
Anthony de la Roché
Encyclopedia
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
merchant
Merchant
A merchant is a businessperson who trades in commodities that were produced by others, in order to earn a profit.Merchants can be one of two types:# A wholesale merchant operates in the chain between producer and retail merchant...
born in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
to a French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
Huguenot
Huguenot
The Huguenots were members of the Protestant Reformed Church of France during the 16th and 17th centuries. Since the 17th century, people who formerly would have been called Huguenots have instead simply been called French Protestants, a title suggested by their German co-religionists, the...
father and an English
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
mother. During a commercial voyage between Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
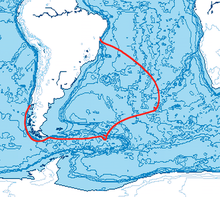
he was blown off course, and visited the Antarctic island of South Georgia
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
, making the first ever discovery of land south of the Antarctic Convergence
Antarctic Convergence
The Antarctic Convergence is a curve continuously encircling Antarctica where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the subantarctic. Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone...
.
Discovery of South Georgia
Hamburg
-History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808...
and obtained permission by the Spanish
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
authorities to trade in Spanish America, la Roché called at the Canary Islands
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union...
in May 1674 and in October that year arrived in the port
Port
A port is a location on a coast or shore containing one or more harbors where ships can dock and transfer people or cargo to or from land....
of Callao
Callao
Callao is the largest and most important port in Peru. The city is coterminous with the Constitutional Province of Callao, the only province of the Callao Region. Callao is located west of Lima, the country's capital, and is part of the Lima Metropolitan Area, a large metropolis that holds almost...
in the Viceroyalty of Peru
Viceroyalty of Peru
Created in 1542, the Viceroyalty of Peru was a Spanish colonial administrative district that originally contained most of Spanish-ruled South America, governed from the capital of Lima...
by way of Le Maire Strait
Le Maire Strait
The Le Maire Strait is a sea passage between Isla de los Estados and the eastern extremity of the Argentine portion of Tierra del Fuego....
and Cape Horn
Cape Horn
Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island...
. On his return voyage, sailing from Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island , also known as Greater Island of Chiloé , is the largest island of the Chiloé Archipelago off the coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean...
(Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
) to Bahia de Todos os Santos
Baía de Todos os Santos
Baía de Todos os Santos is the main and biggest bay of the state of Bahia, Brazil. Its name expanded to include a whole province, now known as the state of Bahia), where the city of São Salvador da Bahia de Todos os Santos was built...
(Salvador, Brazil), in April 1675 la Roché rounded Cape Horn
Cape Horn
Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island...
and was overwhelmed by tempestuous
Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of an astronomical body's atmosphere, especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather...
conditions in the tricky waters off Staten Island (Isla de los Estados)
Isla de los Estados
Isla de los Estados is an Argentine island that lies off the eastern extremity of the Argentine portion of Tierra del Fuego, from which it is separated by the Le Maire Strait...
. His ship failed to make Le Maire Strait
Le Maire Strait
The Le Maire Strait is a sea passage between Isla de los Estados and the eastern extremity of the Argentine portion of Tierra del Fuego....
as desired, nor round the east extremity of Staten Island
Isla de los Estados
Isla de los Estados is an Argentine island that lies off the eastern extremity of the Argentine portion of Tierra del Fuego, from which it is separated by the Le Maire Strait...
(i.e. make the mythical ‘Brouwer's Strait’ present on the old maps since the 1643 Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
expedition of Admiral Hendrik Brouwer
Hendrik Brouwer
Hendrik Brouwer was a Dutch explorer, admiral, and colonial administrator both in Japan and the Dutch East Indies....
), and was carried far away to the east instead. Eventually they found refuge in one of South Georgia
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
’s southern bays
Headlands and bays
Headlands and bays are two related features of the coastal environment.- Geology and geography :Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is surrounded by land on three sides, whereas a headland is surrounded by water on three sides. Headlands are characterized by high,...
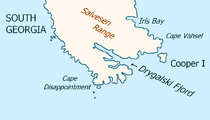
— possibly Drygalski Fjord
Drygalski Fjord
Drygalski Fjord is a bay 1 mile wide which recedes northwest 7 miles , entered immediately north of Nattriss Head along the southeast coast of South Georgia.According to L...
according to some experts — where the battered ship anchor
Anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, that is used to connect a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the vessel from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ancora, which itself comes from the Greek ἄγκυρα .Anchors can either be temporary or permanent...
ed for a fortnight.

Headlands and bays
Headlands and bays are two related features of the coastal environment.- Geology and geography :Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is surrounded by land on three sides, whereas a headland is surrounded by water on three sides. Headlands are characterized by high,...
, in which they anchored close to a Point or Cape
Headlands and bays
Headlands and bays are two related features of the coastal environment.- Geology and geography :Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is surrounded by land on three sides, whereas a headland is surrounded by water on three sides. Headlands are characterized by high,...
which stretches out to the Southeast with 28. 30. and 40. fathom
Fathom
A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems, used especially for measuring the depth of water.There are 2 yards in an imperial or U.S. fathom...
s Sand
Sand
Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles.The composition of sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal...
and Rock
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
”. The surrounding glaciated
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
, mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
ous terrain was described as “some Snow Mountains near the Coast, with much bad Weather.” Once the weather cleared up the ship set sail, and while rounding the southeast extremity of South Georgia
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
they sighted Clerke Rocks
Clerke Rocks
The Clerke Rocks are a group of small rocky islands some southeast of South Georgia that extend from east to west. The Clerke Rocks include The Office Boys at the northeastern end and Nobby at the southeastern end of the group...
further to the southeast.

South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
la Roché came across another uninhabited island, “where they found water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, wood
Wood
Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
and fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
”, and spent six days “without seeing any human being”, thus making what some historians believe was the first landing
Landing operation
A landing operation is a military action aimed at a bringing the landing force usually via landing craft to a shore or to land with the purpose of power projection ashore by forces coming usually from ships and also aircraft and able to fight....
on the South Atlantic
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
island that had been discovered by the Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
navigator Gonçalo Álvares in 1505 or 1506 (and known as Gough Island
Gough Island
Gough Island , also known historically as Gonçalo Álvares or Diego Alvarez, is a volcanic island in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a dependency of Tristan da Cunha and part of the British overseas territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha...
since 1731).
La Roché successfully reached the Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
ian port of Salvador, and eventually arrived in La Rochelle
La Rochelle
La Rochelle is a city in western France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department.The city is connected to the Île de Ré by a bridge completed on 19 May 1988...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
on 29 September 1675.
Captain James Cook
James Cook
Captain James Cook, FRS, RN was a British explorer, navigator and cartographer who ultimately rose to the rank of captain in the Royal Navy...
was aware of la Roché's discovery, mentioning it in his ship journal upon approaching South Georgia
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
in January 1775.
Maps showing la Roché's discovery
Soon after the voyage cartographersCartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
started to depict on their map
Map
A map is a visual representation of an area—a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions, and themes....
s ‘Roché Island’, and ‘Straits de la Roche’ separating the island from an ‘Unknown Land’ to the southeast, honouring the discoverer. In particular, the newly discovered island appeared on the following 18th century maps:
- L'Isle, Guillaume de; J. Covens & C. Mortier. (1700/20). L'Amerique Meridionale. Paris.
- Chatelain, Henry A. (1705/19). Nouvelle Carte de Geographie de la Partie Meridionale de la Amerique. Amsterdam.
- L'Isle, Guillaume de & Henry A. Chatelain. (1705/19). Carte du Paraguai, du Chili, du Detroit de Magellan. Paris.
- Lens, Bernard & George Vertue. (ca. 1710). Map of South America. London.
- Price, Charles. (ca. 1713). South America corrected from the observations communicated to the Royal Society's of London and Paris. London.
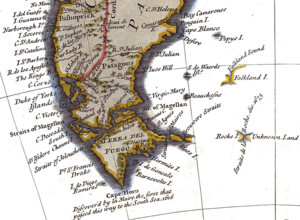
- De Fer, Nicolas. (1720). Partie La Plus Meridionale de L'Amerique, ou se trouve Le Chili, Le Paraguay, et Les Terres Magellaniques avec les Fameux Detroits de Magellan et de le Maire. Paris.
- Homann Heirs. (1733). Typus Geographicus Chili a Paraguay Freti Magellanici. Nuremberg.
- Moll, Herman. (1736). A map of Chili, Patagonia, La Plata and ye South Part of Brasil. London.
- L'Isle, Guillaume de & Girolamo Albrizzi. (1740). Carta Geografica della America Meridionale. Venice.
- Seale, Richard W. (ca. 1745). A Map of South America. With all the European Settlements & whatever else is remarkable from the latest & best observations. London.
- Cowley. (ca. 1745). A Map of South America. London.
- Gibson, John. (1753). South America. London.
- Buache, Philippe. (1754). Carte des Terres Australes, Comprises entre le Tropique du Capricorne et le Pôle Antarctique. Paris.
- Jefferys, Thomas. (1768). South America. London.
- Robert de Vaugondy, Gilles. (1773). Hemisphère Australe ou Antarctique. Paris.
- Arrowsmith, Aaron. (1794). Map of the World on a Globular Projection, Exhibiting Particularly the Nautical Researches of Capn. James Cook, F.R.S. with all the Recent Discoveries to the Present Time. London.
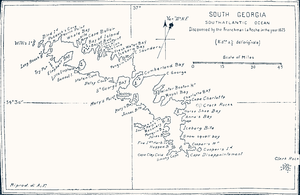
The second ever map
Map
A map is a visual representation of an area—a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions, and themes....
of South Georgia
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
made in 1802 by Captain Isaac Pendleton of the American sealing
Seal hunting
Seal hunting, or sealing, is the personal or commercial hunting of seals. The hunt is currently practiced in five countries: Canada, where most of the world's seal hunting takes place, Namibia, the Danish region of Greenland, Norway and Russia...
vessel Union and reproduced by the Italian
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
polar
Geographical pole
A geographical pole is either of the two points—the north pole and the south pole—on the surface of a rotating planet where the axis of rotation meets the surface of the body...
cartographer
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
A. Faustini
Arnaldo Faustini
Arnaldo Faustini was an Italian polar geographer, writer, and cartographer. He is considered by some to be the first Italian polar specialist. Born in Rome, he received his doctorate at the University of Rome at the age of 21. Faustini worked at a newspaper based in Rome as scientific editor...
in 1906, was entitled ‘South Georgia; Discovered by the Frenchman La Roche in the year 1675’. (Pendleton erred regarding la Roché's nationality due to his French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
last name.)
Honour
Roché Peak
Roché Peak is a conspicuous peak rising to 365 m, the highest feature on Bird Island, South Georgia. Situated 1.6 km west of the east extremity of the island. Named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee in 1960 for the Englishman Anthony de la Roché who discovered South Georgia in 1675.-See...
, the highest feature on Bird Island, South Georgia, and Roché Glacier
Roché Glacier
Roché Glacier is the 5.8 km long and 2 km wide glacier draining the central part of Vinson Plateau in Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica...
in Vinson Massif
Vinson Massif
Vinson Massif is the highest mountain of Antarctica, lying in the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, which stand above the Ronne Ice Shelf near the base of the Antarctic Peninsula. The massif is located about from the South Pole and is about long and wide. At the highest point is Mount...
, Antarctica are named for Anthony de la Roché.

