International Authority for the Ruhr
Encyclopedia
The International Authority for the Ruhr (IAR) was an international body established in 1949 by the Allied powers
to control the coal and steel industry of the Ruhr Area
in West Germany
.
It was agreed at meetings in London
on 20 April and 2 June 1949 by the United States
, United Kingdom
, France
and the Benelux
countries. The London agreement was signed on 28 April of that year. It was abolished by the Treaty of Paris
in 1951, which moved its activities to the European Coal and Steel Community
(ECSC). The IAR ended its work on 27 May 1952.
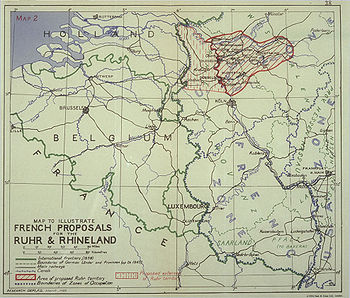 The early French plans were concerned with keeping Germany weak and strengthening the French economy at the expense of that of Germany (see the Monnet Plan
The early French plans were concerned with keeping Germany weak and strengthening the French economy at the expense of that of Germany (see the Monnet Plan
). French foreign policy aimed at dismantling German heavy industry, place the coal rich Ruhr area
and Rhineland
under French control or at a minimum internationalize them, and also to join the coal rich Saarland
with the iron rich province of Lorraine
(which had been handed over from Germany to France again in 1944). When American diplomats reminded the French of what a devastating effect this would have on the German economy, France's response was to suggest the Germans would just have to "make the necessary adjustments" to deal with the inevitable foreign exchange deficit.
In 1947 France removed the Saar from Germany and turned it into a protectorate
under French economic control. The area returned to German administration in January 1, 1957, but France retained the right to mine from its coal mines until 1981. French plans for the complete detachment of the Ruhr from Germany met with greater resistance. In September 1946 the US government stated in the Stuttgart speech Restatement of Policy on Germany
that it would accept the French claims on the Saarland, but that: "the United States will not support any encroachment on territory which is indisputably German or any division of Germany which is not genuinely desired by the people concerned. So far as the United States is aware the people of the Ruhr area and the Rhineland desire to remain united with the rest of Germany. And the United States is not going to oppose their desire."
.
With the West German agreement to join the European Coal and Steel Community in order to lift the restrictions imposed by the IAR, thus also ensuring French security by perpetuating French access to Ruhr coal, the role of the IAR was taken over by the ECSC.
as soon as it had formed a government recognized by the Allies, and that role came to be held by West Germany. Economic costs were shared among the members on the basis of voting rights.
within North Rhine-Westphalia
by listing 36 districts
in the regions
of Düsseldorf
, Münster
, and Arnsberg
.
In Regierungsbezirk Düsseldorf
:
In Regierungsbezirk Münster
:
In Regierungsbezirk Arnsberg
:
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
to control the coal and steel industry of the Ruhr Area
Ruhr Area
The Ruhr, by German-speaking geographers and historians more accurately called Ruhr district or Ruhr region , is an urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With 4435 km² and a population of some 5.2 million , it is the largest urban agglomeration in Germany...
in West Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
.
It was agreed at meetings in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
on 20 April and 2 June 1949 by the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, France
French Fourth Republic
The French Fourth Republic was the republican government of France between 1946 and 1958, governed by the fourth republican constitution. It was in many ways a revival of the Third Republic, which was in place before World War II, and suffered many of the same problems...
and the Benelux
Benelux
The Benelux is an economic union in Western Europe comprising three neighbouring countries, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. These countries are located in northwestern Europe between France and Germany...
countries. The London agreement was signed on 28 April of that year. It was abolished by the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1951)
The Treaty of Paris was signed on 18 April 1951 between France, West Germany, Italy and the three Benelux countries , establishing the European Coal and Steel Community , which subsequently became part of the European Union...
in 1951, which moved its activities to the European Coal and Steel Community
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community was a six-nation international organisation serving to unify Western Europe during the Cold War and create the foundation for the modern-day developments of the European Union...
(ECSC). The IAR ended its work on 27 May 1952.
Background

Monnet Plan
The Monnet plan was proposed by French civil servant Jean Monnet after the end of World War II. It was a reconstruction plan for France that proposed giving France control over the German coal and steel areas of the Ruhr area and Saar and using these resources to bring France to 150% of pre-war...
). French foreign policy aimed at dismantling German heavy industry, place the coal rich Ruhr area
Ruhr Area
The Ruhr, by German-speaking geographers and historians more accurately called Ruhr district or Ruhr region , is an urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With 4435 km² and a population of some 5.2 million , it is the largest urban agglomeration in Germany...
and Rhineland
Rhineland
Historically, the Rhinelands refers to a loosely-defined region embracing the land on either bank of the River Rhine in central Europe....
under French control or at a minimum internationalize them, and also to join the coal rich Saarland
Saarland
Saarland is one of the sixteen states of Germany. The capital is Saarbrücken. It has an area of 2570 km² and 1,045,000 inhabitants. In both area and population, it is the smallest state in Germany other than the city-states...
with the iron rich province of Lorraine
Lorraine (province)
The Duchy of Upper Lorraine was an historical duchy roughly corresponding with the present-day northeastern Lorraine region of France, including parts of modern Luxembourg and Germany. The main cities were Metz, Verdun, and the historic capital Nancy....
(which had been handed over from Germany to France again in 1944). When American diplomats reminded the French of what a devastating effect this would have on the German economy, France's response was to suggest the Germans would just have to "make the necessary adjustments" to deal with the inevitable foreign exchange deficit.
In 1947 France removed the Saar from Germany and turned it into a protectorate
Saar (protectorate)
The Saar Protectorate was a German borderland territory twice temporarily made a protectorate state. Since rejoining Germany the second time in 1957, it is the smallest Federal German Area State , the Saarland, not counting the city-states Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen...
under French economic control. The area returned to German administration in January 1, 1957, but France retained the right to mine from its coal mines until 1981. French plans for the complete detachment of the Ruhr from Germany met with greater resistance. In September 1946 the US government stated in the Stuttgart speech Restatement of Policy on Germany
Restatement of Policy on Germany
"Restatement of Policy on Germany" is a famous speech by James F. Byrnes, the United States Secretary of State, held in Stuttgart on September 6, 1946.Also known as the "Speech of hope" it set the tone of future U.S...
that it would accept the French claims on the Saarland, but that: "the United States will not support any encroachment on territory which is indisputably German or any division of Germany which is not genuinely desired by the people concerned. So far as the United States is aware the people of the Ruhr area and the Rhineland desire to remain united with the rest of Germany. And the United States is not going to oppose their desire."
Overview
The Ruhr Agreement was imposed on the (West) Germans as a condition for permitting them to establish the Federal Republic of Germany. By controlling the production and distribution of coal and steel (i.e. how much coal and steel the Germans themselves would get), the International Authority for the Ruhr in effect controlled the entire West German economy, much to the dismay of the Germans. They were however permitted to send their delegations to the authority after the Petersberg agreementPetersberg agreement
The Petersberg Agreement is an international treaty that extended the rights of the Federal Government of Germany vis-a-vis the occupying forces of Britain, France, and the United States, and is viewed as the first major step of Federal Republic of Germany towards sovereignty...
.
With the West German agreement to join the European Coal and Steel Community in order to lift the restrictions imposed by the IAR, thus also ensuring French security by perpetuating French access to Ruhr coal, the role of the IAR was taken over by the ECSC.
Council
The authority was governed by a council composed of the signatory governments of the London Agreement. The representatives of the Allies each had three votes and the Benelux countries had one vote each. The agreement also stipulated the accession of Occupied GermanyAllied Occupation Zones in Germany
The Allied powers who defeated Nazi Germany in World War II divided the country west of the Oder-Neisse line into four occupation zones for administrative purposes during 1945–49. In the closing weeks of fighting in Europe, US forces had pushed beyond the previously agreed boundaries for the...
as soon as it had formed a government recognized by the Allies, and that role came to be held by West Germany. Economic costs were shared among the members on the basis of voting rights.
- BelgiumBelgiumBelgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, 1 vote - FranceFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, 3 votes - LuxembourgLuxembourgLuxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
, 1 vote - NetherlandsNetherlandsThe Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, 1 vote - United KingdomUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, 3 votes - United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, 3 votes - West GermanyWest GermanyWest Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
, 3 votes
Geography
The London Agreement defines the Ruhr AreaRuhr Area
The Ruhr, by German-speaking geographers and historians more accurately called Ruhr district or Ruhr region , is an urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With 4435 km² and a population of some 5.2 million , it is the largest urban agglomeration in Germany...
within North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia is the most populous state of Germany, with four of the country's ten largest cities. The state was formed in 1946 as a merger of the northern Rhineland and Westphalia, both formerly part of Prussia. Its capital is Düsseldorf. The state is currently run by a coalition of the...
by listing 36 districts
Districts of Germany
The districts of Germany are known as , except in the states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Schleswig-Holstein where they are known simply as ....
in the regions
Regierungsbezirk
In Germany, a Government District, in German: Regierungsbezirk – is a subdivision of certain federal states .They are above the Kreise, Landkreise, and kreisfreie Städte...
of Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf (region)
Düsseldorf is one of the five Regierungsbezirke of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, located in the north-west of the country. It covers the western part of the Ruhr Area, as well as the Niederrheinische Tiefebene, the lower Rhine area. It is the most populated of all German administrative areas of...
, Münster
Münster (region)
Münster is one of the five Regierungsbezirke of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, located in the north of the state, and named after the city of Münster. It includes the area which in medieval times was known as the Dreingau....
, and Arnsberg
Arnsberg (region)
Arnsberg is one of the five Regierungsbezirke of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, located in the south-east of the country. It covers the Sauerland hills as well as the east part of the Ruhr area....
.
In Regierungsbezirk Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf (region)
Düsseldorf is one of the five Regierungsbezirke of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, located in the north-west of the country. It covers the western part of the Ruhr Area, as well as the Niederrheinische Tiefebene, the lower Rhine area. It is the most populated of all German administrative areas of...
:
- Landkreis DinslakenDinslakenDinslaken is a city in the district of Wesel, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is known for its harness horse race track, its now closed coal mine in Lohberg and its wealthy neighborhoods Hiesfeld and Eppinghoven.- Geography :...
- Landkreis Düsseldorf-MettmannMettmann (district)Mettmann is a Kreis in the middle of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring are the Ennepe-Ruhr and thedistrict-free cities Wuppertal, Solingen, Düsseldorf,Duisburg, Mülheim, Essen...
- Landkreis EssenEssen- Origin of the name :In German-speaking countries, the name of the city Essen often causes confusion as to its origins, because it is commonly known as the German infinitive of the verb for the act of eating, and/or the German noun for food. Although scholars still dispute the interpretation of...
- Landkreis GeldernGeldernGeldern ) is a city in the northwest of the federal state North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is part of the district of Cleves, which is part of the Düsseldorfadministrative region.-Location:...
- Landkreis KrefeldKrefeldKrefeld , also known as Crefeld until 1929, is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located northwest of Düsseldorf, its centre lying just a few kilometres to the west of the River Rhine; the borough of Uerdingen is situated directly on the Rhine...
-UerdingenUerdingenUerdingen is a district of the city of Krefeld, Germany, with a population of 18,507, though Uerdingen received its charter as a city as early as 1255, well before Krefeld. Uerdingen was merged with Krefeld in 1929, after which the term “Krefeld-Uerdingen” was used, until, eventually, the use of... - Landkreis MoersMoersMoers is a German city on the left bank of the Rhine. Moers belongs to the district of Wesel...
- Landkreis ReesRees, GermanyRees is a town in the district of Cleves in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located on the right bank of the Rhine, approx. 20 km east of Cleves...
- Stadtkreis DüsseldorfDüsseldorfDüsseldorf is the capital city of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and centre of the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region.Düsseldorf is an important international business and financial centre and renowned for its fashion and trade fairs. Located centrally within the European Megalopolis, the...
- Stadtkreis Duisburg-HambornDuisburg- History :A legend recorded by Johannes Aventinus holds that Duisburg, was built by the eponymous Tuisto, mythical progenitor of Germans, ca. 2395 BC...
- Stadtkreis MülheimMülheimMülheim an der Ruhr, also called "City on the River", is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. It is located in the Ruhr Area between Duisburg, Essen, Oberhausen and Ratingen...
- Stadtkreis NeussRhein-Kreis NeussNeuss is a Kreis in the west of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Nearby are the urban districts Mönchengladbach, Krefeld, Duisburg, Düsseldorf, Cologne, the districts Rhein-Erft-Kreis, Düren, Heinsberg and the district Viersen.-History:...
- Stadtkreis OberhausenOberhausenOberhausen is a city on the river Emscher in the Ruhr Area, Germany, located between Duisburg and Essen . The city hosts the International Short Film Festival Oberhausen and its Gasometer Oberhausen is an anchor point of the European Route of Industrial Heritage. It is also well known for the...
- Stadtkreis RemscheidRemscheidRemscheid is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is, after Wuppertal and Solingen, the third largest municipality in Bergisches Land, being located on the northern edge of the region, on south side of the Ruhr area....
- Stadtkreis SolingenSolingenSolingen is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located on the northern edge of the region called Bergisches Land, south of the Ruhr area, and with a 2009 population of 161,366 is the second largest city in the Bergisches Land...
- Stadtkreis WuppertalWuppertalWuppertal is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in and around the Wupper river valley, and is situated east of the city of Düsseldorf and south of the Ruhr area. With a population of approximately 350,000, it is the largest city in the Bergisches Land...
In Regierungsbezirk Münster
Münster (region)
Münster is one of the five Regierungsbezirke of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, located in the north of the state, and named after the city of Münster. It includes the area which in medieval times was known as the Dreingau....
:
- Landkreis BeckumBeckum, GermanyBeckum is a town in the district of Warendorf, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated approximately 20 km north-east of Hamm and 35 km south-east of Münster...
- Landkreis LüdinghausenLüdinghausenLüdinghausen is a municipality in the district of Coesfeld in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located on the Dortmund-Ems Canal, approx. 25 km south-west of Münster...
- Landkreis RecklinghausenRecklinghausen (district)Recklinghausen is a Kreis in the middle of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Borken, Coesfeld, Unna,district-free cities Dortmund, Bochum, Herne, Essen, Gelsenkirchen and Bottrop, and the district Wesel.-History:...
- Stadtkreis BottropBottropBottrop is a city in west central Germany, on the Rhine-Herne Canal, in North Rhine-Westphalia. Located in the Ruhr industrial area, Bottrop adjoins Essen, Oberhausen, Gladbeck and Dorsten. The city had been a coal-mining and rail center and contains factories producing coal-tar derivatives,...
- Stadtkreis GelsenkirchenGelsenkirchenGelsenkirchen is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the northern part of the Ruhr area. Its population in 2006 was c. 267,000....
- Stadtkreis GladbeckGladbeckGladbeck is a city in the district of Recklinghausen in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.The name ´Gladbeck´ evolves from Low German, originally spoken in the area around Gladbeck. ´Glad´ means something like gleamy and ´beck´ means about brook. However, the brook Gladbeck flows under the ground...
- Stadtkreis RecklinghausenRecklinghausenRecklinghausen is the northernmost city in the Ruhr-Area and the capital of the Recklinghausen district. It borders the rural Münsterland and is characterized by large fields and farms in the north and industry in the south...
In Regierungsbezirk Arnsberg
Arnsberg (region)
Arnsberg is one of the five Regierungsbezirke of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, located in the south-east of the country. It covers the Sauerland hills as well as the east part of the Ruhr area....
:
- Landkreis Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis
- Landkreis IserlohnIserlohnIserlohn is a city in the Märkischer Kreis district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the largest city by population and area within the district and the Sauerland region.-Geography:...
- Landkreis UnnaUnna (district)The Unna district is a Kreis in central North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring authorities are the district of Coesfeld, the city of Hamm, the districts of Soest and Märkischer Kreis, the cities of Hagen and Dortmund, and the district of Recklinghausen.-History:The area of the present...
- Stadtkreis BochumBochumBochum is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, western Germany. It is located in the Ruhr area and is surrounded by the cities of Essen, Gelsenkirchen, Herne, Castrop-Rauxel, Dortmund, Witten and Hattingen.-History:...
- Stadtkreis Castrop-RauxelCastrop-Rauxel-Geography:Castrop-Rauxel is between Dortmund to the east, Bochum , Herne , and to the north, Recklinghausen, Datteln and Waltrop.- Urban Area :The urban area of Castrop-Rauxel has an total expanse of...
- Stadtkreis DortmundDortmundDortmund is a city in Germany. It is located in the Bundesland of North Rhine-Westphalia, in the Ruhr area. Its population of 585,045 makes it the 7th largest city in Germany and the 34th largest in the European Union....
- Stadtkreis HagenHagenHagen is the 39th-largest city in Germany, located in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is located on the eastern edge of the Ruhr area, 15 km south of Dortmund, where the rivers Lenne, Volme and Ennepe meet the river Ruhr...
- Stadtkreis HammHammHamm is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia , Germany. It is located in the northeastern part of the Ruhr area. As of December 2003 its population was 180,849. The city is situated between the A1 motorway and A2 motorway...
- Stadtkreis HerneHerne, GermanyHerne is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the Ruhr area directly between the cities of Bochum and Gelsenkirchen.- History :Like most other cities in the region Herne was a tiny village until the 19th century...
- Stadtkreis IserlohnIserlohnIserlohn is a city in the Märkischer Kreis district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the largest city by population and area within the district and the Sauerland region.-Geography:...
- Stadtkreis Luenen
- Stadtkreis Wanne-Eickel
- Stadtkreis WattenscheidWattenscheidWattenscheid was once a separate town in the North Rhine-Westphalia region of Germany. In 1975 it became part of Bochum. It has a population of about 80,000 citizens. It is a part of the Ruhr area. Some famous firms have their headquarters in Wattenscheid e.g...
- Stadtkreis WittenWittenWitten is a university city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the home of the Witten/Herdecke University, the first private university in Germany.-Bordering municipalities:* Bochum* Dortmund* Herdecke* Wetter * Sprockhoevel* Hattingen...
See also
- History of the Ruhr
- Industrial plans for GermanyIndustrial plans for GermanyThe Industrial plans for Germany were designs the Allies considered imposing on Germany in the aftermath of World War II to reduce and manage Germany's industrial capacity.-Background:...
- Morgenthau PlanMorgenthau PlanThe Morgenthau Plan, proposed by United States Secretary of the Treasury Henry Morgenthau, Jr., advocated that the Allied occupation of Germany following World War II include measures to eliminate Germany's ability to wage war.-Overview:...
- Monnet PlanMonnet PlanThe Monnet plan was proposed by French civil servant Jean Monnet after the end of World War II. It was a reconstruction plan for France that proposed giving France control over the German coal and steel areas of the Ruhr area and Saar and using these resources to bring France to 150% of pre-war...
- Saar protectorateSaar (protectorate)The Saar Protectorate was a German borderland territory twice temporarily made a protectorate state. Since rejoining Germany the second time in 1957, it is the smallest Federal German Area State , the Saarland, not counting the city-states Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen...
External links
- The International Authority for the Ruhr - European NAvigatorEuropean NAvigatorEuropean NAvigator was the former name of the digital library on the history of European integration and related institutions. The research project is now online at www.cvce.eu, a website dedicated to European integration studies....
- Agreement for an International Authority for the Ruhr, April 28, 1949 - European NAvigator
- France, Germany and the Struggle for the War-making Natural Resources of the Rhineland ICE Case Studies, Number 158, August, 2005

