History of Eurasia
Encyclopedia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
is the collective history of a continental area with several distinct peripheral coastal regions: the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
, South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
, East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, and Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe
Steppe
In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes...
of Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
. While geographically on a separate continent, North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
has historically been integrated into Eurasian history. Perhaps beginning with early Silk Road
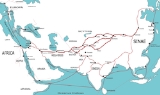
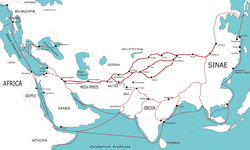
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
trade, the Eurasian view of history seeks establishing genetic, cultural, and linguistic links between European, African and Asian cultures of antiquity. In fact, much interest in this area lies with the presumed origin of the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European language
The Proto-Indo-European language is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans...
and Chariot warfare in Central Eurasia
Central Eurasia
Central Eurasia is a geographic term, which may refer to:* Central Asia, i.e., the five Central Asian Republics as well as the lower Volga Region in Russia, southern Siberia, Iran, Afghanistan, parts of China and Northern Pakistan, Kashmir and sometimes Mongolia and Tibet* The Caucasus region,...
.
Lower Paleolithic
Fossilized remains of Homo georgicusHomo georgicus
Homo georgicus is a species of Homo that was suggested in 2002 to describe fossil skulls and jaws found in Dmanisi, Georgia in 1999 and 2001, which seem intermediate between Homo habilis and H. erectus. A partial skeleton was discovered in 2001. The fossils are about 1.8 million years old...
, Homo ergaster
Homo ergaster
Homo ergaster is an extinct chronospecies of Homo that lived in eastern and southern Africa during the early Pleistocene, about 2.5–1.7 million years ago.There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
and Homo erectus
Homo erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominid that lived from the end of the Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene, about . The species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
between 1.8 and 1.0 million years old have been found in Europe (Georgia (Dmanisi
Dmanisi
Dmanisi is a townlet and archaeological site in Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia approximately 93 km southwest of the nation’s capital Tbilisi in the river valley of Mashavera.- History :...
), Spain), Indonesia (e.g., Sangiran and Trinil), Vietnam, and China (e.g., Shaanxi). (see also:Multiregional hypothesis). The first remains are of Olduwan
Olduwan
The Oldowan, often spelled Olduwan or Oldawan, is the archaeological term used to refer to the stone tool industry that was used by Hominines during the Lower Paleolithic period...
culture, later of Acheulean
Acheulean
Acheulean is the name given to an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture associated with early humans during the Lower Palaeolithic era across Africa and much of West Asia, South Asia and Europe. Acheulean tools are typically found with Homo erectus remains...
and Clactonian
Clactonian
The Clactonian is the name given by archaeologists to an industry of European flint tool manufacture that dates to the early part of the interglacial period known as the Hoxnian, the Mindel-Riss or the Holstein stages . Clactonian tools were made by Homo erectus rather than modern humans...
culture. Finds of later fossils, such as Homo cepranensis
Homo cepranensis
Homo cepranensis is a proposed name for a human species, known from only one skull cap discovered in 1994. The fossil was discovered by archeologist Italo Biddittu and was nicknamed "Ceprano Man" after a nearby town in the province of Frosinone, 89 kilometers Southeast of Rome, Italy.The age of...
, are local in nature, so the extent of human residence in Eurasia during 1,000,000 - 300,000 bp remains a mystery.
Middle Paleolithic
Geologic temperature recordGeologic temperature record
The Geologic temperature record are changes in Earth's environment as determined from geologic evidence on multi-million to billion year time scales...
s indicate two intense ice ages dated around 650000 ybp and 450000 ybp, these would have presented any humans outside tropics
Tropics
The tropics is a region of the Earth surrounding the Equator. It is limited in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the northern hemisphere at approximately N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the southern hemisphere at S; these latitudes correspond to the axial tilt of the Earth...
unprecedented difficulties. Indeed, fossils from this period are very few, and little can be said of human habitats in Eurasia during this period. The few finds are of Homo antecessor
Homo antecessor
Homo antecessor is an extinct human species dating from 1.2 million to 800,000 years ago, that was discovered by Eudald Carbonell, Juan Luis Arsuaga and J. M. Bermúdez de Castro. H. antecessor is one of the earliest known human varieties in Europe. Various archaeologists and anthropologists have...
and Homo heidelbergensis
Homo heidelbergensis
Homo heidelbergensis is an extinct species of the genus Homo which may be the direct ancestor of both Homo neanderthalensis in Europe and Homo sapiens. The best evidence found for these hominins date between 600,000 and 400,000 years ago. H...
. Lantian Man
Lantian Man
Lantian Man , formerly Sinanthropus lantianensis is a subspecies of Homo erectus. Its discovery in 1963 was first described by J. K...
in China.
Homo neanderthalensis, with his Mousterian
Mousterian
Mousterian is a name given by archaeologists to a style of predominantly flint tools associated primarily with Homo neanderthalensis and dating to the Middle Paleolithic, the middle part of the Old Stone Age.-Naming:...
technology emerged, in areas from Europe to western Asia, after this and continued to be the dominant group of humans in Europe and Middle East up until 70000-40000 ybp. Peking man
Peking Man
Peking Man , Homo erectus pekinensis, is an example of Homo erectus. A group of fossil specimens was discovered in 1923-27 during excavations at Zhoukoudian near Beijing , China...
has also been dated to this period. During Eemian Stage humans probably (see f.e. Wolf Cave
Wolf Cave
Wolf Cave is a crack in the Pyhävuori mountain in Kristinestad , near the Karijoki municipality in Finland. The upper part of the crack has been packed with soil, forming a cave. In 1996, some objects were found in the cave that brought about speculations that it could have been inhabited in the...
) spread where ever their technology and skills allowed, Sahara dried up forming a difficult area for peoples to cross.
The birth of first modern humans (Homo sapiens idaltu
Homo sapiens idaltu
Homo sapiens idaltu is an extinct subspecies of Homo sapiens that lived almost 160,000 years ago in Pleistocene Africa. is from the Saho-Afar word meaning "elder or first born"....
) has been dated to be between 200000-130000 BP (see:Mitochondrial Eve
Mitochondrial Eve
In the field of human genetics, Mitochondrial Eve refers to the matrilineal "MRCA" . In other words, she was the woman from whom all living humans today descend, on their mother's side, and through the mothers of those mothers and so on, back until all lines converge on one person...
, Single-origin hypothesis), to the coldest phase of Riss glaciation. Remains of Aterian
Aterian
The Aterian industry is a name given by archaeologists to a type of stone tool manufacturing dating to the Middle Stone Age in the region around the Atlas Mountains and the northern Sahara, it refers the site of Bir el Ater, south of Annaba.The industry was probably created by modern humans ,...
culture appear on the archaeological evidence.
Population bottleneck
In the beginning of the last ice ageWisconsin glaciation
The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period within the current ice age occurring during the last years of the Pleistocene, from approximately 110,000 to 10,000 years ago....
a supervolcano
Toba catastrophe theory
The Toba supereruption was a supervolcanic eruption that occurred some time between 69,000 and 77,000 years ago at Lake Toba . It is recognized as one of the Earth's largest known eruptions...
erupted in Indonesia sometime between 75000 - 70000 BP. Theory states the effects of the eruption caused global climatic changes for many years, effectively obliterating most of the earlier cultures. Y-chromosomal Adam
Y-chromosomal Adam
In human genetics, Y-chromosomal Adam is the theoretical most recent common ancestor from whom all living people are descended patrilineally . Many studies report that Y-chromosomal Adam lived as early as around 142,000 years ago and possibly as recently as 60,000 years ago...
(90000 - 60000 BP) has been dated here. Neanderthal
Neanderthal
The Neanderthal is an extinct member of the Homo genus known from Pleistocene specimens found in Europe and parts of western and central Asia...
s survived this abrupt change in the environment, so it's possible for other human groups too. According to the theory humans survived in Africa, and began to resettle areas north, as the effects of the eruption slowly vanished. Upper Paleolithic revolution began after this extreme event, the earliest finds are dated c.50000 BCE.
A divergence in genetical evidence occurs during the early phase of the glaciation. Descendants of female haplogroup
Haplogroup
In the study of molecular evolution, a haplogroup is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor having the same single nucleotide polymorphism mutation in both haplotypes. Because a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, this is what makes it possible to predict a haplogroup...
s M
Haplogroup M (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup M is a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup. An enormous haplogroup spanning all the continents, the macro-haplogroup M, like its sibling N, is a descendant of haplogroup L3....
, N
Haplogroup N (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup N is a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup. An enormous haplogroup spanning many continents, the macro-haplogroup N, like its sibling M, is a descendant of haplogroup L3....
and male CT
Haplogroup CT (Y-DNA)
In human genetics, Haplogroup CT is a Y-chromosome haplogroup, defining one of the major lines of common ancestry of humanity along father-to-son male lines.Men within this haplogroup have Y chromosomes with the SNP mutation M168, along with P9.1 and M294...
are the ones found among Eurasian peoples today.
Upper Paleolithic, the dispersal of modern humans
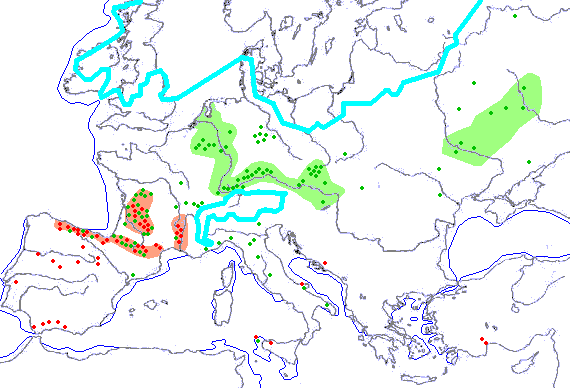
Molecular clock
The molecular clock is a technique in molecular evolution that uses fossil constraints and rates of molecular change to deduce the time in geologic history when two species or other taxa diverged. It is used to estimate the time of occurrence of events called speciation or radiation...
) that modern humans migrated to Eurasia during the early phases of the last glaciation, the findings are very few. Most remains are of neanderthals. It has been suggested that the earliest migrations (through Middle East (Cro magnon in Levant c. 60000 BC)) have happened along coasts of southern Asia. Neanderthal interaction with Cro-Magnons remains a vigorous topic of discussion. Eurasian Upper Paleolithic is traditionally dated to start with the earliest finds (circa 45000 BC) of more developed stone tools gradually replacing the Mousterian (Neanderthal) culture as seen f.e. in Santimamiñe
Santimamiñe
Santimamiñe cave, Kortezubi, Biscay, Basque Country, Spain, is one of the most important archaeological sites of the Basque Country, including a nearly complete sequence from the Middle Paleolithic to the Iron Age....
. Asian finds are few. They've been tributed to Ordos culture
Ordos culture
The Ordos culture comprises the period from Upper Paleolithic to the late Bronze age at the Ordos Desert, in the south of the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China...
. Cultural periods in the ice age include Châtelperronian
Châtelperronian
Châtelperronian was the earliest industry of the Upper Palaeolithic in central and south western France, extending also into Northern Spain. It derives its name from the site of la Grotte des Fées, in Châtelperron, Allier, France....
culture, Aurignacian
Aurignacian
The Aurignacian culture is an archaeological culture of the Upper Palaeolithic, located in Europe and southwest Asia. It lasted broadly within the period from ca. 45,000 to 35,000 years ago in terms of conventional radiocarbon dating, or between ca. 47,000 and 41,000 years ago in terms of the most...
culture, Gravettian
Gravettian
thumb|right|Burins to the Gravettian culture.The Gravettian toolmaking culture was a specific archaeological industry of the European Upper Palaeolithic era prevalent before the last glacial epoch. It is named after the type site of La Gravette in the Dordogne region of France where its...
culture, Solutrean
Solutrean
The Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Palaeolithic, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP.-Details:...
culture and Magdalenian
Magdalenian
The Magdalenian , refers to one of the later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic in western Europe, dating from around 17,000 BP to 9,000 BP...
culture.
see also: Pre-history of the Southern Levant
Pre-history of the Southern Levant
The prehistory of the Southern Levant includes the various cultural changes that occurred, as revealed by archaeological evidence, prior to recorded traditions in the area of the Southern Levant, also referred to by a number of other largely overlapping historical designations, including Canaan,...
Migrations
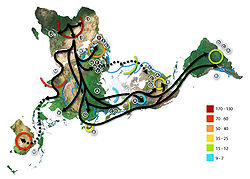
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
s of modern humans by methods of genetic genealogy
Genetic genealogy
Genetic genealogy is the application of genetics to traditional genealogy. Genetic genealogy involves the use of genealogical DNA testing to determine the level of genetic relationship between individuals.-History:...
, can and have been used to produce models of historical migration
Historical migration
It is thought that pre-historical migration of human populations began with the movement of Homo erectus out of Africa across Eurasia about a million years ago. Homo sapiens appears to have colonized all of Africa about 150 millennia ago, moved out of Africa some 80 millennia ago, and spread...
. Though these give indications of the routes taken by ancestral humans, the dating of the various genetic markers is not very accurate. The earliest migrations (dated c. 75.000 BP) from the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
shores have been most likely along southern coast of Asia. After this, tracking and timing genetical markers gets increasingly difficult. What is known, is that on areas, of what is now Iraq, Iran, Pakistan and Afghanistan, genetic markers diversify (from about 60000 BCE), and subsequent migrations emerge to all directions (even backwards to Levant
Levant
The Levant or ) is the geographic region and culture zone of the "eastern Mediterranean littoral between Anatolia and Egypt" . The Levant includes most of modern Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, the Palestinian territories, and sometimes parts of Turkey and Iraq, and corresponds roughly to the...
) from here. Northeastbound were likely the ancestors of Samoyeds and Indigenous Americans (dated 50000 - 40000 BCE), northbound the ancestors of Uralic peoples, eastbound (maybe along Ganges) likely went the ancestors of Chinese. It is still largely unclear what routes different groups of Indo-European
Indo-European
Indo-European may refer to:* Indo-European languages** Aryan race, a 19th century and early 20th century term for those peoples who are the native speakers of Indo-European languages...
ancestors took to Europe (this likely happened later though). Genetic evidence suggests three - four separate migrations (1.Illyrians - Greeks 2.Celts - Italics, (3.Balts, if separately), 4.Goths - Slavs, - not necessarily in this order). Archaeologicical evidence has not been attributed to any particular group. On historical linguistic evidence, see f.e. classification of Thracian
Classification of Thracian
The linguistic classification of the ancient Thracian language has long been a matter of contention and uncertainty, and there are widely varying hypotheses regarding its position among other Paleo-Balkan languages...
. The traditional view of associating early Celts with the chalcolithic Europe
Chalcolithic Europe
Chalcolithic Europe, the Chalcolithic period of Prehistoric Europe lasts roughly 3500 to 1700 BC.It is the period of Megalithic culture, the appearance of the first significant economic stratification, and probably the earliest presence of Indo-European speakers.The economy of the Chalcolithic,...
, European Bronze Age
Bronze Age Europe
The European Bronze Age is characterized by bronze artifacts and the use of bronze implements. The regional Bronze Age succeeds the Neolithic, it starts with the Aegean Bronze Age 3200 BC...
with Germanic peoples, and Roman Empire with first widespread use of iron outside Paleobalkan
Prehistory of Southeastern Europe
The prehistory of Southeastern Europe , defined roughly as the territory of the wider Balkans peninsula covers the period from the Upper Paleolithic, beginning with the presence of Homo sapiens in the area some 44,000 years ago, until the...
area, is not considered good. Most likely there has been trade also in these periods f.e. with amber.
Influences from northern Africa via Gibraltar
Cardium Pottery
Cardium Pottery or Cardial Ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the shell of the Cardium edulis, a marine mollusk...
and Sicilia
Sicani
The Sicani or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization.-History:The Sicani are thought to be the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name...
cannot be readily discounted. Many other questions remain open, too (f.e. Neanderthals were still present at this time). More genetical data is being gathered by various research programs.
Early Holocene
- See:MesolithicMesolithicThe Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
- See also:Synoptic table of the principal old world prehistoric culturesSynoptic table of the principal old world prehistoric culturesThe synoptic table of the principal old world prehistoric cultures gives a rough picture of the relationships between the various principal cultures of prehistory outside the Americas, Antarctica, Australia and Oceania...
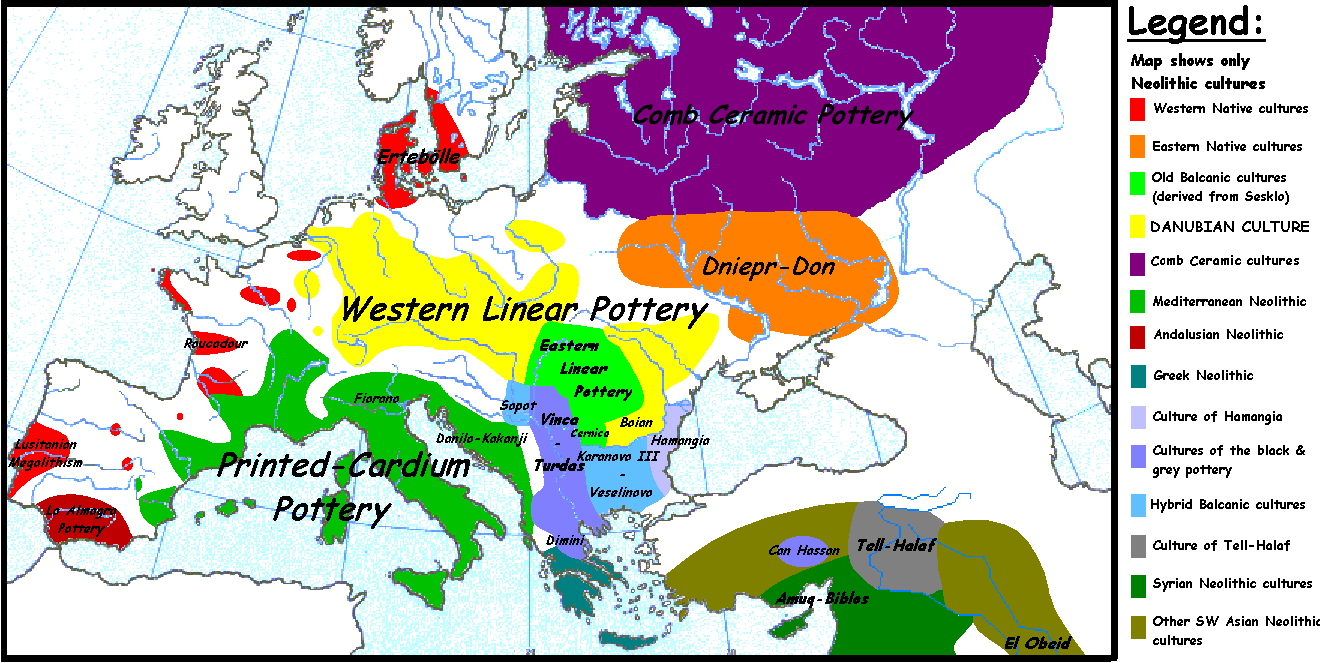
Holocene extinction event
The Holocene extinction refers to the extinction of species during the present Holocene epoch . The large number of extinctions span numerous families of plants and animals including mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles and arthropods; a sizeable fraction of these extinctions are occurring in the...
. At the same time Neolithic revolution
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution was the first agricultural revolution. It was the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture and settlement. Archaeological data indicates that various forms of plants and animal domestication evolved independently in 6 separate locations worldwide circa...
began and humans started to make pottery, began to cultivate crops
History of agriculture
Agriculture was developed at least 10,000 years ago, and it has undergone significant developments since the time of the earliest cultivation. The Fertile Crescent of Western Asia, Egypt, and India were sites of the earliest planned sowing and harvesting of plants that had previously been gathered...
and domesticated some animal species.
Neolithic cultures in Eurasia are many, and best discussed in separate articles. Some of the articles on this subject include: Natufian culture
Natufian culture
The Natufian culture was a Mesolithic culture that existed from 12,500 to 9,500 BC in the Levant, a region in the Eastern Mediterranean. It was unusual in that it was sedentary, or semi-sedentary, before the introduction of agriculture...
, Jomon culture, List of Neolithic cultures of China and Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh , one of the most important Neolithic sites in archaeology, lies on the "Kachi plain" of Balochistan, Pakistan...
. European sites are many, they are discussed f.e. in Prehistoric Europe
Prehistoric Europe
Prehistoric Europe refers to the prehistorical period of Europe, usually taken to refer to human prehistory since the Lower Paleolithic, but in principle also extending to geological time scale - for which see Geological history of Europe....
. The finding of Ötzi the Iceman
Ötzi the Iceman
Ötzi the Iceman , Similaun Man, and Man from Hauslabjoch are modern names for a well-preserved natural mummy of a man who lived about 5,300 years ago. The mummy was found in September 1991 in the Ötztal Alps, near Hauslabjoch on the border between Austria and Italy. The nickname comes from the...
(dated 3300 BC) provides an important insight to Chalcolithic period in Europe. Proto-language
Proto-language
A proto-language in the tree model of historical linguistics is the common ancestor of the languages that form a language family. Occasionally, the German term Ursprache is used instead.Often the proto-language is not known directly...
s of various peoples have been forming in this period, though no literal evidence can (by definition) be found. Later migrations further complicate the study of migrations in this period.
Writing, the civilizations emerge
Origins of writingHistory of writing
The history of writing records the development of expressing language by letters or other marks. In the history of how systems of representation of language through graphic means have evolved in different human civilizations, more complete writing systems were preceded by proto-writing, systems of...
are dated to fourth millennium BC. Writing may have started independently on various areas of Eurasia. It appears the skill spread relatively fast, giving people a new way of communication
Communication
Communication is the activity of conveying meaningful information. Communication requires a sender, a message, and an intended recipient, although the receiver need not be present or aware of the sender's intent to communicate at the time of communication; thus communication can occur across vast...
.
The three eastern regions of the Middle East, East Asia and South Asia developed in a similar manner with each of the three regions developing early civilizations around fertile river valleys. The civilizations in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
, the Indus Valley
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
, and China
History of China
Chinese civilization originated in various regional centers along both the Yellow River and the Yangtze River valleys in the Neolithic era, but the Yellow River is said to be the Cradle of Chinese Civilization. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest...
(along the Yellow River
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He, formerly known as the Hwang Ho, is the second-longest river in China and the sixth-longest in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai Province in western China, it flows through nine provinces of China and empties into...
and the Yangtze
Yangtze River
The Yangtze, Yangzi or Cháng Jiāng is the longest river in Asia, and the third-longest in the world. It flows for from the glaciers on the Tibetan Plateau in Qinghai eastward across southwest, central and eastern China before emptying into the East China Sea at Shanghai. It is also one of the...
) shared many similarities and likely exchanged technologies and ideas such as mathematics
History of mathematics
The area of study known as the history of mathematics is primarily an investigation into the origin of discoveries in mathematics and, to a lesser extent, an investigation into the mathematical methods and notation of the past....
and the wheel
Wheel
A wheel is a device that allows heavy objects to be moved easily through rotating on an axle through its center, facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Common examples found in transport applications. A wheel, together with an axle,...
. Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
also shared this model. These civilizations were most likely in more or less regular contact with each other by the early versions of the silk road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
.
Europe was different, however. It was somewhat further north and contained no river systems to support agriculture. Thus Europe remained comparatively undeveloped, with only the southern tips of the region (Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
and Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
) being able to fully borrow crops, technologies, and ideas from the Middle East and North Africa. Similarly, civilization didn't arise in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
until contact was made with ancient India
History of India
The history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent from...
, which gave rise to Indianized kingdoms in Indochina
Indochina
The Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly southwest of China, and east of India. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, as a combination of the names of "China" and "India", and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory...
and the Malay archipelago
Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago refers to the archipelago between mainland Southeastern Asia and Australia. The name was derived from the anachronistic concept of a Malay race....
. The steppe region had long been inhabited by mounted nomads, and from the central steppes they could reach all areas of the Asian continent. The northern part of the silk road traversed this region.
One such central expansion out of the steppe is that of the Proto-Indo-Europeans
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans were the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language , a reconstructed prehistoric language of Eurasia.Knowledge of them comes chiefly from the linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics...
which spread their languages into the Middle East, India, Europe, and to the borders of China (with the Tocharians
Tocharians
The Tocharians were the Tocharian-speaking inhabitants of the Tarim Basin, making them the easternmost speakers of Indo-European languages in antiquity. They were known as, or at least closely related to, the Yuezhi of Chinese sources...
). Throughout their history, up to the development of gunpowder
Gunpowder
Gunpowder, also known since in the late 19th century as black powder, was the first chemical explosive and the only one known until the mid 1800s. It is a mixture of sulfur, charcoal, and potassium nitrate - with the sulfur and charcoal acting as fuels, while the saltpeter works as an oxidizer...
, all the areas of Eurasia would be repeatedly menaced by the Indo-Iranian
Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples are a linguistic group consisting of the Indo-Aryan, Iranian, Dardic and Nuristani peoples; that is, speakers of Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European language family....
, Turkic
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
and Mongol
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
nomads from the steppe.
A difference between Europe and most of the regions of Eurasia is that each of the latter regions has few obstructions internally even though it is ringed by mountains and deserts. This meant that it was easier to establish unified control over the entire region, and this did occur with massive empires consistently dominating the Middle East, China, and at times, much of India. Europe, however, is riddled with internal mountain ranges: The Carpathians
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians are a range of mountains forming an arc roughly long across Central and Eastern Europe, making them the second-longest mountain range in Europe...
, the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
, the Pyrenees
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees is a range of mountains in southwest Europe that forms a natural border between France and Spain...
and many others. Throughout its history, Europe has thus usually been divided into many small states, much like the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
and Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
for much of their history.
The Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
made large stands of timber essential to a nation's success because smelting iron required so much fuel, and the pinnacles of human civilizations gradually moved as forests were destroyed. In Europe the Mediterranean region was supplanted by the German and Frankish lands. In the Middle East the main power center became Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
with the once dominant Mesopotamia its vassal. In China, the economical, agricultural, and industrial center moved from the northern Yellow River to the southern Yangtze, though the political center remained in the north. In part this is linked to technological developments, such as the mouldboard plough
Plough
The plough or plow is a tool used in farming for initial cultivation of soil in preparation for sowing seed or planting. It has been a basic instrument for most of recorded history, and represents one of the major advances in agriculture...
, that made life in once undeveloped areas more bearable.
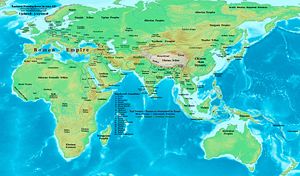
The civilizations in China
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
, India
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire originally formed in the early 1st century AD under Kujula Kadphises in the territories of ancient Bactria on either side of the middle course of the Oxus in what is now northern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and southern Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.During the 1st and early 2nd centuries...
, and Mediterranean
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, connected by the silk road, became the principal civilizations in Eurasia in early CE times. Later development of Eurasian history of mankind is told in other articles.
See also
- History of AsiaHistory of AsiaThe history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as, East Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe....
- History of EuropeHistory of EuropeHistory of Europe describes the history of humans inhabiting the European continent since it was first populated in prehistoric times to present, with the first human settlement between 45,000 and 25,000 BC.-Overview:...
- History of the Middle EastHistory of the Middle EastThis article is a general overview of the history of the Middle East. For more detailed information, see articles on the histories of individual countries and regions...
- History of South AsiaHistory of South AsiaThe term South Asia refers to the contemporary political entities of the Indian subcontinent and associated island. These are the states of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and the island nations of Sri Lanka and the Maldives....
- History of East AsiaHistory of East Asia-Prehistory:In East Asia, the Neolithic period may have begun as early as 7500 BC. The earliest evidence suggests the existence of the Pengtoushan culture in northern Hunan province from about 7500 BC to 6100 BC and of the Peiligang culture in Henan province around from about 7000 BC to 5000...
- History of Southeast AsiaHistory of Southeast AsiaThe history of Southeast Asia has been characterized as interaction between regional players and foreign powers. Each country is intertwined with all the others. For instance, the Malay empires of Srivijaya and Malacca covered modern day Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore while the Burmese, Thai,...
- History of Central AsiaHistory of Central AsiaThe history of Central Asia has been determined primarily by the area's climate and geography. The aridity of the region makes agriculture difficult, and its distance from the sea cut it off from much trade. Thus, few major cities developed in the region...
- History of the WorldHistory of the worldThe history of the world or human history is the history of humanity from the earliest times to the present, in all places on Earth, beginning with the Paleolithic Era. It excludes non-human natural history and geological history, except insofar as the natural world substantially affects human lives...
- Indo-European studiesIndo-European studiesIndo-European studies is a field of linguistics dealing with Indo-European languages, both current and extinct. Its goal is to amass information about the hypothetical proto-language from which all of these languages are descended, a language dubbed Proto-Indo-European , and its speakers, the...

