Political parties in the United States
Encyclopedia
This article presents the historical development and role of political parties in United States politics
, and outlines more extensively the significant modern political parties
. Throughout most of its history, American politics have been dominated by a two-party system
. However, the United States Constitution
has always been silent on the issue of political parties; at the time it was signed in 1787, there were no parties in the nation. Indeed, no nation in the world had voter-based political parties. The need to win popular support in a republic
led to the formation of political parties in the 1790s. Americans were especially innovative in devising new campaign techniques that linked public opinion with public policy through the party.
Political scientists and historians have divided the development of America's two-party system into five eras. The modern two-party system consists of the Democratic Party and the Republican Party. In general, since the 1930s the Democratic Party positions itself left-of-center
in American politics while the Republican Party positions itself as right-of-center
.
Several third parties
also operate in the United States, and from time to time achieve relatively minor representation at the national and state levels.
has never formally addressed the issue of political parties. The Founding Fathers
did not originally intend for American politics to be partisan. In Federalist Papers No. 9
and No. 10
, Alexander Hamilton
and James Madison
, respectively, wrote specifically about the dangers of domestic political faction
s. In addition, the first President of the United States
, George Washington
, was not a member of any political party at the time of his election or throughout his tenure as president. Furthermore, he hoped that political parties would not be formed, fearing conflict and stagnation. Nevertheless, the beginnings of the American two-party system
emerged from his immediate circle of advisers, including Hamilton and Madison.
and the Democratic-Republican Party
. The Federalist Party grew from Washington's Secretary of the Treasury
, Alexander Hamilton
, who favored a strong united central government, close ties to Britain, an effective banking system, and close links between the government and men of wealth. The Democratic-Republican Party was founded by James Madison
and by Washington's Secretary of State, Thomas Jefferson
, who strongly opposed Hamilton's agenda.
The Era of Good Feelings
(1816–1824), marked the end of the First Party System. The elitism of the Federalists had diminished their appeal, and their refusal to support the War of 1812
verged on secession and was a devastating blow when the war ended well. The Era of Good Feelings
under President James Monroe (1816-24) marked a brief period in which partisanship was minimal. These good feelings inspired the first short-lived "era of internal improvements
" from the 18th
through the 25th Congress
, which ended with the panic of 1837
.
, who grew into the modern Democratic Party
, led by Andrew Jackson
, and the Whig Party
, led by Henry Clay
. The Democrats supported the primacy of the Presidency over the other branches of government, and opposed the Bank of the United States
as well as modernizing programs that they felt would build up industry
at the expense of the taxpayer. The Whigs, on the other hand, advocated the primacy of Congress
over the executive branch
as well as policies of modernization and economic protectionism. Central political battles of this era were the Bank War
and the Spoils system
of federal patronage.
The 1850s saw the collapse of the Whig party, largely as a result of deaths in its leadership and a major intra-party split over slavery as a result of the Compromise of 1850
. In addition, the fading of old economic issues removed many of the unifying forces holding the party together.
, and was dominated by the Republican Party.
beginning in 1933.
dominated by the Democratic Party
and the Republican Party
. These two parties have won every United States presidential election
since 1852 and have controlled the United States Congress
since at least 1856. Several other third parties
from time to time achieve relatively minor representation at the national and state levels.
political parties in the United States. It is the oldest political party in the United States and among the oldest in the world.
The Democratic Party, since the division of the Republican Party in the election of 1912
, has consistently positioned itself to the left
of the Republican Party in economic as well as social matters. The economically left-leaning philosophy of Franklin D. Roosevelt
, which has strongly influenced American liberalism
, has shaped much of the party's economic agenda since 1932
. Roosevelt's New Deal coalition
usually controlled the national government until the 1970s.
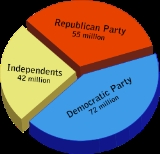
In 2004, it was the largest political party, with 72 million voters (42.6% of 169 million registered) claiming affiliation. The president of the United States, Barack Obama
, is the 15th Democrat to hold the office, and since the 2006 midterm elections
, the Democratic Party is the majority party
for the United States Senate
.
Founded in 1854 by anti-slavery
expansion activists and modernizers, the Republican Party rose to prominence with the election of Abraham Lincoln
, the first Republican president. The party presided over the American Civil War
and Reconstruction but was harried by internal factions and scandals toward the end of the 19th century. Today, the Republican Party supports an American conservative platform, with further foundations in economic liberalism
, fiscal conservatism
, and social conservatism
.
Former President George W. Bush
is the 19th Republican to hold that office. The party's nominee for President of the United States
in the 2008 presidential election
was Senator John McCain
of Arizona
. It is currently the second largest party with 55 million registered members, encompassing roughly one third of the electorate. Since the 2010 midterm elections
, the Republicans have held a majority in the United States House of Representatives.
According to ballot access expert Richard Winger
, the editor of Ballot Access News
, who periodically compiles and analyzes voter registration statistics as reported by state voter agencies, it ranks third nationally amongst all United States political parties
in registered voters, with 438,222 registered members as of October 2008. This makes it currently the largest third party in the United States.
The Constitution Party advocates a platform that they believe reflects the Founding Fathers
' original intent
of the U.S. Constitution
, principles found in the U.S. Declaration of Independence, and morals taken from the Bible
.
In 2006, Rick Jore
of Montana
became the first Constitution Party candidate elected to a state-level office, though the Constitution Party of Montana had disaffiliated itself from the national party a short time before the election.
The Constitution Party's 2008 presidential nominee was Chuck Baldwin
.
, the Green Party has been active as a third party
since the 1980s. The party first gained widespread public attention during Ralph Nader
's second presidential run in 2000. Currently, the primary national Green Party organization in the U.S. is the Green Party of the United States, which has eclipsed the earlier Greens/Green Party USA
.
The Green Party in the United States has won elected office mostly at the local
level; most winners of public office in the United States who are considered Greens have won nonpartisan
-ballot elections (that is, elections in which the candidates' party affiliations were not printed on the ballot
. In 2005, the Party had 305,000 registered members in states that allow party registration. During the 2006 elections the party had ballot access
in 31 states.
Greens emphasize environmentalism
, non-hierarchical
participatory democracy
, social justice
, respect for diversity
, peace
and nonviolence
.
The 2008 Green Party presidential nominee was Cynthia McKinney
.
in the United States, claiming more than 200,000 registered voters and more than 600 people in public office, including mayor
s, county executives, county-council members, school-board members, and other local officials. It has more people in office than all other minor parties combined.
The political platform of the Libertarian Party reflects that group's particular brand of libertarianism
, favoring minimally regulated, laissez-faire
markets, strong civil liberties
, minimally regulated migration across borders, and non-interventionism
in foreign policy that respects freedom of trade
and travel to all foreign countries.
The 2008 Libertarian Party nominee for United States President was Bob Barr
.
where positions diverge. Nuances may be found in the parties' respective platforms
. It must be remembered that not all members of a party subscribe to all of its officially held positions, the usual degree of variation generally being higher for the larger parties. Note that party members may hold different views on legislation to be enacted at the state or federal levels—most Libertarians, for example, believe that the federal government has no proper role at all with regard to adult consumption of drugs, abortion, or marriages of any sort, but some believe that the several states have the right to legislate.
Politics of the United States
The United States is a federal constitutional republic, in which the President of the United States , Congress, and judiciary share powers reserved to the national government, and the federal government shares sovereignty with the state governments.The executive branch is headed by the President...
, and outlines more extensively the significant modern political parties
Political party
A political party is a political organization that typically seeks to influence government policy, usually by nominating their own candidates and trying to seat them in political office. Parties participate in electoral campaigns, educational outreach or protest actions...
. Throughout most of its history, American politics have been dominated by a two-party system
Two-party system
A two-party system is a system where two major political parties dominate voting in nearly all elections at every level of government and, as a result, all or nearly all elected offices are members of one of the two major parties...
. However, the United States Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
has always been silent on the issue of political parties; at the time it was signed in 1787, there were no parties in the nation. Indeed, no nation in the world had voter-based political parties. The need to win popular support in a republic
Republicanism in the United States
Republicanism is the political value system that has been a major part of American civic thought since the American Revolution. It stresses liberty and inalienable rights as central values, makes the people as a whole sovereign, supports activist government to promote the common good, rejects...
led to the formation of political parties in the 1790s. Americans were especially innovative in devising new campaign techniques that linked public opinion with public policy through the party.
Political scientists and historians have divided the development of America's two-party system into five eras. The modern two-party system consists of the Democratic Party and the Republican Party. In general, since the 1930s the Democratic Party positions itself left-of-center
Centre-left
Centre-left is a political term that describes individuals, political parties or organisations such as think tanks whose ideology lies between the centre and the left on the left-right spectrum...
in American politics while the Republican Party positions itself as right-of-center
Centre-right
The centre-right or center-right is a political term commonly used to describe or denote individuals, political parties, or organizations whose views stretch from the centre to the right on the left-right spectrum, excluding far right stances. Centre-right can also describe a coalition of centrist...
.
Several third parties
Third party (United States)
The term third party is used in the United States for any and all political parties in the United States other than one of the two major parties . The term can also refer to independent politicians not affiliated with any party at all and to write-in candidates.The United States has had a...
also operate in the United States, and from time to time achieve relatively minor representation at the national and state levels.
History
The United States ConstitutionUnited States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
has never formally addressed the issue of political parties. The Founding Fathers
Founding Fathers of the United States
The Founding Fathers of the United States of America were political leaders and statesmen who participated in the American Revolution by signing the United States Declaration of Independence, taking part in the American Revolutionary War, establishing the United States Constitution, or by some...
did not originally intend for American politics to be partisan. In Federalist Papers No. 9
Federalist No. 9
Federalist No. 9 is an essay by Alexander Hamilton and the ninth of the Federalist Papers. It was published on November 21, 1787 under the pseudonym Publius, the name under which all the Federalist Papers were published. Federalist No...
and No. 10
Federalist No. 10
Federalist No. 10 is an essay written by James Madison and the tenth of the Federalist Papers, a series arguing for the ratification of the United States Constitution. It was published on Friday, November 22, 1787, under the pseudonym Publius, the name under which all the Federalist Papers were...
, Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton was a Founding Father, soldier, economist, political philosopher, one of America's first constitutional lawyers and the first United States Secretary of the Treasury...
and James Madison
James Madison
James Madison, Jr. was an American statesman and political theorist. He was the fourth President of the United States and is hailed as the “Father of the Constitution” for being the primary author of the United States Constitution and at first an opponent of, and then a key author of the United...
, respectively, wrote specifically about the dangers of domestic political faction
Political faction
A political faction is a grouping of individuals, such as a political party, a trade union, or other group with a political purpose. A faction or political party may include fragmented sub-factions, “parties within a party," which may be referred to as power blocs, or voting blocs. The individuals...
s. In addition, the first President of the United States
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
, George Washington
George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
, was not a member of any political party at the time of his election or throughout his tenure as president. Furthermore, he hoped that political parties would not be formed, fearing conflict and stagnation. Nevertheless, the beginnings of the American two-party system
Two-party system
A two-party system is a system where two major political parties dominate voting in nearly all elections at every level of government and, as a result, all or nearly all elected offices are members of one of the two major parties...
emerged from his immediate circle of advisers, including Hamilton and Madison.
First Party System
The First Party System of The United States featured the Federalist PartyFederalist Party (United States)
The Federalist Party was the first American political party, from the early 1790s to 1816, the era of the First Party System, with remnants lasting into the 1820s. The Federalists controlled the federal government until 1801...
and the Democratic-Republican Party
Democratic-Republican Party (United States)
The Democratic-Republican Party or Republican Party was an American political party founded in the early 1790s by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison. Political scientists use the former name, while historians prefer the latter one; contemporaries generally called the party the "Republicans", along...
. The Federalist Party grew from Washington's Secretary of the Treasury
United States Secretary of the Treasury
The Secretary of the Treasury of the United States is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, which is concerned with financial and monetary matters, and, until 2003, also with some issues of national security and defense. This position in the Federal Government of the United...
, Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton was a Founding Father, soldier, economist, political philosopher, one of America's first constitutional lawyers and the first United States Secretary of the Treasury...
, who favored a strong united central government, close ties to Britain, an effective banking system, and close links between the government and men of wealth. The Democratic-Republican Party was founded by James Madison
James Madison
James Madison, Jr. was an American statesman and political theorist. He was the fourth President of the United States and is hailed as the “Father of the Constitution” for being the primary author of the United States Constitution and at first an opponent of, and then a key author of the United...
and by Washington's Secretary of State, Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
, who strongly opposed Hamilton's agenda.
The Era of Good Feelings
Era of Good Feelings
The Era of Good Feelings was a period in United States political history in which partisan bitterness abated. It lasted approximately from 1815 to 1825, during the administration of U.S...
(1816–1824), marked the end of the First Party System. The elitism of the Federalists had diminished their appeal, and their refusal to support the War of 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
verged on secession and was a devastating blow when the war ended well. The Era of Good Feelings
Era of Good Feelings
The Era of Good Feelings was a period in United States political history in which partisan bitterness abated. It lasted approximately from 1815 to 1825, during the administration of U.S...
under President James Monroe (1816-24) marked a brief period in which partisanship was minimal. These good feelings inspired the first short-lived "era of internal improvements
Internal improvements
Internal improvements is the term used historically in the United States for public works from the end of the American Revolution through much of the 19th century, mainly for the creation of a transportation infrastructure: roads, turnpikes, canals, harbors and navigation improvements...
" from the 18th
18th United States Congress
The Eighteenth United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1823 to March 3, 1825, during the seventh and eighth...
through the 25th Congress
25th United States Congress
-House of Representatives:-Leadership:- Senate :* President: Richard Mentor Johnson * President pro tempore: William R. King - House of Representatives :* Speaker: James K. Polk -Members:This list is arranged by chamber, then by state...
, which ended with the panic of 1837
Panic of 1837
The Panic of 1837 was a financial crisis or market correction in the United States built on a speculative fever. The end of the Second Bank of the United States had produced a period of runaway inflation, but on May 10, 1837 in New York City, every bank began to accept payment only in specie ,...
.
Second Party System
In 1828, The Second Party System saw a split of the Democratic-Republican Party into the Jacksonian DemocratsJacksonian democracy
Jacksonian democracy is the political movement toward greater democracy for the common man typified by American politician Andrew Jackson and his supporters. Jackson's policies followed the era of Jeffersonian democracy which dominated the previous political era. The Democratic-Republican Party of...
, who grew into the modern Democratic Party
History of the United States Democratic Party
The history of the Democratic Party of the United States is an account of the oldest political party in the United States and arguably the oldest democratic party in the world....
, led by Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson was the seventh President of the United States . Based in frontier Tennessee, Jackson was a politician and army general who defeated the Creek Indians at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend , and the British at the Battle of New Orleans...
, and the Whig Party
Whig Party (United States)
The Whig Party was a political party of the United States during the era of Jacksonian democracy. Considered integral to the Second Party System and operating from the early 1830s to the mid-1850s, the party was formed in opposition to the policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic...
, led by Henry Clay
Henry Clay
Henry Clay, Sr. , was a lawyer, politician and skilled orator who represented Kentucky separately in both the Senate and in the House of Representatives...
. The Democrats supported the primacy of the Presidency over the other branches of government, and opposed the Bank of the United States
Second Bank of the United States
The Second Bank of the United States was chartered in 1816, five years after the First Bank of the United States lost its own charter. The Second Bank of the United States was initially headquartered in Carpenters' Hall, Philadelphia, the same as the First Bank, and had branches throughout the...
as well as modernizing programs that they felt would build up industry
Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
at the expense of the taxpayer. The Whigs, on the other hand, advocated the primacy of Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
over the executive branch
Executive (government)
Executive branch of Government is the part of government that has sole authority and responsibility for the daily administration of the state bureaucracy. The division of power into separate branches of government is central to the idea of the separation of powers.In many countries, the term...
as well as policies of modernization and economic protectionism. Central political battles of this era were the Bank War
Bank War
The Bank War is the name given to the controversy over the Second Bank of the United States and the attempts to destroy it by President Andrew Jackson. At that time, it was the only nationwide bank and, along with its president Nicholas Biddle, exerted tremendous influence over the nation's...
and the Spoils system
Spoils system
In the politics of the United States, a spoil system is a practice where a political party, after winning an election, gives government jobs to its voters as a reward for working toward victory, and as an incentive to keep working for the party—as opposed to a system of awarding offices on the...
of federal patronage.
The 1850s saw the collapse of the Whig party, largely as a result of deaths in its leadership and a major intra-party split over slavery as a result of the Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five bills, passed in September 1850, which defused a four-year confrontation between the slave states of the South and the free states of the North regarding the status of territories acquired during the Mexican-American War...
. In addition, the fading of old economic issues removed many of the unifying forces holding the party together.
Third Party System
The Third Party System stretched from 1854 to the mid 1890s, and was characterized by the emergence of the anti-slavery Republican Party, which adopted many of the economic policies of the Whigs, such as national banks, railroads, high tariffs, homesteads and aid to land grant colleges.Fourth Party System
The Fourth Party System, 1896 to 1932, retained the same primary parties as the Third Party System, but saw major shifts in the central issues of debate. This period also corresponded to the Progressive EraProgressive Era
The Progressive Era in the United States was a period of social activism and political reform that flourished from the 1890s to the 1920s. One main goal of the Progressive movement was purification of government, as Progressives tried to eliminate corruption by exposing and undercutting political...
, and was dominated by the Republican Party.
Fifth Party System
The Fifth Party System emerged with the New Deal CoalitionNew Deal coalition
The New Deal Coalition was the alignment of interest groups and voting blocs that supported the New Deal and voted for Democratic presidential candidates from 1932 until the late 1960s. It made the Democratic Party the majority party during that period, losing only to Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1952...
beginning in 1933.
Modern U.S. political party system
The modern political party system in the United States is a two-party systemTwo-party system
A two-party system is a system where two major political parties dominate voting in nearly all elections at every level of government and, as a result, all or nearly all elected offices are members of one of the two major parties...
dominated by the Democratic Party
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
and the Republican Party
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
. These two parties have won every United States presidential election
United States presidential election
Elections for President and Vice President of the United States are indirect elections in which voters cast ballots for a slate of electors of the U.S. Electoral College, who in turn directly elect the President and Vice President...
since 1852 and have controlled the United States Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
since at least 1856. Several other third parties
Third party (United States)
The term third party is used in the United States for any and all political parties in the United States other than one of the two major parties . The term can also refer to independent politicians not affiliated with any party at all and to write-in candidates.The United States has had a...
from time to time achieve relatively minor representation at the national and state levels.
Democratic Party
The Democratic Party is one of two majorMajor party
A major party is a political party that holds substantial influence in a country's politics, standing in contrast to a minor party. It should not be confused with majority party.According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary:...
political parties in the United States. It is the oldest political party in the United States and among the oldest in the world.
The Democratic Party, since the division of the Republican Party in the election of 1912
United States presidential election, 1912
The United States presidential election of 1912 was a rare four-way contest. Incumbent President William Howard Taft was renominated by the Republican Party with the support of its conservative wing. After former President Theodore Roosevelt failed to receive the Republican nomination, he called...
, has consistently positioned itself to the left
Left-wing politics
In politics, Left, left-wing and leftist generally refer to support for social change to create a more egalitarian society...
of the Republican Party in economic as well as social matters. The economically left-leaning philosophy of Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
, which has strongly influenced American liberalism
Liberalism in the United States
Liberalism in the United States is a broad political philosophy centered on the unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion for all belief systems, and the separation of church and state, right to due process...
, has shaped much of the party's economic agenda since 1932
United States presidential election, 1932
The United States presidential election of 1932 took place as the effects of the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930, the Revenue Act of 1932, and the Great Depression were being felt intensely across the country. President Herbert Hoover's popularity was falling as...
. Roosevelt's New Deal coalition
New Deal coalition
The New Deal Coalition was the alignment of interest groups and voting blocs that supported the New Deal and voted for Democratic presidential candidates from 1932 until the late 1960s. It made the Democratic Party the majority party during that period, losing only to Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1952...
usually controlled the national government until the 1970s.
In 2004, it was the largest political party, with 72 million voters (42.6% of 169 million registered) claiming affiliation. The president of the United States, Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
, is the 15th Democrat to hold the office, and since the 2006 midterm elections
United States general elections, 2006
The 2006 United States midterm elections were held on Tuesday, November 7, 2006. All United States House of Representatives seats and one third of the United States Senate seats were contested in this election, as well as 36 state governorships, many state legislatures, four territorial...
, the Democratic Party is the majority party
Two-party system
A two-party system is a system where two major political parties dominate voting in nearly all elections at every level of government and, as a result, all or nearly all elected offices are members of one of the two major parties...
for the United States Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
.
Republican Party
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States of America. It is often referred to as the Grand Old Party, GOP, and "Gallant Old Party".Founded in 1854 by anti-slavery
Abolitionism
Abolitionism is a movement to end slavery.In western Europe and the Americas abolitionism was a movement to end the slave trade and set slaves free. At the behest of Dominican priest Bartolomé de las Casas who was shocked at the treatment of natives in the New World, Spain enacted the first...
expansion activists and modernizers, the Republican Party rose to prominence with the election of Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
, the first Republican president. The party presided over the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
and Reconstruction but was harried by internal factions and scandals toward the end of the 19th century. Today, the Republican Party supports an American conservative platform, with further foundations in economic liberalism
Economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is the ideological belief in giving all people economic freedom, and as such granting people with more basis to control their own lives and make their own mistakes. It is an economic philosophy that supports and promotes individual liberty and choice in economic matters and...
, fiscal conservatism
Fiscal conservatism
Fiscal conservatism is a political term used to describe a fiscal policy that advocates avoiding deficit spending. Fiscal conservatives often consider reduction of overall government spending and national debt as well as ensuring balanced budget of paramount importance...
, and social conservatism
Social conservatism
Social Conservatism is primarily a political, and usually morally influenced, ideology that focuses on the preservation of what are seen as traditional values. Social conservatism is a form of authoritarianism often associated with the position that the federal government should have a greater role...
.
Former President George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
is the 19th Republican to hold that office. The party's nominee for President of the United States
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
in the 2008 presidential election
United States presidential election, 2008
The United States presidential election of 2008 was the 56th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on November 4, 2008. Democrat Barack Obama, then the junior United States Senator from Illinois, defeated Republican John McCain, the senior U.S. Senator from Arizona. Obama received 365...
was Senator John McCain
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III is the senior United States Senator from Arizona. He was the Republican nominee for president in the 2008 United States election....
of Arizona
Arizona
Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
. It is currently the second largest party with 55 million registered members, encompassing roughly one third of the electorate. Since the 2010 midterm elections
United States elections, 2010
The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010. During this midterm election year, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 37 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate were contested in this election along with 38 state and territorial...
, the Republicans have held a majority in the United States House of Representatives.
Constitution Party
The Constitution Party is a conservative United States political party. It was founded as the U.S. Taxpayers Party in 1992. The party's official name was changed to the Constitution Party in 1999; however, some state affiliate parties are known under different names.According to ballot access expert Richard Winger
Richard Winger
Richard Lee Winger is the publisher and editor of Ballot Access News. He sits on the editorial board of the Election Law Journal and has been accepted as an expert on election law in federal courts in nine states, including California...
, the editor of Ballot Access News
Ballot Access News
Ballot Access News is a U.S.-based monthly online newsletter edited and published by Richard Winger of California, an expert on ballot access law in the United States...
, who periodically compiles and analyzes voter registration statistics as reported by state voter agencies, it ranks third nationally amongst all United States political parties
Political party
A political party is a political organization that typically seeks to influence government policy, usually by nominating their own candidates and trying to seat them in political office. Parties participate in electoral campaigns, educational outreach or protest actions...
in registered voters, with 438,222 registered members as of October 2008. This makes it currently the largest third party in the United States.
The Constitution Party advocates a platform that they believe reflects the Founding Fathers
Founding Fathers of the United States
The Founding Fathers of the United States of America were political leaders and statesmen who participated in the American Revolution by signing the United States Declaration of Independence, taking part in the American Revolutionary War, establishing the United States Constitution, or by some...
' original intent
Originalism
In the context of United States constitutional interpretation, originalism is a principle of interpretation that tries to discover the original meaning or intent of the constitution. It is based on the principle that the judiciary is not supposed to create, amend or repeal laws but only to uphold...
of the U.S. Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
, principles found in the U.S. Declaration of Independence, and morals taken from the Bible
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
.
In 2006, Rick Jore
Rick Jore
Rick Jore, a Montana politician and businessman, was a member of the 2006 Montana House of Representatives and chairman of the education committee. Jore was born and raised in Ronan, Montana and received his associates degree from North Idaho College in 1978...
of Montana
Montana
Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
became the first Constitution Party candidate elected to a state-level office, though the Constitution Party of Montana had disaffiliated itself from the national party a short time before the election.
The Constitution Party's 2008 presidential nominee was Chuck Baldwin
Chuck Baldwin
Charles Obadiah "Chuck" Baldwin is an American politician and founder-pastor of Crossroad Baptist Church in Pensacola, Florida. He was the presidential nominee of the Constitution Party for the 2008 U.S. presidential election and had previously been its nominee for U.S. vice president in 2004...
.
Green Party
In the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the Green Party has been active as a third party
Third party (United States)
The term third party is used in the United States for any and all political parties in the United States other than one of the two major parties . The term can also refer to independent politicians not affiliated with any party at all and to write-in candidates.The United States has had a...
since the 1980s. The party first gained widespread public attention during Ralph Nader
Ralph Nader
Ralph Nader is an American political activist, as well as an author, lecturer, and attorney. Areas of particular concern to Nader include consumer protection, humanitarianism, environmentalism, and democratic government....
's second presidential run in 2000. Currently, the primary national Green Party organization in the U.S. is the Green Party of the United States, which has eclipsed the earlier Greens/Green Party USA
Greens/Green Party USA
In the United States, people speak generally of the "Green Party," but there is actually more than one national-level Green political organization in the United States.- History :...
.
The Green Party in the United States has won elected office mostly at the local
Local government
Local government refers collectively to administrative authorities over areas that are smaller than a state.The term is used to contrast with offices at nation-state level, which are referred to as the central government, national government, or federal government...
level; most winners of public office in the United States who are considered Greens have won nonpartisan
Nonpartisan
In political science, nonpartisan denotes an election, event, organization or person in which there is no formally declared association with a political party affiliation....
-ballot elections (that is, elections in which the candidates' party affiliations were not printed on the ballot
Ballot
A ballot is a device used to record choices made by voters. Each voter uses one ballot, and ballots are not shared. In the simplest elections, a ballot may be a simple scrap of paper on which each voter writes in the name of a candidate, but governmental elections use pre-printed to protect the...
. In 2005, the Party had 305,000 registered members in states that allow party registration. During the 2006 elections the party had ballot access
Ballot access
Ballot access rules, called nomination rules outside the United States, regulate the conditions under which a candidate or political party is either entitled to stand for election or to appear on voters' ballots...
in 31 states.
Greens emphasize environmentalism
Environmentalism
Environmentalism is a broad philosophy, ideology and social movement regarding concerns for environmental conservation and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seeks to incorporate the concerns of non-human elements...
, non-hierarchical
Hierarchy
A hierarchy is an arrangement of items in which the items are represented as being "above," "below," or "at the same level as" one another...
participatory democracy
Participatory democracy
Participatory Democracy, also known as Deliberative Democracy, Direct Democracy and Real Democracy , is a process where political decisions are made directly by regular people...
, social justice
Social justice
Social justice generally refers to the idea of creating a society or institution that is based on the principles of equality and solidarity, that understands and values human rights, and that recognizes the dignity of every human being. The term and modern concept of "social justice" was coined by...
, respect for diversity
Diversity (politics)
In the political arena, the term diversity is used to describe political entities with members who have identifiable differences in their backgrounds or lifestyles....
, peace
Peace
Peace is a state of harmony characterized by the lack of violent conflict. Commonly understood as the absence of hostility, peace also suggests the existence of healthy or newly healed interpersonal or international relationships, prosperity in matters of social or economic welfare, the...
and nonviolence
Nonviolence
Nonviolence has two meanings. It can refer, first, to a general philosophy of abstention from violence because of moral or religious principle It can refer to the behaviour of people using nonviolent action Nonviolence has two (closely related) meanings. (1) It can refer, first, to a general...
.
The 2008 Green Party presidential nominee was Cynthia McKinney
Cynthia McKinney
Cynthia Ann McKinney is a former US Congresswoman and a member of the Green Party since 2007. As a member of the Democratic Party, she served six terms as a member of the United States House of Representatives. In 2008, the Green Party nominated McKinney for President of the United States...
.
Libertarian Party
The Libertarian Party was founded on December 11, 1971. It is one of the largest continuing third partiesThird party (United States)
The term third party is used in the United States for any and all political parties in the United States other than one of the two major parties . The term can also refer to independent politicians not affiliated with any party at all and to write-in candidates.The United States has had a...
in the United States, claiming more than 200,000 registered voters and more than 600 people in public office, including mayor
Mayor
In many countries, a Mayor is the highest ranking officer in the municipal government of a town or a large urban city....
s, county executives, county-council members, school-board members, and other local officials. It has more people in office than all other minor parties combined.
The political platform of the Libertarian Party reflects that group's particular brand of libertarianism
Libertarianism
Libertarianism, in the strictest sense, is the political philosophy that holds individual liberty as the basic moral principle of society. In the broadest sense, it is any political philosophy which approximates this view...
, favoring minimally regulated, laissez-faire
Laissez-faire
In economics, laissez-faire describes an environment in which transactions between private parties are free from state intervention, including restrictive regulations, taxes, tariffs and enforced monopolies....
markets, strong civil liberties
Civil liberties
Civil liberties are rights and freedoms that provide an individual specific rights such as the freedom from slavery and forced labour, freedom from torture and death, the right to liberty and security, right to a fair trial, the right to defend one's self, the right to own and bear arms, the right...
, minimally regulated migration across borders, and non-interventionism
Non-interventionism
Nonintervention or non-interventionism is a foreign policy which holds that political rulers should avoid alliances with other nations, but still retain diplomacy, and avoid all wars not related to direct self-defense...
in foreign policy that respects freedom of trade
Free trade
Under a free trade policy, prices emerge from supply and demand, and are the sole determinant of resource allocation. 'Free' trade differs from other forms of trade policy where the allocation of goods and services among trading countries are determined by price strategies that may differ from...
and travel to all foreign countries.
The 2008 Libertarian Party nominee for United States President was Bob Barr
Bob Barr
Robert Laurence "Bob" Barr, Jr. is a former federal prosecutorand a former member of the United States House of Representatives. He represented Georgia's 7th congressional district as a Republican from 1995 to 2003. Barr attained national prominence as one of the leaders of the impeachment of...
.
Politics comparison
The following table lists some political ideologies most often associated with the five U.S. political parties with the most members, as well the official party positions on a number of reformist issuesPoliticized issue
A politicized issue or hot-button issue is a social, economic, theological, spiritual, scientific or legal issue which has become a political issue, as a result of deliberate action or otherwise, whereby people become politically active over that issue....
where positions diverge. Nuances may be found in the parties' respective platforms
Party platform
A party platform, or platform sometimes also referred to as a manifesto, is a list of the actions which a political party, individual candidate, or other organization supports in order to appeal to the general public for the purpose of having said peoples' candidates voted into political office or...
. It must be remembered that not all members of a party subscribe to all of its officially held positions, the usual degree of variation generally being higher for the larger parties. Note that party members may hold different views on legislation to be enacted at the state or federal levels—most Libertarians, for example, believe that the federal government has no proper role at all with regard to adult consumption of drugs, abortion, or marriages of any sort, but some believe that the several states have the right to legislate.
| Issue | Green Party Green Party (United States) The Green Party of the United States is a nationally recognized political party which officially formed in 1991. It is a voluntary association of state green parties. Prior to national formation, many state affiliates had already formed and were recognized by other state parties... |
Democratic Party Democratic Party (United States) The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous... |
Libertarian Party Libertarian Party (United States) The Libertarian Party is the third largest and fastest growing political party in the United States. The political platform of the Libertarian Party reflects its brand of libertarianism, favoring minimally regulated, laissez-faire markets, strong civil liberties, minimally regulated migration... |
Republican Party Republican Party (United States) The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S... |
Constitution Party Constitution Party (United States) The Constitution Party is a paleoconservative political party in the United States. It was founded as the U.S. Taxpayers' Party by Howard Philips in 1991. Phillips was the party's candidate in the 1992, 1996 and 2000 presidential elections... |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary related ideologies |
|
Progressivism in the United States Progressivism in the United States is a broadly based reform movement that reached its height early in the 20th century and is generally considered to be middle class and reformist in nature. It arose as a response to the vast changes brought by modernization, such as the growth of large... |
Libertarianism Libertarianism, in the strictest sense, is the political philosophy that holds individual liberty as the basic moral principle of society. In the broadest sense, it is any political philosophy which approximates this view... Classical liberalism Classical liberalism is the philosophy committed to the ideal of limited government, constitutionalism, rule of law, due process, and liberty of individuals including freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, and free markets.... |
American conservatism Conservatism in the United States has played an important role in American politics since the 1950s. Historian Gregory Schneider identifies several constants in American conservatism: respect for tradition, support of republicanism, preservation of "the rule of law and the Christian religion", and... Neoconservatism Neoconservatism in the United States is a branch of American conservatism. Since 2001, neoconservatism has been associated with democracy promotion, that is with assisting movements for democracy, in some cases by economic sanctions or military action.... |
Paleoconservatism Paleoconservatism is a term for a conservative political philosophy found primarily in the United States stressing tradition, limited government, civil society, anti-colonialism, anti-corporatism and anti-federalism, along with religious, regional, national and Western identity. Chilton... |
|
| Issues framed as changes to the status quo Status quo Statu quo, a commonly used form of the original Latin "statu quo" – literally "the state in which" – is a Latin term meaning the current or existing state of affairs. To maintain the status quo is to keep the things the way they presently are... . |
Abortion restrictions Abortion law Abortion law is legislation and common law which pertains to the provision of abortion. Abortion has been a controversial subject in many societies through history because of the moral, ethical, practical, and political power issues that surround it. It has been banned frequently and otherwise... |
|||||
| Public campaign finance | ||||||
| Legal same-sex marriage Same-sex marriage in the United States The federal government does not recognize same-sex marriage in the United States, but such marriages are recognized by some individual states. The lack of federal recognition was codified in 1996 by the Defense of Marriage Act, before Massachusetts became the first state to grant marriage licenses... |
||||||
| Universal health care Universal health care Universal health care is a term referring to organized health care systems built around the principle of universal coverage for all members of society, combining mechanisms for health financing and service provision.-History:... |
||||||
| More progressive taxation | ||||||
| Strengthening Immigration Laws Immigration to the United States Immigration to the United States has been a major source of population growth and cultural change throughout much of the history of the United States. The economic, social, and political aspects of immigration have caused controversy regarding ethnicity, economic benefits, jobs for non-immigrants,... |
||||||
| End capital punishment Capital punishment in the United States Capital punishment in the United States, in practice, applies only for aggravated murder and more rarely for felony murder. Capital punishment was a penalty at common law, for many felonies, and was enforced in all of the American colonies prior to the Declaration of Independence... |
||||||
| Drug liberalization Drug liberalization Drug liberalization is the process of eliminating or reducing drug prohibition laws. Variations of drug liberalization include drug relegalization, drug legalization, and drug decriminalization -Policies:... |
||||||
| Civilian gun control Gun politics in the United States Gun politics in the United States refers to an ongoing political and social debate regarding both the restriction and availability of firearms within the United States. It has long been among the most controversial and intractable issues in American politics... |
||||||
| Non-interventionism Non-interventionism Nonintervention or non-interventionism is a foreign policy which holds that political rulers should avoid alliances with other nations, but still retain diplomacy, and avoid all wars not related to direct self-defense... |
||||||
| Instant-runoff voting Instant-runoff voting Instant-runoff voting , also known as preferential voting, the alternative vote and ranked choice voting, is a voting system used to elect one winner. Voters rank candidates in order of preference, and their ballots are counted as one vote for their first choice candidate. If a candidate secures a... |
||||||

