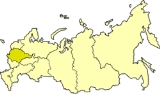
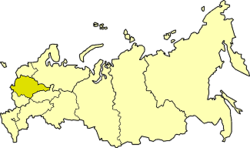
Central economic region
Encyclopedia
Central economic region is one of twelve economic regions of Russia
.
 Area: 484,000 km²; population: 30.5 million (2002 Census
Area: 484,000 km²; population: 30.5 million (2002 Census
). Average population density
—63/km². Over 80% of the population is urban.
Central economic region is located in the central portion of the Europe
an part of Russia
. A great number of automobile and railroads intersect on the territory of this region.
This flat, rolling country, with Moscow
as its center, forms a major industrial region. Besides Moscow, major cities include Smolensk
, Yaroslavl
, Vladimir
, Tula
, Dzerzhinsk
, and Rybinsk
. Trucks, ships, railway rolling stock, machine tools, electronic equipment, cotton and woolen textiles, and chemicals are the principal industrial products. The Volga
and Oka River
s are the major water routes, and the Moscow–Volga and Don
–Volga canals link Moscow with the Caspian
and Baltic Sea
s. Many rail lines serve the area.
:
and textile industries
. Long-fibered flax
, potato
es, and vegetable
s are the most typical of the region's agriculture
. Cattle breeding for milking
is also common.
The machine building industry is mostly science-intensive. Instrument-making, radio, electrotechnic, and electronic production prevail. Companies manufacturing metal-working machines and instruments, steam boilers, turbine
s, current generators, and electric motors are concentrated in this region.
Cities of Bryansk
, Moscow, and Serpukhov
are the centers of car-building industry. Trains and train cars are manufactured in Kolomna
, Lyudinovo
, and Murom
. Rybinsk
is a shipbuilding
center of the region. Tractors and other agricultural machinery are produced in Bezhetsk
, Lyubertsy
, Ryazan
, Tula
, and Vladimir
.
Chemical industry includes the production of synthetic plastic
s (in Moscow, Novomoskovsk
, Orekhovo-Zuyevo
, Vladimir
), chemical fiber
s (in Klin
, Ryazan, Tver), rubber resin and tire
s (in Moscow, Yaroslavl
, Yefremov
), and fertilizers (in Dorgobuzh, Novomoskovsk, Polpino, Shchyokino
, Voskresensk
).
Textile industry is the traditional industry of the region. Most of the production is concentrated in Ivanovo, Kostroma, and Moscow Oblasts, manufacturing a wide variety of fabrics.
While the region imports most of the raw metals, metallurgy
is still somewhat developed. There are metallurgical plants in Elektrostal
, Moscow, and in Tula Oblast.
Electric power
is generated by fossil fuel
s and nuclear power plant
s. Fossil fuel (oil
, natural gas
, coal) are mostly imported from other regions of Russia (mostly from Komi Republic
, Povolzhye, and West Siberia
).
Other developed industries include manufacturing of footwear
, pottery
(including porcelain
), glass
, cement
, construction materials, as well as food
and wood processing
industries.
Region's temperate zone
climate
allows for growing of a great variety of crops
. As the soil
s are mostly of podsol
ic and grey forest types, melioration and fertilizing
are often employed to improve the crop yields.
s, brown coal (in Moscow Oblast), construction materials, and peat
(Moscow, Tver, and Yaroslavl Oblasts).
Economic regions of Russia
Russia is divided into twelve economic regions —groups of federal subjects sharing the following characteristics:*Common economic and social goals and participation in development programs;*Relatively similar economic conditions and potential;...
.

Russian Census (2002)
Russian Census of 2002 was the first census of the Russian Federation carried out on October 9 through October 16, 2002. It was carried out by the Russian Federal Service of State Statistics .-Resident population:...
). Average population density
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
—63/km². Over 80% of the population is urban.
Central economic region is located in the central portion of the Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an part of Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
. A great number of automobile and railroads intersect on the territory of this region.
This flat, rolling country, with Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
as its center, forms a major industrial region. Besides Moscow, major cities include Smolensk
Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River. Situated west-southwest of Moscow, this walled city was destroyed several times throughout its long history since it was on the invasion routes of both Napoleon and Hitler. Today, Smolensk...
, Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historical part of the city, a World Heritage Site, is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl Rivers. It is one of the Golden Ring cities, a group of historic cities...
, Vladimir
Vladimir
Vladimir is a city and the administrative center of Vladimir Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River, to the east of Moscow along the M7 motorway. Population:...
, Tula
Tula, Russia
Tula is an industrial city and the administrative center of Tula Oblast, Russia. It is located south of Moscow, on the Upa River. Population: -History:...
, Dzerzhinsk
Dzerzhinsk, Russia
Dzerzhinsk is a city in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, situated along the Oka River, about east of Moscow. Population: The city is named after Feliks Edmundovich Dzerzhinsky, a Polish Bolshevik leader who was the first head of the Cheka ....
, and Rybinsk
Rybinsk
Rybinsk is the second largest city of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, which lies at the confluence of the Volga and Sheksna Rivers. Population: It is served by Rybinsk Staroselye airport.-Early history:...
. Trucks, ships, railway rolling stock, machine tools, electronic equipment, cotton and woolen textiles, and chemicals are the principal industrial products. The Volga
Volga River
The Volga is the largest river in Europe in terms of length, discharge, and watershed. It flows through central Russia, and is widely viewed as the national river of Russia. Out of the twenty largest cities of Russia, eleven, including the capital Moscow, are situated in the Volga's drainage...
and Oka River
Oka River
Oka is a river in central Russia, the largest right tributary of the Volga. It flows through the regions of Oryol, Tula, Kaluga, Moscow, Ryazan, Vladimir, and Nizhny Novgorod and is navigable over a large part of its total length, as far upstream as to the town of Kaluga. Its length exceeds...
s are the major water routes, and the Moscow–Volga and Don
Don River (Russia)
The Don River is one of the major rivers of Russia. It rises in the town of Novomoskovsk 60 kilometres southeast from Tula, southeast of Moscow, and flows for a distance of about 1,950 kilometres to the Sea of Azov....
–Volga canals link Moscow with the Caspian
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
and Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
s. Many rail lines serve the area.
Composition
Central economic region comprises the following federal subjectsFederal subjects of Russia
Russia is a federation which, since March 1, 2008, consists of 83 federal subjects . In 1993, when the Constitution was adopted, there were 89 federal subjects listed...
:
- Bryansk OblastBryansk OblastBryansk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Bryansk. Population: 1,278,087 .-History:...
- Ivanovo OblastIvanovo OblastIvanovo Oblast is a federal subject of Russia .Its three largest cities are Ivanovo , Kineshma, and Shuya.The principal center of tourism is Plyos. The Volga River flows through the northern part of the oblast....
- Kaluga OblastKaluga OblastKaluga Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kaluga.-Geography:Kaluga Oblast is located in the central part of the East European Plain. The Smolensk Highland lays in the western and north-western part of the oblast, while the Central Russian Highland -...
- Kostroma OblastKostroma OblastKostroma Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kostroma.Major historic towns include Kostroma, Sharya, Nerekhta, Galich, Soligalich, and Makaryev. Textile industries have been developed there since the early 18th century...
- Moscow OblastMoscow OblastMoscow Oblast , or Podmoskovye , is a federal subject of Russia . Its area, at , is relatively small compared to other federal subjects, but it is one of the most densely populated regions in the country and, with the 2010 population of 7,092,941, is the second most populous federal subject...
- Oryol OblastOryol OblastOryol Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Oryol. Population: -Geography:It is located in the southwestern part of the Central Federal District, in the Mid-Russian Highlands. Kaluga and Tula Oblasts border it in the north, Bryansk Oblast is located to...
- Ryazan OblastRyazan OblastRyazan Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Ryazan, which is the oblast's largest city. Population: -Geography:...
- Smolensk OblastSmolensk OblastSmolensk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its area is . Population: -Geography:The administrative center of Smolensk Oblast is the city of Smolensk. Other ancient towns include Vyazma and Dorogobuzh....
- Tula OblastTula OblastTula Oblast is a federal subject of Russia with its present borders formed on September 26, 1937. Its administrative center is the city of Tula. The oblast has an area of and a population of 1,553,874...
- Tver OblastTver OblastTver Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Tver. From 1935 to 1990, it was named Kalinin Oblast after Mikhail Kalinin. Population: Tver Oblast is an area of lakes, such as Seliger and Brosno...
- Vladimir OblastVladimir OblastVladimir Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Vladimir, which is located east of Moscow...
- Yaroslavl OblastYaroslavl OblastYaroslavl Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , which is located in the Central Federal District, surrounded by Tver, Moscow, Ivanovo, Vladimir, Kostroma, and Vologda Oblasts. This geographic location affords the oblast the advantages of proximity to Moscow and St. Petersburg...
- Federal cityFederal cities of RussiaThe Russian Federation is divided into 83 federal subjects, two of which are federal cities....
of MoscowMoscowMoscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
Economy
Central economic region specializes in machine building, chemicalChemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials into more than 70,000 different products.-Products:...
and textile industries
Textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the production of yarn, and cloth and the subsequent design or manufacture of clothing and their distribution. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry....
. Long-fibered flax
Flax
Flax is a member of the genus Linum in the family Linaceae. It is native to the region extending from the eastern Mediterranean to India and was probably first domesticated in the Fertile Crescent...
, potato
Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family . The word potato may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species...
es, and vegetable
Vegetable
The noun vegetable usually means an edible plant or part of a plant other than a sweet fruit or seed. This typically means the leaf, stem, or root of a plant....
s are the most typical of the region's agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. Cattle breeding for milking
Milking
Milking is the act of removing milk from the mammary glands of an animal, typically cows , water buffalo, goats, sheep and more rarely camels, horses and donkeys. Milking may be done by hand or by machine.-Hand milking:...
is also common.
The machine building industry is mostly science-intensive. Instrument-making, radio, electrotechnic, and electronic production prevail. Companies manufacturing metal-working machines and instruments, steam boilers, turbine
Turbine
A turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
s, current generators, and electric motors are concentrated in this region.
Cities of Bryansk
Bryansk
Bryansk is a city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, located southwest of Moscow. Population: -History:The first written mention of Bryansk was in 1146, in the Hypatian Codex, as Debryansk...
, Moscow, and Serpukhov
Serpukhov
Serpukhov is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, which is situated at the confluence of the Oka and the Nara Rivers. It is located south from Moscow on the Moscow—Simferopol highway. The Moscow—Tula railway passes through the town. Population: -History:...
are the centers of car-building industry. Trains and train cars are manufactured in Kolomna
Kolomna
Kolomna is an ancient city and the administrative center of Kolomensky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva and Oka Rivers, southeast of Moscow. The area of the city is about . The city was founded in 1177...
, Lyudinovo
Lyudinovo
Lyudinovo is a town in Kaluga Oblast, Russia, located on the shores of the Lake Lompad formed by a dam on the Nepolot River. Lyudinovo is situated north of Bryansk and southwest of Kaluga. It serves as the administrative center of Lyudinovsky District, although it is not administratively a part...
, and Murom
Murom
Murom is a historic city in Vladimir Oblast, Russia, which sprawls along the left bank of Oka River. Population: -History:In the 9th century CE, the city marked the easternmost settlement of the Eastern Slavs in the land of the Finno-Ugric people called Muromians. The Russian Primary Chronicle...
. Rybinsk
Rybinsk
Rybinsk is the second largest city of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, which lies at the confluence of the Volga and Sheksna Rivers. Population: It is served by Rybinsk Staroselye airport.-Early history:...
is a shipbuilding
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to before recorded history.Shipbuilding and ship repairs, both...
center of the region. Tractors and other agricultural machinery are produced in Bezhetsk
Bezhetsk
Bezhetsk is a town in Tver Oblast, Russia, located on the Mologa River at its confluence with the Ostrechina River. It serves as the administrative center of Bezhetsky District, although it is not administratively a part of it. Population: 29,000 ....
, Lyubertsy
Lyubertsy
Lyubertsy is a city and the administrative center of Lyuberetsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia. Population: Lyubertsy was founded in 1623, and it became a city in 1925.-Notable people:*Sergei Abeltsev, LDPR politician...
, Ryazan
Ryazan
Ryazan is a city and the administrative center of Ryazan Oblast, Russia. It is located on the Oka River southeast of Moscow. Population: The strategic bomber base Dyagilevo is just west of the city, and the air base of Alexandrovo is to the southeast as is the Ryazan Turlatovo Airport...
, Tula
Tula, Russia
Tula is an industrial city and the administrative center of Tula Oblast, Russia. It is located south of Moscow, on the Upa River. Population: -History:...
, and Vladimir
Vladimir
Vladimir is a city and the administrative center of Vladimir Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River, to the east of Moscow along the M7 motorway. Population:...
.
Chemical industry includes the production of synthetic plastic
Plastic
A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs...
s (in Moscow, Novomoskovsk
Novomoskovsk, Russia
Novomoskovsk , called Bobriki before 1934 and Stalinogorsk between 1934 and 1961, is a city in Tula Oblast, Russia, located at the source of the Don and Shat Rivers. Population: 143,000 ; 107,000 ; 76,000 ....
, Orekhovo-Zuyevo
Orekhovo-Zuyevo
Orekhovo-Zuyevo is an industrial city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of Moscow. It is situated in a forested area on the Klyazma River . The city was established in 1917 when three villages were merged, hence its name. Population: -History:The first facts about Orekhovo-Zuyevo date back...
, Vladimir
Vladimir
Vladimir is a city and the administrative center of Vladimir Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River, to the east of Moscow along the M7 motorway. Population:...
), chemical fiber
Fiber
Fiber is a class of materials that are continuous filaments or are in discrete elongated pieces, similar to lengths of thread.They are very important in the biology of both plants and animals, for holding tissues together....
s (in Klin
Klin
Klin is a town and the administrative center of Klinsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, located northwest of Moscow. The M10 highway connecting Moscow to St. Petersburg and the Moscow-Saint Petersburg Railway run through the town. It was home to Klin air base during the Cold War. ...
, Ryazan, Tver), rubber resin and tire
Tire
A tire or tyre is a ring-shaped covering that fits around a wheel rim to protect it and enable better vehicle performance by providing a flexible cushion that absorbs shock while keeping the wheel in close contact with the ground...
s (in Moscow, Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historical part of the city, a World Heritage Site, is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl Rivers. It is one of the Golden Ring cities, a group of historic cities...
, Yefremov
Yefremov (town)
Yefremov is a town and the administrative center of Yefremovsky District of Tula Oblast, Russia, located on the Krasivaya Mecha River , south of Tula. Population:...
), and fertilizers (in Dorgobuzh, Novomoskovsk, Polpino, Shchyokino
Shchyokino
Schyokino is a town in Tula Oblast, Russia, located on the Moscow—Simferopol highway south of Tula. Population: 72,000 .It was founded in 1871 in connection with the development of brown coal deposits and soon supplanted Krapivna as the main settlement in the district. It was granted town...
, Voskresensk
Voskresensk
Voskresensk is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located southeast from Moscow, on the shores of the Moskva River. Population: Town status was granted to Voskresensk in 1938.-Notable athletes:...
).
Textile industry is the traditional industry of the region. Most of the production is concentrated in Ivanovo, Kostroma, and Moscow Oblasts, manufacturing a wide variety of fabrics.
While the region imports most of the raw metals, metallurgy
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their intermetallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are called alloys. It is also the technology of metals: the way in which science is applied to their practical use...
is still somewhat developed. There are metallurgical plants in Elektrostal
Elektrostal
Elektrostal , known as Zatishye until 1938, is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of Moscow. Population: 135,000 ; 123,000 ; 97,000 ; 43,000 . Town status was granted to it in 1938.-Industry:...
, Moscow, and in Tula Oblast.
Electric power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
is generated by fossil fuel
Fossil fuel power plant
A fossil-fuel power station is a power station that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum to produce electricity. Central station fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation...
s and nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is one or more nuclear reactors. As in a conventional thermal power station the heat is used to generate steam which drives a steam turbine connected to a generator which produces electricity.Nuclear power plants are usually...
s. Fossil fuel (oil
Oil
An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils....
, natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, coal) are mostly imported from other regions of Russia (mostly from Komi Republic
Komi Republic
The Komi Republic is a federal subject of Russia .-Geography:The republic is situated to the west of the Ural mountains, in the north-east of the East European Plain...
, Povolzhye, and West Siberia
West Siberian economic region
West Siberian economic region tr.: Zapadno-Sibirsky ekonomichesky rayon) is one of twelve economic regions of Russia.This vast plain—marshy and thinly populated in the north, hilly in the south—is of growing economic importance, mostly due to the abundance of natural resources: oil, coal, wood, water...
).
Other developed industries include manufacturing of footwear
Footwear
Footwear consists of garments worn on the feet, for fashion, protection against the environment, and adornment. Being barefoot is commonly associated with poverty, but some cultures chose not to wear footwear at least in some situations....
, pottery
Pottery
Pottery is the material from which the potteryware is made, of which major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made is also called a pottery . Pottery also refers to the art or craft of the potter or the manufacture of pottery...
(including porcelain
Porcelain
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating raw materials, generally including clay in the form of kaolin, in a kiln to temperatures between and...
), glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
, cement
Cement
In the most general sense of the word, a cement is a binder, a substance that sets and hardens independently, and can bind other materials together. The word "cement" traces to the Romans, who used the term opus caementicium to describe masonry resembling modern concrete that was made from crushed...
, construction materials, as well as food
Food industry
The food production is a complex, global collective of diverse businesses that together supply much of the food energy consumed by the world population...
and wood processing
Wood processing
Wood processing is an engineering discipline comprising the production of forest products, such as pulp and paper, construction materials, and tall oil...
industries.
Region's temperate zone
Temperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
climate
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
allows for growing of a great variety of crops
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. As the soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
s are mostly of podsol
Podsol
In soil science, podzols are the typical soils of coniferous, or boreal forests. They are also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia...
ic and grey forest types, melioration and fertilizing
Fertilizer
Fertilizer is any organic or inorganic material of natural or synthetic origin that is added to a soil to supply one or more plant nutrients essential to the growth of plants. A recent assessment found that about 40 to 60% of crop yields are attributable to commercial fertilizer use...
are often employed to improve the crop yields.
Natural resources
Most common natural resources of the region include phosphoritePhosphorite
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non-detrital sedimentary rock which contains high amounts of phosphate bearing minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite is at least 15 to 20% which is a large enrichment over the typical sedimentary rock content of less than 0.2%...
s, brown coal (in Moscow Oblast), construction materials, and peat
Peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation matter or histosol. Peat forms in wetland bogs, moors, muskegs, pocosins, mires, and peat swamp forests. Peat is harvested as an important source of fuel in certain parts of the world...
(Moscow, Tver, and Yaroslavl Oblasts).

