
Yield (chemistry)
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
, yield, also referred to as chemical yield and reaction yield, is the amount
of product
obtained in a chemical reaction
. The absolute yield can be given as the weight in gram
s or in moles
(molar yield). The fractional yield, relative yield, or percentage yield, which serve to measure the effectiveness of a synthetic procedure
, is calculated by dividing the amount of the obtained product by the theoretical yield (the unit of measure for both must be the same):
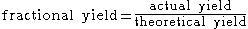
One or more reactants in a chemical reaction are often used in excess. The theoretical yield is therefore calculated based on the molar amount of the limiting reactant, taking into account the stoichiometry
of the reaction. For the calculation it is usually assumed that there is only one reaction involved.
The ideal or theoretical yield of a chemical reaction would be 100%, a value that is impossible to achieve due to limitations in measurement accuracy. According to Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, yields around 100% are called quantitative, yields above about 90% are called excellent, yields above about 80% very good, yields above about 70% are called good, yields below about 50% are called fair, yields below about 40% are called poor. Yields may appear to be above 100% when products are impure. Purification steps always lower the yield and the reported yields usually refer to the yield of the final purified product.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, yield, also referred to as chemical yield and reaction yield, is the amount
Amount of substance
Amount of substance is a standards-defined quantity that measures the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. It is sometimes referred to as chemical amount. The International System of Units defines the amount of substance to be...
of product
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
obtained in a chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
. The absolute yield can be given as the weight in gram
Gram
The gram is a metric system unit of mass....
s or in moles
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
(molar yield). The fractional yield, relative yield, or percentage yield, which serve to measure the effectiveness of a synthetic procedure
Chemical synthesis
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is purposeful execution of chemical reactions to get a product, or several products. This happens by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions...
, is calculated by dividing the amount of the obtained product by the theoretical yield (the unit of measure for both must be the same):
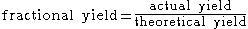
One or more reactants in a chemical reaction are often used in excess. The theoretical yield is therefore calculated based on the molar amount of the limiting reactant, taking into account the stoichiometry
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers...
of the reaction. For the calculation it is usually assumed that there is only one reaction involved.
The ideal or theoretical yield of a chemical reaction would be 100%, a value that is impossible to achieve due to limitations in measurement accuracy. According to Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, yields around 100% are called quantitative, yields above about 90% are called excellent, yields above about 80% very good, yields above about 70% are called good, yields below about 50% are called fair, yields below about 40% are called poor. Yields may appear to be above 100% when products are impure. Purification steps always lower the yield and the reported yields usually refer to the yield of the final purified product.

