80
Encyclopedia
Leap year starting on Saturday
This is the calendar for any leap year starting on Saturday, January 1 , such as 1972, 2000, 2028 or 2056.Previous year | Next year-Trivia:...
(link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar began in 45 BC as a reform of the Roman calendar by Julius Caesar. It was chosen after consultation with the astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria and was probably designed to approximate the tropical year .The Julian calendar has a regular year of 365 days divided into 12 months...
. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus
Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
and Domitianus
Domitianus
-Introduction:Domitianus was probably a Roman soldier of the mid-third century AD who was acclaimed Emperor, probably in northern Gaul, in late 270 or early 271 AD and struck coins to advertise his elevation...
(or, less frequently, year 833 Ab urbe condita
Ab urbe condita
Ab urbe condita is Latin for "from the founding of the City ", traditionally set in 753 BC. AUC is a year-numbering system used by some ancient Roman historians to identify particular Roman years...
). The denomination 80 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
Anno Domini
and Before Christ are designations used to label or number years used with the Julian and Gregorian calendars....
calendar era
Calendar era
A calendar era is the year numbering system used by a calendar. For example, the Gregorian calendar numbers its years in the Western Christian era . The instant, date, or year from which time is marked is called the epoch of the era...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Roman Empire
- Emperor TitusTitusTitus , was Roman Emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death, thus becoming the first Roman Emperor to come to the throne after his own father....
inaugurates the ColosseumColosseumThe Colosseum, or the Coliseum, originally the Flavian Amphitheatre , is an elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, the largest ever built in the Roman Empire...
with 100 days of gamesInaugural games of the Flavian AmphitheatreThe inaugural games of the Flavian Amphitheatre were held in AD 80, on the orders of the Roman Emperor Titus, to celebrate the completion of the Colosseum, then known as the Flavian Amphitheatre . Vespasian began construction of the amphitheatre around AD 70, and it was completed by Titus...
. - The earliest stage of LullingstoneLullingstoneLullingstone is a village in the county of Kent, England. It is best known for its castle, Roman villa and its public golf course.- Pre-Roman :It is believed that an Iron Age hill fort is sited on the hill above the castle, although this is unconfirmed....
Roman villaRoman villaA Roman villa is a villa that was built or lived in during the Roman republic and the Roman Empire. A villa was originally a Roman country house built for the upper class...
is built. - The Roman occupation of BritainRoman conquest of BritainThe Roman conquest of Britain was a gradual process, beginning effectively in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, whose general Aulus Plautius served as first governor of Britannia. Great Britain had already frequently been the target of invasions, planned and actual, by forces of the Roman Republic and...
reaches the River TyneRiver TyneThe River Tyne is a river in North East England in Great Britain. It is formed by the confluence of two rivers: the North Tyne and the South Tyne. These two rivers converge at Warden Rock near Hexham in Northumberland at a place dubbed 'The Meeting of the Waters'.The North Tyne rises on the...
–Solway FirthSolway FirthThe Solway Firth is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in Cumbria, to the Mull of Galloway, on the western end of Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very...
frontier area. Gnaeus Julius AgricolaGnaeus Julius AgricolaGnaeus Julius Agricola was a Roman general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. His biography, the De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae, was the first published work of his son-in-law, the historian Tacitus, and is the source for most of what is known about him.Born to a noted...
creates a fleet for conquest of CaledoniaCaledoniaCaledonia is the Latinised form and name given by the Romans to the land in today's Scotland north of their province of Britannia, beyond the frontier of their empire...
, he finally proves that Britannia is an island. - Legio II AdiutrixLegio II AdiutrixLegio secunda Adiutrix , was a Roman legion levied by emperor Vespasian in 70, from Roman navy marines of the classis Ravennatis. There are still records of II Adiutrix in the Rhine border in the beginning of the 4th century...
is stationed at Lindum ColoniaLindum ColoniaLindum Colonia was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is called Lincoln, in the English county of Lincolnshire.-Fort and name:...
(modern LincolnLincoln, LincolnshireLincoln is a cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England.The non-metropolitan district of Lincoln has a population of 85,595; the 2001 census gave the entire area of Lincoln a population of 120,779....
). The city is an important settlement for retired Roman legionaries. - The original Roman PantheonPantheon, RomeThe Pantheon ,Rarely Pantheum. This appears in Pliny's Natural History in describing this edifice: Agrippae Pantheum decoravit Diogenes Atheniensis; in columnis templi eius Caryatides probantur inter pauca operum, sicut in fastigio posita signa, sed propter altitudinem loci minus celebrata.from ,...
is destroyed in a fire, together with many other buildings. - The Eifel AqueductEifel AqueductThe Eifel Aqueduct was one of the longest aqueducts of the Roman Empire.The aqueduct, constructed in AD 80, carried water some from the hilly Eifel region of what is now Germany to the ancient city of Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium . If the auxiliary spurs to additional springs are included,...
is constructed to bring water 95 km (59 mi) from the EifelEifelThe Eifel is a low mountain range in western Germany and eastern Belgium. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the south of the German-speaking Community of Belgium....
region to Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensum (modern CologneCologneCologne is Germany's fourth-largest city , and is the largest city both in the Germany Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia and within the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area, one of the major European metropolitan areas with more than ten million inhabitants.Cologne is located on both sides of the...
).
Asia
- Some 30,000 AsiaAsiaAsia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
n tribespeople migrateHuman migrationHuman migration is physical movement by humans from one area to another, sometimes over long distances or in large groups. Historically this movement was nomadic, often causing significant conflict with the indigenous population and their displacement or cultural assimilation. Only a few nomadic...
from the steppes to the west with 40,000 horseHorseThe horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
s and 100,000 cattleCattleCattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
, joining with IranIranIran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
ian tribespeople and with MongolsMongolsMongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
from the SiberiaSiberiaSiberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
n forests to form a group that will be known in EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
as the HunsHunsThe Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
.
Arts and sciences
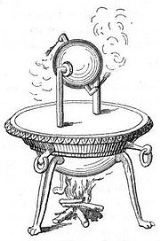
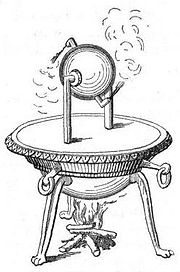
- The aeolipileAeolipileAn aeolipile , also known as a Hero engine, is a rocket style jet engine which spins when heated. In the 1st century AD, Hero of Alexandria described the device, and many sources give him the credit for its invention.The aeolipile Hero described is considered to be the first recorded steam engine...
, the first steam engineSteam engineA steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
, is described by Hero of AlexandriaHero of AlexandriaHero of Alexandria was an ancient Greek mathematician and engineerEnc. Britannica 2007, "Heron of Alexandria" who was active in his native city of Alexandria, Roman Egypt...
.
Religion
- The Gospel of LukeGospel of LukeThe Gospel According to Luke , commonly shortened to the Gospel of Luke or simply Luke, is the third and longest of the four canonical Gospels. This synoptic gospel is an account of the life and ministry of Jesus of Nazareth. It details his story from the events of his birth to his Ascension.The...
and Acts of the ApostlesActs of the ApostlesThe Acts of the Apostles , usually referred to simply as Acts, is the fifth book of the New Testament; Acts outlines the history of the Apostolic Age...
are written (approximate date).
Births
- AśvaghoṣaAsvaghosa' was an Indian philosopher-poet, born in Saketa in northern India to a Brahmin family. He is believed to have been the first Sanskrit dramatist, and is considered the greatest Indian poet prior to Kālidāsa. He was the most famous in a group of Buddhist court writers, whose epics rivaled the...
, Indian poet (approximate date) - CarpocratesCarpocratesCarpocrates of Alexandria was the founder of an early Gnostic sect from the first half of the 2nd century. As with many Gnostic sects, we know of the Carpocratians only through the writings of the Church Fathers, principally Irenaeus of Lyons and Clement of Alexandria. As the former strongly...
, religious philosopher
Deaths
- Vologases IIVologases II of ParthiaVologases II of Parthia was the son of Vologases I of Parthia and ruled the Parthian Empire from about 77 to 80. Little is known about him. It seems that Vologases II was defeated and deposed by his uncle, Pacorus II of Parthia ....
, kingMonarchA monarch is the person who heads a monarchy. This is a form of government in which a state or polity is ruled or controlled by an individual who typically inherits the throne by birth and occasionally rules for life or until abdication...
of ParthiaParthiaParthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire.... - Saint Timothy, bishopBishopA bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
of EphesusEphesusEphesus was an ancient Greek city, and later a major Roman city, on the west coast of Asia Minor, near present-day Selçuk, Izmir Province, Turkey. It was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League during the Classical Greek era...
(traditional date) - TalhaeTalhae of SillaTalhae of Silla was the fourth king of Silla, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. He is commonly called Talhae Isageum or Seok Talhae, isageum being the royal title in early Silla.-Background:...
, ruler of the KoreaKoreaKorea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
n kingdom of SillaSillaSilla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...

