no outer membrane—notably Enterococcus faecium
and Enterococcus faecalis
(including vancomycin-resistant enterococci
), Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA), Streptococcus agalactiae
, Streptococcus pneumoniae
, Streptococcus pyogenes
, the viridans group streptococci, Listeria monocytogenes, and Corynebacterium
species (the latter being among the most susceptible to linezolid, with minimum inhibitory concentration
s routinely below 0.5 mg/L). Linezolid is also highly active in vitro
against several mycobacteria
. It appears to be very effective against Nocardia
, but because of high cost and potentially serious adverse effects, authors have recommended that it be combined with other antibiotics or reserved for cases that have failed traditional treatment.
Linezolid is considered bacteriostatic
against most organisms—that is, it stops their growth and reproduction without actually killing them—but has some bactericidal (killing) activity against streptococci. Some authors have noted that, despite its bacteriostatic effect in vitro, linezolid "behaves" as a bactericidal antibiotic in vivo because it inhibits the production of toxin
s by staphylococci and streptococci. It also has a post-antibiotic effect
lasting one to four hours for most bacteria, meaning that bacterial growth is temporarily suppressed even after the drug is discontinued.
and the Enterobacteriaceae
, for instance, are not susceptible. In vitro, it is active against Pasteurella multocida
, Fusobacterium
, Moraxella catarrhalis
, Legionella
, Bordetella
, and Elizabethkingia meningoseptica, and moderately active (having a minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of strains of 8 mg/L) against Haemophilus influenzae
. It has also been used to great effect as a second-line treatment for Capnocytophaga
infections.
vancomycin
, which has long been the standard for treatment of MRSA infections, and the two drugs are often compared. Other comparable antibiotics include teicoplanin
(trade name Targocid, a glycopeptide like vancomycin), quinupristin/dalfopristin
(Synercid, a combination of two streptogramin
s, not active against E. faecalis), and daptomycin
(Cubicin, a lipopeptide
), and some agents still being developed, such as ceftobiprole
, dalbavancin
, and telavancin
. Linezolid is the only one that can be taken by mouth. In the future, oritavancin
and iclaprim
may be useful oral alternatives to linezolid—both are in the early stages of clinical development.
infection who received the drug through a compassionate use
program. Linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
was first isolated in 2001.
In the United States, resistance to linezolid has been monitored and tracked since 2004 through a program named LEADER, which (as of 2007) was conducted in 60 medical institutions throughout the country. Resistance has remained stable and extremely low—less than one-half of one percent of isolates overall, and less than one-tenth of one percent of S. aureus samples. A similar, worldwide program—the "Zyvox Annual Appraisal of Potency and Spectrum Study", or ZAAPS—has been conducted since 2002. , overall resistance to linezolid in 23 countries was less than 0.2%, and nonexistent among streptococci. Resistance was only found in Brazil, China, Ireland, and Italy, among coagulase-negative staphylococci (0.28% of samples resistant), enterococci (0.11%), and S. aureus (0.03%). In the United Kingdom and Ireland, no resistance was found in staphylococci collected from bacteremia
cases between 2001 and 2006, although resistance in enterococci has been reported. Some authors have predicted that resistance in E. faecium will increase if linezolid use continues at current levels or increases.
, which actively
"pump" linezolid out of the cell faster than it can accumulate.
Gram-positive bacteria usually develop resistance to linezolid as the result of a point mutation
known as G2576T, in which a guanine
base is replaced with thymine
in base pair
2576 of the genes coding for 23S ribosomal RNA. This is the most common mechanism of resistance in staphylococci, and the only one known to date in isolates of E. faecium. Other mechanisms have been identified in Streptococcus pneumoniae
(including mutations in an RNA methyltransferase
that methylates G2445 of the 23S rRNA and mutations causing increased expression
of ABC transporter genes) and in Staphylococcus epidermidis
.
s have been known as monoamine oxidase inhibitor
s since the late 1950s. Their antimicrobial properties were discovered by researchers at E.I. duPont de Nemours
in the 1970s. In 1978, DuPont patent
ed a series of oxazolidinone derivatives as being effective in the treatment of bacteria
l and fungal
plant diseases, and in 1984, another patent described their usefulness in treating bacterial infections in mammal
s. In 1987, DuPont scientists presented a detailed description of the oxazolidinones as a new class of antibiotics with a novel mechanism of action
. Early compounds were found to produce liver toxicity
, however, and development
was discontinued.
Pharmacia &
Upjohn
(now part of Pfizer) started its own oxazolidinone research program in the 1990s. Studies of the compounds' structure–activity relationship
s led to the development of several subclasses of oxazolidinone derivatives, with varying safety profiles and antimicrobial activity. Two compounds were considered drug candidates: eperezolid
(codenamed PNU-100592) and linezolid (PNU-100766). In the preclinical stages of development, they were similar in safety and antibacterial activity, so they were taken to Phase I clinical trial
s to identify any difference in pharmacokinetics
. Linezolid was found to have a pharmacokinetic advantage—requiring only twice-daily dosage, while eperezolid needed to be given three times a day to achieve similar exposure—and therefore proceeded to further trials. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved linezolid on April 18, 2000. Approval followed in Brazil (June 2000), the United Kingdom (January 2001), Japan and Canada (April 2001), Europe (throughout 2001), and other countries in Latin America and Asia.
, linezolid is the only oxazolidinone antibiotic available. Other members of this class have entered development, such as posizolid
(AZD2563), ranbezolid
(RBx 7644), torezolid
(TR-701), and radezolid
(RX-1741).
reduces the overall cost of treatment, even though linezolid may have a higher acquisition cost—that is, it may be more expensive—than comparable antibiotics.
Studies have been conducted in several countries with different health care system
models to assess the cost-effectiveness of linezolid compared to glycopeptides such as vancomycin or teicoplanin. In most countries, linezolid was more cost-effective than comparable antibiotics for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia and complicated skin and skin structure infections, either due to higher cure and survival rates or lower overall treatment costs.
In 2009, Pfizer paid $2.3 billion and entered a corporate integrity agreement to settle charges that it had misbranded and illegally promoted four drugs, and caused false claims to be submitted to government healthcare programs for uses that were not medically accepted. $1.3 billion was paid to settle criminal charges of illegally marketing the anti-inflammatory valdecoxib
, while $1 billion was paid in civil fines regarding illegal marketing of three other drugs, including Zyvox.
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
used for the treatment of serious infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
s caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
to several other antibiotics. A member of the oxazolidinone
2-Oxazolidone
2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring.-Evans auxiliaries:Oxazolidinones are a class of compounds containing 2-oxazolidone in the structure. In chemistry, they are useful as Evans auxiliaries, which are used for chiral synthesis....
class of drugs, linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci
Streptococcus
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the phylum Firmicutes and the lactic acid bacteria group. Cellular division occurs along a single axis in these bacteria, and thus they grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning...
, vancomycin-resistant enterococci
Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, or vancomycin-resistant enterococci , are bacterial strains of the genus Enterococcus that are resistant to the antibiotic vancomycin. To become VRE, vancomycin-sensitive enterococci typically obtain new DNA in the form of plasmids or transposons which encode...
(VRE), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It is also called multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus...
(MRSA). The main indications
Indication (medicine)
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. The opposite of indication is contraindication.-Drugs:...
of linezolid are infections of the skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
and soft tissue
Soft tissue
In anatomy, the term soft tissue refers to tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body, not being bone. Soft tissue includes tendons, ligaments, fascia, skin, fibrous tissues, fat, and synovial membranes , and muscles, nerves and blood vessels .It is sometimes...
s and pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
(particularly hospital-acquired pneumonia
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
Hospital-acquired pneumonia or nosocomial pneumonia refers to any pneumonia contracted by a patient in a hospital at least 48–72 hours after being admitted. It is usually caused by a bacterial infection, rather than a virus....
), although off-label use
Off-label use
Off-label use is the practice of prescribing pharmaceuticals for an unapproved indication or in an unapproved age group, unapproved dose or unapproved form of administration...
for a variety of other infections is becoming popular. Linezolid is marketed by Pfizer
Pfizer
Pfizer, Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical corporation. The company is based in New York City, New York with its research headquarters in Groton, Connecticut, United States...
under the trade names Zyvox (in the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and several other countries), Zyvoxid (in Europe), and Zyvoxam (in Canada and Mexico). Generics are also available in India, such as Linospan (Cipla
Cipla
Cipla Limited is a prominent Indian pharmaceutical company, best-known outside its home country for manufacturing low-cost anti-AIDS drugs for HIV-positive patients in developing countries...
).
Discovered in the 1990s and first approved for use in 2000, linezolid was the first commercially available 1,3-oxazolidinone antibiotic. , it is the only marketed oxazolidinone, although others are in development. As a protein synthesis inhibitor
Protein synthesis inhibitor
A protein synthesis inhibitor is a substance that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins....
, it stops the growth of bacteria by disrupting their production of proteins
Protein biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis is the process in which cells build or manufacture proteins. The term is sometimes used to refer only to protein translation but more often it refers to a multi-step process, beginning with amino acid synthesis and transcription of nuclear DNA into messenger RNA, which is then...
. Although many antibiotics work this way, the exact mechanism of action
Mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect...
of linezolid appears to be unique to the oxazolidinone class. Bacterial resistance to linezolid has remained very low since it was first detected in 1999, although it may be increasing.
When administered for short periods, linezolid is a relatively safe drug; it can be used in patients of all ages and in people with liver disease
Liver disease
Liver disease is a broad term describing any single number of diseases affecting the liver.-Diseases:* Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons , autoimmunity or hereditary conditions...
or poor kidney function
Renal failure
Renal failure or kidney failure describes a medical condition in which the kidneys fail to adequately filter toxins and waste products from the blood...
. Common adverse effect
Adverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
s of short-term use include headache
Headache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
, and nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
. Long-term use, however, has been associated with serious adverse effects; linezolid can cause bone marrow suppression
Bone marrow suppression
Bone marrow suppression or myelotoxicity or myelosuppression, is the decrease in cells responsible for providing immunity, carrying oxygen, and those responsible for normal blood clotting is a serious side effect of chemotherapy and certain drugs affecting the immune system such as azathioprine...
and low platelet counts
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a relative decrease of platelets in blood.A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. These limits are determined by the 2.5th lower and upper percentile, so values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease...
, particularly when used for more than two weeks. If used for longer periods still, it may cause peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the term for damage to nerves of the peripheral nervous system, which may be caused either by diseases of or trauma to the nerve or the side-effects of systemic illness....
(which can be irreversible), optic nerve damage
Optic neuropathy
The optic nerve contains axons of nerve cells that emerge from the retina, leave the eye at the optic disc, and go to the visual cortex where input from the eye is processed into vision. There are 1.2 million optic nerve fibers that derive from the retinal ganglion cells of the inner retina. Optic...
, and lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a physiological condition characterized by low pH in body tissues and blood accompanied by the buildup of lactate especially D-lactate, and is considered a distinct form of metabolic acidosis. The condition typically occurs when cells receive too little oxygen , for example...
(a buildup of lactic acid
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
in the body), all most likely due to mitochondrial toxicity
Mitochondrial toxicity
Mitochondrial toxicity is a condition in which the mitochondria of a body's cells become damaged or decline significantly in number; it occurs as a side effect of certain antiretroviral drugs used to treat human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV.-Causes:...
.
Linezolid is quite expensive, as a course of treatment (20 tablets 600 mg) can cost between one and two thousand U.S. dollars; nonetheless, it appears to be more cost-effective than comparable antibiotics, mostly because of the possibility of switching from intravenous
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
to oral administration
Route of administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the path by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.-Classification:Routes of administration are usually classified by application location...
as soon as patients are stable enough, without the need for dose adjustments.
Medical uses
The main indicationIndication (medicine)
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. The opposite of indication is contraindication.-Drugs:...
of linezolid is the treatment of severe infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
to other antibiotics; it should not be used against bacteria that are sensitive to drugs with a narrower spectrum of activity, such as penicillin
Penicillin
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. They include penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V....
s and cephalosporin
Cephalosporin
The cephalosporins are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from Acremonium, which was previously known as "Cephalosporium".Together with cephamycins they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems.-Medical use:...
s. In both the popular press and the scientific literature, linezolid has been called a "reserve antibiotic"—one that should be used sparingly so that it will remain effective as a drug of last resort
Drug of last resort
Drugs of last resort are drugs only used when all other options are exhausted. Many of the best known are antibiotics, antivirals, or chemotherapy agents. In those cases, they have the most potent antibiotic, antiviral, or anticancer effects, and/or are drugs for which no resistant strains are...
against potentially intractable infections.
In the United States, the indications for linezolid use approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
(FDA) are: vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus infection, with or without bacterial invasion of the bloodstream
Bacteremia
Bacteremia is the presence of bacteria in the blood. The blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of bacteria in the blood is always abnormal....
; hospital- and community-acquired pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia is a term used to describe one of several diseases in which individuals who have not recently been hospitalized develop an infection of the lungs . CAP is a common illness and can affect people of all ages. CAP often causes problems like difficulty in breathing, fever,...
caused by S. aureus or S. pneumoniae; complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) caused by susceptible bacteria, including diabetic foot
Diabetic foot
Diabetic foot ulcer is one of the major complications of diabetes mellitus, and probably the major component of the diabetic foot. It occurs in 15% of all patients with diabetes and precedes 84% of all lower leg amputations...
infection, unless complicated by osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis simply means an infection of the bone or bone marrow...
(infection of the bone and bone marrow); and uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infections caused by S. pyogenes or S. aureus. The manufacturer advises against the use of linezolid for community-acquired pneumonia or uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infections caused by MRSA. In the United Kingdom, pneumonia and cSSSIs are the only indications noted in the product labeling.
Linezolid appears to be as safe and effective for use in children and newborns as it is in adults.
Skin and soft tissue infections
A large meta-analysisMeta-analysis
In statistics, a meta-analysis combines the results of several studies that address a set of related research hypotheses. In its simplest form, this is normally by identification of a common measure of effect size, for which a weighted average might be the output of a meta-analyses. Here the...
of randomized controlled trials found linezolid to be more effective than glycopeptide antibiotics (such as vancomycin and teicoplanin
Teicoplanin
Teicoplanin is an antibiotic used in the prophylaxis and treatment of serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. It is a glycopeptide antibiotic extracted from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus, with a similar...
) and beta-lactam antibiotic
Beta-lactam antibiotic
β-Lactam antibiotics are a broad class of antibiotics, consisting of all antibiotic agents that contains a β-lactam nucleus in its molecular structure. This includes penicillin derivatives , cephalosporins , monobactams, and carbapenems...
s in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) caused by Gram-positive bacteria, and smaller studies appear to confirm its superiority over teicoplanin in the treatment of all serious Gram-positive infections.
In the treatment of diabetic foot infections, linezolid appears to be cheaper and more effective than vancomycin. In a 2004 open-label study, it was as effective as ampicillin/sulbactam
Ampicillin/sulbactam
Ampicillin/sulbactam is a combination of the common penicillin-derived antibiotic ampicillin and sulbactam, an inhibitor of bacterial beta-lactamase. Two different forms of the drug exist. The first, developed in 1987 and marketed in the United States under the tradename Unasyn, is an intravenous...
and co-amoxiclav
Co-amoxiclav
Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid or co-amoxiclav is a combination antibiotic consisting of amoxicillin trihydrate, a β-lactam antibiotic, and potassium clavulanate, a β-lactamase inhibitor...
, and far superior in patients with foot ulcers and no osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis simply means an infection of the bone or bone marrow...
, but with significantly higher rates of adverse effects. A 2008 meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials, however, found that linezolid treatment failed as often as other antibiotics, regardless of whether patients had osteomyelitis.
Some authors have recommended that combinations of cheaper or more cost-effective drugs (such as co-trimoxazole
Co-trimoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or co-trimoxazole is a sulfonamide antibiotic combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole, in the ratio of 1 to 5, used in the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections.The name co-trimoxazole is the British Approved Name, and has been marketed worldwide...
with rifampicin
Rifampicin
Rifampicin or rifampin is a bactericidal antibiotic drug of the rifamycin group. It is a semisynthetic compound derived from Amycolatopsis rifamycinica ...
or clindamycin
Clindamycin
Clindamycin rINN is a lincosamide antibiotic. It is usually used to treat infections with anaerobic bacteria but can also be used to treat some protozoal diseases, such as malaria...
) be tried before linezolid in the treatment of SSTIs when susceptibility of the causative organism allows it.
Pneumonia
There appears to be no significant difference in treatment success rates between linezolid, glycopeptides, or appropriate beta-lactam antibiotics in the treatment of pneumonia. Clinical guidelines for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia developed by the American Thoracic SocietyAmerican Thoracic Society
American Thoracic Society , established in 1905, is an independently incorporated, international, educational and scientific society, serving its 18,000 members worldwide who are dedicated in respiratory and critical care medicine...
and the Infectious Diseases Society of America
Infectious Diseases Society of America
The Infectious Diseases Society of America is a medical association representing physicians, scientists and other health care professionals who specialize in infectious diseases. As of 2010, IDSA had approximately 9,000 members...
recommend that linezolid be reserved for cases in which MRSA has been confirmed as the causative organism, or when MRSA infection is suspected based on the clinical presentation. The guidelines of the British Thoracic Society
British Thoracic Society
The British Thoracic Society was formed in 1982 by the amalgamation of the British Thoracic Association and the Thoracic Society. It is a registered charity and a company limited by guarantee.-Function:...
do not recommend it as first-line treatment, but rather as an alternative to vancomycin. Linezolid is also an acceptable second-line treatment for community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia when penicillin resistance is present.
U.S. guidelines recommend either linezolid or vancomycin as the first-line treatment for hospital-acquired (nosocomial) MRSA pneumonia. Some studies have suggested that linezolid is better than vancomycin against nosocomial pneumonia, particularly ventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia is a sub-type of hospital-acquired pneumonia which occurs in people who are receiving mechanical ventilation. VAP is not characterized by the causative agents; rather, as its name implies, definition of VAP is restricted to patients undergoing mechanical...
caused by MRSA, perhaps because the penetration of linezolid into bronchial fluids is much higher than that of vancomycin. Several issues in study design have been raised, however, calling into question results that suggest the superiority of linezolid. Regardless, linezolid's advantages include its high bioavailability
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is used to describe the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered...
(because it allows easy switching to oral therapy), and the fact that poor kidney function is not an obstacle to use (whereas achieving the correct dosage of vancomycin in patients with renal insufficiency
Renal failure
Renal failure or kidney failure describes a medical condition in which the kidneys fail to adequately filter toxins and waste products from the blood...
is very difficult).
Other
It is traditionally believed that so-called "deep" infections—such as osteomyelitis or infective endocarditisInfective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is a form of endocarditis, or inflammation, of the inner tissue of the heart, such as its valves, caused by infectious agents. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also be responsible....
—should be treated with bactericidal antibiotics, not bacteriostatic ones. Nevertheless, preclinical studies were conducted to assess the efficacy of linezolid for these infections, and the drug has been used successfully to treat them in clinical practice. Linezolid appears to be a reasonable therapeutic option for infective endocarditis caused by multi-resistant Gram-positive bacteria, despite a lack of high-quality evidence to support this use. Results in the treatment of enterococcal endocarditis have varied, with some cases treated successfully and others not responding to therapy. Low- to medium-quality evidence is also mounting for its use in bone and joint infections, including chronic osteomyelitis, although adverse effects are a significant concern when long-term use is necessary.
In combination with other drugs, linezolid has been used to treat tuberculosis
Tuberculosis treatment
Tuberculosis treatment refers to the medical treatment of the infectious disease tuberculosis .The standard "short" course treatment for TB is isoniazid, rifampicin , pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for two months, then isoniazid and rifampicin alone for a further four months...
. The optimal dose for this purpose has not been established. In adults, daily and twice-daily dosing have been used to good effect. Many months of treatment are often required, and the rate of adverse effects is high regardless of dosage. There is not enough reliable evidence of efficacy and safety to support this indication as a routine use.
Linezolid has been studied as an alternative to vancomycin in the treatment of febrile neutropenia
Febrile neutropenia
Febrile neutropenia is the development of fever, often with other signs of infection, in a patient with neutropenia, an abnormally low number of neutrophil granulocytes in the blood. The term neutropenic sepsis is also applied, although it tends to be reserved for patients who are less well...
in cancer patients when Gram-positive infection is suspected. It is also one of few antibiotics that diffuse into the vitreous humor, and may therefore be effective in treating endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis is an inflammation of the internal coats of the eye. It is a dreaded complication of all intraocular surgeries, particularly cataract surgery, with possible loss of vision and the eye itself. Infectious etiology is the most common and various bacteria and fungi have been isolated as...
(inflammation of the inner linings and cavities of the eye) caused by susceptible bacteria. Again, there is little evidence for its use in this setting, as infectious endophthalmitis is treated widely and effectively with vancomycin injected directly into the eye
Intravitreal administration
Intravitreal is a route of administration of a drug, or other substance, in which the substance is delivered via an eye. "Intravitreal" literally means "inside an eye"...
.
Infections of the central nervous system
In animal studies of meningitisMeningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, linezolid was found to penetrate well into cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
, but its effectiveness was inferior to that of other antibiotics. There does not appear to be enough high-quality evidence to support the routine use of linezolid to treat bacterial meningitis. Nonetheless, it has been used successfully in many cases of central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
infection—including meningitis—caused by susceptible bacteria, and has also been suggested as a reasonable choice for this indication when treatment options are limited or when other antibiotics have failed. The guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend linezolid as the first-line drug of choice for VRE meningitis, and as an alternative to vancomycin for MRSA meningitis. Linezolid appears superior to vancomycin in treating community-acquired MRSA infections of the central nervous system, although very few cases of such infections have been published (as of 2009).
Catheter-related infections
In March 2007, the FDA reported the results of a randomizedRandomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
, open-label
Open-label trial
An open-label trial or open trial is a type of clinical trial in which both the researchers and participants know which treatment is being administered....
, phase III clinical trial comparing linezolid to vancomycin in the treatment of catheter-related bloodstream infections. Patients treated with vancomycin could be switched to oxacillin
Oxacillin
Oxacillin sodium is a narrow spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.It was developed by Beecham.-Uses:...
or dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria. It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, which would otherwise be resistant to most...
if the bacteria that caused their infection was found to be susceptible, and patients in both groups (linezolid and vancomycin) could receive specific treatment against Gram-negative bacteria if necessary. The study itself was published in January 2009.
Linezolid was associated with significant
Statistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
ly greater mortality than the comparator antibiotics. When data from all participants were pooled, the study found that 21.5% of those given linezolid died, compared to 16% of those not receiving it. The difference was found to be due to the inferiority of linezolid in the treatment of Gram-negative infections alone or mixed Gram-negative/Gram-positive infections. In participants whose infection was due to Gram-positive bacteria alone, linezolid was as safe and effective as vancomycin. In light of these results, the FDA issued an alert reminding healthcare professionals that linezolid is not approved for the treatment of catheter-related infections or infections caused by Gram-negative organisms, and that more appropriate therapy should be instituted whenever a Gram-negative infection is confirmed or suspected.
Adverse effects
When used for short periods, linezolid is a relatively safe drug. Common side effectsAdverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
of linezolid use (those occurring in more than 1% of people taking linezolid) include diarrhea (reported by 3–11% of clinical trial participants), headache (1–11%), nausea (3–10%), vomiting (1–4%), rash (2%), constipation (2%), altered taste perception (1–2%), and discoloration of the tongue (0.2–1%). Fungal infections such as thrush
Oral candidiasis
Oral candidiasis is an infection of yeast fungi of the genus Candida on the mucous membranes of the mouth. It is frequently caused by Candida albicans, or less commonly by Candida glabrata or Candida tropicalis...
and vaginal candidiasis
Candidal vulvovaginitis
Candidal vulvovaginitis is an infection of the vagina’s mucous membranes by Candida albicans. Up to 75% of women will have thrush at some point in their lives, and approximately 5% will have recurring episodes.-Cause and pathophysiology:...
may also occur as linezolid suppresses normal bacterial flora and opens a niche for fungi (so-called antibiotic candidiasis
Antibiotic candidiasis
Antibiotic candidiasis is a Candidal infection caused by antibiotic use.- Causes :Antibiotic candidiasis can result from overuse or over-presciption of broad-spectrum antibiotics . Consequently, it is now rare for such antibiotics to be prescribed for extended periods...
). Less common (and potentially more serious) adverse effects include allergic reactions, pancreatitis
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. It occurs when pancreatic enzymes that digest food are activated in the pancreas instead of the small intestine. It may be acute – beginning suddenly and lasting a few days, or chronic – occurring over many years...
, and elevated transaminases
Elevated transaminases
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase , may be an indicator of liver damage...
, which may be a sign of liver damage. Unlike some antibiotics, such as erythromycin
Erythromycin
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that has an antimicrobial spectrum similar to or slightly wider than that of penicillin, and is often used for people who have an allergy to penicillins. For respiratory tract infections, it has better coverage of atypical organisms, including mycoplasma and...
and the quinolone
Quinolone
The quinolones are a family of synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotics. The term quinolone refers to potent synthetic chemotherapeutic antibacterials....
s, linezolid has no effect on the QT interval
QT interval
In cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
, a measure of cardiac electrical conduction. Adverse effects in children are similar to those that occur in adults.
Like nearly all antibiotics, linezolid has been associated with Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea
Clostridium difficile
Clostridium difficile , also known as "CDF/cdf", or "C...
(CDAD) and pseudomembranous colitis
Pseudomembranous colitis
Pseudomembranous colitis, a cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea , is an infection of the colon. It is often, but not always, caused by the bacterium Clostridium difficile. Because of this, the informal name C. difficile colitis is also commonly used. The illness is characterized by...
, although the latter is uncommon, occurring in about one in two thousand patients in clinical trials. C. difficile appears to be susceptible to linezolid in vitro, and linezolid was even considered as a possible treatment for CDAD.
, linezolid is a "black triangle drug
Black triangle (pharmacology)
A black triangle appearing after the trade name of a British medicine indicates that the medication is new to the market, or that an existing medicine is being used for a new reason or by a new route of administration....
" in the United Kingdom, meaning that it is under intensive postmarketing surveillance
Postmarketing surveillance
Postmarketing surveillance is the practice of monitoring the safety of a pharmaceutical drug or device after it has been released on the market and is an important part of the science of pharmacovigilance...
by the Commission on Human Medicines
Commission on Human Medicines
The Commission on Human Medicines is a committee of the UK's Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. It was formed in October 2005 by the amalgamation of the Medicines Commission and the Committee on Safety of Medicines....
of the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency is the UK government agency which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe....
.
Long-term use
Bone marrow suppressionBone marrow suppression
Bone marrow suppression or myelotoxicity or myelosuppression, is the decrease in cells responsible for providing immunity, carrying oxygen, and those responsible for normal blood clotting is a serious side effect of chemotherapy and certain drugs affecting the immune system such as azathioprine...
, characterized particularly by thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a relative decrease of platelets in blood.A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. These limits are determined by the 2.5th lower and upper percentile, so values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease...
(low platelet count), may occur during linezolid treatment; it appears to be the only adverse effect that occurs significantly
Statistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
more frequently with linezolid than with glycopeptides or beta-lactams. It is uncommon in patients who receive the drug for 14 days or fewer, but occurs much more frequently in patients who receive longer courses or who have renal failure. A 2004 case report
Case report
In medicine, a case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports may contain a demographic profile of the patient, but usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence....
suggested that pyridoxine
Pyridoxine
Pyridoxine is one of the compounds that can be called vitamin B6, along with pyridoxal and pyridoxamine. It differs from pyridoxamine by the substituent at the '4' position. It is often used as 'pyridoxine hydrochloride'.-Chemistry:...
(a form of vitamin B6
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin and is part of the vitamin B complex group. Several forms of the vitamin are known, but pyridoxal phosphate is the active form and is a cofactor in many reactions of amino acid metabolism, including transamination, deamination, and decarboxylation...
) could reverse the anemia and thrombocytopenia caused by linezolid, but a later, larger study found no protective effect.
Long-term use of linezolid has also been associated with peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the term for damage to nerves of the peripheral nervous system, which may be caused either by diseases of or trauma to the nerve or the side-effects of systemic illness....
and optic neuropathy
Optic neuropathy
The optic nerve contains axons of nerve cells that emerge from the retina, leave the eye at the optic disc, and go to the visual cortex where input from the eye is processed into vision. There are 1.2 million optic nerve fibers that derive from the retinal ganglion cells of the inner retina. Optic...
, which is most common after several months of treatment and may be irreversible., Although the mechanism of injury is still poorly understood, mitochondrial toxicity
Mitochondrial toxicity
Mitochondrial toxicity is a condition in which the mitochondria of a body's cells become damaged or decline significantly in number; it occurs as a side effect of certain antiretroviral drugs used to treat human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV.-Causes:...
has been proposed as a cause; linezolid is toxic to mitochondria, probably because of the similarity between mitochondrial and bacterial ribosome
Ribosome
A ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
s. Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a physiological condition characterized by low pH in body tissues and blood accompanied by the buildup of lactate especially D-lactate, and is considered a distinct form of metabolic acidosis. The condition typically occurs when cells receive too little oxygen , for example...
, a potentially life-threatening buildup of lactic acid
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
in the body, may also occur due to mitochondrial toxicity. Because of these long-term effects, the manufacturer recommends weekly complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count , also known as full blood count or full blood exam or blood panel, is a test panel requested by a doctor or other medical professional that gives information about the cells in a patient's blood...
s during linezolid therapy to monitor for possible bone marrow suppression, and recommends that treatment last no more than 28 days. A more extensive monitoring protocol for early detection of toxicity in seriously ill patients receiving linezolid has been developed and proposed by a team of researchers in Melbourne, Australia. The protocol includes twice-weekly blood tests and liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests , are groups of clinical biochemistry laboratory blood assays designed to give information about the state of a patient's liver. The parameters measured include PT/INR, aPTT, albumin, billirubin and others...
; measurement of serum lactate
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
levels, for early detection of lactic acidosis; a review of all medications taken by the patient, interrupting the use of those that may interact
Drug interaction
A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance affects the activity of a drug, i.e. the effects are increased or decreased, or they produce a new effect that neither produces on its own. Typically, interaction between drugs come to mind...
with linezolid; and periodic eye and neurological exams in patients set to receive linezolid for longer than four weeks.
The adverse effects of long-term linezolid therapy were first identified during postmarketing surveillance. Bone marrow suppression was not identified during Phase III trials, in which treatment did not exceed 21 days. Although some participants of early trials did experience thrombocytopenia, it was found to be reversible and did not occur significantly more frequently than in controls (participants not taking linezolid). There have also been postmarketing reports of seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s, and, , a single case each of Bell's palsy
Bell's palsy
Bell's palsy is a form of facial paralysis resulting from a dysfunction of the cranial nerve VII that results in the inability to control facial muscles on the affected side. Several conditions can cause facial paralysis, e.g., brain tumor, stroke, and Lyme disease. However, if no specific cause...
(paralysis of the facial nerve
Facial nerve
The facial nerve is the seventh of twelve paired cranial nerves. It emerges from the brainstem between the pons and the medulla, and controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and oral cavity...
) and kidney toxicity
Nephrotoxicity
Nephrotoxicity is a poisonous effect of some substances, both toxic chemicals and medication, on the kidneys. There are various forms of toxicity. Nephrotoxicity should not be confused with the fact that some medications have a predominantly renal excretion and need their dose adjusted for the...
.
Interactions
Linezolid is a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitorMonoamine oxidase inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are a class of antidepressant drugs prescribed for the treatment of depression. They are particularly effective in treating atypical depression....
(MAOI), and should not be used concomitantly with other MAOIs, large amounts of tyramine
Tyramine
Tyramine is a naturally occurring monoamine compound and trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent...
-rich foods (such as pork, aged cheeses, alcoholic beverages, or smoked and pickled foods), or serotonergic
Serotonergic
Serotonergic or serotoninergic means "related to the neurotransmitter serotonin". A synapse is serotonergic if it uses serotonin as its neurotransmitter...
drugs. There have been postmarketing reports
Postmarketing surveillance
Postmarketing surveillance is the practice of monitoring the safety of a pharmaceutical drug or device after it has been released on the market and is an important part of the science of pharmacovigilance...
of serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening adverse drug reaction that may occur following therapeutic drug use, inadvertent interactions between drugs, overdose of particular drugs, or the recreational use of certain drugs...
when linezolid was given with or soon after the discontinuation of serotonergic drugs, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors or serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitor are a class of compounds typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of depression, anxiety disorders, and some personality disorders. The efficacy of SSRIs is disputed...
s such as paroxetine
Paroxetine
Paroxetine is an SSRI antidepressant. Marketing of the drug began in 1992 by the pharmaceutical company SmithKline Beecham, now GlaxoSmithKline...
and sertraline
Sertraline
Sertraline hydrochloride is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor class. It was introduced to the market by Pfizer in 1991. Sertraline is primarily used to treat major depression in adult outpatients as well as obsessive–compulsive, panic, and social anxiety disorders in...
. It may also enhance the blood pressure-increasing effects of sympathomimetic drugs such as pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It is used as a nasal/sinus decongestant and stimulant, or as a wakefulness-promoting agent....
or phenylpropanolamine
Phenylpropanolamine
Phenylpropanolamine , also known as the stereoisomers norephedrine and norpseudoephedrine, is a psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes which is used as a stimulant, decongestant, and anorectic agent. It is commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough...
. It should also not be given in combination with pethidine
Pethidine
Pethidine or meperidine Pethidine (INN) or meperidine (USAN) Pethidine (INN) or meperidine (USAN) (commonly referred to as Demerol but also referred to as: isonipecaine; lidol; pethanol; piridosal; Algil; Alodan; Centralgin; Dispadol; Dolantin; Mialgin (in Indonesia); Petidin Dolargan (in Poland);...
(meperidine) under any circumstance due to the risk of serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening adverse drug reaction that may occur following therapeutic drug use, inadvertent interactions between drugs, overdose of particular drugs, or the recreational use of certain drugs...
.
Linezolid does not inhibit
Enzyme inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to enzymes and decreases their activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used as herbicides and pesticides...
or induce
Regulation of gene expression
Gene modulation redirects here. For information on therapeutic regulation of gene expression, see therapeutic gene modulation.Regulation of gene expression includes the processes that cells and viruses use to regulate the way that the information in genes is turned into gene products...
the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, which is responsible for the metabolism of many commonly used drugs, and therefore does not have any CYP-related interactions.
The FDA has received reports of serious central nervous system (CNS) reactions when the drug linezolid (Zyvox) is given to patients taking psychiatric medications that work through the serotonin system of the brain.
Mechanism of action

Protein synthesis inhibitor
A protein synthesis inhibitor is a substance that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins....
s: they stop the growth and reproduction of bacteria by disrupting translation
Prokaryotic translation
Prokaryotic translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in prokaryotes.-Initiation:Initiation of translation in prokaryotes involves the assembly of the components of the translation system which are: the two ribosomal subunits , the mRNA to be translated, the...
of messenger RNA
Messenger RNA
Messenger RNA is a molecule of RNA encoding a chemical "blueprint" for a protein product. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries coding information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosomes. Here, the nucleic acid polymer is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein...
(mRNA) into protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s in the ribosome
Ribosome
A ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
. Although its mechanism of action is not fully understood, linezolid appears to work on the first step of protein synthesis, initiation, unlike most other protein synthesis inhibitors, which inhibit elongation.
It does so by preventing the formation of the initiation complex, composed of the 30S
30S
30S is the smaller subunit of the 70S ribosome of prokaryotes. It is a complex of ribosomal RNA and ribonucleoproteins that functions in mRNA translation...
and 50S
50S
50S is the larger subunit of the 70S ribosome of prokaryotes. It is the site of inhibition for antibiotics such as macrolides, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, and the pleuromutilins. It includes the subunits 5S and 23S.-Structure:...
subunits of the ribosome, tRNA
Transfer RNA
Transfer RNA is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 73 to 93 nucleotides in length, that is used in biology to bridge the three-letter genetic code in messenger RNA with the twenty-letter code of amino acids in proteins. The role of tRNA as an adaptor is best understood by...
, and mRNA. Linezolid binds to the 23S
23S ribosomal RNA
The 23S rRNA is a 2904 nt long component of the large prokaryotic subunit The ribosomal peptidyl transferase activity resides in this rRNA...
portion of the 50S subunit (the center of peptidyl transferase
Peptidyl transferase
The Peptidyl transferase is an aminoacyltransferase as well as the primary enzymatic function of the ribosome, which forms peptide links between adjacent amino acids using tRNAs during the translation process of protein biosynthesis....
activity), close to the binding site
Binding site
In biochemistry, a binding site is a region on a protein, DNA, or RNA to which specific other molecules and ions—in this context collectively called ligands—form a chemical bond...
s of chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic antimicrobial that became available in 1949. It is considered a prototypical broad-spectrum antibiotic, alongside the tetracyclines, and as it is both cheap and easy to manufacture it is frequently found as a drug of choice in the third world.Chloramphenicol is...
, lincomycin
Lincomycin
Lincomycin is a lincosamide antibiotic that comes from the actinomyces Streptomyces lincolnensis. It has been structurally modified by thionyl chloride to its more commonly known 7-chloro-7-deoxy derivative, clindamycin...
, and other antibiotics. Due to this unique mechanism of action, cross-resistance
Cross-resistance
Cross-resistance is the tolerance to a usually toxic substance as a result of exposure to a similarly acting substance. It is a phenomenon affecting e.g. pesticides and antibiotics. As an example rifabutin and rifampin cross react in the treatment of tuberculosis. This sort of resistance is also...
between linezolid and other protein synthesis inhibitors is highly infrequent or nonexistent.
In 2008, the crystal structure
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
of linezolid bound to the 50S subunit of a ribosome from the archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
n Haloarcula marismortui was elucidated by a team of scientists from Yale University
Yale University
Yale University is a private, Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States...
and deposited in the Protein Data Bank
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
. Another team in 2008 determined the structure of linezolid bound to a 50S subunit of Deinococcus radiodurans
Deinococcus radiodurans
Deinococcus radiodurans is an extremophilic bacterium, one of the most radioresistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and is therefore known as a polyextremophile and has been listed as the world's toughest bacterium in The Guinness Book Of World Records.-Name...
. The authors proposed a refined model for the mechanism of action of oxazolidinones, finding that linezolid occupies the A site of the 50S ribosomal subunit, inducing a conformational change
Conformational change
A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. It can change its shape in response to changes in its environment or other factors; each possible shape is called a conformation, and a transition between them is called a conformational change...
that prevents tRNA from entering the site and ultimately forcing tRNA to separate from the ribosome.
Chemistry
At physiological pH, linezolid exists in an uncharged state. It is moderately water-soluble (approximately 3 mg/mL), with a logPPartition coefficient
In chemistry and the pharmaceutical sciences, a partition- or distribution coefficient is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in the two phases of a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. The terms "gas/liquid partition coefficient" and "air/water partition coefficient" are...
of 0.55.
The oxazolidinone pharmacophore
Pharmacophore
thumb|right|300px|An example of a pharmacophore model.A pharmacophore is an abstract description of molecular features which are necessary for molecular recognition of a ligand by a biological macromolecule....
—the chemical "template" essential for antimicrobial activity
Biological activity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or pharmacophore but can be modified by the other...
—consists of a 1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
2-Oxazolidone
2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring.-Evans auxiliaries:Oxazolidinones are a class of compounds containing 2-oxazolidone in the structure. In chemistry, they are useful as Evans auxiliaries, which are used for chiral synthesis....
moiety
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
with an aryl
Aryl
In the context of organic molecules, aryl refers to any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, be it phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, indolyl, etc....
group at position 3 and an S-methyl group
Methyl group
Methyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion...
, with another substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
attached to it, at position 5 (the R-enantiomer
Enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable , much as one's left and right hands are the same except for opposite orientation. It can be clearly understood if you try to place your hands one over the other without...
s of all oxazolidinones are devoid of antibiotic properties). In addition to this essential core, linezolid also contains several structural characteristics that improve its effectiveness and safety. An acetamide
Acetamide
Acetamide is an organic compound with the formula CH3CONH2. It is the simplest amide derived from acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent...
substituent on the 5-methyl group is the best choice in terms of antibacterial efficacy, and is used in all of the more active oxazolidinones developed thus far; in fact, straying too far from an acetamide group at this position makes the drug lose its antimicrobial power, although weak to moderate activity is maintained when some isosteric
Bioisostere
In medicinal chemistry, bioisosteres are substituents or groups with similar physical or chemical properties which produce broadly similar biological properties to a chemical compound. In drug design, the purpose of exchanging one bioisostere for another is to enhance the desired biological or...
groups are used. A fluorine
Fluorine
Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic...
atom at the 3′ position practically doubles in vitro and in vivo activity, and the electron-donating
Electron donor
An electron donor is a chemical entity that donates electrons to another compound. It is a reducing agent that, by virtue of its donating electrons, is itself oxidized in the process....
nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom in the morpholine
Morpholine
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O2NH. This heterocycle, pictured at right, features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium...
ring helps maintain high antibiotic potency and an acceptable safety profile.
The anticoagulant
Anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that prevents coagulation of blood. A group of pharmaceuticals called anticoagulants can be used in vivo as a medication for thrombotic disorders. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as test tubes, blood transfusion bags, and renal dialysis...
rivaroxaban
Rivaroxaban
Rivaroxaban is an oral anticoagulant invented and manufactured by Bayer; in a number of countries it is marketed as Xarelto. In the United States, it is marketed by Janssen Pharmaceutica. It is the first available orally active direct factor Xa inhibitor. Rivaroxaban is well absorbed from the gut...
(Xarelto) bears a striking structural similarity to linezolid; both drugs share the oxazolidinone pharmacophore, differing in only three areas (an extra ketone and chlorothiophene
Thiophene
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a flat five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. Related to thiophene are benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene, containing the thiophene ring fused with one and two benzene...
, and missing the fluorine atom). However this similarity appears to carry no clinical significance.
Synthesis
Linezolid is a completely syntheticOrganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
drug: it does not occur in nature (unlike erythromycin and many other antibiotics) and was not developed by building upon a naturally occurring skeleton (unlike most beta-lactam
Beta-lactam antibiotic
β-Lactam antibiotics are a broad class of antibiotics, consisting of all antibiotic agents that contains a β-lactam nucleus in its molecular structure. This includes penicillin derivatives , cephalosporins , monobactams, and carbapenems...
s, which are semisynthetic). Many approaches are available for oxazolidinone synthesis, and several routes for the synthesis of linezolid have been reported in the chemistry literature. Despite good yields
Yield (chemistry)
In chemistry, yield, also referred to as chemical yield and reaction yield, is the amount of product obtained in a chemical reaction. The absolute yield can be given as the weight in grams or in moles...
, the original method (developed by Upjohn for pilot plant
Pilot plant
A pilot plant is a small chemical processing system which is operated to generate information about the behavior of the system for use in design of larger facilities....
-scale production of linezolid and eperezolid) is lengthy, requires the use of expensive chemicals—such as palladium on carbon
Palladium on carbon
Palladium on carbon, often referred to as Pd/C, is a form of palladium used for catalysis. It is usually used for catalytic hydrogenations in organic chemistry...
and the highly sensitive reagents methanesulfonyl chloride
Methanesulfonyl chloride
Methanesulfonyl chloride is a compound containing a sulfonyl chloride used to make methanesulfonates and to generate sulfene.-Preparation, manufacture and handling:Methanesulfonyl chloride is highly toxic, moisture sensitive, corrosive, and a lachrymator...
and n-butyllithium
N-Butyllithium
n-Butyllithium is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene...
—and needs low-temperature conditions. Much of the high cost of linezolid has been attributed to the expense of its synthesis. A somewhat more concise and cost-effective route better suited to large-scale production was patented by Upjohn in 1998.
Later syntheses have included an "atom-economical
Atom economy
Atom economy describes the conversion efficiency of a chemical process in terms of all atoms involved . In an ideal chemical process, the amount of starting materials or reactants equals the amount of all products generated and no atom is wasted...
" method starting from D-mannitol, developed by Indian pharmaceutical company Dr. Reddy's
Dr. Reddy's Laboratories
Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. is an integrated pharmaceutical company focused on providing medicines through its three business segments: Global Generics segment, Pharmaceutical Services and Active Ingredients segment and Proprietary Products segment. The company was founded by Dr...
and reported in 1999, and a route starting from (S)-glyceraldehyde acetonide (prepared from vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
), developed by a team of researchers from Hunan Normal University
Hunan Normal University
Hunan Normal University , founded in 1938, is a higher education institution located in Changsha, Hunan Province, People's Republic of China. It has existed for 72 years...
in Changsha, Hunan
Hunan
' is a province of South-Central China, located to the south of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and south of Lake Dongting...
, China. On June 25, 2008, during the 12th Annual Green Chemistry and Engineering Conference in New York, Pfizer reported the development of their "second-generation" synthesis of linezolid: a convergent
Convergent synthesis
In chemistry a convergent synthesis is a strategy that aims to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical synthesis, most often in organic synthesis...
, green
Green chemistry
Green chemistry, also called sustainable chemistry, is a philosophy of chemical research and engineering that encourages the design of products and processes that minimize the use and generation of hazardous substances...
synthesis starting from (S)-epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. This is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organic solvents. Epichlorohydrin is a highly reactive compound and is used in the production of glycerol, plastics,...
, with higher yield and a 56% reduction in total waste.
Pharmacokinetics
One of the advantages of linezolid is its high bioavailabilityBioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is used to describe the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered...
(close to 100%) when given by mouth: the entire dose reaches the bloodstream, as if it had been given intravenously
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
. This means that people receiving intravenous linezolid may be switched to oral linezolid as soon as their condition allows it, whereas comparable antibiotics (such as vancomycin and quinupristin/dalfopristin) can only be given intravenously.
Taking linezolid with food somewhat slows its absorption, but the area under the curve is not affected.
Linezolid has low plasma protein binding
Plasma protein binding
A drug's efficiency may be affected by the degree to which it binds to the proteins within blood plasma. The less bound a drug is, the more efficiently it can traverse cell membranes or diffuse. Common blood proteins that drugs bind to are human serum albumin, lipoprotein, glycoprotein, α, β‚ and γ...
(approximately 31%, but highly variable) and an apparent volume of distribution
Volume of distribution
The volume of distribution , also known as apparent volume of distribution, is a pharmacological term used to quantify the distribution of a medication between plasma and the rest of the body after oral or parenteral dosing...
at steady state
Steady state
A system in a steady state has numerous properties that are unchanging in time. This implies that for any property p of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero:...
of around 40–50 liters. Peak serum concentrations (Cmax) are reached one to two hours after administration of the drug. Linezolid is readily distributed to all tissues in the body apart from bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
matrix and white adipose tissue
White adipose tissue
White adipose tissue or white fat is one of the two types of adipose tissue found in mammals. The other kind of adipose tissue is brown adipose tissue....
. Notably, the concentration of linezolid in the epithelial lining fluid of the lower respiratory tract
Lower respiratory tract
The term lower respiratory tract refers to the portions of the respiratory system from the trachea to the lungs.Lower respiratory tract infections can be the cause of several serious illnesses, including pneumonia....
is at least equal to, and often higher than, that achieved in serum (some authors have reported bronchial
Bronchus
A bronchus is a passage of airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The bronchus branches into smaller tubes, which in turn become bronchioles....
fluid concentrations up to four times higher than serum concentrations), which may account for its efficacy
Efficacy
Efficacy is the capacity to produce an effect. It has different specific meanings in different fields. In medicine, it is the ability of an intervention or drug to reproduce a desired effect in expert hands and under ideal circumstances.- Healthcare :...
in treating pneumonia. Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
(CSF) concentrations vary; peak CSF concentrations are lower than serum ones, due to slow diffusion across the blood-brain barrier
Blood-brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier is a separation of circulating blood and the brain extracellular fluid in the central nervous system . It occurs along all capillaries and consists of tight junctions around the capillaries that do not exist in normal circulation. Endothelial cells restrict the diffusion...
, and trough concentrations in the CSF are higher for the same reason. The average half-life is three hours in children, four hours in teenagers, and five hours in adults.
Linezolid is metabolized
Drug metabolism
Drug metabolism is the biochemical modification of pharmaceutical substances by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. This is a form of xenobiotic metabolism. Drug metabolism often converts lipophilic chemical compounds into more readily excreted polar products...
in the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, by oxidation
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
of the morpholine
Morpholine
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O2NH. This heterocycle, pictured at right, features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium...
ring, without involvement of the cytochrome P450 system. This metabolic pathway leads to two major inactive metabolite
Metabolite
Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial...
s (which each account for around 45% and 10% of an excreted dose at steady state), one minor metabolite, and several trace metabolites, none of which accounts for more than 1% of an excreted dose. Clearance
Clearance (medicine)
In medicine, the clearance is a measurement of the renal excretion ability. Although clearance may also involve other organs than the kidney, it is almost synonymous with renal clearance or renal plasma clearance. Each substance has a specific clearance that depends on its filtration characteristics...
of linezolid varies with age and gender; it is fastest in children (which accounts for the shorter half-life), and appears to be 20% lower in women than in men.
Use in special populations
In adults and children over the age of 12, linezolid is usually given every 12 hours, whether orally or intravenously. In younger children and infants, it is given every eight hours. No dosage adjustments are required in the elderly, in people with mild-to-moderate liver failure, or in those with impaired kidney function. In people requiring hemodialysisHemodialysis
In medicine, hemodialysis is a method for removing waste products such as creatinine and urea, as well as free water from the blood when the kidneys are in renal failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies .Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy...
, care should be taken to give linezolid after a session, because dialysis removes 30–40% of a dose from the body; no dosage adjustments are needed in people undergoing continuous hemofiltration
Hemofiltration
In medicine, hemofiltration, also haemofiltration, is a renal replacement therapy similar to hemodialysis which is used almost exclusively in the intensive care setting...
, although more frequent administration may be warranted in some cases. According to one study, linezolid may need to be given more frequently than normal in people with burn
Burn
A burn is an injury to flesh caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation, or friction.Burn may also refer to:*Combustion*Burn , type of watercourses so named in Scotland and north-eastern England...
s affecting more than 20% of body area
Total body surface area
Total body surface area is an assessment measure of burns of the skin. In adults, the "rule of nines" is used to determine the total percentage of area burned for each major section of the body...
, due to increased nonrenal clearance of the drug.
Linezolid is in U.S. pregnancy category
Pregnancy category
The pregnancy category of a pharmaceutical agent is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does not include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their metabolites that are present in breast...
C, meaning there have been no adequate studies of its safety when used by pregnant women, and although animal studies have shown mild toxicity to the fetus, the benefits of using the drug may outweigh its risks. It also passes into breast milk
Breast milk
Breast milk, more specifically human milk, is the milk produced by the breasts of a human female for her infant offspring...
, although the clinical significance of this (if any) is unknown.
Spectrum of activity
Linezolid is effective against all clinically important Gram-positive bacteriaBacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
—those whose cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
contains a thick layer of peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan, also known as murein, is a polymer consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane of bacteria , forming the cell wall. The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β- linked N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid...
and no outer membrane—notably Enterococcus faecium
Enterococcus faecium
Enterococcus faecium is a Gram-positive, alpha hemolytic or nonhemolytic bacterium in the genus Enterococcus. It can be commensal in the human intestine, but it may also be pathogenic, causing diseases such as neonatal meningitis.Vancomycin-resistant E. faecium is often referred to as VRE.Some...
and Enterococcus faecalis
Enterococcus faecalis
Enterococcus faecalis – formerly classified as part of the Group D Streptococcus system – is a Gram-positive, commensal bacterium inhabiting the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and other mammals. It is among the main constituents of some probiotic food supplements. Like other species in the genus...
(including vancomycin-resistant enterococci
Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, or vancomycin-resistant enterococci , are bacterial strains of the genus Enterococcus that are resistant to the antibiotic vancomycin. To become VRE, vancomycin-sensitive enterococci typically obtain new DNA in the form of plasmids or transposons which encode...
), Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA), Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus agalactiae is a beta-hemolytic Gram-positive streptococcus.- Identification :The CAMP test is an important test for identification...
, Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic, aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. A significant human pathogenic bacterium, S...
, Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes is a spherical, Gram-positive bacterium that is the cause of group A streptococcal infections. S. pyogenes displays streptococcal group A antigen on its cell wall. S...
, the viridans group streptococci, Listeria monocytogenes, and Corynebacterium
Corynebacterium
Corynebacterium is a genus of Gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria. They are widely distributed in nature and are mostly innocuous. Some are useful in industrial settings such as C. glutamicum. Others can cause human disease. C...
species (the latter being among the most susceptible to linezolid, with minimum inhibitory concentration
Minimum inhibitory concentration
In microbiology, minimum inhibitory concentration is the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight incubation. Minimum inhibitory concentrations are important in diagnostic laboratories to confirm resistance of microorganisms...
s routinely below 0.5 mg/L). Linezolid is also highly active in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
against several mycobacteria
Mycobacterium
Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. The genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy...
. It appears to be very effective against Nocardia
Nocardia
Nocardia is a genus of weakly staining Gram-positive, catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria. It forms partially acid-fast beaded branching filaments . It has a total of 85 species. Some species are non-pathogenic while others are responsible for nocardiosis. Nocardia are found worldwide in soil...
, but because of high cost and potentially serious adverse effects, authors have recommended that it be combined with other antibiotics or reserved for cases that have failed traditional treatment.
Linezolid is considered bacteriostatic
Bacteriostatic agent
A bacteriostatic agent or bacteriostat, abbreviated Bstatic, is a biological or chemical agent that stops bacteria from reproducing, while not necessarily harming them otherwise. Depending on their application, bacteriostatic antibiotics, disinfectants, antiseptics and preservatives can be...
against most organisms—that is, it stops their growth and reproduction without actually killing them—but has some bactericidal (killing) activity against streptococci. Some authors have noted that, despite its bacteriostatic effect in vitro, linezolid "behaves" as a bactericidal antibiotic in vivo because it inhibits the production of toxin
Exotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin excreted by a microorganism, like bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host...
s by staphylococci and streptococci. It also has a post-antibiotic effect
Antimicrobial pharmacodynamics
Antimicrobial pharmacodynamics is a term used to describe the relationship between concentration of antibiotic and its ability to inhibit vital processes of endo- or ectoparasites and microbial organisms...
lasting one to four hours for most bacteria, meaning that bacterial growth is temporarily suppressed even after the drug is discontinued.
Gram-negative bacteria
Linezolid has no clinically significant effect on most Gram-negative bacteria. PseudomonasPseudomonas
Pseudomonas is a genus of gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae containing 191 validly described species.Recently, 16S rRNA sequence analysis has redefined the taxonomy of many bacterial species. As a result, the genus Pseudomonas includes strains formerly classified in the...
and the Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae
The Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of bacteria that includes many of the more familiar pathogens, such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, Klebsiella and Shigella. This family is the only representative in the order Enterobacteriales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the...
, for instance, are not susceptible. In vitro, it is active against Pasteurella multocida
Pasteurella multocida
Pasteurella multocida is a Gram-negative, non-motile coccobacillus that is penicillin-sensitive and belongs to the Pasteurellaceae family . It can cause avian cholera in birds and a zoonotic infection in humans, which typically is a result of bites or scratches from domestic pets...
, Fusobacterium
Fusobacterium
Fusobacterium is a genus of filamentous, anaerobic, Gram-negative bacteria, similar to Bacteroides.Fusobacterium contribute to several human diseases, including periodontal diseases, Lemierre's syndrome, and topical skin ulcers...
, Moraxella catarrhalis
Moraxella catarrhalis
Moraxella catarrhalis is a fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase-positive diplococcus that can cause infections of the respiratory system, middle ear, eye, central nervous system and joints of humans.-History:...
, Legionella
Legionella
Legionella is a pathogenic Gram negative bacterium, including species that cause legionellosis or Legionnaires' disease, most notably L. pneumophila. It may be readily visualized with a silver stain....
, Bordetella
Bordetella
Bordetella is a genus of small , Gram-negative coccobacilli of the phylum proteobacteria. Bordetella species, with the exception of B. petrii, are obligate aerobes as well as highly fastidious, or difficult to culture. Three species are human pathogens ; one of these Bordetella is a genus of small...
, and Elizabethkingia meningoseptica, and moderately active (having a minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of strains of 8 mg/L) against Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae, formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or Bacillus influenzae, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium first described in 1892 by Richard Pfeiffer during an influenza pandemic. A member of the Pasteurellaceae family, it is generally aerobic, but can grow as a facultative anaerobe. H...
. It has also been used to great effect as a second-line treatment for Capnocytophaga
Capnocytophaga
Capnocytophaga is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Normally found in the oropharyngeal tract of mammals, they are involved in the pathogenesis of some animal bite wounds as well as periodontal diseases....
infections.
Comparable antibiotics
Linezolid's spectrum of activity against Gram-positive bacteria is similar to that of the glycopeptide antibioticGlycopeptide antibiotic
Glycopeptide antibiotics are a class of antibiotic drugs. The class is composed of glycosylated cyclic or polycyclic nonribosomal peptides. Significant glycopeptide antibiotics include vancomycin, teicoplanin, telavancin, bleomycin, ramoplanin, and decaplanin....
vancomycin
Vancomycin
Vancomycin INN is a glycopeptide antibiotic used in the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. It has traditionally been reserved as a drug of "last resort", used only after treatment with other antibiotics had failed, although the emergence of...
, which has long been the standard for treatment of MRSA infections, and the two drugs are often compared. Other comparable antibiotics include teicoplanin
Teicoplanin
Teicoplanin is an antibiotic used in the prophylaxis and treatment of serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. It is a glycopeptide antibiotic extracted from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus, with a similar...
(trade name Targocid, a glycopeptide like vancomycin), quinupristin/dalfopristin
Quinupristin/dalfopristin
Quinupristin/dalfopristin is a combination of two antibiotics used to treat infections by staphylococci and by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium....
(Synercid, a combination of two streptogramin
Streptogramin
Streptogramins are a class of antibiotics.Streptogramins are effective in the treatment of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus , two of the most rapidly-growing strains of multidrug-resistant bacteria...
s, not active against E. faecalis), and daptomycin
Daptomycin
Daptomycin is a novel lipopeptide antibiotic used in the treatment of certain infections caused by Gram-positive organisms. It is a naturally occurring compound found in the soil saprotroph Streptomyces roseosporus. Its distinct mechanism of action means that it may be useful in treating infections...
(Cubicin, a lipopeptide
Lipopeptide
A lipopeptide is a molecule consisting of a lipid connected to a peptide. Bacteria express these molecules. They are bound by TLR 1, and other, Toll-like receptors.Certain lipopeptides are used as antibiotics....
), and some agents still being developed, such as ceftobiprole
Ceftobiprole
Ceftobiprole is a 4th generation cephalosporin antibiotic with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococci. It was discovered by Basilea Pharmaceutica and was developed by Johnson & Johnson...
, dalbavancin
Dalbavancin
Dalbavancin is a novel second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic. It belongs to the same class as vancomycin, the most widely-used and one of the few treatments available to patients infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus .Dalbavancin is a novel semisynthetic...
, and telavancin
Telavancin
Telavancin is a bactericidal lipoglycopeptide for use in MRSA or other Gram-positive infections. Telavancin is a synthetic derivative of vancomycin....
. Linezolid is the only one that can be taken by mouth. In the future, oritavancin
Oritavancin
Oritavancin is a novel semi-synthetic glycopeptide antibiotic being developed for the treatment of serious Gram-positive infections...
and iclaprim
Iclaprim
Iclaprim , codenamed AR-100 and RO-48-2622, is a diaminopyrimidine dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor being developed for the treatment of complicated skin and soft tissue infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. It is structurally related to trimethoprim...
may be useful oral alternatives to linezolid—both are in the early stages of clinical development.
Resistance
Acquired resistance to linezolid was reported as early as 1999, in two patients with severe, multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faeciumEnterococcus faecium
Enterococcus faecium is a Gram-positive, alpha hemolytic or nonhemolytic bacterium in the genus Enterococcus. It can be commensal in the human intestine, but it may also be pathogenic, causing diseases such as neonatal meningitis.Vancomycin-resistant E. faecium is often referred to as VRE.Some...
infection who received the drug through a compassionate use
Expanded access
Expanded access refers to the use of an investigational drug outside of a clinical trial by patients with serious or life-threatening conditions who do not meet the enrollment criteria for the clinical trial in progress...
program. Linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a facultative anaerobic Gram-positive coccal bacterium. It is frequently found as part of the normal skin flora on the skin and nasal passages. It is estimated that 20% of the human population are long-term carriers of S. aureus. S. aureus is the most common species of...
was first isolated in 2001.
In the United States, resistance to linezolid has been monitored and tracked since 2004 through a program named LEADER, which (as of 2007) was conducted in 60 medical institutions throughout the country. Resistance has remained stable and extremely low—less than one-half of one percent of isolates overall, and less than one-tenth of one percent of S. aureus samples. A similar, worldwide program—the "Zyvox Annual Appraisal of Potency and Spectrum Study", or ZAAPS—has been conducted since 2002. , overall resistance to linezolid in 23 countries was less than 0.2%, and nonexistent among streptococci. Resistance was only found in Brazil, China, Ireland, and Italy, among coagulase-negative staphylococci (0.28% of samples resistant), enterococci (0.11%), and S. aureus (0.03%). In the United Kingdom and Ireland, no resistance was found in staphylococci collected from bacteremia
Bacteremia
Bacteremia is the presence of bacteria in the blood. The blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of bacteria in the blood is always abnormal....
cases between 2001 and 2006, although resistance in enterococci has been reported. Some authors have predicted that resistance in E. faecium will increase if linezolid use continues at current levels or increases.
Mechanism
The intrinsic resistance of most Gram-negative bacteria to linezolid is due to the activity of efflux pumpsEfflux (microbiology)
Active efflux is a mechanism responsible for extrusion of toxic substances and antibiotics outside the cell; this is considered to be a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism...
, which actively
Active transport
Active transport is the movement of a substance against its concentration gradient . In all cells, this is usually concerned with accumulating high concentrations of molecules that the cell needs, such as ions, glucose, and amino acids. If the process uses chemical energy, such as from adenosine...
"pump" linezolid out of the cell faster than it can accumulate.
Gram-positive bacteria usually develop resistance to linezolid as the result of a point mutation
Point mutation
A point mutation, or single base substitution, is a type of mutation that causes the replacement of a single base nucleotide with another nucleotide of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. Often the term point mutation also includes insertions or deletions of a single base pair...
known as G2576T, in which a guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
base is replaced with thymine
Thymine
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at...
in base pair
Base pair
In molecular biology and genetics, the linking between two nitrogenous bases on opposite complementary DNA or certain types of RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds is called a base pair...
2576 of the genes coding for 23S ribosomal RNA. This is the most common mechanism of resistance in staphylococci, and the only one known to date in isolates of E. faecium. Other mechanisms have been identified in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic, aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. A significant human pathogenic bacterium, S...
(including mutations in an RNA methyltransferase
Methyltransferase
A methyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that transfers a methyl group from a donor to an acceptor.Methylation often occurs on nucleic bases in DNA or amino acids in protein structures...
that methylates G2445 of the 23S rRNA and mutations causing increased expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
of ABC transporter genes) and in Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus epidermidis is one of thirty-three known species belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is part of human skin flora, and consequently part of human flora. It can also be found in the mucous membranes and in animals. Due to contamination, it is probably the most common species...
.
History
The oxazolidinone2-Oxazolidone
2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring.-Evans auxiliaries:Oxazolidinones are a class of compounds containing 2-oxazolidone in the structure. In chemistry, they are useful as Evans auxiliaries, which are used for chiral synthesis....
s have been known as monoamine oxidase inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are a class of antidepressant drugs prescribed for the treatment of depression. They are particularly effective in treating atypical depression....
s since the late 1950s. Their antimicrobial properties were discovered by researchers at E.I. duPont de Nemours
DuPont
E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company , commonly referred to as DuPont, is an American chemical company that was founded in July 1802 as a gunpowder mill by Eleuthère Irénée du Pont. DuPont was the world's third largest chemical company based on market capitalization and ninth based on revenue in 2009...
in the 1970s. In 1978, DuPont patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
ed a series of oxazolidinone derivatives as being effective in the treatment of bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
l and fungal
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
plant diseases, and in 1984, another patent described their usefulness in treating bacterial infections in mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s. In 1987, DuPont scientists presented a detailed description of the oxazolidinones as a new class of antibiotics with a novel mechanism of action
Mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect...
. Early compounds were found to produce liver toxicity
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure...
, however, and development
Drug development
Drug development is a blanket term used to define the process of bringing a new drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery...
was discontinued.
Pharmacia &
Pharmacia
Pharmacia was a pharmaceutical and biotechnological company in Sweden.-History:Pharmacia was founded in 1911 in Stockholm, Sweden by pharmacist Gustav Felix Grönfeldt at the Elgen Pharmacy. The company is named after the Greek word φαρμακεία, transliterated pharmakeia, which means 'sorcery'...
Upjohn
Upjohn
The Upjohn Company was a pharmaceutical manufacturing firm founded in 1886 in Kalamazoo, Michigan by Dr. William E. Upjohn, an 1875 graduate of the University of Michigan medical school. The company was originally formed to make friable pills, which were specifically designed to be easily digested...
(now part of Pfizer) started its own oxazolidinone research program in the 1990s. Studies of the compounds' structure–activity relationship
Structure-activity relationship
The structure–activity relationship is the relationship between the chemical or 3D structure of a molecule and its biological activity. The analysis of SAR enables the determination of the chemical groups responsible for evoking a target biological effect in the organism...
s led to the development of several subclasses of oxazolidinone derivatives, with varying safety profiles and antimicrobial activity. Two compounds were considered drug candidates: eperezolid
Eperezolid
Eperezolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic....
(codenamed PNU-100592) and linezolid (PNU-100766). In the preclinical stages of development, they were similar in safety and antibacterial activity, so they were taken to Phase I clinical trial
Clinical trial
Clinical trials are a set of procedures in medical research and drug development that are conducted to allow safety and efficacy data to be collected for health interventions...
s to identify any difference in pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to the determination of the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism...
. Linezolid was found to have a pharmacokinetic advantage—requiring only twice-daily dosage, while eperezolid needed to be given three times a day to achieve similar exposure—and therefore proceeded to further trials. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved linezolid on April 18, 2000. Approval followed in Brazil (June 2000), the United Kingdom (January 2001), Japan and Canada (April 2001), Europe (throughout 2001), and other countries in Latin America and Asia.
, linezolid is the only oxazolidinone antibiotic available. Other members of this class have entered development, such as posizolid
Posizolid
Posizolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic under investigation for the treatment of bacterial infections....
(AZD2563), ranbezolid
Ranbezolid
Ranbezolid is a novel, oxazolidinone antibacterial. It competitively inhibits monoamine oxidase-A ....
(RBx 7644), torezolid
Torezolid
Torezolid is an oxazolidinone drug in phase-II clinical trials for complicated skin and skin-structure infections , including those caused by Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ....
(TR-701), and radezolid
Radezolid
Radezolid is a novel oxazolidinone antibiotic being developed by Rib-X Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for the treatment of serious multi-drug–resistant infections. Radezolid has completed two phase-II clinical trials...
(RX-1741).
Economics
Linezolid is quite expensive; a course of treatment may cost one or two thousand U.S. dollars for the drug alone, not to mention other costs (such as those associated with hospital stay). However, because intravenous linezolid may be switched to an oral formulation (tablets or oral solution) without jeopardizing efficacy, patients may be discharged from hospital relatively early and continue treatment at home, whereas home treatment with injectable antibiotics may be impractical. Reducing the length of hospital stayLength of stay
Length of stay is a term commonly used to measure the duration of a single episode of hospitalization. Inpatient days are calculated by subtracting day of admission from day of discharge. However, persons entering and leaving a hospital on the same day have a length of stay of one...
reduces the overall cost of treatment, even though linezolid may have a higher acquisition cost—that is, it may be more expensive—than comparable antibiotics.
Studies have been conducted in several countries with different health care system
Health care system
A health care system is the organization of people, institutions, and resources to deliver health care services to meet the health needs of target populations....
models to assess the cost-effectiveness of linezolid compared to glycopeptides such as vancomycin or teicoplanin. In most countries, linezolid was more cost-effective than comparable antibiotics for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia and complicated skin and skin structure infections, either due to higher cure and survival rates or lower overall treatment costs.
In 2009, Pfizer paid $2.3 billion and entered a corporate integrity agreement to settle charges that it had misbranded and illegally promoted four drugs, and caused false claims to be submitted to government healthcare programs for uses that were not medically accepted. $1.3 billion was paid to settle criminal charges of illegally marketing the anti-inflammatory valdecoxib
Valdecoxib
Valdecoxib is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and painful menstruation and menstrual symptoms. It is a cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitor....
, while $1 billion was paid in civil fines regarding illegal marketing of three other drugs, including Zyvox.

