
History of Calais
Encyclopedia

Calais
Calais is a town in Northern France in the department of Pas-de-Calais, of which it is a sub-prefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's capital is its third-largest city of Arras....
dates back centuries and is chiefly influenced by its being the closest major port
Port
A port is a location on a coast or shore containing one or more harbors where ships can dock and transfer people or cargo to or from land....
to Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
.
To the 13th century
The origins of Calais are obscure though its site might be expected to be have been inhabited from early times. In Roman times the name was Caletum. In medieval times the town was part of a Dutch speaking area extending into present north France; in those times the Dutch name was Kales. It stands on the foreshore of the last piece of solid geology on the south and east coast of the North SeaNorth Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
between France and the UK. It is also at the western edge of the early medieval estuary of the River Aa
Aa River (France)
The Aa is an 89 km long river in northern France. Its source is near the village Bourthes. It flows through the following départements and cities:* Pas-de-Calais: Saint-Omer.* Nord: Gravelines....
. As the pebble and sand ridge extended eastwards from Calais, the haven behind it developed into fen
Fen
A fen is a type of wetland fed by mineral-rich surface water or groundwater. Fens are characterised by their water chemistry, which is neutral or alkaline, with relatively high dissolved mineral levels but few other plant nutrients...
so that the estuary progressively filled with silt and peat. Subsequently, canals were cut between Saint-Omer
Saint-Omer
Saint-Omer , a commune and sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department west-northwest of Lille on the railway to Calais. The town is named after Saint Audomar, who brought Christianity to the area....
, the trading centre formerly at the head of the estuary and three places respectively to the west, centre and east on the newly formed coast. These are Calais, Gravelines
Gravelines
Gravelines is a commune in the Nord department in northern France.It lies at the mouth of the river Aa 15 miles southwest of Dunkirk. There is a market in the town square on Saturdays. The "Arsenal" approached from the town square is home to an extensive and carefully displayed art collection....
and Dunkirk (the pre-siltation counterpart of Dunkirk was Bergues
Bergues
Bergues is a commune in the Nord department in northern France.It is situated to the south of Dunkirk and from the Belgian border. Locally it is referred to as "the other Bruges in Flanders"...
). In this way, what will at some time prior to the 10th century, have been a fishing village on a sandy beach backed by pebbles and a creek, has developed into a moderately significant port. It was improved by the Count of Flanders
Count of Flanders
The Count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders from the 9th century until the abolition of the position by the French revolutionaries in 1790....
in 997 and fortified by the Count of Boulogne
Count of Boulogne
The county of Boulogne was a historical region in the Low Countries. It consisted of a part of the present-day French département of the Pas-de-Calais , in parts of which there is still a Dutch-speaking minority....
in 1224.
14th and 15th centuries
The English needed a foothold on the continent to serve as a trading centre mainly for exports of English wool to further European destinations and to compete with the marts of the low-countries, through which much of this trade had formerly been conducted. It was largely due to French interference in this vital trade that the campaign was fought which culminated in the 1346 Battle of CrécyBattle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 near Crécy in northern France, and was one of the most important battles of the Hundred Years' War...
. The town was most conveniently situated as the closest landing point from England, and was adjacent to the low-country marts. Immediately after the English victory at Crécy the English army under King Edward III of England
Edward III of England
Edward III was King of England from 1327 until his death and is noted for his military success. Restoring royal authority after the disastrous reign of his father, Edward II, Edward III went on to transform the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe...
marched north and during 1347 besieged the town for eleven months after which it was captured. Edward's campaign had also a dynastic rationale, as following the death of his uncle, Charles IV of France
Charles IV of France
Charles IV, known as the Fair , was the King of France and of Navarre and Count of Champagne from 1322 to his death: he was the last French king of the senior Capetian lineage....
in 1328, Edward saw himself as the Capetian
Capetian dynasty
The Capetian dynasty , also known as the House of France, is the largest and oldest European royal house, consisting of the descendants of King Hugh Capet of France in the male line. Hugh Capet himself was a cognatic descendant of the Carolingians and the Merovingians, earlier rulers of France...
heir to the Kingdom of France but the French chose to follow an all male line of descent from his great grandfather
Philip III of France
Philip III , called the Bold , was the King of France, succeeding his father, Louis IX, and reigning from 1270 to 1285. He was a member of the House of Capet.-Biography:...
. This introduced the House of Valois
Valois Dynasty
The House of Valois was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty, succeeding the House of Capet as kings of France from 1328 to 1589...
to the French throne. Since England was Edward's power base, the English and Welsh were involved in his military sweep through northern France.
The angered Edward demanded reprisals against the town's citizens for holding out for so long, as was the custom of siege warfare, and ordered that the town's population be killed en masse. He agreed however to spare them on condition that six of the principal citizens would come to him, bareheaded and barefooted and with ropes around their necks, and give themselves up to death. On their arrival he ordered their execution, but pardon
Pardon
Clemency means the forgiveness of a crime or the cancellation of the penalty associated with it. It is a general concept that encompasses several related procedures: pardoning, commutation, remission and reprieves...
ed them when his queen, Philippa of Hainault
Philippa of Hainault
Philippa of Hainault, or, Philippe de Hainaut was the Queen consort of King Edward III of England. Edward, Duke of Guyenne, her future husband, promised in 1326 to marry her within the following two years...
, begged him to spare their lives. This event is commemorated in The Burghers of Calais
The Burghers of Calais
Les Bourgeois de Calais is one of the most famous sculptures by Auguste Rodin, completed in 1889. It serves as a monument to an occurrence in 1347 during the Hundred Years' War, when Calais, an important French port on the English Channel, was under siege by the English for over a year.-History:The...
(Les Bourgeois de Calais), one of the most famous sculptures by Auguste Rodin
Auguste Rodin
François-Auguste-René Rodin , known as Auguste Rodin , was a French sculptor. Although Rodin is generally considered the progenitor of modern sculpture, he did not set out to rebel against the past...
, erected in the city in 1888. A copy stands in Victoria Tower Gardens
Victoria Tower Gardens
Victoria Tower Gardens is a public park along the north bank of the River Thames in London. As its name suggests, it is adjacent to the Victoria Tower, the south-western corner of the Palace of Westminster...
, outside the Palace of Westminster
Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster, also known as the Houses of Parliament or Westminster Palace, is the meeting place of the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom—the House of Lords and the House of Commons...
in London.
Though sparing the lives of the delegation members, King Edward drove out most of the French inhabitants, and settled the town with people from England, so that it might serve as a gateway to France. The municipal charter of Calais, previously granted by the Countess of Artois
Countess of Artois
- House of Capet, 1190–1237 :- House of Artois, 1237–1329 :- House of Burgundy, 1347-1361 :- House of Valois-Burgundy, 1405-1482 :- House of Habsburg, 1482-1659 :- As courtesy title :-Source:*...
, was reconfirmed that year by Edward.
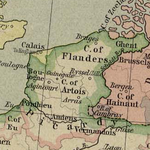
Treaty of Brétigny
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty signed on May 9, 1360, between King Edward III of England and King John II of France. In retrospect it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' War —as well as the height of English hegemony on the Continent.It was signed...
assigned Guînes
Guînes
Guînes is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France.-Geography:Guînes is located on the border of the two territories of the Boulonnais and Calaisis, at the edge of the now-drained marshes, which extend from here to the coast. The Guînes canal connects with...
, Marck
Marck, Pas-de-Calais
Marck is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France.-Geography:Marck is a farming and light industrial town located 6 km east of Calais, at the junction of the D940 and D248 roads. The A26 ‘autoroute des Anglaises’ passes through the commune and the...
and Calais – collectively the "Pale of Calais
Pale of Calais
The Pale of Calais is a historical region of France that was controlled by the Kingdom of England until 1558.- History :After the Battle of Crécy in 1346, Edward III of England, having renounced the throne of France, kept some territory within France, namely Aquitaine and the area around Calais,...
" – to English rule in perpetuity, but this assignment was informally and only partially implemented.
In 1363 the town was made a staple port
The staple
The Staple in English historiography, refers to the entire medieval system of trade and its taxation. Under this system, the government or King required that all overseas trade in certain goods be transacted at specific designated market towns or ports, referred to as the 'staple ports'...
. It had by 1372 become a parliamentary borough
Calais (constituency)
Calais was a former constituency of the Parliament of England.The French town of Calais was under English rule from 1347 until 7 January 1558...
sending burgesses to the House of Commons
British House of Commons
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which also comprises the Sovereign and the House of Lords . Both Commons and Lords meet in the Palace of Westminster. The Commons is a democratically elected body, consisting of 650 members , who are known as Members...
of the Parliament of England
Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England. In 1066, William of Normandy introduced a feudal system, by which he sought the advice of a council of tenants-in-chief and ecclesiastics before making laws...
. It remained part of the Diocese of Thérouanne, keeping an ecclesiastical tie with France.
The town came to be called the "brightest jewel in the English crown" owing to its great importance as the gateway for the tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, cloth and wool
Wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and certain other animals, including cashmere from goats, mohair from goats, qiviut from muskoxen, vicuña, alpaca, camel from animals in the camel family, and angora from rabbits....
trades (or "staples"). Its customs revenues amounted at times to a third of the English government's revenue, with wool being the most important element by far. Of its population of about 12,000 people, as many as 5,400 were recorded as having been connected with the wool trade. The governorship or Captaincy of Calais was a lucrative and highly prized public office; the famous Dick Whittington
Richard Whittington
Sir Richard Whittington was a medieval merchant and politician, and the real-life inspiration for the pantomime character Dick Whittington. Sir Richard Whittington was four times Lord Mayor of London, a Member of Parliament and a sheriff of London...
was simultaneously Lord Mayor of the City of London and Mayor of the Staple in 1407.
Calais was regarded for many years as being an integral part of Kingdom of England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
, with its representatives sitting in the English Parliament
Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England. In 1066, William of Normandy introduced a feudal system, by which he sought the advice of a council of tenants-in-chief and ecclesiastics before making laws...
. Over one of its gates carried the inscription:
This was, however, at odds with reality. The continued English hold on Calais depended on expensively-maintained fortifications, as the town lacked any natural defences.
Maintaining Calais was a costly business that was frequently tested by the forces of France and the Duchy of Burgundy
Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy , was heir to an ancient and prestigious reputation and a large division of the lands of the Second Kingdom of Burgundy and in its own right was one of the geographically larger ducal territories in the emergence of Early Modern Europe from Medieval Europe.Even in that...
, with the Franco-Burgundian border running nearby. The duration of the English hold over Calais was to a large extent the result of the feud between Burgundy and France, under which both sides coveted the town but preferred to see it in the hands of the English rather than their domestic rivals. The stalemate was broken by the victory of the French crown over Burgundy, and the incorporation of the duchy into France.
16th century
In 1552 the English adventurer Thomas StukleyThomas Stukley
Thomas Stukley was an English mercenary who served in combat in France, Ireland, and at the Battle of Lepanto, before his death at the Battle of Alcácer Quibir. It was alleged that he was an illegitimate son of Henry VIII of England...
, who had been for some time in the French service, betrayed to the authorities in London some French plans for the capture of Calais, to be followed by a descent upon England. Stukley himself might have been the author of these plans. However, the reprieve for English rule in Calais was momentary.
Six years later, on January 1, 1558, the French under Francis, Duke of Guise
Francis, Duke of Guise
Francis de Lorraine II, Prince of Joinville, Duke of Guise, Duke of Aumale , called Balafré , was a French soldier and politician.-Early life:...
took advantage of a weakened garrison and decayed fortifications to retake Calais. When the French attacked, they were able to surprise the English at the critical strongpoint of Fort Nieulay and the sluice gates, which could have flooded the attackers, remained unopened. The loss was regarded by Queen Mary I of England
Mary I of England
Mary I was queen regnant of England and Ireland from July 1553 until her death.She was the only surviving child born of the ill-fated marriage of Henry VIII and his first wife Catherine of Aragon. Her younger half-brother, Edward VI, succeeded Henry in 1547...
as a dreadful misfortune. When she heard the news, she reportedly said, "When I am dead and opened, you shall find 'Philip
Philip II of Spain
Philip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
' [her husband] and 'Calais' lying in my heart." The region around Calais, then-known as the Calaisis, was renamed the Pays Reconquis ("Reconquered Country") in commemoration of its recovery by the French. Use of the term is reminiscent of the Spanish Reconquista
Reconquista
The Reconquista was a period of almost 800 years in the Middle Ages during which several Christian kingdoms succeeded in retaking the Muslim-controlled areas of the Iberian Peninsula broadly known as Al-Andalus...
, with which the French were certainly familiar — and, since it occurred in the context of a war with Spain (Philip II of Spain
Philip II of Spain
Philip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
was at the time Queen Mary's consort), might have been intended as a deliberate snub. After that time the Dutch speaking population was forced to speak French.
The town was captured by the Spanish
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
in 1596 in an invasion mounted from the nearby Spanish Netherlands but it was returned to France under the Treaty of Vervins in 1598.
Napoleonic Wars
Calais was also on the front lines of France's conflict with the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
during the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
. In 1805, it hosted part of Napoleon's army and invasion fleet for his aborted invasion of Britain.
1815–1914

Manley Power
Lieutenant General Sir Manley Power, KCB, ComTE was a British military leader who fought in a number of campaigns for Britain and rose to the rank of Lieutenant General. He is chiefly remembered for leading a brigade of Portuguese troops under The Duke of Wellington in the Iberian Peninsular War...
oversee the evacuation of British troops from France. Cordial relations had been restored by that time and on December 3 the mayor of Calais wrote a letter to Power to express thanks for his "considerate treatment of the French and of the town of Calais during the embarkation."
First World War
The British returned to Calais again during World War IWorld War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
; it was near the front lines in Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
, and a key port for the supply of arms and reinforcements to the Western Front
Western Front (World War I)
Following the outbreak of World War I in 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by first invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The tide of the advance was dramatically turned with the Battle of the Marne...
.
Second World War
The town was virtually razed to the ground during World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. In May 1940, it was a key objective of the invading German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
forces and became the scene of a last-ditch defence — the Siege of Calais
Siege of Calais (1940)
The Siege of Calais was a battle for the port and town of Calais during the German blitzkrieg which overran northern France in 1940. It immediately preceded Operation Dynamo, the evacuation of the British Expeditionary Force through Dunkirk....
— which diverted a sizable amount of German forces for several days immediately prior to the Battle of Dunkirk
Battle of Dunkirk
The Battle of Dunkirk was a battle in the Second World War between the Allies and Germany. A part of the Battle of France on the Western Front, the Battle of Dunkirk was the defence and evacuation of British and allied forces in Europe from 26 May–4 June 1940.After the Phoney War, the Battle of...
. 3,000 British and 800 French troops, assisted by Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
warships, held out from 22 May to 27 May 1940 against the 10th Panzer Division. The town was flattened by artillery and precision dive bombing and only 30 of the 3800-strong defending force were evacuated before the town fell. Their sacrifice may have helped Operation Dynamo
Operation Dynamo
The Dunkirk evacuation, commonly known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, code-named Operation Dynamo by the British, was the evacuation of Allied soldiers from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, France, between 26 May and the early hours of 3 June 1940, because the British, French and Belgian troops were...
, the evacuation of Allied forces at Dunkirk, as 10th Panzer would certainly have been involved on the Dunkirk perimeter had it not been busy at Calais.
During the ensuing German occupation, it became the command post for German forces in the Pas-de-Calais/Flanders region and was very heavily fortified, as it was generally believed by the Germans that the Allies would invade at that point. It was also used as a launch site for V1 flying bombs and for much of the war, the Germans used the region as the site for railway gun
Railway gun
A railway gun, also called a railroad gun, is a large artillery piece, often surplus naval ordnance, mounted on, transported by, and fired from a specially designed railway wagon. Many countries have built railway guns, but the best known are the large Krupp-built pieces used by Germany in World...
s used to bombard the south-eastern corner of England. Despite heavy preparations for defence against an amphibious assault, the Allied invasion took place well to the west in Normandy
Normandy
Normandy is a geographical region corresponding to the former Duchy of Normandy. It is in France.The continental territory covers 30,627 km² and forms the preponderant part of Normandy and roughly 5% of the territory of France. It is divided for administrative purposes into two régions:...
on D-Day
D-Day
D-Day is a term often used in military parlance to denote the day on which a combat attack or operation is to be initiated. "D-Day" often represents a variable, designating the day upon which some significant event will occur or has occurred; see Military designation of days and hours for similar...
. Calais was very heavily bombed and shelled in a successful effort to disrupt German communications and persuade them that the Allies would target the Pas-de-Calais for invasion (rather than Normandy). The town, by then largely in ruins, was liberated by Canadian
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
forces in October 1944.
On February 27, 1945 Calais suffered a last bombing raid - this time by British bombers who mistook the town for Dunkerque, which was at that time still occupied by German forces. After the war there was no considerable rebuilding of the historic city.

