
Hashshashin
Encyclopedia
The Assassins were an order of Nizari
Ismailis, particularly those of Persia (and Syria
) that existed from around 1092 to 1265. Posing a strong military threat to Sunni Saljuq authority within the Persian territories, the Nizari Ismailis captured and inhabited many mountain fortresses under the leadership of Hassan-i Sabbah.
The name 'Assassin', from the Arabic Hashishin or "users of hashish
", was originally derogatory and used by their adversaries during the Middle Ages
. The modern word 'assassin
' is derived from this name. However, Amin Malouf states that "The truth is different. According to texts that have come down to us from Alamut
, Hassan-i Sabbah liked to call his disciples Asasiyun, meaning people who are faithful to the Asās, meaning 'foundation' of the faith. This is the word, misunderstood by foreign travelers, that seemed similar to 'hashish'".
The Masyaf
branch of the Assassins was taken over by the Mamluk
Sultan
Baibars
in 1273. The Mamluk
s however, continued to use the services of the remaining Assassins: Ibn Battuta
reported in the 14th century their fixed rate of pay per murder. In exchange, the higher authorities allowed them to exist. The mention of Assassins were also preserved within European sources, such as the writings of Marco Polo
, in which they are depicted as trained killers, responsible for the systematic elimination of opposing figures.
around 1080. It is difficult to find out much information about the origins of the Assassins because most early sources are either written by enemies of the cult or based on legends. Most sources dealing with the order’s inner working were destroyed with the capture of Alamut
, the Assassins' headquarters. However, it is possible to trace the beginnings of the cult back to its first Grandmaster, Hasan-i Sabbah. A passionate believer of the Isma’ili beliefs, Hasan-i-Sabbah was well liked throughout Cairo
, Syria
, and most of the Middle East by other Isma’ili, which led to a number of people becoming his followers. Using his fame and popularity, Sabbah founded the Order of the Assassins. While his motives for founding this order are ultimately unknown, it has been speculated that it was for his own political and personal gain and to also exact vengeance on his enemies. His motivation for political power probably came through what he thought to be dealings with other Muslims in the Middle East, particularly Sunnis, but because of the unrest in the holy land caused by the calling of the Crusades
, Hasan-i-Sabbah found himself not only fighting for power with other Muslims, but also with the invading Christian forces.
After creating the Order, Sabbah searched for a location that would be fit for a sturdy headquarters and decided on the fortress at Alamut in what is now northwestern Iran
. It is still disputed whether Sabbah built the fortress himself or if it was already built at the time of his arrival. Whether he created it himself or not, Sabbah adapted the fortress to suit his needs of not only defense from hostile forces, but also indoctrination of his followers. After laying claim to the fortress at Alamut, Sabbah began expanding his influence outward to nearby towns and districts, using his agents to gain political favour and intimidate the local populations.
Spending most of his days at Alamut working on religious works and doctrines for his Order, Sabbah was never to leave his fortress again in his lifetime. He had established a secret society of deadly assassins, one which was built in a hierarchical format. Below Sabbah, the Grand Headmaster of the Order, were those known as “Greater Propagandists”, followed by the normal "Propagandists", the Rafiqs ("Companions"), and the Lasiqs ("Adherents"). It was the Lasiqs who were trained to become some of the most feared assassins, or as they were called, "Fida’i" (self-sacrificing agent), in the known world.
It is, however, unknown how Hassan-i-Sabbah was able to get his "Fida’i" to perform with such fervent loyalty. One theory, possibly the most well known but also the most criticized, comes from the observations from Marco Polo
during his travels to the Orient. He describes how the "Old Man of the Mountain" (Sabbah) would drug his young followers with hashish, lead them to a "paradise", and then claim that only he had the means to allow for their return. Perceiving that Sabbah was either a prophet or some kind of magic man, his disciples, believing that only he could return them to "paradise", were fully committed to his cause and willing to carry out his every request. With his new weapons, Sabbah began to order assassinations, ranging from politicians to great generals. Assassins rarely would attack ordinary citizens though and tended not to be hostile towards them.
Although the "Fida’i" were the lowest rank in Sabbah’s order and only used as expendable pawns to do the Grandmaster’s bidding, much time and many resources were put in to training them. The Assassins were generally young in age giving them the physical strength and stamina which would be required to carry out these murders. However, physical prowess was not the only trait that was required to be a "Fida’i". To get to their targets, the Assassins had to be patient, cold, and calculating. They were generally intelligent and well read because they were required to possess not only knowledge about their enemy, but his or her culture and their native language. They were trained by their masters to disguise themselves, sneak in to enemy territory and perform the assassinations instead of simply attacking their target outright.
As tensions in the Middle East grew during the Crusades, the Assassins were also known for taking contracts from outside sources on either side of the war, whether it was from the invading Crusaders or the Saracen
forces, so long as the assassination fit in to the Grandmaster's plan.
to the Arabic hashish using their variant names assassin and assissini in the 19th century. Citing the example of one of the first written applications of the Arabic term hashish to the Ismailis by 13th century historian Abu Shama, de Sacy demonstrated its connection to the name given to the Ismailis throughout Western scholarship.p. 14 The first known usage of the term hashishi has been traced back to 1122 CE when the Fatimid
caliph
al-Āmir
employed it in derogatory reference to the Syrian Nizaris.p. 14 Used figuratively, the term hashishi connoted meanings such as outcasts or rabble.p. 14 Without actually accusing the group of using the hashish drug, the Caliph
used the term in a pejorative manner. This label was quickly adopted by anti-Ismaili historians and applied to the Ismailis of Syria and Persia. The spread of the term was further facilitated through military encounters between the Nizaris and the Crusaders
, whose chroniclers adopted the term and disseminated it across Europe.
During the medieval period, Western scholarship on the Ismailis contributed to the popular view of the community as a radical sect of assassins, believed to be trained for the precise murder of their adversaries. By the 14th century CE, European scholarship on the topic had not advanced much beyond the work and tales from the Crusaders.p. 14 The origins of the word forgotten, across Europe the term Assassin had taken the meaning of "professional murderer".p. 14 In 1603 the first Western publication on the topic of the Assassins was authored by a court official for King Henry IV
and was mainly based on the narratives of Marco Polo
from his visits to the Near East
. While he assembled the accounts of many Western travelers, the author failed to explain the etymology of the term Assassin.p. 15
According to Lebanese writer Amin Maalouf
:
Another modern author, Edward Burman, states that:
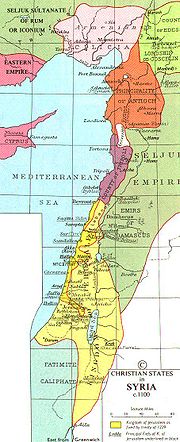 Their support and involvement with a series of killings of famous scholars, Imams and other noble personalities has given them title of one of the very first terrorist organizations in the world. Some of the famous killings and events in those dark centuries by Assassins included the following;
Their support and involvement with a series of killings of famous scholars, Imams and other noble personalities has given them title of one of the very first terrorist organizations in the world. Some of the famous killings and events in those dark centuries by Assassins included the following;
After the death of Hassan some notable events included the following;
 In pursuit of their religious and political goals, the Ismailis adopted various military strategies popular in the Middle Ages
In pursuit of their religious and political goals, the Ismailis adopted various military strategies popular in the Middle Ages
. One such method was that of assassination, the selective elimination of prominent rival figures. The murders of political adversaries were usually carried out in public spaces, creating resounding intimidation for other possible enemies.p. 129 Throughout history, many groups have resorted to assassination as a means of achieving political ends. In the Ismaili context, these assignments were performed by fida’is (devotees) of the Ismaili mission. They were unique in that civilians were never targeted. The assassinations were against those whose elimination would most greatly reduce aggression against the Ismailis and, in particular, against those who had perpetrated massacres against the community. A single assassination was usually employed in favour of widespread bloodshed resulting from factional combat. The first instance of assassination in the effort to establish an Nizari Ismaili state in Persia is widely considered to be the murder of Seljuq vizier
, Nizam al-Mulk
.p. 29 Carried out by a man dressed as a Sufi whose identity remains unclear, the vizier's murder in a Seljuq court is distinctive of exactly the type of visibility for which missions of the fida’is have been significantly exaggerated.p. 29 While the Seljuqs and Crusaders
both employed assassination as a military means of disposing of factional enemies, during the Alamut period almost any murder of political significance in the Islamic lands was attributed to the Ismailis.p. 129 So inflated had this association grown, that in the work of orientalist scholars such as Bernard Lewis
, the Ismailis were equated to the politically active fida’is and thus regarded as a radical and heretical
sect known as the Assassins.
The military approach of the Nizari Ismaili state was largely a defensive one, with strategically chosen sites that appeared to avoid confrontation wherever possible without the loss of life.p. 58 But the defining characteristic of the Nizari Ismaili state was that it was scattered geographically throughout Persia and Syria. The Alamut castle therefore was only one of a nexus of strongholds throughout the regions where Ismailis could retreat to safety if necessary. West of Alamut in the Shahrud Valley, the major fortress of Lamasar served as just one example of such a retreat. In the context of their political uprising, the various spaces of Ismaili military presence took on the name dar al-hijra . The notion of the dar al-hijra originates from the time of Muhammad
, who migrated with his supporters from intense persecution to safe haven in Yathrib (Medina
). In this way, the Fatimid
s found their dar al-hijra in North Africa. Likewise during the revolt against the Seljuqs, several fortresses served as spaces of refuge for the Ismailis.
 The Assassins were eradicated by the Mongol Empire
The Assassins were eradicated by the Mongol Empire
during the well documented invasion of Khwarizm. They probably dispatched their assassins to kill Mongke Khan
. Thus a decree was handed over to the Mongol commander Kitbuqa
who began to assault several Hashshashin fortresses in 1253 before Hulagu's
advance in 1256. The Mongols
besieged Alamut
on December 15, 1256. The Assassins recaptured and held Alamut for a few months in 1275, but they were crushed and their political power was lost forever.
The Syrian branch of the Assassins was taken over by the Mamluk
Sultan Baibars
in 1273. The Mamluks continued to use the services of the remaining Assassins: Ibn Battuta
reported in the 14th century their fixed rate of pay per murder. In exchange, they were allowed to exist. Eventually, they resorted to the act of Taqq'iya
(dissimulation), hiding their true identities until their Imams would awaken them.
According to the historian Yaqut al-Hamawi
, the Böszörmény
, (Izmaleita or Ismaili/Nizari
) denomination of the Muslims who lived in the Kingdom of Hungary
in the 10–13th centuries, were employed as mercenaries by the kings of Hungary. However following the establishment of the Christian Kingdom of Hungary
their community was vanquished by the end of the 13th century due to the Inquisition
s ordered by the Catholic Church during the reign of Coloman, King of Hungary.
 The legends of the Assassins had much to do with the training and instruction of Nizari fida’is, famed for their public missions during which they often gave their lives to eliminate adversaries. Misinformation from the Crusader accounts and the works of anti-Ismaili historians have contributed to the tales of fida’is being fed with hashish as part of their training. Whether fida’is were actually trained or dispatched by Nizari leaders is unconfirmed, but scholars including Vladimir Ivanov
The legends of the Assassins had much to do with the training and instruction of Nizari fida’is, famed for their public missions during which they often gave their lives to eliminate adversaries. Misinformation from the Crusader accounts and the works of anti-Ismaili historians have contributed to the tales of fida’is being fed with hashish as part of their training. Whether fida’is were actually trained or dispatched by Nizari leaders is unconfirmed, but scholars including Vladimir Ivanov
purport that the assassination of key figures including Saljuq vizier Nizam al-Mulk likely provided encouraging impetus to others in the community who sought to secure the Nizaris from political aggression. In fact, the Saljuqs and Crusaders both employed assassination as a military means of disposing of factional enemies. Yet during the Alamut period almost any murder of political significance in the Islamic lands became attributed to the Ismailis.p. 129 So inflated had this association grown, that in the work of orientalist scholars such as Bernard Lewis the Ismailis were virtually equated to the politically active fida’is. Thus the Nizari Ismaili community was regarded as a radical and heretical sect known as the Assassins. Originally, a "local and popular term" first applied to the Ismailis of Syria, the label was orally transmitted to Western historians and thus found itself in their histories of the Nizaris.
The tales of the fida’is’ training collected from anti-Ismaili historians and orientalists writers were confounded and compiled in Marco Polo's account, in which he described a "secret garden of paradise".p. 16 After being drugged, the Ismaili devotees were said be taken to a paradise-like garden filled with attractive young maidens and beautiful plants in which these fida’is would awaken. Here, they were told by an "old" man that they were witnessing their place in Paradise and that should they wish to return to this garden permanently, they must serve the Nizari cause. So went the tale of the "Old Man in the Mountain", assembled by Marco Polo and accepted by Joseph von Hammer-Purgstall, an 18th century Austrian
orientalist writer responsible for much of the spread of this legend. Until the 1930s, von Hammer's retelling of the Assassin legends served as the standard account of the Nizaris across Europe.p. 16
Modern works on the Nizaris have elucidated the history of the Nizaris and in doing so, dispelled popular histories from the past as mere legends. In 1933, under the direction of the Imam
Sultan Muhammad Shah, Aga Khan III
, the Islamic Research Association was developed. Historian Vladimir Ivanov was central to both this institution and the 1946 Ismaili Society of Bombay. Cataloguing a number of Ismaili texts, Ivanov provided the ground for great strides in modern Ismaili scholarship.p. 17
In recent years, Peter Willey has provided interesting evidence against the Assassin folklore of earlier scholars. Drawing on its established esoteric doctrine, Willey asserts that the Ismaili understanding of Paradise is a deeply symbolic one. While the Qur'an
ic description of Heaven includes natural imagery, Willey argues that no Nizari fida’i would seriously believe that he was witnessing Paradise simply by awakening in a beauteous garden.p. 55 The Nizaris' symbolic interpretation of the Qur'anic description of Paradise serves as evidence against the possibility of such an exotic garden used as motivation for the devotees to carry out their armed missions. Furthermore, Willey points out that a courtier of Hulagu Khan
, Juvayni
, surveyed the Alamut castle just before the Mongol invasion. In his reports about of the fortress, there are elaborate descriptions of sophisticated storage facilities and the famous Alamut library. However, even this anti-Ismaili historian makes no mention of the gardens on the Alamut grounds.p. 55 Having destroyed a number of texts of the library's collection, deemed by Juvayni to be heretical, it would be expected that he would pay significant attention to the Nizari gardens, particularly if they were the site of drug use and temptation. Having not once mentioned such gardens, Willey concludes that there is no sound evidence in favour of these fictitious legends.
These legends feature in certain works of fiction, including Vladimir Bartol
's 1938 novel Alamut
, and Simon Acland's First Crusade novels The Waste Land and The Flowers of Evil. In the latter the author suggests that the origin of the name Assassin is the Turkish word hashhash meaning opium, partly on the basis that this drug is more suitable for producing the effects suggested in the legends than hashish.
In the Assassin's Creed
series of historical
action-adventure video games
, the first game followed a fictional version of the Syrian wing of the sect, while subsequent games and Assassin's Creed media would depict its successor organizations opposed to a Templar conspiracy. The series imagines the Assassins as being active in various eras and locations: from 12th-century Syria
during the Third Crusade
(this incarnation depicted in the first game and the one recorded by the Polos in-universe), to 15th-century Renaissance
Italy
and Turkey
, up to the 21st century.
In the movie Prince Of Persia the Sands of Time
a group of mystical warriors active in ancient Persia are identified as Hashahsins.
gives prominent focus to what he terms "the order of Assassins", in section 24 of On the Genealogy of Morality
. Nietzsche's signature work is to point to the worthlessness of religion, and to attempt at the transvaluation of values
, that is, to transcend the inherited Jewish and Christian politics, psychology and ethics of ressentiment
or guilt. He aims at going beyond the categories of good and evil since they suppress the full potential of the strong and talented. Nietzsche heralds the arrival of the so-called 'free spirits' who no longer believe in truth. Thus, they alone are capable of redeeming the world of the modern ills of comfort, mediocrity, and nihilism.
Importantly, Nietzsche attacks the false spirits who are the host of self-describing 'unbelievers' of modern times who claim to reject religious deception as scholars and philosophers and yet retain the traditional beliefs in good and evil, and truth. Nietzsche compares the genuine free spirits with the Assassins: "When the Christian crusaders in the Orient came across that invincible order of Assassins – that order of free spirits par excellence whose lowest order received, through some channel or other, a hint about that symbol and spell reserved for the uppermost echelons alone, as their secret: "nothing is true, everything is permitted". Now that was freedom of the spirit, with that, belief in truth itself was renounced."
Nizari
'The Shī‘a Imami Ismā‘īlī Tariqah also referred to as the Ismā‘īlī or Nizārī , is a path of Shī‘a Islām, emphasizing social justice, pluralism, and human reason within the framework of the mystical tradition of Islam. The Nizari are the second largest branch of Shia Islam and form the majority...
Ismailis, particularly those of Persia (and Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
) that existed from around 1092 to 1265. Posing a strong military threat to Sunni Saljuq authority within the Persian territories, the Nizari Ismailis captured and inhabited many mountain fortresses under the leadership of Hassan-i Sabbah.
The name 'Assassin', from the Arabic Hashishin or "users of hashish
Hashish
Hashish is a cannabis preparation composed of compressed stalked resin glands, called trichomes, collected from the unfertilized buds of the cannabis plant. It contains the same active ingredients but in higher concentrations than unsifted buds or leaves...
", was originally derogatory and used by their adversaries during the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. The modern word 'assassin
Assassination
To carry out an assassination is "to murder by a sudden and/or secret attack, often for political reasons." Alternatively, assassination may be defined as "the act of deliberately killing someone, especially a public figure, usually for hire or for political reasons."An assassination may be...
' is derived from this name. However, Amin Malouf states that "The truth is different. According to texts that have come down to us from Alamut
Alamut
Alamut was a mountain fortress located in the South Caspian province of Daylam near the Rudbar region in Iran, approximately 100 kilometres from present-day Tehran, Iran...
, Hassan-i Sabbah liked to call his disciples Asasiyun, meaning people who are faithful to the Asās, meaning 'foundation' of the faith. This is the word, misunderstood by foreign travelers, that seemed similar to 'hashish'".
The Masyaf
Masyaf
Masyaf is a city in Syria, in the Hama Governorate, notable for its large medieval castle.It was used by Hashashins as their headquarters after the destruction of Alamut....
branch of the Assassins was taken over by the Mamluk
Mamluk
A Mamluk was a soldier of slave origin, who were predominantly Cumans/Kipchaks The "mamluk phenomenon", as David Ayalon dubbed the creation of the specific warrior...
Sultan
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
Baibars
Baibars
Baibars or Baybars , nicknamed Abu l-Futuh , was a Mamluk Sultan of Egypt. He was one of the commanders of the forces which inflicted a devastating defeat on the Seventh Crusade of King Louis IX of France and he led the vanguard of the Egyptian army at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, which marked...
in 1273. The Mamluk
Mamluk
A Mamluk was a soldier of slave origin, who were predominantly Cumans/Kipchaks The "mamluk phenomenon", as David Ayalon dubbed the creation of the specific warrior...
s however, continued to use the services of the remaining Assassins: Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad Ibn Battuta , or simply Ibn Battuta, also known as Shams ad–Din , was a Muslim Moroccan Berber explorer, known for his extensive travels published in the Rihla...
reported in the 14th century their fixed rate of pay per murder. In exchange, the higher authorities allowed them to exist. The mention of Assassins were also preserved within European sources, such as the writings of Marco Polo
Marco Polo
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
, in which they are depicted as trained killers, responsible for the systematic elimination of opposing figures.
Origins
The origins of the Assassins trace back to just before the First CrusadeFirst Crusade
The First Crusade was a military expedition by Western Christianity to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquest of the Levant, ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem...
around 1080. It is difficult to find out much information about the origins of the Assassins because most early sources are either written by enemies of the cult or based on legends. Most sources dealing with the order’s inner working were destroyed with the capture of Alamut
Alamut
Alamut was a mountain fortress located in the South Caspian province of Daylam near the Rudbar region in Iran, approximately 100 kilometres from present-day Tehran, Iran...
, the Assassins' headquarters. However, it is possible to trace the beginnings of the cult back to its first Grandmaster, Hasan-i Sabbah. A passionate believer of the Isma’ili beliefs, Hasan-i-Sabbah was well liked throughout Cairo
Cairo
Cairo , is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world and Africa, and the 16th largest metropolitan area in the world. Nicknamed "The City of a Thousand Minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture, Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life...
, Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, and most of the Middle East by other Isma’ili, which led to a number of people becoming his followers. Using his fame and popularity, Sabbah founded the Order of the Assassins. While his motives for founding this order are ultimately unknown, it has been speculated that it was for his own political and personal gain and to also exact vengeance on his enemies. His motivation for political power probably came through what he thought to be dealings with other Muslims in the Middle East, particularly Sunnis, but because of the unrest in the holy land caused by the calling of the Crusades
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
, Hasan-i-Sabbah found himself not only fighting for power with other Muslims, but also with the invading Christian forces.
After creating the Order, Sabbah searched for a location that would be fit for a sturdy headquarters and decided on the fortress at Alamut in what is now northwestern Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
. It is still disputed whether Sabbah built the fortress himself or if it was already built at the time of his arrival. Whether he created it himself or not, Sabbah adapted the fortress to suit his needs of not only defense from hostile forces, but also indoctrination of his followers. After laying claim to the fortress at Alamut, Sabbah began expanding his influence outward to nearby towns and districts, using his agents to gain political favour and intimidate the local populations.
Spending most of his days at Alamut working on religious works and doctrines for his Order, Sabbah was never to leave his fortress again in his lifetime. He had established a secret society of deadly assassins, one which was built in a hierarchical format. Below Sabbah, the Grand Headmaster of the Order, were those known as “Greater Propagandists”, followed by the normal "Propagandists", the Rafiqs ("Companions"), and the Lasiqs ("Adherents"). It was the Lasiqs who were trained to become some of the most feared assassins, or as they were called, "Fida’i" (self-sacrificing agent), in the known world.
It is, however, unknown how Hassan-i-Sabbah was able to get his "Fida’i" to perform with such fervent loyalty. One theory, possibly the most well known but also the most criticized, comes from the observations from Marco Polo
Marco Polo
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
during his travels to the Orient. He describes how the "Old Man of the Mountain" (Sabbah) would drug his young followers with hashish, lead them to a "paradise", and then claim that only he had the means to allow for their return. Perceiving that Sabbah was either a prophet or some kind of magic man, his disciples, believing that only he could return them to "paradise", were fully committed to his cause and willing to carry out his every request. With his new weapons, Sabbah began to order assassinations, ranging from politicians to great generals. Assassins rarely would attack ordinary citizens though and tended not to be hostile towards them.
Although the "Fida’i" were the lowest rank in Sabbah’s order and only used as expendable pawns to do the Grandmaster’s bidding, much time and many resources were put in to training them. The Assassins were generally young in age giving them the physical strength and stamina which would be required to carry out these murders. However, physical prowess was not the only trait that was required to be a "Fida’i". To get to their targets, the Assassins had to be patient, cold, and calculating. They were generally intelligent and well read because they were required to possess not only knowledge about their enemy, but his or her culture and their native language. They were trained by their masters to disguise themselves, sneak in to enemy territory and perform the assassinations instead of simply attacking their target outright.
As tensions in the Middle East grew during the Crusades, the Assassins were also known for taking contracts from outside sources on either side of the war, whether it was from the invading Crusaders or the Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
forces, so long as the assassination fit in to the Grandmaster's plan.
Etymology
The Assassins were finally linked by the 19th century orientalist scholar Silvestre de SacySilvestre de Sacy
Antoine Isaac, Baron Silvestre de Sacy , was a French linguist and orientalist. His son, Ustazade Silvestre de Sacy, became a journalist.-Early life:...
to the Arabic hashish using their variant names assassin and assissini in the 19th century. Citing the example of one of the first written applications of the Arabic term hashish to the Ismailis by 13th century historian Abu Shama, de Sacy demonstrated its connection to the name given to the Ismailis throughout Western scholarship.p. 14 The first known usage of the term hashishi has been traced back to 1122 CE when the Fatimid
Fatimid
The Fatimid Islamic Caliphate or al-Fāṭimiyyūn was a Berber Shia Muslim caliphate first centered in Tunisia and later in Egypt that ruled over varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and Hijaz from 5 January 909 to 1171.The caliphate was ruled by the Fatimids, who established the...
caliph
Caliph
The Caliph is the head of state in a Caliphate, and the title for the ruler of the Islamic Ummah, an Islamic community ruled by the Shari'ah. It is a transcribed version of the Arabic word which means "successor" or "representative"...
al-Āmir
Al-Amir
Al-Āmir bi'Aḥkāmi l-Lah was the tenth Fatimid Caliph , and recognised as the 20th imam by the Mustaali Ismaili Shi'a sect....
employed it in derogatory reference to the Syrian Nizaris.p. 14 Used figuratively, the term hashishi connoted meanings such as outcasts or rabble.p. 14 Without actually accusing the group of using the hashish drug, the Caliph
Caliph
The Caliph is the head of state in a Caliphate, and the title for the ruler of the Islamic Ummah, an Islamic community ruled by the Shari'ah. It is a transcribed version of the Arabic word which means "successor" or "representative"...
used the term in a pejorative manner. This label was quickly adopted by anti-Ismaili historians and applied to the Ismailis of Syria and Persia. The spread of the term was further facilitated through military encounters between the Nizaris and the Crusaders
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
, whose chroniclers adopted the term and disseminated it across Europe.
During the medieval period, Western scholarship on the Ismailis contributed to the popular view of the community as a radical sect of assassins, believed to be trained for the precise murder of their adversaries. By the 14th century CE, European scholarship on the topic had not advanced much beyond the work and tales from the Crusaders.p. 14 The origins of the word forgotten, across Europe the term Assassin had taken the meaning of "professional murderer".p. 14 In 1603 the first Western publication on the topic of the Assassins was authored by a court official for King Henry IV
Henry IV of France
Henry IV , Henri-Quatre, was King of France from 1589 to 1610 and King of Navarre from 1572 to 1610. He was the first monarch of the Bourbon branch of the Capetian dynasty in France....
and was mainly based on the narratives of Marco Polo
Marco Polo
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
from his visits to the Near East
Near East
The Near East is a geographical term that covers different countries for geographers, archeologists, and historians, on the one hand, and for political scientists, economists, and journalists, on the other...
. While he assembled the accounts of many Western travelers, the author failed to explain the etymology of the term Assassin.p. 15
According to Lebanese writer Amin Maalouf
Amin Maalouf
Amin Maalouf , born 25 February 1949 in Beirut, is a Lebanese-born French author. Although his native language is Arabic, he writes in French, and his works have been translated into many languages. He received the Prix Goncourt in 1993 for his novel The Rock of Tanios...
:
Another modern author, Edward Burman, states that:
Timeline

- 1092: The famous SeljuqGreat Seljuq EmpireThe Great Seljuq Empire was a medieval Persianate, Turko-Persian Sunni Muslim empire, originating from the Qynyq branch of Oghuz Turks. The Seljuq Empire controlled a vast area stretching from the Hindu Kush to eastern Anatolia and from Central Asia to the Persian Gulf...
vizier Nizam al-Mulk was murdered by an Assassin in Baghdad. He becomes their first victim. - 1094: Al-Mustansir dies, and Hassan does not recognize the new caliph, al-Mustali. He and his followers transferred their allegiance to his brother Nizar. The followers of Hassan soon even came at odds with the caliph in Baghdad too.
- 1113: Following the death of Aleppo's ruler, Ridwan, the Assassins are driven out of the city by the troops of Ibn al-Khashab.
- 1110's: The Assassins in Syria change their strategy, and start undercover work and build cells in all cities around the region.
- 1123: Ibn al-Khashab is killed by an Assassin.
- 1124: Hassan dies in AlamutAlamutAlamut was a mountain fortress located in the South Caspian province of Daylam near the Rudbar region in Iran, approximately 100 kilometres from present-day Tehran, Iran...
, but the organization lives on stronger than ever. — The leading qadi Abu Saad al-Harawi is killed by an Assassin.
After the death of Hassan some notable events included the following;
- 1126 November 26: Emir Porsuki of Aleppo and Mosul is killed by an Assassin .
- 12th century: The Assassins extend their activities into Syria, where they could get much support from the local Shi'i minority as the Seljuq sultanate had captured this territory.
- The Assassins capture a group of castles in the Nusayriyya Mountains (modern Syria). The most important of these castles was the MasyafMasyafMasyaf is a city in Syria, in the Hama Governorate, notable for its large medieval castle.It was used by Hashashins as their headquarters after the destruction of Alamut....
, from which the "The Old Man of Mountain", Rashideddin Sinan ruled practically independent from the main leaders of the Assassins. - 1173: The Assassins of Syria enter negotiations with Amalric IAmalric I of JerusalemAmalric I of Jerusalem was King of Jerusalem 1163–1174, and Count of Jaffa and Ascalon before his accession. Amalric was the second son of Melisende of Jerusalem and Fulk of Jerusalem...
, King of Jerusalem, with the aim of converting to Christianity. But as the Assassins by now were numerous and often worked as peasants, they paid high taxes to local Christian landlords, that Christian peasants were exempted from. Their conversion was opposed by the landlords, and this year the Assassin negotiators were murdered by Christian knights. After this, there was no more talk of conversion. - 1175: Rashideddin's men make two attempts on the life of SaladinSaladinṢalāḥ ad-Dīn Yūsuf ibn Ayyūb , better known in the Western world as Saladin, was an Arabized Kurdish Muslim, who became the first Sultan of Egypt and Syria, and founded the Ayyubid dynasty. He led Muslim and Arab opposition to the Franks and other European Crusaders in the Levant...
, the leader of the Ayyubids. The second time, the Assassin came so close that wounds were inflicted upon Saladin. - 1192: Conrad of MontferratConrad of MontferratConrad of Montferrat was a northern Italian nobleman, one of the major participants in the Third Crusade. He was the de facto King of Jerusalem, by marriage, from 24 November 1190, but officially elected only in 1192, days before his death...
, King of Jerusalem, is stabbed to death by Assassins before his coronation. - 1256: Alamut fortress falls to the Mongols under the leadership of Hülegü. Before this happened, several other fortresses had been captured, and finally Alamut was weak and with little support.
- 1257: The Mongol warlord Hülegü attacks and destroys the fortress at Alamut. The Assassin library is fully razed, hence destroying a crucial source of information about the Assassins.
- Around 1265: The Assassin strongholds in Syria fall to the MamlukMamlukA Mamluk was a soldier of slave origin, who were predominantly Cumans/Kipchaks The "mamluk phenomenon", as David Ayalon dubbed the creation of the specific warrior...
sultan Baybars I.
Military tactics

Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. One such method was that of assassination, the selective elimination of prominent rival figures. The murders of political adversaries were usually carried out in public spaces, creating resounding intimidation for other possible enemies.p. 129 Throughout history, many groups have resorted to assassination as a means of achieving political ends. In the Ismaili context, these assignments were performed by fida’is (devotees) of the Ismaili mission. They were unique in that civilians were never targeted. The assassinations were against those whose elimination would most greatly reduce aggression against the Ismailis and, in particular, against those who had perpetrated massacres against the community. A single assassination was usually employed in favour of widespread bloodshed resulting from factional combat. The first instance of assassination in the effort to establish an Nizari Ismaili state in Persia is widely considered to be the murder of Seljuq vizier
Vizier
A vizier or in Arabic script ; ; sometimes spelled vazir, vizir, vasir, wazir, vesir, or vezir) is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in a Muslim government....
, Nizam al-Mulk
Nizam al-Mulk
Abu Ali al-Hasan al-Tusi Nizam al-Mulk, better known as Khwaja Nizam al-Mulk Tusi ; born in 1018 – 14 October 1092) was a Persian scholar and vizier of the Seljuq Empire...
.p. 29 Carried out by a man dressed as a Sufi whose identity remains unclear, the vizier's murder in a Seljuq court is distinctive of exactly the type of visibility for which missions of the fida’is have been significantly exaggerated.p. 29 While the Seljuqs and Crusaders
Crusaders
The Crusaders are a New Zealand professional rugby union team based in Christchurch that competes in the Super Rugby competition. They are the most successful team in Super Rugby history with seven titles...
both employed assassination as a military means of disposing of factional enemies, during the Alamut period almost any murder of political significance in the Islamic lands was attributed to the Ismailis.p. 129 So inflated had this association grown, that in the work of orientalist scholars such as Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis, FBA is a British-American historian, scholar in Oriental studies, and political commentator. He is the Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near Eastern Studies at Princeton University...
, the Ismailis were equated to the politically active fida’is and thus regarded as a radical and heretical
Heresy
Heresy is a controversial or novel change to a system of beliefs, especially a religion, that conflicts with established dogma. It is distinct from apostasy, which is the formal denunciation of one's religion, principles or cause, and blasphemy, which is irreverence toward religion...
sect known as the Assassins.
The military approach of the Nizari Ismaili state was largely a defensive one, with strategically chosen sites that appeared to avoid confrontation wherever possible without the loss of life.p. 58 But the defining characteristic of the Nizari Ismaili state was that it was scattered geographically throughout Persia and Syria. The Alamut castle therefore was only one of a nexus of strongholds throughout the regions where Ismailis could retreat to safety if necessary. West of Alamut in the Shahrud Valley, the major fortress of Lamasar served as just one example of such a retreat. In the context of their political uprising, the various spaces of Ismaili military presence took on the name dar al-hijra . The notion of the dar al-hijra originates from the time of Muhammad
Muhammad
Muhammad |ligature]] at U+FDF4 ;Arabic pronunciation varies regionally; the first vowel ranges from ~~; the second and the last vowel: ~~~. There are dialects which have no stress. In Egypt, it is pronounced not in religious contexts...
, who migrated with his supporters from intense persecution to safe haven in Yathrib (Medina
Medina
Medina , or ; also transliterated as Madinah, or madinat al-nabi "the city of the prophet") is a city in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia, and serves as the capital of the Al Madinah Province. It is the second holiest city in Islam, and the burial place of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, and...
). In this way, the Fatimid
Fatimid
The Fatimid Islamic Caliphate or al-Fāṭimiyyūn was a Berber Shia Muslim caliphate first centered in Tunisia and later in Egypt that ruled over varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and Hijaz from 5 January 909 to 1171.The caliphate was ruled by the Fatimids, who established the...
s found their dar al-hijra in North Africa. Likewise during the revolt against the Seljuqs, several fortresses served as spaces of refuge for the Ismailis.
Downfall and aftermath

Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire , initially named as Greater Mongol State was a great empire during the 13th and 14th centuries...
during the well documented invasion of Khwarizm. They probably dispatched their assassins to kill Mongke Khan
Möngke Khan
Möngke Khan , born Möngke, , was the fourth Great Khan of the Mongol Empire from July 1, 1251 – August 11, 1259. He was the first Great Khan from the Toluid line, and made significant reforms to improve the administration of the Empire during his reign...
. Thus a decree was handed over to the Mongol commander Kitbuqa
Kitbuqa
Kitbuqa Noyan was a Nestorian Christian and a member of the Naiman Turks, a group that was subservient to the Mongol Empire. He was a lieutenant and confidant of the Mongol Ilkhan Hulagu, assisting him in his conquests in the Middle East...
who began to assault several Hashshashin fortresses in 1253 before Hulagu's
Hulagu Khan
Hulagu Khan, also known as Hülegü, Hulegu , was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Southwest Asia...
advance in 1256. The Mongols
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
besieged Alamut
Alamut
Alamut was a mountain fortress located in the South Caspian province of Daylam near the Rudbar region in Iran, approximately 100 kilometres from present-day Tehran, Iran...
on December 15, 1256. The Assassins recaptured and held Alamut for a few months in 1275, but they were crushed and their political power was lost forever.
The Syrian branch of the Assassins was taken over by the Mamluk
Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo)
The Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt was the final independent Egyptian state prior to the establishment of the Muhammad Ali Dynasty in 1805. It lasted from the overthrow of the Ayyubid Dynasty until the Ottoman conquest of Egypt in 1517. The sultanate's ruling caste was composed of Mamluks, Arabised...
Sultan Baibars
Baibars
Baibars or Baybars , nicknamed Abu l-Futuh , was a Mamluk Sultan of Egypt. He was one of the commanders of the forces which inflicted a devastating defeat on the Seventh Crusade of King Louis IX of France and he led the vanguard of the Egyptian army at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, which marked...
in 1273. The Mamluks continued to use the services of the remaining Assassins: Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad Ibn Battuta , or simply Ibn Battuta, also known as Shams ad–Din , was a Muslim Moroccan Berber explorer, known for his extensive travels published in the Rihla...
reported in the 14th century their fixed rate of pay per murder. In exchange, they were allowed to exist. Eventually, they resorted to the act of Taqq'iya
Taqiyya
Taqiyya , meaning religious dissimulation, is a practice emphasized in Shi'a Islam whereby adherents may conceal their religion when they are under threat, persecution, or compulsion...
(dissimulation), hiding their true identities until their Imams would awaken them.
According to the historian Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yāqūt ibn-'Abdullah al-Rūmī al-Hamawī) was an Islamic biographer and geographer renowned for his encyclopedic writings on the Muslim world. "al-Rumi" refers to his Greek descent; "al-Hamawi" means that he is from Hama, Syria, and ibn-Abdullah is a reference to his father's name, Abdullah...
, the Böszörmény
Böszörmény
Böszörmény, also Izmaelita or Szerecsen , is a name for the Muslims who lived in the Kingdom of Hungary in the 10-13th centuries. Some of the böszörmény probably joined the federation of the seven Magyar tribes during the 9th century, and later smaller groups of Muslims arrived to the Carpathian...
, (Izmaleita or Ismaili/Nizari
Nizari
'The Shī‘a Imami Ismā‘īlī Tariqah also referred to as the Ismā‘īlī or Nizārī , is a path of Shī‘a Islām, emphasizing social justice, pluralism, and human reason within the framework of the mystical tradition of Islam. The Nizari are the second largest branch of Shia Islam and form the majority...
) denomination of the Muslims who lived in the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
in the 10–13th centuries, were employed as mercenaries by the kings of Hungary. However following the establishment of the Christian Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
their community was vanquished by the end of the 13th century due to the Inquisition
Inquisition
The Inquisition, Inquisitio Haereticae Pravitatis , was the "fight against heretics" by several institutions within the justice-system of the Roman Catholic Church. It started in the 12th century, with the introduction of torture in the persecution of heresy...
s ordered by the Catholic Church during the reign of Coloman, King of Hungary.
Legends and folklore

Vladimir Alexeyevich Ivanov
Vladimir Alekseevich Ivanov was a Russian orientalist. He was born in Saint Petersburg, Russia and died in Tehran, Iran. His work on Ismailism has opened new doors for the modern researchers on Islam. He graduated in 1907 and joined the faculty of Oriental Languages of the University of St...
purport that the assassination of key figures including Saljuq vizier Nizam al-Mulk likely provided encouraging impetus to others in the community who sought to secure the Nizaris from political aggression. In fact, the Saljuqs and Crusaders both employed assassination as a military means of disposing of factional enemies. Yet during the Alamut period almost any murder of political significance in the Islamic lands became attributed to the Ismailis.p. 129 So inflated had this association grown, that in the work of orientalist scholars such as Bernard Lewis the Ismailis were virtually equated to the politically active fida’is. Thus the Nizari Ismaili community was regarded as a radical and heretical sect known as the Assassins. Originally, a "local and popular term" first applied to the Ismailis of Syria, the label was orally transmitted to Western historians and thus found itself in their histories of the Nizaris.
The tales of the fida’is’ training collected from anti-Ismaili historians and orientalists writers were confounded and compiled in Marco Polo's account, in which he described a "secret garden of paradise".p. 16 After being drugged, the Ismaili devotees were said be taken to a paradise-like garden filled with attractive young maidens and beautiful plants in which these fida’is would awaken. Here, they were told by an "old" man that they were witnessing their place in Paradise and that should they wish to return to this garden permanently, they must serve the Nizari cause. So went the tale of the "Old Man in the Mountain", assembled by Marco Polo and accepted by Joseph von Hammer-Purgstall, an 18th century Austrian
Austrians
Austrians are a nation and ethnic group, consisting of the population of the Republic of Austria and its historical predecessor states who share a common Austrian culture and Austrian descent....
orientalist writer responsible for much of the spread of this legend. Until the 1930s, von Hammer's retelling of the Assassin legends served as the standard account of the Nizaris across Europe.p. 16
Modern works on the Nizaris have elucidated the history of the Nizaris and in doing so, dispelled popular histories from the past as mere legends. In 1933, under the direction of the Imam
Imam
An imam is an Islamic leadership position, often the worship leader of a mosque and the Muslim community. Similar to spiritual leaders, the imam is the one who leads Islamic worship services. More often, the community turns to the mosque imam if they have a religious question...
Sultan Muhammad Shah, Aga Khan III
Aga Khan III
Sir Sultan Muhammed Shah, Aga Khan III, GCSI, GCMG, GCIE, GCVO, PC was the 48th Imam of the Shia Ismaili Muslims. He was one of the founders and the first president of the All-India Muslim League, and served as President of the League of Nations from 1937-38. He was nominated to represent India to...
, the Islamic Research Association was developed. Historian Vladimir Ivanov was central to both this institution and the 1946 Ismaili Society of Bombay. Cataloguing a number of Ismaili texts, Ivanov provided the ground for great strides in modern Ismaili scholarship.p. 17
In recent years, Peter Willey has provided interesting evidence against the Assassin folklore of earlier scholars. Drawing on its established esoteric doctrine, Willey asserts that the Ismaili understanding of Paradise is a deeply symbolic one. While the Qur'an
Qur'an
The Quran , also transliterated Qur'an, Koran, Alcoran, Qur’ān, Coran, Kuran, and al-Qur’ān, is the central religious text of Islam, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God . It is regarded widely as the finest piece of literature in the Arabic language...
ic description of Heaven includes natural imagery, Willey argues that no Nizari fida’i would seriously believe that he was witnessing Paradise simply by awakening in a beauteous garden.p. 55 The Nizaris' symbolic interpretation of the Qur'anic description of Paradise serves as evidence against the possibility of such an exotic garden used as motivation for the devotees to carry out their armed missions. Furthermore, Willey points out that a courtier of Hulagu Khan
Hulagu Khan
Hulagu Khan, also known as Hülegü, Hulegu , was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Southwest Asia...
, Juvayni
Ata al-Mulk Juvayni
Atâ-Malek Jovayni was a Persian historian who wrote an account of the Mongol Empire entitled Ta' rīkh-i jahān-gushā .He was born in Juvain, a city in Khorasan in northeastern Iran...
, surveyed the Alamut castle just before the Mongol invasion. In his reports about of the fortress, there are elaborate descriptions of sophisticated storage facilities and the famous Alamut library. However, even this anti-Ismaili historian makes no mention of the gardens on the Alamut grounds.p. 55 Having destroyed a number of texts of the library's collection, deemed by Juvayni to be heretical, it would be expected that he would pay significant attention to the Nizari gardens, particularly if they were the site of drug use and temptation. Having not once mentioned such gardens, Willey concludes that there is no sound evidence in favour of these fictitious legends.
These legends feature in certain works of fiction, including Vladimir Bartol
Vladimir Bartol
Vladimir Bartol was a Slovene writer, most famous for his novel Alamut. Alamut was published in 1938 and translated into numerous languages, becoming the most popular work of Slovene literature around the world.-Biography:Bartol was born on February 24, 1903 in San Giovanni , a suburb of the...
's 1938 novel Alamut
Alamut
Alamut was a mountain fortress located in the South Caspian province of Daylam near the Rudbar region in Iran, approximately 100 kilometres from present-day Tehran, Iran...
, and Simon Acland's First Crusade novels The Waste Land and The Flowers of Evil. In the latter the author suggests that the origin of the name Assassin is the Turkish word hashhash meaning opium, partly on the basis that this drug is more suitable for producing the effects suggested in the legends than hashish.
In the Assassin's Creed
Assassin's Creed
Assassin's Creed is an award-winning historical third person, stealth action-adventure video game developed by Ubisoft for PlayStation 3, Xbox 360 and Microsoft Windows. The bulk of the game takes place during the Third Crusade, with the plot revolving around a sect known as the Secret Order of...
series of historical
Historical fiction
Historical fiction tells a story that is set in the past. That setting is usually real and drawn from history, and often contains actual historical persons, but the principal characters tend to be fictional...
action-adventure video games
Action-adventure game
An action-adventure game is a video game that combines elements of the adventure game genre with various action game elements. It is perhaps the broadest and most diverse genre in gaming, and can include many games which might better be categorized under narrow genres...
, the first game followed a fictional version of the Syrian wing of the sect, while subsequent games and Assassin's Creed media would depict its successor organizations opposed to a Templar conspiracy. The series imagines the Assassins as being active in various eras and locations: from 12th-century Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
during the Third Crusade
Third Crusade
The Third Crusade , also known as the Kings' Crusade, was an attempt by European leaders to reconquer the Holy Land from Saladin...
(this incarnation depicted in the first game and the one recorded by the Polos in-universe), to 15th-century Renaissance
Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance began the opening phase of the Renaissance, a period of great cultural change and achievement in Europe that spanned the period from the end of the 13th century to about 1600, marking the transition between Medieval and Early Modern Europe...
Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, up to the 21st century.
In the movie Prince Of Persia the Sands of Time
Prince of Persia: The Sands of Time (film)
Prince of Persia: The Sands of Time is a 2010 sword-and-sorcery action film written by Jordan Mechner, Boaz Yakin, Doug Miro, and Carlo Bernard; directed by Mike Newell; produced by Jerry Bruckheimer; and distributed by Walt Disney Pictures...
a group of mystical warriors active in ancient Persia are identified as Hashahsins.
Friedrich Nietzsche
The 19th century philosopher Friedrich NietzscheFriedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche was a 19th-century German philosopher, poet, composer and classical philologist...
gives prominent focus to what he terms "the order of Assassins", in section 24 of On the Genealogy of Morality
On the Genealogy of Morality
On the Genealogy of Morality, or On the Genealogy of Morals , subtitled "A Polemic" , is a work by German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche, composed and first published in 1887 with the intention of expanding and following through on certain new doctrines sketched out in his previous work Beyond...
. Nietzsche's signature work is to point to the worthlessness of religion, and to attempt at the transvaluation of values
Transvaluation of values
The revaluation of all values or the transvaluation of all values is a concept from the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche.Elaborating the concept in The Antichrist, Nietzsche asserts that Christianity, not merely as a religion but also as the predominant moral system of the Western world, in fact...
, that is, to transcend the inherited Jewish and Christian politics, psychology and ethics of ressentiment
Ressentiment
Ressentiment , in philosophy and psychology, is a particular form of resentment or hostility. It is the French word for "resentment" . Ressentiment is a sense of hostility directed at that which one identifies as the cause of one's frustration, that is, an assignment of blame for one's frustration...
or guilt. He aims at going beyond the categories of good and evil since they suppress the full potential of the strong and talented. Nietzsche heralds the arrival of the so-called 'free spirits' who no longer believe in truth. Thus, they alone are capable of redeeming the world of the modern ills of comfort, mediocrity, and nihilism.
Importantly, Nietzsche attacks the false spirits who are the host of self-describing 'unbelievers' of modern times who claim to reject religious deception as scholars and philosophers and yet retain the traditional beliefs in good and evil, and truth. Nietzsche compares the genuine free spirits with the Assassins: "When the Christian crusaders in the Orient came across that invincible order of Assassins – that order of free spirits par excellence whose lowest order received, through some channel or other, a hint about that symbol and spell reserved for the uppermost echelons alone, as their secret: "nothing is true, everything is permitted". Now that was freedom of the spirit, with that, belief in truth itself was renounced."
See also
- History of the Shī‘a Imāmī Ismā'īlī ṬarīqahHistory of the Shī‘a Imāmī Ismā'īlī ṬarīqahThe History of the Shī‘a Imāmī Ismā'īlī Ṭarīqah from the founding of Islam covers a period of over 1400 years. It begins with the mission of the prophet Muhammad to restore to humanity the universality and knowledge of the oneness of the divine within the Abrahamic tradition, through the final...
- Index of Middle Ages in modern culture: Assassins
- SicariiSicariiSicarii is a term applied, in the decades immediately preceding the destruction of Jerusalem in 70 AD, to an extremist splinter group of the Jewish Zealots, who attempted to expel the Romans and their partisans from Judea using concealed daggers .-History:The Sicarii used...
- NinjaNinjaA or was a covert agent or mercenary of feudal Japan specializing in unorthodox arts of war. The functions of the ninja included espionage, sabotage, infiltration, and assassination, as well as open combat in certain situations...
- CrusadesCrusadesThe Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...

