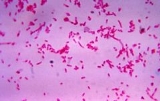
Fusobacterium
Encyclopedia
Fusobacterium is a genus of filamentous, anaerobic
, Gram-negative
bacteria, similar to Bacteroides
.
Fusobacterium contribute to several human diseases, including periodontal disease
s, Lemierre's syndrome
, and topical skin ulcers. Although older resources have stated that Fusobacterium is a common occurrence in the human oropharynx
, the current consensus is that Fusobacterium should always be treated as a pathogen. In 2011, researchers discovered that this bacteria flourishes in colon cancer cells, and is often also associated with ulcerative colitis
, although researchers have not determined if the organism actually causes these diseases or if it simply flourishes in the environment these diseases create.
In contrast to Bacteroides
spp., Fusobacteria have a potent lipopolysaccharide
.
Clindamycin
was the most active antibiotic against Fusobacterium species, followed by Chloramphenicol
, Carbenicillin
, and Cefoperazone
(which were about equally active) and then Cefamandole
Anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen for growth. It could possibly react negatively and may even die if oxygen is present...
, Gram-negative
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain crystal violet dye in the Gram staining protocol. In a Gram stain test, a counterstain is added after the crystal violet, coloring all Gram-negative bacteria with a red or pink color...
bacteria, similar to Bacteroides
Bacteroides
Bacteroides is a genus of Gram-negative, bacillus bacteria. Bacteroides species are non-endospore-forming, anaerobes, and may be either motile or non-motile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40-48% GC. Unusual in bacterial organisms, Bacteroides membranes contain sphingolipids...
.
Fusobacterium contribute to several human diseases, including periodontal disease
Periodontal disease
Periodontitis is a set of inflammatory diseases affecting the periodontium, i.e., the tissues that surround and support the teeth. Periodontitis involves progressive loss of the alveolar bone around the teeth, and if left untreated, can lead to the loosening and subsequent loss of teeth...
s, Lemierre's syndrome
Lemierre's syndrome
Lemierre's syndrome is a form of thrombophlebitis usually caused by the bacterium Fusobacterium necrophorum, and occasionally by other members of the genus Fusobacterium and usually affects young, healthy adults...
, and topical skin ulcers. Although older resources have stated that Fusobacterium is a common occurrence in the human oropharynx
Oropharynx
The Oropharynx reaches from the Uvula to the level of the hyoid bone.It opens anteriorly, through the isthmus faucium, into the mouth, while in its lateral wall, between the two palatine arches, is the palatine tonsil....
, the current consensus is that Fusobacterium should always be treated as a pathogen. In 2011, researchers discovered that this bacteria flourishes in colon cancer cells, and is often also associated with ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease . Ulcerative colitis is a form of colitis, a disease of the colon , that includes characteristic ulcers, or open sores. The main symptom of active disease is usually constant diarrhea mixed with blood, of gradual onset...
, although researchers have not determined if the organism actually causes these diseases or if it simply flourishes in the environment these diseases create.
In contrast to Bacteroides
Bacteroides
Bacteroides is a genus of Gram-negative, bacillus bacteria. Bacteroides species are non-endospore-forming, anaerobes, and may be either motile or non-motile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40-48% GC. Unusual in bacterial organisms, Bacteroides membranes contain sphingolipids...
spp., Fusobacteria have a potent lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides , also known as lipoglycans, are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide joined by a covalent bond; they are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, act as endotoxins and elicit strong immune responses in animals.-Functions:LPS is the major...
.
Clindamycin
Clindamycin
Clindamycin rINN is a lincosamide antibiotic. It is usually used to treat infections with anaerobic bacteria but can also be used to treat some protozoal diseases, such as malaria...
was the most active antibiotic against Fusobacterium species, followed by Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic antimicrobial that became available in 1949. It is considered a prototypical broad-spectrum antibiotic, alongside the tetracyclines, and as it is both cheap and easy to manufacture it is frequently found as a drug of choice in the third world.Chloramphenicol is...
, Carbenicillin
Carbenicillin
Carbenicillin is a bacteriolytic antibiotic belonging to the carboxypenicillin subgroup of the penicillins. It was discovered by scientists at Beecham and marketed as Pyopen. It has Gram-negative coverage which includes Pseudomonas aeruginosa but limited Gram-positive coverage...
, and Cefoperazone
Cefoperazone
Cefoperazone is a third generation cephalosporin antibiotic, marketed by Pfizer under the name Cefobid, and also marked by pharco B international under the name of Cefazoneand also marketed by "sigmatec " under the name " cefoperazone"...
(which were about equally active) and then Cefamandole
Cefamandole
Cefamandole is a second-generation broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic. The clinically used form of cefamandole is the formate ester cefamandole nafate, a prodrug which is administered parenterally....
External links
- Anaerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli chapter in Baron's Medical Microbiology (online at the NCBINational Center for Biotechnology InformationThe National Center for Biotechnology Information is part of the United States National Library of Medicine , a branch of the National Institutes of Health. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by Senator Claude Pepper...
bookshelf). - Fusobacterium From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource

