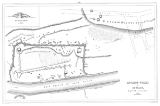
Aztalan State Park
Encyclopedia
Wisconsin
Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is...
state park
State park
State parks are parks or other protected areas managed at the federated state level within those nations which use "state" as a political subdivision. State parks are typically established by a state to preserve a location on account of its natural beauty, historic interest, or recreational...
located just south of the town of Aztalan, Wisconsin
Aztalan, Wisconsin
Aztalan is a town in Jefferson County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 1,447 at the 2000 census. The unincorporated communities of Aztalan and Jefferson Junction are located in the town.-Aztalan State Park:...
at latitude N 43° 4' and longitude W 88° 52', and established in 1952. It was also designated a National Historic Landmark
National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark is a building, site, structure, object, or district, that is officially recognized by the United States government for its historical significance...
in 1964 and added to the National Register of Historic Places
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places is the United States government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures, and objects deemed worthy of preservation...
in 1966. The park covers 172 acres (0.7 km2 or 70 ha
Hectare
The hectare is a metric unit of area defined as 10,000 square metres , and primarily used in the measurement of land. In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the are was defined as being 100 square metres and the hectare was thus 100 ares or 1/100 km2...
) along the Crawfish River
Crawfish River
The Crawfish River is a tributary of the Rock River, long, in south-central Wisconsin in the United States. Via the Rock River, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River....
.
Aztalan is the site of an ancient Native American
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
settlement that flourished during the 10th to 13th centuries.
Pre-history (900–1300)
Aztalan was first settled around 900 by a Native American culture known as the Middle Mississippian TraditionMississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1500 CE, varying regionally....
. The most famous example of a Middle Mississippian settlement is at Cahokia
Cahokia
Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site is the area of an ancient indigenous city located in the American Bottom floodplain, between East Saint Louis and Collinsville in south-western Illinois, across the Mississippi River from St. Louis, Missouri. The site included 120 human-built earthwork mounds...
, Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
. These settlements are characterized by the construction of mound
Mound
A mound is a general term for an artificial heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. The most common use is in reference to natural earthen formation such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. The term may also be applied to any rounded area of topographically...
s, stockade
Fortification
Fortifications are military constructions and buildings designed for defence in warfare and military bases. Humans have constructed defensive works for many thousands of years, in a variety of increasingly complex designs...
s, and house
House
A house is a building or structure that has the ability to be occupied for dwelling by human beings or other creatures. The term house includes many kinds of different dwellings ranging from rudimentary huts of nomadic tribes to free standing individual structures...
s, by decorated Mississippian culture pottery
Mississippian culture pottery
Mississippian culture pottery is the ceramic tradition of the Mississippian culture found as artifacts in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. It is often characterized by the adoption and use of riverine shell-tempering agents in the clay paste. Shell tempering is one of...
and agricultural practices
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. There are also elements of the Woodland culture found here.
The residents were involved in long distance trade. Some of the items found include copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
from Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
's Upper Peninsula
Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan is the northern of the two major land masses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan. It is commonly referred to as the Upper Peninsula, the U.P., or Upper Michigan. It is also known as the land "above the Bridge" linking the two peninsulas. The peninsula is bounded...
, shells from the coast of the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
, and stone such as Mill Creek chert
Mill Creek chert
Mill Creek chert is a type of chert found in Southern Illinois and heavily exploited by members of the Mississippian culture . Artifacts made from this material are found in archeological sites throughout the American Midwest and Southeast. It is named for a village and stream near the quarrys,...
from other areas of the Midwest.
Sometime between the years 1200 and 1300, the Aztalan settlement was abandoned for reasons that remain unknown to this day.
Life in Aztalan
Most of the residents dwelled in circular or rectangular houses between the river and the Eastern secondary wall. The placement of the structures suggests that the layout was planned, but not in rows such as are found along streetStreet
A street is a paved public thoroughfare in a built environment. It is a public parcel of land adjoining buildings in an urban context, on which people may freely assemble, interact, and move about. A street can be as simple as a level patch of dirt, but is more often paved with a hard, durable...
s. Instead, it is thought that houses were constructed around a central plaza area that may have been used for rituals. Posts for the house frames were either placed in individual holes, or in a trench dug slightly narrower than the posts. Wall
Wall
A wall is a usually solid structure that defines and sometimes protects an area. Most commonly, a wall delineates a building and supports its superstructure, separates space in buildings into rooms, or protects or delineates a space in the open air...
s were then completed with wattle and daub
Wattle and daub
Wattle and daub is a composite building material used for making walls, in which a woven lattice of wooden strips called wattle is daubed with a sticky material usually made of some combination of wet soil, clay, sand, animal dung and straw...
, a plaster mixture of grass
Poaceae
The Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
and clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
, and the roof
Roof
A roof is the covering on the uppermost part of a building. A roof protects the building and its contents from the effects of weather. Structures that require roofs range from a letter box to a cathedral or stadium, dwellings being the most numerous....
covered with bark
Bark
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner...
or thatch. The doorway usually faced south to keep out the winter's north winds. Inside, a single family slept on pole frame beds, covered with tamarack boughs, deer
Deer
Deer are the ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. Species in the Cervidae family include white-tailed deer, elk, moose, red deer, reindeer, fallow deer, roe deer and chital. Male deer of all species and female reindeer grow and shed new antlers each year...
skins, and furs. Sometimes a fire was kept in the middle of the house and a hole in the roof let out the smoke
Smoke
Smoke is a collection of airborne solid and liquid particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires , but may also be used for pest...
. Pits in the house stored foods like corn
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, nut
Nut (fruit)
A nut is a hard-shelled fruit of some plants having an indehiscent seed. While a wide variety of dried seeds and fruits are called nuts in English, only a certain number of them are considered by biologists to be true nuts...
s, and seed
Seed
A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant...
s in woven bags, while perishable foods like meat
Meat
Meat is animal flesh that is used as food. Most often, this means the skeletal muscle and associated fat and other tissues, but it may also describe other edible tissues such as organs and offal...
were probably stored outside prior to cooking. Pits outside were also used for garbage and community resources.
The site was well chosen to provide a variety of food sources, and other resources. The staple of the diet
Diet (nutrition)
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. Dietary habits are the habitual decisions an individual or culture makes when choosing what foods to eat. With the word diet, it is often implied the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management...
was corn or maize, and other plants were also gathered as food, such as acorn
Acorn
The acorn, or oak nut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives . It usually contains a single seed , enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and borne in a cup-shaped cupule. Acorns vary from 1–6 cm long and 0.8–4 cm broad...
s, hickory
Hickory
Trees in the genus Carya are commonly known as hickory, derived from the Powhatan language of Virginia. The genus includes 17–19 species of deciduous trees with pinnately compound leaves and big nuts...
nuts, and berries
Berry
The botanical definition of a berry is a fleshy fruit produced from a single ovary. Grapes are an example. The berry is the most common type of fleshy fruit in which the entire ovary wall ripens into an edible pericarp. They may have one or more carpels with a thin covering and fleshy interiors....
. Tobacco was also grown at this time for rituals, as tobacco seeds have been found at this site. The main source of meat was deer, especially in the winter, and they also caught and ate beaver
American Beaver
The North American Beaver is the only species of beaver in the Americas, native to North America and introduced to South America. In the United States and Canada, where no other species of beaver occurs, it is usually simply referred to as "beaver"...
, elk
Elk
The Elk is the large deer, also called Cervus canadensis or wapiti, of North America and eastern Asia.Elk may also refer to:Other antlered mammals:...
, fox
Fox
Fox is a common name for many species of omnivorous mammals belonging to the Canidae family. Foxes are small to medium-sized canids , characterized by possessing a long narrow snout, and a bushy tail .Members of about 37 species are referred to as foxes, of which only 12 species actually belong to...
, muskrat
Muskrat
The muskrat , the only species in genus Ondatra, is a medium-sized semi-aquatic rodent native to North America, and introduced in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America. The muskrat is found in wetlands and is a very successful animal over a wide range of climates and habitats...
s, and raccoon
Raccoon
Procyon is a genus of nocturnal mammals, comprising three species commonly known as raccoons, in the family Procyonidae. The most familiar species, the common raccoon , is often known simply as "the" raccoon, as the two other raccoon species in the genus are native only to the tropics and are...
s. They also hunted bird
Bird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
s, turtle
Turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order Testudines , characterised by a special bony or cartilaginous shell developed from their ribs that acts as a shield...
s, and mussel
Mussel
The common name mussel is used for members of several families of clams or bivalvia mollusca, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which are often more or less rounded or oval.The...
s, and caught fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
in the Crawfish River directly next to the site, where they had set up rock barriers called fish weir
Weir
A weir is a small overflow dam used to alter the flow characteristics of a river or stream. In most cases weirs take the form of a barrier across the river that causes water to pool behind the structure , but allows water to flow over the top...
s at key points, one of which is still visible when the river is low. Some of the fish found have been catfish
Catfish
Catfishes are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the heaviest and longest, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia and the second longest, the wels catfish of Eurasia, to detritivores...
, bass
Bass (fish)
Bass is a name shared by many different species of popular gamefish. The term encompasses both freshwater and marine species. All belong to the large order Perciformes, or perch-like fishes, and in fact the word bass comes from Middle English bars, meaning "perch."-Types of basses:*The temperate...
, sucker
Catostomidae
Catostomidae is the sucker family of the order Cypriniformes. There are 80 species in this family of freshwater fishes. Catostomidae are found in North America, east central China, and eastern Siberia...
s, buffalo fish, pike, drum fish, and gar
Gar
In American English the name gar is strictly applied to members of the Lepisosteidae, a family including seven living species of fish in two genera that inhabit fresh, brackish, and occasionally marine, waters of eastern North America, Central America, and the Caribbean islands.-Etymology:In...
. Shell middens have been found where thousands of mussel shells were disposed, creating layers of shells several feet thick.
Raw materials for tool
Tool
A tool is a device that can be used to produce an item or achieve a task, but that is not consumed in the process. Informally the word is also used to describe a procedure or process with a specific purpose. Tools that are used in particular fields or activities may have different designations such...
s and building were available in the area, or could be obtained through trade
Trade
Trade is the transfer of ownership of goods and services from one person or entity to another. Trade is sometimes loosely called commerce or financial transaction or barter. A network that allows trade is called a market. The original form of trade was barter, the direct exchange of goods and...
from remote places. Tree
Tree
A tree is a perennial woody plant. It is most often defined as a woody plant that has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground on a single main stem or trunk with clear apical dominance. A minimum height specification at maturity is cited by some authors, varying from 3 m to...
s nearby provided wood
Wood
Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
for posts for house walls and stockades, bow
Bow (weapon)
The bow and arrow is a projectile weapon system that predates recorded history and is common to most cultures.-Description:A bow is a flexible arc that shoots aerodynamic projectiles by means of elastic energy. Essentially, the bow is a form of spring powered by a string or cord...
s and arrow
Arrow
An arrow is a shafted projectile that is shot with a bow. It predates recorded history and is common to most cultures.An arrow usually consists of a shaft with an arrowhead attached to the front end, with fletchings and a nock at the other.- History:...
shafts, bowl
Bowl (vessel)
A bowl is a common open-top container used in many cultures to serve food, and is also used for drinking and storing other items. They are typically small and shallow, although some, such as punch bowls and salad bowls, are larger and often intended to serve many people.Bowls have existed for...
s and spoon
Spoon
A spoon is a utensil consisting of a small shallow bowl, oval or round, at the end of a handle. A type of cutlery , especially as part of a place setting, it is used primarily for serving. Spoons are also used in food preparation to measure, mix, stir and toss ingredients...
s, and firewood. Smaller tree branches and grass were used for bedding and roofs. Shells from the river could be used for jewelry, bead
Bead
A bead is a small, decorative object that is usually pierced for threading or stringing. Beads range in size from under to over in diameter. A pair of beads made from Nassarius sea snail shells, approximately 100,000 years old, are thought to be the earliest known examples of jewellery. Beadwork...
s, spoons, and digging tools, and clay was dug for pottery
Pottery
Pottery is the material from which the potteryware is made, of which major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made is also called a pottery . Pottery also refers to the art or craft of the potter or the manufacture of pottery...
. Ornamental and exotic objects, or objects made from foreign materials are commonly associated with status.
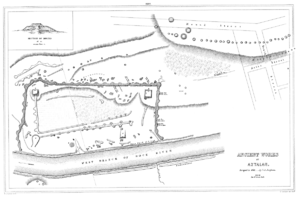
Physical features
The most obvious features of Aztalan are its pyramidPyramid
A pyramid is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge at a single point. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilateral, or any polygon shape, meaning that a pyramid has at least three triangular surfaces...
-shaped platform mounds and its stockade
Stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls made of logs placed side by side vertically with the tops sharpened to provide security.-Stockade as a security fence:...
s.
Mounds
There are three platform mounds on the site. The largest is the one in the southwest corner of the stockade; one almost as large is located in the northwest corner. The smallest of the three is along the east side of the settlement, near the Crawfish River (labeled "West Branch of Rock River" on the plates). The hill in the southeast corner is a natural gravelGravel
Gravel is composed of unconsolidated rock fragments that have a general particle size range and include size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments. Gravel can be sub-categorized into granule and cobble...
knoll, not built by the inhabitants.
The largest mound was built in three stages, with a set of steps leading to the top, where a structure was built over the entire flat top. The mound was covered with a clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
cap, probably to enhance its appearance. Corn
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
was stored in pits inside the structure, but there are several theories about why this corn was kept here, and the reason for the structure itself. This may have been the storage facility for the entire village; storage for food just for the top village officials; it may have been used for ceremonies and rituals; or it could have been a house for the village officials. This structure was rebuilt each time a larger stage of the mound was built on top of the old.
The northwestern mound was also built in three stages. A special structure, approximately 4 metres (13.1 ft) by 2 metres (6.6 ft), with its long axis towards the northeast/southwest, was built on the west side of the mound, with a doorway in its southwest corner, and covered with a mixture of clay, willow
Willow
Willows, sallows, and osiers form the genus Salix, around 400 species of deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere...
branches, and grass. The floor was covered with a mat of what may have been cattails, on which ten people were placed side by side, with their heads towards the doorway, and the bones of another person were bundled together with cord. Once this construction was complete, and the bodies were inside, the building was burned.
The eastern mound had a large open-walled structure, about 12 metres (39.4 ft) by 27 metres (88.6 ft), built on top of it, with firepits lined with white sand inside. The function of this mound and structure remain unclear.
Additionally, to the northwest of the stockaded area, a row of round mounds extends northward. When archaeologist
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
s dug in these mounds during the 1920s, they did not find the burial
Burial
Burial is the act of placing a person or object into the ground. This is accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing an object in it, and covering it over.-History:...
sites they had expected. Instead, each mound had a large post set in a pit in its center, surrounded by gravel and soil, with the pit capped with clay and gravel to hold the post steady. These mounds have been termed "marker mounds" because they may have been used to mark the site for travelers, but this is not certain; they may also have been used for announcements, message relays, or for calculations of astronomical
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
phenomena.
Stockade
The settlement was surrounded on the north, west, and south sides by a palisadePalisade
A palisade is a steel or wooden fence or wall of variable height, usually used as a defensive structure.- Typical construction :Typical construction consisted of small or mid sized tree trunks aligned vertically, with no spacing in between. The trunks were sharpened or pointed at the top, and were...
, a wall of logs set into the ground vertically. These were made by digging narrow holes in the ground with digging sticks, then lifting the posts into position and setting them into the holes. The stockade was then finished by weaving flexible willow branches through the posts, and plastering the whole with a mixture of clay and grass to fill in the gaps, a technique similar to wattle and daub
Wattle and daub
Wattle and daub is a composite building material used for making walls, in which a woven lattice of wooden strips called wattle is daubed with a sticky material usually made of some combination of wet soil, clay, sand, animal dung and straw...
.
A smaller stockade was built within the outer one, around the housing areas, at some point. It is not clear whether both stockades existed simultaneously, for a layered defense
Defense (military)
Defense has several uses in the sphere of military application.Personal defense implies measures taken by individual soldiers in protecting themselves whether by use of protective materials such as armor, or field construction of trenches or a bunker, or by using weapons that prevent the enemy...
, or one was built after the other fell into disuse.
The outer stockade was described by Lapham (v.i.) as being "631 feet (192.3 m) long at the north end, 1149 feet (350.2 m) long on the west side and 700 feet (213.4 m) on the south side; making a total length of wall of 2750 feet (838.2 m). The ridge or wall is about 22 feet (6.7 m), and from 1 foot (0.3048 m) to 5 feet (1.5 m)) in height." It had at least 33 square bastion
Bastion
A bastion, or a bulwark, is a structure projecting outward from the main enclosure of a fortification, situated in both corners of a straight wall , facilitating active defence against assaulting troops...
s at regular intervals along its length, remarkably similar in form and placement to some European fortifications, in addition to some more along the secondary walls. Rather than having a gate to protect the entrance, though, the builders constructed the entrance in such a way that it was camouflage
Camouflage
Camouflage is a method of concealment that allows an otherwise visible animal, military vehicle, or other object to remain unnoticed, by blending with its environment. Examples include a leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier and a leaf-mimic butterfly...
d when one looked at it from the outside, blending in with the wall around it.
During the time Aztalan was inhabited, two sets of outer stockades were built. The posts of the first one eventually rotted, and the second one burned and was never rebuilt. It is not clear whether the purpose of the stockade was to keep out invaders, or if the occupants built it for another reason.
Modern discovery (1835–1919)
A young man named Timothy Johnson discovered the ruinsRuins
Ruins are the remains of human-made architecture: structures that were once complete, as time went by, have fallen into a state of partial or complete disrepair, due to lack of maintenance or deliberate acts of destruction...
of the ancient settlement in December of 1835. However in January 1836, N. F. Hyer conducted the first rough survey of the site, publishing the discovery in the Milwaukie Advertiser of January 1837. According to Lapham:
- "The name Aztalan was given to this place by Mr. Hyer, because, according to HumboldtAlexander von HumboldtFriedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander Freiherr von Humboldt was a German naturalist and explorer, and the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt...
, the AztecAztecThe Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
s, or ancient inhabitants of MexicoMexicoThe United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, had a tradition that their ancestors came from a country at the north, which they called AztalanAztlánAztlán is the mythical ancestral home of the Nahua peoples, one of the main cultural groups in Mesoamerica. And, by extension, is the mythical homeland of the Uto-Aztecan peoples. Aztec is the Nahuatl word for "people from Aztlan".-Legend:...
; and the possibility that these may have been remains of their occupancy, suggested the idea of restoring the name. It is made up of two Mexican words, atl, water, and an, near; and the country was probably so named from its proximity to large bodies of water. Hence the natural inference that the country about these great lakes was the ancient residence of the Aztecs."
Hyer wrote that "We are determined to preserve these ruins from being ruined." However, in 1838, President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren was the eighth President of the United States . Before his presidency, he was the eighth Vice President and the tenth Secretary of State, under Andrew Jackson ....
refused a request by Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
statesman Edward Everett
Edward Everett
Edward Everett was an American politician and educator from Massachusetts. Everett, a Whig, served as U.S. Representative, and U.S. Senator, the 15th Governor of Massachusetts, Minister to Great Britain, and United States Secretary of State...
to withdraw the site from public sale, and the site was sold for $22. In the following years, the surface was plowed, the mounds were leveled for easier farming, pottery shards and "Aztalan brick" were hauled away by the wagonload to fill in potholes in township roads, and souvenir hunters took numerous artifacts.
In 1850, Increase A. Lapham, an author, scientist, and naturalist, surveyed the site, and urged its preservation. At the time, the stockade was still standing, though not in the condition it had once been.
State park foundation and reconstruction (1919–present)

In 1920, the Landmarks Committee of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin under Publius V. Lawson started a new effort to save what remained of Aztalan, supported by the Friends of Our Native Landscape and the Wisconsin Archeological Society. They made their first purchase of some of the land in 1921, three acres (12,000 m2) west of the stockade with eight conical mounds, and presented it to the Wisconsin Archeological Society.
Work for preservation continued. In 1936, the state's archeological and historical societies petitioned the federal government for funds to reconstruct the stockade without success. In 1941, the newly-founded Lake Mills-Aztalan Historical Society began an energetic campaign to preserve the stockade area.
In 1945, the Wisconsin State Assembly
Wisconsin State Assembly
The Wisconsin State Assembly is the lower house of the Wisconsin Legislature. Together with the smaller Wisconsin Senate, the two constitute the legislative branch of the U.S. state of Wisconsin....
passed a bill directing the State Planning Board to study the possibility of establishing a state park at Aztalan. In 1947, the Wisconsin State Legislature passed a resolution requesting the State Conservation Commission to purchase Aztalan. 120 acres (490,000 m2) were purchased to this end in 1948, and the Wisconsin Archeological Society and the Lake Mills-Aztalan Historical Society donated their holdings. Aztalan opened to the public as Aztalan State Park in 1952.
Aztalan was designated a registered National Historic Landmark
National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark is a building, site, structure, object, or district, that is officially recognized by the United States government for its historical significance...
in 1964 and added to the National Register of Historic Places
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places is the United States government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures, and objects deemed worthy of preservation...
in 1966.
In 1968, portions of the stockade wall were reconstructed by placing new posts in the original holes. A section of this was also covered with the wattle and daub, but this has since worn away or been removed.
External links
- Aztalan State Park, Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources
- The Antiquities of Wisconsin, Increase A. Lapham, 1855 — University of Wisconsin Library
- Aztalan and Aztalan Mound Park markers
- Aztalan Site History, Milwaukee Public Museum

