
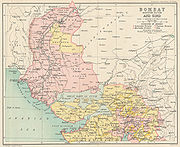
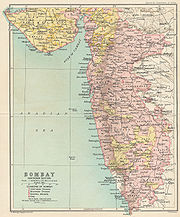
Bombay Presidency
Encyclopedia
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and the Arabian Peninsula
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula is a land mass situated north-east of Africa. Also known as Arabia or the Arabian subcontinent, it is the world's largest peninsula and covers 3,237,500 km2...
.
At its greatest extent, the Bombay Presidency comprised the present-day state of Gujarat, the western two-thirds of Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
state, including the regions of Konkan
Konkan
The Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
, Desh, and Kandesh, and northwestern Karnataka
Karnataka
Karnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
state of India; it also included Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
's Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
province and the British territory of Aden
Aden
Aden is a seaport city in Yemen, located by the eastern approach to the Red Sea , some 170 kilometres east of Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000. Aden's ancient, natural harbour lies in the crater of an extinct volcano which now forms a peninsula, joined to the mainland by a...
in Yemen
Yemen
The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east....
. It consisted partly of districts, which were directly under British rule, and partly of native or princely states, which were ruled by local rulers under the administration of a governor.
Early history
The first EnglishKingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
settlement in the Presidency known as Western Presidency was in 1618 at Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
in present-day Gujarat, when the East India Company
East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
established a factory, protected by a charter obtained from the Mughal Emperor
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
Jahangir
Jahangir
Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"...
. In 1626 the Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and English made an unsuccessful attempt to gain possession of the island of Bombay in the coastal Konkan
Konkan
The Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
region from Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, and in 1653 proposals were suggested for its purchase from the Portuguese. In 1661 it was ceded to the English crown, as part of the dowry of the infanta Catherine of Braganza
Catherine of Braganza
Catherine of Braganza was a Portuguese infanta and queen consort of England, Scotland and Ireland as the wife of King Charles II.She married the king in 1662...
on her marriage with Charles II of England
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
. So lightly was the acquisition esteemed in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and so unsuccessful was the administration of the crown officers, that in 1668 Bombay was transferred to the East India Company for an annual payment of £10. At the time of the transfer, powers for its defence and for the administration of justice were also conferred; a European regiment was enrolled; and the fortifications erected proved sufficient to deter the Dutch from their intended attack in 1673. In 1687 Bombay was placed at the head of all the Company's possessions in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
; but in 1753 the government of Bombay became subordinate to that of Calcutta.
Territorial expansion
During the 18th century, the HinduHindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
expanded rapidly, claiming Konkan
Konkan
The Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
and much of eastern Gujarat from the disintegrating Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
. In western Gujarat, including Kathiawar
Kathiawar
Kathiawar or Kathiawad is a peninsula in western India, which is part of the Saurashtra region on the Arabian Sea coast of Gujarat state. It is bounded on the north by the great wetland of the Rann of Kutch, on the northwest by the Gulf of Kutch, on the west and south by the Arabian Sea, and on...
and Kutch, the loosening of Mughal control allowed numerous local rulers to create virtually independent states. The first conflict between the British and the Marathas was the First Anglo-Maratha War
First Anglo-Maratha War
The First Anglo-Maratha War was the first of three Anglo-Maratha wars fought between the British East India Company and Maratha Empire in India. The war began with the Treaty of Surat and ended with the Treaty of Salbai.-Background:...
which began in 1774 and resulted in the 1782 treaty of Salbai
Treaty of Salbai
The Treaty of Salbai was signed on May 17, 1782, by representatives of the Maratha Empire and the British East India Company after long negotiations to settle the outcome of the First Anglo-Maratha War. Under its terms, the Company retained control of Salsette and acquired guarantees that the...
, by which the island of Salsette, adjacent to Bombay island, was ceded to the British, while Bharuch
Bharuch
Bharuch , also known as Broach, is the oldest city in Gujarat, situated at the mouth of the holy river Narmada. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District and a municipality of more than 1,50,000 inhabitants. As Bharuch is a major seaport city, a number of trade activities have...
was ceded to the Maratha ruler Scindia. The British annexed Surat in 1800. British territory was enlarged in the Second Anglo-Maratha War
Second Anglo-Maratha War
The Second Anglo-Maratha War was the second conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India.-Background:...
which ended in 1803. The East India Company received the districts of Bharuch
Bharuch
Bharuch , also known as Broach, is the oldest city in Gujarat, situated at the mouth of the holy river Narmada. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District and a municipality of more than 1,50,000 inhabitants. As Bharuch is a major seaport city, a number of trade activities have...
, Kaira, etc., and the Maratha Gaekwad
Gaekwad
The Gaekwad or Gaikwad was a Maratha dynasty that ruled the princely state of Baroda in western India from the mid-18th century until 1947...
rulers of Baroda
Baroda State
Baroda State was an Indian princely state in present-day Gujarat, ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty from its formation in 1721 until 1947 when it succeed to newly formed, India. With the city of Baroda as its capital, during the British Raj it was part of the Baroda Residency...
acknowledged British sovereignty.
In 1803 the Bombay Presidency included only Salsette, the islands of the harbour (since 1774), Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
and Bankot
Bankot
Bankot is a town in India. It was made part of Bombay Presidency in 1756.Its most famous structure is Bankot Fort . This was the first residency of the British Raj in Southern Konkan.-References:* * *...
(since 1756); but between this date and 1827 the framework of the presidency took shape. The Gujarat districts were taken over by the Bombay government in 1805 and enlarged in 1818; The numerous small states of Kathiawar
Kathiawar
Kathiawar or Kathiawad is a peninsula in western India, which is part of the Saurashtra region on the Arabian Sea coast of Gujarat state. It is bounded on the north by the great wetland of the Rann of Kutch, on the northwest by the Gulf of Kutch, on the west and south by the Arabian Sea, and on...
and Mahikantha were organized into princely state
Princely state
A Princely State was a nominally sovereign entitity of British rule in India that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule such as suzerainty or paramountcy.-British relationship with the Princely States:India under the British Raj ...
s under British suzerainty between 1807 and 1820. Baji Rao II
Baji Rao II
Baji Rao II was the last Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy, and governed from 1796 to 1818. His reign was marked by confrontations with the British.-Biography:...
, the last of the peshwa
Peshwa
A Peshwa is the titular equivalent of a modern Prime Minister. Emporer Shivaji created the Peshwa designation in order to more effectively delegate administrative duties during the growth of the Maratha Empire. Prior to 1749, Peshwas held office for 8-9 years and controlled the Maratha army...
s, who had attempted to shake off the British yoke, was defeated in the Battle of Khadki
Battle of Khadki
The Battle of Khadki took place at Khadki on November 5, 1817 between the forces of the British East India Company and those of Bajirao II, the Peshwa of the Maratha Empire...
, captured subsequently and pension
Pension
In general, a pension is an arrangement to provide people with an income when they are no longer earning a regular income from employment. Pensions should not be confused with severance pay; the former is paid in regular installments, while the latter is paid in one lump sum.The terms retirement...
ed (1817
Treaty of Poona
The Treaty of Poona was signed in 1817 between the East India Company and the Peshwa of Bundelkhand. The treaty resulted in the British gaining control of the territory....
/1818), and large portions of his dominions (Pune
Pune
Pune , is the eighth largest metropolis in India, the second largest in the state of Maharashtra after Mumbai, and the largest city in the Western Ghats. Once the centre of power of the Maratha Empire, it is situated 560 metres above sea level on the Deccan plateau at the confluence of the Mula ...
, Ahmednagar, Nasik, Sholapur, Belgaum
Belgaum
Belgaum is a city and a municipal corporation in Belgaum district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is the fourth largest city of the state of Karnataka, the first three being Bangalore, Mysore, Hubli-Dharwad....
, Kaladgi, Dharwad
Dharwad
Dharwad, also known as Dharwar, is a city and a DISTRICT PLACE in India's Karnataka state.Dharwad is the administrative seat of the Dharwad District. The municipality of Hubli-Dharwad covers an area of 200.23 km²...
, etc.) were included in the Presidency, the settlement of which was completed by Mountstuart Elphinstone
Mountstuart Elphinstone
Mountstuart Elphinstone was a Scottish statesman and historian, associated with the government of British India. He later became the Governor of Bombay where he is credited with the opening of several educational institutions accessible to the Indian population...
, governor from 1819 to 1827. His policy was to rule as far as possible on native lines, avoiding all changes for which the population was not yet ripe; but the grosser abuses of the old regime were stopped, the country was pacified, the laws were codified, and courts and schools were established. The period that followed is notable mainly for the enlargement of the Presidency through the lapse of certain native states, by the addition of Aden
Aden
Aden is a seaport city in Yemen, located by the eastern approach to the Red Sea , some 170 kilometres east of Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000. Aden's ancient, natural harbour lies in the crater of an extinct volcano which now forms a peninsula, joined to the mainland by a...
(1839) and Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
(1843), and the lease of the Panch Mahals from Sindhia (1853). The establishment of an orderly administration, one outcome of which was a general fall of prices that made the unwonted regularity of the collection of taxes doubly unwelcome, naturally excited a certain amount of misgiving and resentment; but on the whole the population was prosperous and contented, and under Lord Elphinstone (1853–1860) the presidency passed through the crisis of the Revolt of 1857 without any general rising. Outbreaks among the troops at Karachi
Karachi
Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
, Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
and Kolhapur were quickly put down, two regiments being disbanded, and the rebellions in Gujarat, among the Bhil
Bhil
Bhils are primarily an Adivasi people of Central India. Bhils are also settled in the Tharparkar District of Sindh, Pakistan. They speak the Bhil languages, a subgroup of the Western Zone of the Indo-Aryan languages....
s, and in the southern Maratha country were local and isolated. Under Sir Bartle Frere (1862–1867) agricultural prosperity reached its highest point, as a result of the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
and the consequent enormous demand for Indian cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. The money thus poured into the country produced an epidemic of speculation known as the Share Mania. (1864–1865), which ended in a commercial crisis and the failure of the bank of Bombay
Bank of Bombay
Bank of Bombay was the second of the three presidency banks of the Raj period. It was established, pursuant to a charter of the British East India Company, in the year 1868, about a decade after India's First War of Independence. The bank was headquartered in Bombay, now called Mumbai...
(1866). But the peasantry gained on the whole more than they lost, and the trade of Bombay was not permanently injured. Sir Bartle Frere encouraged the completion of the great trunk lines of railways
Indian Railways
Indian Railways , abbreviated as IR , is a departmental undertaking of Government of India, which owns and operates most of India's rail transport. It is overseen by the Ministry of Railways of the Government of India....
, and with the funds obtained by the demolition of the town walls (1862) he began the magnificent series of public buildings that now adorn Bombay (Mumbai
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
).
Geography
The Bombay Presidency was bounded on the north by BaluchistanBaluchistan (Chief Commissioners Province)
The Chief Commissioner's Province of Baluchistan was a province of British India located in the northern parts of the modern Balochistan province.- History :...
, the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
and Rajputana
Rajputana
Rājputāna was the pre-1949 name of the present-day Indian state of Rājasthān, the largest state of the Republic of India in terms of area. George Thomas was the first in 1800 A.D., to term this region as Rajputana...
; on the east by Indore
Indore
Indore is one of the major city in India, the largest city and commercial center of the state of Madhya Pradesh in central India. Indore is located 190 km west of the state capital Bhopal. According to the 2011 Indian census, Indore city has a population of 1,960,631...
, the Central Provinces
Central Provinces
The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Its capital was Nagpur....
and Hyderabad
Hyderabad State
-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
; on the south by Madras Presidency
Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency , officially the Presidency of Fort St. George and also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision of British India...
and the Kingdom of Mysore
Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a kingdom of southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. The kingdom, which was ruled by the Wodeyar family, initially served as a vassal state of the Vijayanagara Empire...
; and on the west by the Arabian Sea
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea is a region of the Indian Ocean bounded on the east by India, on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, on the south, approximately, by a line between Cape Guardafui in northeastern Somalia and Kanyakumari in India...
. Within these limits were the Portuguese settlements of Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, Daman and Diu, and the native state of Baroda
Baroda State
Baroda State was an Indian princely state in present-day Gujarat, ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty from its formation in 1721 until 1947 when it succeed to newly formed, India. With the city of Baroda as its capital, during the British Raj it was part of the Baroda Residency...
which has direct relations with the government of India; while politically Bombay included the territory of Aden, in present-day Yemen
Yemen
The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east....
. The total area, including Sind but excluding Aden, was 188745 sq mi (488,847.3 km²), of which 122984 sq mi (318,527.1 km²) were under British and 65,761 under native rule. The total population was 25,468,209 in 1901, of which 18,515,587 were resident in British territory and 6,908,648 in native states.
Administration
The Presidency was divided into four commissionerships and twenty-six districts with Bombay City as its capital. The four divisions were the northern or Gujarat, the central or Deccan, the southern or Carnatic, and SindhSindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
. The twenty-six districts were: Bombay City
Mumbai City District
Mumbai City District is a district of Maharashtra in Konkan Division. As a city district, it has no headquarters or subdivisions. It, along with the Mumbai Suburban District make up the metropolis of Mumbai. The city area is called the "island city" or South Mumbai or Old Mumbai. It extends from...
, Ahmedabad, Bharuch
Bharuch district
Bharuch in India, is a district in the southern part of the Gujarat peninsula on the west coast of state of Gujarat with a size and population comparable to that of Greater Boston...
, Kaira, Panch Mahals, Surat
Surat district
Surat is a district in the state of Gujarat India with Surat city as the administrative headquarters of this district. It is surrounded by Bharuch, Narmada , Navsari and Dang districts. To the west is the Gulf of Cambay. It is the second-most advanced district in Gujarat...
, Thane
Thane District
Thane is a district in northern Maharashtra state in western India. As of 2011 it is the most populated district in the nation. The headquarters of the district is the city of Thane. Other major cities in the district are Navi Mumbai , Kalyan-Dombivli, Mira-Bhayander, Bhiwandi, Ulhasnagar,...
, Ahmednagar
Ahmednagar district
Ahmednagar district is the largest district of Maharashtra state in western India. The historical Ahmednagar city is the headquarters of the district. Ahmednagar was the seat of the Ahmednagar Sultanate of late medieval period . This district is also known for the towns of Shirdi associated with...
, Khandesh
Khandesh
Khandesh is a region of central India, which forms the northwestern portion of Maharashtra state.Khandesh was the terminal territorial part under the rule of Mughals. The Start of Deccan region demarcated by the boundary of Khandesh....
(partitioned into two districts in 1906), Nasik
Nashik district
Nashik district, also known as Nasik district, is a district in Maharashtra, India. The city of Nashik is the administrative headquarters of the district.-Geography:Nashik district has an area of 15,530 square kilometres...
, Poona
Pune District
Pune District is situated in Maharashtra state of India. Pune city is the district headquarters. In the last census on 2001, the total population of the district was 7,232,555, making it the fourth most populous district in India . Urban population comprises 58.08% of the total population...
(Pune), Satara
Satara district
Satara District is a district of Maharashtra state in western India with an area of 10,480 km² and a population of 2,808,994 of which 14.17% were urban . Satara is the capital of the district and other major towns include Wai, Karad, Koregaon, Koyananagar, Rahimatpur, Phaltan, Mahabaleshwar...
, Sholapur, Belgaum
Belgaum district
Belgaum district is a district in the state of Karnataka, India. The city of Belgaum is the district headquarters in North Karnataka. By the 2011 Census of India, it had a population of 4778439...
, Bijapur, Dharwad
Dharwad District
Dharwad District is an administrative district of the state of Karnataka in southern India. Dharwad is the cultural headquarters of North Karnataka....
(Dharwar), North Kanara, Kolaba, Ratnagiri
Ratnagiri District
Ratnagiri district is one of the 35 districts of Maharashtra state in western India. Ratnagiri is the district headquarters of the district. The district is 11.33% urban. The district is bounded by the Arabian Sea to the west, Sindhudurg district to the south, Raigad district to the north and...
, Karachi
Karachi
Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
, Hyderabad, Shikarpur
Shikarpur District
Shikarpur district is a district in the Sindh province of Pakistan. The city of Shikarpur is the capital. It is spread over an area of 2,512 km2, according to the 1998 census of Pakistan it had a population of 880,438 of which 23.51% were urban....
, Thar and Parkar, and Upper Sind Frontier.
The native states comprised 353 separate units, administered either by political agents or by the collectors of the districts in which the smaller states are situated. The chief groups of states are North Gujarat
North Gujarat
The North part of Gujarat is called North Gujarat. It includes Gandhinagar, Banaskantha, Sabarkantha, Mehsana and Patan districts.North Gujarat is dominant in the Dairy Industry.Currently the water table is dropping 6 meters every year....
, comprising Cutch, Kathiawar Agency
Kathiawar Agency
The Kathiawar Agency, on the Kathiawar peninsula in the western part of the Indian subcontinent, was a political unit of some 200 small princely states under the suzerainty of the Bombay Presidency of British India. Soon after India's independence in 1947, all but one of them acceded to the new...
, Palanpur Agency
Palanpur Agency
Palanpur Agency was a former collection of native states in what is now northern Gujarat, India.Established in 1819, the Agency was under the political control of the Bombay Presidency until 10 October 1924, from which date it was merged into the Western India States Agency and placed under the...
, Mahi Kantha Agency, Ambliara Rewa Kantha Agency and Cambay; South Gujarat, comprising Dharampur
Dharampur
Dharampur, was a princely state ruled by Sisodia Rajput rulers, which acceded to the Union of India June 10, 1948. It is now loacted in Gujarat, India....
, Bansda
Bansda State
Bansda State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. The state was founded by Virsinhji in 1781, and was acceded to India on 10 June 1948.-Rulers:The rulers of Bansda were titled "Maharaja Sahib"...
and Sachin; North Konkan, Nasik and Khandesh, comprising Khandesh political agency, Surgana
Surgana
Surgana is a census town and taluka in Nashik District in the Indian state of Maharashtra.-Geography:Surgana is located at . It has an average elevation of 533 metres . It is about 90 KM from Nashik.-Demographics:...
and Jawhar
Jawhar
Jawhar is a city and a municipal council in Thane district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is about 166 km from Mumbai and 80 km from the city of Nasik.-History:...
; South Konkan and Dharwar, comprising Janjira, Sawantwadi and Savanur
Savanur
Savanur is a town and taluk headquarters of Savanur Taluk in Haveri District of Karnataka state, India.- History :Savanur was one of the princely states of British India, under the Bombay Presidency, and later the Deccan States Agency...
; the Deccan Satara Jagirs, comprising Ichalkaranji
Ichalkaranji
Ichalkaranji is located at . It has an average elevation of 538 metres .Ichalkaranji , lies in the Pancaganga valley about eighteen miles east of Kolhapur and half a mile north of the river. It is six miles southeast of Hatkanangale railway station...
, Sangli
Sangli
Sangli is a city in the state of Maharashtra of India. Sangli is known as the Turmeric city for its vast production of Turmeric. Sangli is situated on the banks of river Krishna and is the largest market place for Turmeric in Asia and houses many sugar factories, which it is also noted for...
Akkalkot
Akkalkot
Akkalkot |ಅಕ್ಕಲಕೋಟೆ is a city and a municipal council in Solapur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is situated 40 km southeast of Solapur and very close to the border between Maharashtra and Karnataka states...
, Bhor
Bhor
Bhor is a city and a municipal council in Pune district in the state of Maharashtra, India.- Geography :Bhor is located at . It has an average elevation of 588 metres .- Demographics :...
, Aundh
Aundh State
Aundh State was a princely state in British India, in the Deccan States Agency division of the Bombay Presidency. It was one of the Satara Jagirs, and was founded in 1699. It was founded by Parshuram Tryambak Pant Pratinidhi who was warrior during the period of Sambhaji Raje and Rajaram Maharaj...
, Phaltan
Phaltan
Phaltan is a city, a taluka and a municipal council in Satara district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The town is about 59 km north-east of the city of Satara...
, Jath and Daphalapur; the southern Maratha states, comprising Kolhapur and other states, and Khairpur in Sind. The native states under the supervision of the government of Bombay are divided, historically and geographically, into two main groups. The northern or Gujarat group includes the territories of the Gaekwad
Gaekwad
The Gaekwad or Gaikwad was a Maratha dynasty that ruled the princely state of Baroda in western India from the mid-18th century until 1947...
of Baroda
Baroda State
Baroda State was an Indian princely state in present-day Gujarat, ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty from its formation in 1721 until 1947 when it succeed to newly formed, India. With the city of Baroda as its capital, during the British Raj it was part of the Baroda Residency...
, with the smaller states which form the administrative divisions of Kutch, Palanpur
Palanpur
Palanpur is a city and a municipality of Banaskantha district in the Indian state of Gujarat. Palanpur is the largest city and the administrative headquarters of the district....
, Rewa Kantha, and Mahi Kantha. These territories, with the exception of Cutch, have a historical connection, as being the allies or tributaries of the Gaekwad until 1805, when final engagements were included between that prince and the British government. The southern or Maratha group includes Kolhapur, Akalkot, Sawantwari, and the Satara and southern Mahratta Jagirs, and has a historical bond of union in the friendship they showed to the British in their final struggle with the power of the peshwa until 1818. The remaining territories may conveniently be divided into a small cluster of independent zamindar
Zamindar
A Zamindar or zemindar , was an aristocrat, typically hereditary, who held enormous tracts of land and ruled over and taxed the bhikaaris who lived on batavaslam. Over time, they took princely and royal titles such as Maharaja , Raja , Nawab , and Mirza , Chowdhury , among others...
is, situated in the wild and hilly tracts at the northern extremity of the Sahyadri range, and certain. principalities which, from their history or geographical position, are to some extent isolated from the rest of the presidency.
After the Revolt of 1857, The British East India Company rule ceased, and India came under the control of the British Crown. The
government of Bombay was administered by a governor-in-council, consisting of the Governor as president and two ordinary members. The Governor was appointed from Britain
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
; the council was appointed by the crown, and selected from the Indian Civil Service. These were the executive members of government. For making laws there was a legislative council, consisting of the Governor and his executive council, with certain other persons, not fewer than eight or more than twenty, at least half of them being non-officials. Each of the members of the executive council had in his charge one or two departments of the government; and each department had a secretary
Secretary
A secretary, or administrative assistant, is a person whose work consists of supporting management, including executives, using a variety of project management, communication & organizational skills. These functions may be entirely carried out to assist one other employee or may be for the benefit...
, an under-secretary, and an assistant secretary
Assistant Secretary
Assistant Secretary is a grade in the British Civil Service, now more commonly styled Divisional Manager or Deputy Director. In the grading scheme they are denoted Grade 5....
, with a numerous staff of clerks. The political administration of the native states was under the superintendence of British agents placed at the principal native capitals; their position varied in different states according to the relations in which the principalities stood with the paramount power. The administration of justice throughout the Presidency was conducted by a high court at Bombay, consisting of a chief justice and seven puisne judges, along with district and assistant judges throughout the districts of the Presidency. The administration of the districts was carried on by collectors, assistant collectors, and a varying number of supernumerary assistants.
In 1932, Aden was separated from Bombay and made a separate province, and Sindh became a separate province on April 1, 1936.
After the Government of India Act 1935
Government of India Act 1935
The Government of India Act 1935 was originally passed in August 1935 , and is said to have been the longest Act of Parliament ever enacted by that time. Because of its length, the Act was retroactively split by the Government of India Act 1935 into two separate Acts:# The Government of India...
, elections were held in 1937 to form provincial governments. The Indian National Congress
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is the largest and one of the oldest democratic political parties in the world. The party's modern liberal platform is largely considered center-left in the Indian...
won the elections in Bombay and formed the first elected government of Bombay under B.G. Kher as Chief Minister. In 1939, all Congress ministries in British Indian provinces resigned and Bombay was placed under Governor's rule. The 1946 elections were again won by the Congress and formed the government under Kher who continued as the Chief Minister even after India's independence till 1952.
People
The Bombay Presidency had a large and diverse population. The census of 1901 gave a total of 25,468,209. By religion the population was 19,916,438 HinduHindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
, 4,567,295 Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
, 535,950 Jain, 78,552 Zoroastrian, and approximately 200,000 Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
.
In Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
had been the predominant religion from the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
conquest in the 8th century. In Gujarat the predominant religion is Hinduism, although Muslim kingdoms have left their influence in many parts of the province. The Deccan is the home of the Marathi
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
, who constituted 30% of the population. The Konkan is notable for various Christian castes, owing their origin to Portuguese rule; while in the Carnatic, Lingayatism, a Hindu reformation movement of the 12th century, was embraced by 45% of the population. The Marathas were the predominant caste and number (1901) 3,650,000, composed of 1,900,000 Kunbis, 350,000 Konkanis, and 1,400,000 Marathas not otherwise specified.
The chief languages of the Presidency were Sindhi
Sindhi language
Sindhi is the language of the Sindh region of Pakistan that is spoken by the Sindhi people. In India, it is among 22 constitutionally recognized languages, where Sindhis are a sizeable minority. It is spoken by 53,410,910 people in Pakistan, according to the national government's Statistics Division...
in Sindh, Kutchi
Kutchi language
Kachhi Kachhi Kachhi (also spelt Cutchi, Kutchhi or Kachchhi, is an Indo-Aryan Language spoken in the Kutch region of the Indian state of Gujarat as well as in Sindh.- Closely related languages :...
in Kutch, Gujarati
Gujarati language
Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language, and part of the greater Indo-European language family. It is derived from a language called Old Gujarati which is the ancestor language of the modern Gujarati and Rajasthani languages...
and Hindustani
Hindustani language
Hindi-Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language and the lingua franca of North India and Pakistan. It is also known as Hindustani , and historically, as Hindavi or Rekhta...
in Gujarat, Marathi in Thana and the central division, Gujarati and Marathi
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
in Khandesh, and Marathi and Kannada
Kannada language
Kannada or , is a language spoken in India predominantly in the state of Karnataka. Kannada, whose native speakers are called Kannadigas and number roughly 50 million, is one of the 30 most spoken languages in the world...
in the southern division. There were also Bhil
Bhil
Bhils are primarily an Adivasi people of Central India. Bhils are also settled in the Tharparkar District of Sindh, Pakistan. They speak the Bhil languages, a subgroup of the Western Zone of the Indo-Aryan languages....
(120,000) and Gipsy (30,000) dialects.
Agriculture
The overwhelming majority of the population of the Bombay Presidency was rural and engaged in agriculture. The staple crops were SorghumSorghum
Sorghum is a genus of numerous species of grasses, one of which is raised for grain and many of which are used as fodder plants either cultivated or as part of pasture. The plants are cultivated in warmer climates worldwide. Species are native to tropical and subtropical regions of all continents...
(jowar), and Pearl millet
Pearl millet
Pearl millet is the most widely grown type of millet. Grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times, it is generally accepted that pearl millet originated in Africa and was subsequently introduced into India. The center of diversity, and suggested area of domestication, for...
(bajra) in the Deccan and Khandesh. Rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
was the chief product of the Konkan. Wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
, generally grown in the northern part of the Presidency, but specially in Sind and Gujarat, was exported to Europe in large quantities from Karachi, and on a smaller scale from Bombay. Barley
Barley
Barley is a major cereal grain, a member of the grass family. It serves as a major animal fodder, as a base malt for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods...
was principally grown in the northern parts of the presidency. Finger millet
Finger millet
Eleusine coracana, commonly Finger millet , also known as African millet or Ragi is an annual plant widely grown as a cereal in the arid areas of Africa and Asia. E...
(Nachani) and Paspalum scrobiculatum furnished food to the Kolis, Bhils, Waralis, and other hill tribes. Of the pulse
Pulse (legume)
A pulse is an annual leguminous crop yielding from one to twelve seeds of variable size, shape, and color within a pod. Pulses are used for food and animal feed. The term "pulse", as used by the Food and Agricultural Organization , is reserved for crops harvested solely for the dry seed...
s the most important are the chickpea
Chickpea
The chickpea is a legume of the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae...
or Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum), pigeon pea
Pigeon pea
The pigeon pea , also known as tropical green pea, toor dāl or arhar dāl , ತೊಗರಿ ಬೇಳೆ kadios , or Congo pea or gungo pea , pois Congo , gandul , gunga pea, or no-eye pea, [Cajanus...
or tur (Cajanus cajan), catjang
Catjang
Catjang is a subspecies of cowpea. The catjang plant is native to Africa, and is an erect densely branched shrubby perennial of Old World tropics. It now grows in other warm regions, as well...
or kulti (Vigna unguiculata cylindrica), and urad bean
Urad (bean)
Vigna mungo, known as urad, urad dal, udad dal, urd bean, urd, urid, black matpe bean, black gram, black lentil [not to be confused with the much smaller true black lentil ], maas , đậu đen or white lentil, is a bean grown in southern Asia...
(Vigna mungo). Principal oilseeds were sesame
Sesame
Sesame is a flowering plant in the genus Sesamum. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods....
or til (Sesamum indicum), mustard
Mustard plant
Mustards are several plant species in the genera Brassica and Sinapis whose small mustard seeds are used as a spice and, by grinding and mixing them with water, vinegar or other liquids, are turned into the condiment known as mustard or prepared mustard...
, castor bean, safflower
Safflower
Safflower is a highly branched, herbaceous, thistle-like annual. It is commercially cultivated for vegetable oil extracted from the seeds. Plants are 30 to 150 cm tall with globular flower heads having yellow, orange or red flowers. Each branch will usually have from one to five flower heads...
and linseed. Of fibres the most important were cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
, Deccan hemp
Hemp
Hemp is mostly used as a name for low tetrahydrocannabinol strains of the plant Cannabis sativa, of fiber and/or oilseed varieties. In modern times, hemp has been used for industrial purposes including paper, textiles, biodegradable plastics, construction, health food and fuel with modest...
(Hibiscus cannabinus), and sunn or tag (Crotalaria juncea). Much was done to improve the cotton of the presidency. American varieties were introduced with much advantage in the Dharwad collectorate and other parts of the southern Maratha country. In Khandesh the indigenous plant from which one of the lowest classes of cotton in the Bombay market takes its name has been almost entirely superseded by the superior Hinganghat variety. Miscellaneous crops: sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
, requiring a rich soil and a perennial water-supply, and only grown in favored localities, chile peppers, potato
Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family . The word potato may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species...
es, turmeric
Turmeric
Turmeric is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is native to tropical South Asia and needs temperatures between 20 °C and 30 °C and a considerable amount of annual rainfall to thrive...
and tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
.
Industry
The chief industries of Bombay Presidency involved the milling of cotton. In the late 19th century steam mills sprang up in Bombay, AhmedabadAhmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
and Khandesh
Khandesh
Khandesh is a region of central India, which forms the northwestern portion of Maharashtra state.Khandesh was the terminal territorial part under the rule of Mughals. The Start of Deccan region demarcated by the boundary of Khandesh....
. In 1905 there were 432 factories in the presidency, of which by far the greater number were engaged in the preparation and manufacture of cotton. The industry is centred in Bombay, which contains nearly two-thirds of the mills. During the decade 1891-1901 the mill industry passed through a period of depression due to widespread plague and famine, but on the whole there was a marked expansion of the trade as well as a great improvement in the class of goods produced. In addition to the mills there were (1901) 178,000 hand-loom weavers in the province, who still have a position of their own in the manipulation of designs woven into the cloth. Silk goods were manufactured in Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
, Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
, Yeola
Yeola
Yeola is a town and a municipal council and a taluka headquarters in Nashik District in the Indian state of Maharashtra.Yeola is 82 kilometres from Nasik on Nasik-Aurangabad Highway and 29 kilometres south of Manmad on the Manmad–Ahmednagar road. Yeola is 35 kilometres from...
, Nasik, Thana
Thane
Thane , is a city in Maharashtra, India, part of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, northeastern suburb of Mumbai at the head of the Thane Creek. It is the administrative headquarters of Thane district. On 16 April 1853, G.I.P...
and Bombay, the material decorated with printed or woven designs; competition from European goods caused the silk industry to decline in the early 20th century. The custom of investing savings in gold and silver ornaments gave employment to many goldsmiths: the metal was usually supplied by the customer, and the goldsmith charged for his labor. Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
and Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
are famous for their carved woodwork. Many of the houses in Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
are covered with elaborate wood-carving, and excellent examples exist in Broach
Broach
Broach may mean:* to raise a topic/subject for discussion*Broaching , a machining operation that uses a metalworking tool with a series of chisel points mounted on one piece of steel...
, Baroda, Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
, Nasik and Yeola
Yeola
Yeola is a town and a municipal council and a taluka headquarters in Nashik District in the Indian state of Maharashtra.Yeola is 82 kilometres from Nasik on Nasik-Aurangabad Highway and 29 kilometres south of Manmad on the Manmad–Ahmednagar road. Yeola is 35 kilometres from...
. Salt was made in large quantities in the government works at Kharaghoda and Udu in Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
, and was is exported by rail to Gujarat and central India. There was one brewery at Dapuri near Pune
Pune
Pune , is the eighth largest metropolis in India, the second largest in the state of Maharashtra after Mumbai, and the largest city in the Western Ghats. Once the centre of power of the Maratha Empire, it is situated 560 metres above sea level on the Deccan plateau at the confluence of the Mula ...
.
Transportation
The province was well supplied with railways, all of which, with one exception, concentrated at Bombay City. The exception is the North-Western line, which enters Sind from the PunjabPunjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
and terminated at Karachi. The other chief lines are the Great Indian Peninsula, Indian Midland, Bombay, Baroda & Central India, and the Rajputana
Rajputana
Rājputāna was the pre-1949 name of the present-day Indian state of Rājasthān, the largest state of the Republic of India in terms of area. George Thomas was the first in 1800 A.D., to term this region as Rajputana...
, Malwa & Southern Mahratta systems. In 1905 the total length of railway under the Bombay government open for traffic was 7980 miles (12,842.5 km), which did not include the railway system in Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
.
Military
The East India Company had raised armies in each of the presidencies, Bombay, BengalBengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency originally comprising east and west Bengal, was a colonial region of the British Empire in South-Asia and beyond it. It comprised areas which are now within Bangladesh, and the present day Indian States of West Bengal, Assam, Bihar, Meghalaya, Orissa and Tripura.Penang and...
and Madras
Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency , officially the Presidency of Fort St. George and also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision of British India...
. The Bombay army consisted of a number of infantry regiments, sapper and miner units and irregular cavalry. A number of these continue to exist today in the Indian Army
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
; examples being the Maratha Light Infantry
Maratha Light Infantry
The Maratha Light Infantry is a light infantry regiment of the Indian Army. It was formed as the 103rd Maharattas in 1768, making it the most senior light infantry regiment of the Army....
and the Grenadiers, amongst others, in the case of infantry, the Bombay Sappers as engineers and the Poona Horse amongst the cavalry.
Under Lord Kitchener
Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener
Field Marshal Horatio Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener KG, KP, GCB, OM, GCSI, GCMG, GCIE, ADC, PC , was an Irish-born British Field Marshal and proconsul who won fame for his imperial campaigns and later played a central role in the early part of the First World War, although he died halfway...
's re-arrangement of the Indian army
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
in 1904 the old Bombay command was abolished and its place was taken by the Western army corps under a lieutenant-general. The army corps was divided into three divisions under major-generals. The 4th (Quetta) Division, with headquarters at Quetta
Quetta
is the largest city and the provincial capital of the Balochistan Province of Pakistan. Known as the "Fruit Garden of Pakistan" due to the diversity of its plant and animal wildlife, Quetta is home to the Hazarganji Chiltan National Park, which contains some of the rarest species of wildlife in the...
, comprised the troops in the Quetta and Sind districts. The 5th division, with headquarters at Mhow, consisted of three brigades, located at Nasirabad
Nasirabad
Nasirabad may refer to:* Mymensingh Town, the former name of Mymensingh Town, Bangladesh* Nasirabad, India in Rajasthan, India* Nasirabad, Raibareli in Uttar Pradesh, India* Nasirabad, Ardabil, Iran* Nasirabad, alternate name of Nasrabad, Isfahan, Iran...
, Jabalpur and Jhansi
Jhansi
Jhansi Hindi:झाँसी, , Marathi: झाशी, is a historical city of India. Jhansi is the administrative headquarters of Jhansi District and Jhansi Division. The original walled city grew up around its stone fort, which crowns a neighboring rock. This district is on the bank of river Betwa.The National...
, and included the previous Mhow, Deesa, Nagpur
Nagpur
Nāgpur is a city and winter capital of the state of Maharashtra, the largest city in central India and third largest city in Maharashtra after Mumbai and Pune...
, Narmada
Narmada district
Narmada district is an administrative district in the state of Gujarat in India. The district headquarters are located at Rajpipla. The district is bounded by Vadodara district in the north, by Maharashtra state in the east, by Tapi district in the south and by Bharuch district in the west...
and Bundelkhand
Bundelkhand
Bundelkhand anciently known as Chedi Kingdom is a geographic region of central India...
districts, with the Bombay district north of the Tapti
Tapti River
The Tapi River ancient original name Tapi River , is a river in central India. It is one of the major rivers of peninsular India with a length of around 724 km...
. The 6th division, with headquarters at Pune, consisted of three brigades, located at Bombay, Ahmednagar and Aden. It comprised the previous Poona district, Bombay district south of the Tapti, Belgaum
Belgaum
Belgaum is a city and a municipal corporation in Belgaum district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is the fourth largest city of the state of Karnataka, the first three being Bangalore, Mysore, Hubli-Dharwad....
district north of the Tungabhadra, and Dharwar and Aurangabad districts.
Education
The University of Bombay was established in 1857, and had an administration consisting of a chancellor, vice-chancellor and fellows. The governor of Bombay was ex-officio chancellor. The education department was under a director of public instruction, who was responsible for the administration of the department in accordance with the general educational policy of the state. The native states generally adopted the government system. Baroda and the Kathiawar states employed their own inspectors. In 1905 the total number of educational institutions was 10,194 with 593,431 pupils. There were ten art colleges, of which two were managed by government, three by native states, and five were under private management. It was in the year 1913 that the first college of commerce in Asia "Sydenham CollegeSydenham College
Sydenham College or Sydenham College of Commerce and Economics is the first college of commerce in Asia.It is an institute in Mumbai , affiliated to the University of Bombay, and offering undergraduate degrees in commerce and undergraduate and postgraduate degrees in management...
" was established. According to the census of 1901, out of a population of 25.5 million nearly 24 million were illiterate.
20th century reforms
British India's Montagu-Chelmsford reforms of 1919, enacted in 1921, expanded the Legislative Council to include more elected Indian members, and introduced the principle of dyarchy, whereby certain responsibilities, including agriculture, health, education, and local government, were devolved from the central government to the provinces. The Government of India Act 1935Government of India Act 1935
The Government of India Act 1935 was originally passed in August 1935 , and is said to have been the longest Act of Parliament ever enacted by that time. Because of its length, the Act was retroactively split by the Government of India Act 1935 into two separate Acts:# The Government of India...
made the Bombay Presidency into a regular province, and made Sind a separate province, with the princely state of Khairpur under the authority of Sindh. It enlarged the elected provincial assembly, and expanded provincial autonomy vis a vis the central government.
Baroda (Vadodara), one of the residencies of British India
Residencies of British India
The Residencies of British India were political offices, each managed by a Resident, which dealt with the relations between British India and a large number of princely states....
, was combined in the 1930s with the princely states of northern Bombay Presidency to form the "Baroda, Western States and Gujarat Agency".
After independence
In 1947 Bombay Province became part of newly-independent India, and Sindh Province became part of PakistanPakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. In 1950 Bombay Province was reorganized into Bombay State
Bombay State
The Bombay State was a state of India, dissolved with the formation of Maharashtra and Gujarat states on May 1, 1960.-History:During British rule, portions of the western coast of India under direct British rule were part of the Bombay Presidency...
, which included the princely states formerly under the political authority of Bombay Province; these princely states were merged into the new state after their rulers acceded to India.
Film production
The film production era is said to have commenced in Bombay from 1913 when the first film Raja HarishchandraRaja Harishchandra
Raja Harishchandra , is a 1913 silent Indian film directed and produced by Dadasaheb Phalke, and is the first full-length Indian feature film...
was shown by Dadasaheb Phalke
Dadasaheb Phalke
Dhundiraj Govind Phalke, popularly known as Dadasaheb Phalke was an Indian producer-director-screenwriter, known as the father of Indian cinema...
. Phalke made his first film, Raja Harishchandra, in 1912; it was first shown publicly on 3 May 1913 at Mumbai's Coronation Cinema
Coronation Cinema
Coronation Cinema was in Girgaon area of south Mumbai. On 3 May 1913 Raja Harishchandra , a silent Indian film directed and produced by Dadasaheb Phalke, which was also the first full-length Indian feature film and also the first India's first fully indigenous...
, effectively marking the beginning of the Indian film industry. Around one year before, Ramchandra Gopal (known as Dadasaheb Torne
Dadasaheb Torne
Ram Chandra Gopal "Dadasaheb" Torne रामचंद्र गोपाळ "दादासाहेब" तोरणे was the first Indian to make an Indian language feature film, as established by an advertisement in the Times of India newspaper of 25 May 1912....
) had filmed a stage drama called Pundalik and shown it in the same theater. However, the credit for making the first Indian feature film is attributed to Dadasaheb Phalke.
Other producers at Bombay were B. R. Chopra, S. Mukherjee, and Raj Kapoor. Ever since production of movies took place, there started the trend of film making that established and further progressed, resulting in formation of the film industry
Film industry
The film industry consists of the technological and commercial institutions of filmmaking: i.e. film production companies, film studios, cinematography, film production, screenwriting, pre-production, post production, film festivals, distribution; and actors, film directors and other film crew...
and new film production companies as well as studios.
External links
- View historical, early 20th century, photographs of Bombay at the University of Houston Digital Library
- Coins of the Bombay Presidency

