
Transformer types
Encyclopedia
A variety of types of electrical transformer
are made for different purposes. Despite their design differences, the various types employ the same basic principle as discovered in 1831 by Michael Faraday
, and share several key functional parts.
 This is the most common type of transformer, widely used in appliances to convert mains voltage to low voltage to power electronics
This is the most common type of transformer, widely used in appliances to convert mains voltage to low voltage to power electronics
 Doughnut shaped toroidal
Doughnut shaped toroidal
transformers are used to save space compared to EI cores, and sometimes to reduce external magnetic field. These use a ring shaped core, copper windings wrapped round this ring (and thus threaded through the ring during winding), and tape for insulation.
Toroidal transformers compared to EI core transformers:
has only a single winding, which is tapped at some point along the winding. AC or pulsed voltage is applied across a portion of the winding, and a higher (or lower) voltage is produced across another portion of the same winding. The higher voltage will be connected to the ends of the winding, and the lower voltage from one end to a tap. For example, a transformer with a tap at the center of the winding can be used with 230 V across the entire winding, and 115 volts between one end and the tap. It can be connected to a 230 V supply to drive 115 V equipment, or reversed to drive 230 V equipment from 115 V. Since the current in the windings is lower, the transformer is smaller, lighter cheaper and more efficient. For voltage ratios not exceeding about 3:1, an autotransformer is cheaper, lighter, smaller and more efficient than an isolating (two-winding) transformer of the same rating. Large three-phase autotransformers are used in electric power distribution systems, for example, to interconnect 33 kV and 66 kV sub-transmission networks.
, an autotransformer with a near-continuously variable turns ratio can be obtained, allowing for wide voltage adjustment in very small increments.
but it is essentially a transformer whose output voltage is varied by rotating its secondary relative to the primary i.e. rotating the angular position of the rotor. It can be seen as a power transformer exploiting rotating magnetic field
s. The major advantage of the induction regulator is that unlike variacs, they are practical for transformers over 5 kVA. Hence, such regulators find windspread use in high-voltage laboratories.
Stray field transformers are used for arc welding
and high voltage discharge lamps (cold cathode fluorescent lamps, series connected up to 7.5 kV AC working voltage). It acts both as voltage transformer and magnetic ballast.
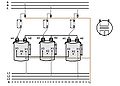 For three-phase power
For three-phase power
, three separate single-phase transformers can be used, or all three phases can be connected to a single polyphase transformer. The three primary windings are connected together and the three secondary windings are connected together. The most common connections are Y-Delta, Delta-Y, Delta-Delta and Y-Y. A vector group
indicates the configuration of the windings and the phase angle
difference between them. If a winding is connected to earth (grounded
), the earth connection point is usually the center point of a Y winding. If the secondary is a Delta winding, the ground may be connected to a center tap on one winding (high leg delta
) or one phase may be grounded (corner grounded delta). A special purpose polyphase transformer is the zigzag transformer
. There are many possible configurations that may involve more or fewer than six windings and various tap connections.
 A resonant
A resonant
transformer operates at the resonant frequency of one or more of its coils and (usually) an external capacitor
. The resonant coil, usually the secondary, acts as an inductor
, and is connected in series with a capacitor
. When the primary coil is driven by a periodic source of alternating current
, such as a square
or sawtooth wave
at the resonant frequency, each pulse of current helps to build up an oscillation in the secondary coil. Due to resonance, a very high voltage can develop across the secondary, until it is limited by some process such as electrical breakdown
. These devices are used to generate high alternating voltages, and the current available can be much larger than that from electrostatic machines such as the Van de Graaff generator
or Wimshurst machine
.
Examples:
Other applications of resonant transformers are as coupling between stages of a superheterodyne receiver
, where the selectivity of the receiver is provided by the tuned transformers of the intermediate-frequency amplifiers.
tank circuit (a capacitor and an additional winding), a transformer can be arranged to automatically keep the secondary winding voltage relatively constant for varying primary supply without additional circuitry or manual adjustment. Ferro-resonant transformers run hotter than standard power transformers, because regulating action depends on core saturation, which reduces efficiency. The output waveform is heavily distorted unless careful measures are taken to prevent this. Saturating transformers provide a simple rugged method to stabilize an AC power supply.
core power transformers are widely used in switched-mode power supplies (SMPSs). The powder core enables high-frequency operation, and hence much smaller size-to-power ratio than laminated-iron transformers.
Ferrite transformers are not used as power transformers at mains frequency since laminated iron cores cost less than an equivalent ferrite core.
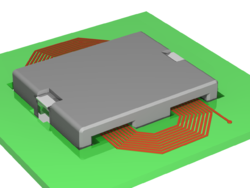
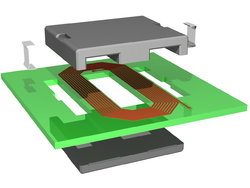 Manufacturers etch spiral patterns on a printed circuit board
Manufacturers etch spiral patterns on a printed circuit board
to form the "windings" of a planar transformer.
(Manufacturers literally wind pieces of wire on some core or bobbin to form the windings of other kinds of transformers).
Some planar transformers are commercially sold as discrete components—the transformer is the only thing on that printed circuit board.
Other planar transformers are one of many components on one large printed circuit board.
which cools and insulates. Oil circulates through ducts in the coil and around the coil and core assembly, moved by convection. The oil is cooled by the outside of the tank in small ratings, and in larger ratings an air-cooled radiator is used. Where a higher rating is required, or where the transformer is used in a building or underground, oil pumps are used to circulate the oil and an oil-to-water heat exchanger may also be used. Formerly, indoor transformers required to be fire-resistant used PCB
liquids; since these are now banned, substitute fire-resistant liquids such as silicone
oils are instead used.
However the term 'isolating transformer' is normally applied to mains transformers providing isolation rather than voltage transformation. They are simply 1:1 laminated core transformers. Extra voltage tappings are sometimes included, but to earn the name 'isolating transformer' it is expected that they will usually be used at 1:1 ratio.
 A current transformer (CT) is a measurement device designed to provide a current in its secondary coil proportional to the current flowing in its primary. Current transformers are commonly used in metering
A current transformer (CT) is a measurement device designed to provide a current in its secondary coil proportional to the current flowing in its primary. Current transformers are commonly used in metering
and protective relay
s in the electrical power industry
where they allow safe measurement of large currents, often in the presence of high voltage
s. The current transformer safely isolates measurement and control circuitry from the high voltages typically present on the circuit being measured.
Current transformers are often constructed by passing a single primary turn (either an insulated
cable or an uninsulated bus bar) through a well-insulated toroidal
core wrapped with many turns of wire. The CT is typically described by its current ratio from primary to secondary. For example, a 4000:5 CT would provide an output current of 5 amperes when the primary was passing 4000 amperes. The secondary winding can be single ratio or have several tap
points to provide a range of ratios. Care must be taken that the secondary winding is not disconnected from its load while current flows in the primary, as this will produce a dangerously high voltage across the open secondary and may permanently affect the accuracy of the transformer.
Specially constructed wideband
CTs are also used, usually with an oscilloscope
, to measure high frequency
waveform
s or pulsed currents within pulsed power
systems. One type provides a voltage output that is proportional to the measured current; another, called a Rogowski coil
, requires an external integrator
in order to provide a proportional output.
equipment can be operated at a lower potential. Typically the secondary of a voltage transformer is rated for 69 V or 120 V at rated primary voltage, to match the input ratings of protective relays.
The transformer winding high-voltage connection points are typically labeled as H1, H2 (sometimes H0 if it is internally grounded) and X1, X2 and sometimes an X3 tap may be present. Sometimes a second isolated winding (Y1, Y2, Y3) may also be available on the same voltage transformer. The high side (primary) may be connected phase to ground or phase to phase. The low side (secondary) is usually phase to ground.
The terminal identifications (H1, X1, Y1, etc.) are often referred to as polarity. This applies to current transformers as well. At any instant terminals with the same suffix numeral have the same polarity and phase. Correct identification of terminals and wiring is essential for proper operation of metering and protective relays.
Some meters operate directly on the secondary service voltages at or below 600 V. VTs are typically used for higher voltages (for example, 765 kV for power transmission
) , or where isolation is desired between the meter and the measured circuit.
). Small versions called signal types are used in digital logic and telecommunications circuits, often for matching logic drivers to transmission line
s. Medium-sized power versions are used in power-control circuits such as camera flash controllers. Larger power versions are used in the electrical power distribution industry to interface low-voltage control circuitry to the high-voltage gates of power semiconductor
s. Special high voltage
pulse transformers are also used to generate high power pulses for radar
, particle accelerators, or other high energy pulsed power
applications.
To minimise distortion of the pulse shape, a pulse transformer needs to have low values of leakage inductance and distributed capacitance, and a high open-circuit inductance. In power-type pulse transformers, a low coupling capacitance (between the primary and secondary) is important to protect the circuitry on the primary side from high-powered transients created by the load. For the same reason, high insulation resistance and high breakdown voltage are required. A good transient response is necessary to maintain the rectangular pulse shape at the secondary, because a pulse with slow edges would create switching losses in the power semiconductors.
The product of the peak pulse voltage and the duration of the pulse (or more accurately, the voltage-time integral) is often used to characterise pulse transformers. Generally speaking, the larger this product, the larger and more expensive the transformer.
Pulse transformers by definition have a duty cycle of less than 0.5, whatever energy stored in the coil during the pulse must be "dumped" out before the pulse is fired again.
(RF) work. Steel laminations are not suitable for RF.
. Such transformers may be nothing more than a few turns of wire soldered onto a printed circuit board
.
(IF) stages in superheterodyne radio receivers. are mostly tuned transformers, containing a threaded ferrite slug that is screwed in or out to adjust IF tuning. The transformers are usually canned for stability and to reduce interference.
use, transformers are sometimes made from configurations of transmission line, sometimes bifilar or coaxial
cable, wound around ferrite
or other types of core. This style of transformer gives an extremely wide bandwidth but only a limited number of ratios (such as 1:9, 1:4 or 1:2) can be achieved with this technique.
The core material increases the inductance dramatically, thereby raising its Q factor
. The cores of such transformers help improve performance at the lower frequency end of the band.
RF transformers sometimes used a third coil (called a tickler winding) to inject feedback
into an earlier (detector
) stage in antique
regenerative
radio receivers
.
circuits. These are sometimes made from configurations of transmission line and sometimes bifilar or coaxial
cable and are similar to transmission line transformers in construction and operation.
 Audio transformers are usually the factor which limit sound quality when used; electronic circuits with wide frequency response
Audio transformers are usually the factor which limit sound quality when used; electronic circuits with wide frequency response
and low distortion
are relatively simple to design.
Transformers are also used in DI boxes to convert high-impedance instrument signals (e.g. bass guitar
) to low impedance signals to enable them to be connected to a microphone input on the mixing console
.
A particularly critical component is the output transformer of an audio
power amplifier. Valve circuits for quality reproduction have long been produced with no other (inter-stage) audio transformers, but an output transformer is needed to couple
the relatively high impedance (up to a few hundred ohms depending upon configuration) of the output valve(s) to the low impedance of a loudspeaker
. (The valves can deliver a low current at a high voltage; the speakers require high current at low voltage.) Most solid-state power amplifiers need no output transformer at all.
For good low-frequency response a relatively large iron core
is required; high power handling increases the required core size. Good high-frequency response requires carefully designed and implemented windings without excessive leakage inductance
or stray capacitance. All this makes for an expensive component.
Early transistor
audio power amplifiers often had output transformers, but they were eliminated as designers discovered how to design amplifiers without them.
transformers can be used to allow many individual loudspeakers to be powered from a single audio circuit operated at higher-than normal loudspeaker voltages. This application is common in industrial public address
applications. Such circuits are commonly referred to as constant voltage speaker system
s, although the audio waveform is a changing voltage. Such systems are also known by other terms such as 25-, 70- and 100-volt speaker systems, referring to the nominal voltage of the loudspeaker line.
At the audio amplifier, a large audio transformer may be used to step-up the low impedance, low-voltage output of the amplifier to the designed line voltage of the loudspeaker circuit. At the distant loudspeaker location, a smaller step-down transformer returns the voltage and impedance to ordinary loudspeaker levels. The loudspeaker transformers commonly have multiple primary taps, allowing the volume at each speaker to be adjusted in discrete steps.
Microphones may also be matched to their load with a small transformer, which is mumetal shielded to minimise noise pickup. These transformers are less widely used today, as transistorized buffers are now cheaper.
Firm clamping of laminations and varnish help to avoid buzz.
Enamelled copper wire is wound round the central half of the length of a bundle of insulated iron wire (eg florists' wire), to make the windings. The ends of the iron wires are then bent around the electrical winding to complete the magnetic circuit, and the whole is wrapped with tape or string to hold it together.
Pancake coil variocouplers were common in 1920s radios for variable RF coupling. The two planar coils were arranged to swing away from each other and for the angle between them to increase to 90 degrees, thus giving wide variation in coupling. No core was used. These were mostly used to control reaction. The pancake structure was a means to minimize stray capacitance.
In another design of variocoupler, two coils were wound on two circular bands, and housed one inside the other, with provision for rotating the inner coil. Coupling varies as one coil is rotated between 0 and 90 degrees from the other. These had higher stray capacitance than the pancake type.
Wall wart
s: small power supplies with integral mains plug. These can contain a transformer and other circuitry. Most use a laminated iron transformer, but an increasing number now contain a small switched-mode power supply
. These are smaller and much lighter.
Halogen lighting transformers: Toroidal transformers are sometimes used for this task, but most halogen 'transformers' are switched-mode power supplies.
Transformers rely on a linear relationship between the currents in primary and secondary circuits. Interesting and useful power control devices such as the saturable reactor
and the magnetic amplifier
rely on controlled saturation of a ferromagnetic core. Such devices can provide considerable power amplification without use of transistors or vacuum tubes. Although they resemble transformers with cores and sets of windings, the operating principles and purposes are different.
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
are made for different purposes. Despite their design differences, the various types employ the same basic principle as discovered in 1831 by Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday, FRS was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry....
, and share several key functional parts.
Laminated core

- Widely available in power ratings ranging from mW to MW
- Insulated lamination minimizes eddy current losses
- Small appliance and electronic transformers may use a split bobbin, giving a high level of insulation between the windings
- Rectangular core
- Core laminate stampings are usually in EI shape pairs. Other shape pairs are sometimes used
- Mu-metal shields can be fitted to reduce EMI (electromagnetic interference)
- A screen winding is occasionally used between the 2 power windings
- Small appliance and electronics transformers may have a thermal cut out built in
- Occasionally seen in low profile format for use in restricted spaces
- Laminated core made with silicon steel with high permeability
Toroidal

Toroidal inductors and transformers
Toroidal inductors and transformers are electronic components, typically consisting of a circular ring-shaped magnetic core of iron powder, ferrite, or other material around which wire is coiled to make an inductor. Toroidal coils are used in a broad range of applications, such as high-frequency...
transformers are used to save space compared to EI cores, and sometimes to reduce external magnetic field. These use a ring shaped core, copper windings wrapped round this ring (and thus threaded through the ring during winding), and tape for insulation.
Toroidal transformers compared to EI core transformers:
- Lower external magnetic field
- Smaller for a given power rating
- Higher cost in most cases, as winding requires more complex and slower equipment
- Less robust
- Central fixing is either
- bolt, large metal washers and rubber pads
- bolt and potting resin
- Over-tightening the central fixing bolt may short the windings
- Greater inrush current at switch-on
Autotransformer
An autotransformerAutotransformer
An autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding. The auto prefix refers to the single coil acting on itself rather than any automatic mechanism. In an autotransformer portions of the same winding act as both the primary and secondary. The winding has at least three taps where...
has only a single winding, which is tapped at some point along the winding. AC or pulsed voltage is applied across a portion of the winding, and a higher (or lower) voltage is produced across another portion of the same winding. The higher voltage will be connected to the ends of the winding, and the lower voltage from one end to a tap. For example, a transformer with a tap at the center of the winding can be used with 230 V across the entire winding, and 115 volts between one end and the tap. It can be connected to a 230 V supply to drive 115 V equipment, or reversed to drive 230 V equipment from 115 V. Since the current in the windings is lower, the transformer is smaller, lighter cheaper and more efficient. For voltage ratios not exceeding about 3:1, an autotransformer is cheaper, lighter, smaller and more efficient than an isolating (two-winding) transformer of the same rating. Large three-phase autotransformers are used in electric power distribution systems, for example, to interconnect 33 kV and 66 kV sub-transmission networks.
Variac
By exposing part of the winding coils of an autotransformer, and making the secondary connection through a sliding carbon brushBrush (electric)
A brush is a device which conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, most commonly in a rotating shaft. Typical applications include electric motors, alternators and electric generators.-Etymology:...
, an autotransformer with a near-continuously variable turns ratio can be obtained, allowing for wide voltage adjustment in very small increments.
Induction regulator
The induction regulator is similar in design to a wound-rotor induction motorInduction motor
An induction or asynchronous motor is a type of AC motor where power is supplied to the rotor by means of electromagnetic induction. These motors are widely used in industrial drives, particularly polyphase induction motors, because they are robust and have no brushes...
but it is essentially a transformer whose output voltage is varied by rotating its secondary relative to the primary i.e. rotating the angular position of the rotor. It can be seen as a power transformer exploiting rotating magnetic field
Rotating magnetic field
A rotating magnetic field is a magnetic field which changes direction at a constant angular rate. This is a key principle in the operation of the alternating-current motor. Nikola Tesla claimed in his autobiography that he identified the concept of the rotating magnetic field in 1882. In 1885,...
s. The major advantage of the induction regulator is that unlike variacs, they are practical for transformers over 5 kVA. Hence, such regulators find windspread use in high-voltage laboratories.
Stray field transformer
A stray field transformer has a significant stray field or a (sometimes adjustable) magnetic bypass in its core. It can act as a transformer with inherent current limitation due to its lower coupling between the primary and the secondary winding, which is unwanted in most other cases. The output and input currents are low enough to prevent thermal overload under each load condition - even if the secondary is shorted.Stray field transformers are used for arc welding
Arc welding
Arc welding is a type of welding that uses a welding power supply to create an electric arc between an electrode and the base material to melt the metals at the welding point. They can use either direct or alternating current, and consumable or non-consumable electrodes...
and high voltage discharge lamps (cold cathode fluorescent lamps, series connected up to 7.5 kV AC working voltage). It acts both as voltage transformer and magnetic ballast.
Polyphase transformers

Three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads...
, three separate single-phase transformers can be used, or all three phases can be connected to a single polyphase transformer. The three primary windings are connected together and the three secondary windings are connected together. The most common connections are Y-Delta, Delta-Y, Delta-Delta and Y-Y. A vector group
Vector group
In electrical engineering, a vector group is the International Electrotechnical Commission method of categorizing the primary and secondary winding configurations of three-phase transformers...
indicates the configuration of the windings and the phase angle
Phase angle
In the context of vectors and phasors, the term phase angle refers to the angular component of the polar coordinate representation. The notation A\ang \!\ \theta, for a vector with magnitude A and phase angle θ, is called angle notation.In the context of periodic phenomena, such as a wave,...
difference between them. If a winding is connected to earth (grounded
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
), the earth connection point is usually the center point of a Y winding. If the secondary is a Delta winding, the ground may be connected to a center tap on one winding (high leg delta
High leg delta
High-leg delta is a type of electrical service connection often found in older three-phase electric power installations...
) or one phase may be grounded (corner grounded delta). A special purpose polyphase transformer is the zigzag transformer
Zigzag transformer
A Zigzag transformer is a special purpose transformer with a zigzag arrangement. It has primary windings but no secondary winding. One application is to derive an earth reference point for an ungrounded electrical system. Another is to control harmonic currents.As with other three-phase...
. There are many possible configurations that may involve more or fewer than six windings and various tap connections.
Resonant transformers

Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
transformer operates at the resonant frequency of one or more of its coils and (usually) an external capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
. The resonant coil, usually the secondary, acts as an inductor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
, and is connected in series with a capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
. When the primary coil is driven by a periodic source of alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
, such as a square
Square wave
A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
or sawtooth wave
Sawtooth wave
The sawtooth wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is named a sawtooth based on its resemblance to the teeth on the blade of a saw....
at the resonant frequency, each pulse of current helps to build up an oscillation in the secondary coil. Due to resonance, a very high voltage can develop across the secondary, until it is limited by some process such as electrical breakdown
Electrical breakdown
The term electrical breakdown or electric breakdown has several similar but distinctly different meanings. For example, the term can apply to the failure of an electric circuit....
. These devices are used to generate high alternating voltages, and the current available can be much larger than that from electrostatic machines such as the Van de Graaff generator
Van de Graaff generator
A Van de Graaff generator is an electrostatic generator which uses a moving belt to accumulate very high voltages on a hollow metal globe on the top of the stand. It was invented in 1929 by American physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff. The potential differences achieved in modern Van de Graaff...
or Wimshurst machine
Wimshurst machine
The Wimshurst influence machine is an electrostatic generator, a machine for generating high voltages developed between 1880 and 1883 by British inventor James Wimshurst ....
.
Examples:
- Tesla coilTesla coilA Tesla coil is a type of resonant transformer circuit invented by Nikola Tesla around 1891. It is used to produce high voltage, low current, high frequency alternating current electricity. Tesla coils produce higher current than the other source of high voltage discharges, electrostatic machines...
- Oudin coilOudin coilAn Oudin coil, also called an Oudin oscillator or Oudin resonator, is a disruptive discharge coil wired as a transformer designed to produce high voltage arcs and discharges, similar to a Tesla coil...
(or Oudin resonator; named after its inventor Paul OudinPaul OudinPaul Marie Oudin was a French doctor. He was born, and later died, in Épinal. He developed the "Oudin coil", which is an autotransforming resonator.-External links:*...
) - D'ArsonvalJacques-Arsène d'ArsonvalJacques-Arsène d'Arsonval was born in La Porcherie and was a French physician, physicist and inventor of the moving-coil galvanometer and probably of the thermocouple ammeter...
apparatus - Ignition coilIgnition coilAn ignition coil is an induction coil in an automobile's ignition system which transforms the battery's 12 volts to the thousands of volts needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs to ignite the fuel...
or induction coilInduction coilAn induction coil or "spark coil" is a type of disruptive discharge coil. It is a type of electrical transformer used to produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage direct current supply...
used in the ignition systemIgnition systemAn ignition system is a system for igniting a fuel-air mixture. Ignition systems are well known in the field of internal combustion engines such as those used in petrol engines used to power the majority of motor vehicles, but they are also used in many other applications such as in oil-fired and...
of a petrol enginePetrol engineA petrol engine is an internal combustion engine with spark-ignition, designed to run on petrol and similar volatile fuels.... - Flyback transformerFlyback transformerA flyback transformer , also called a line output transformer , is a special transformer, which is used for conversion of energy in electronic circuits. It was initially designed to generate high current sawtooth signals at a relatively high frequency...
of a CRTCathode ray tubeThe cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
televisionTelevisionTelevision is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
set or video monitor. - Electrical breakdownElectrical breakdownThe term electrical breakdown or electric breakdown has several similar but distinctly different meanings. For example, the term can apply to the failure of an electric circuit....
and insulation testing of high voltage equipment and cables. In the latter case, the transformer's secondary is resonated with the cable's capacitance.
Other applications of resonant transformers are as coupling between stages of a superheterodyne receiver
Superheterodyne receiver
In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver uses frequency mixing or heterodyning to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency, which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency...
, where the selectivity of the receiver is provided by the tuned transformers of the intermediate-frequency amplifiers.
Constant voltage transformer
By arranging particular magnetic properties of a transformer core, and installing a ferro-resonantFerroresonance
See also: ferroresonant transformer .Ferroresonance or nonlinear resonance is a complex electrical phenomenon...
tank circuit (a capacitor and an additional winding), a transformer can be arranged to automatically keep the secondary winding voltage relatively constant for varying primary supply without additional circuitry or manual adjustment. Ferro-resonant transformers run hotter than standard power transformers, because regulating action depends on core saturation, which reduces efficiency. The output waveform is heavily distorted unless careful measures are taken to prevent this. Saturating transformers provide a simple rugged method to stabilize an AC power supply.
Ferrite core
FerriteFerrite (magnet)
Ferrites are chemical compounds consisting of ceramic materials with iron oxide as their principal component. Many of them are magnetic materials and they are used to make permanent magnets, ferrite cores for transformers, and in various other applications.Many ferrites are spinels with the...
core power transformers are widely used in switched-mode power supplies (SMPSs). The powder core enables high-frequency operation, and hence much smaller size-to-power ratio than laminated-iron transformers.
Ferrite transformers are not used as power transformers at mains frequency since laminated iron cores cost less than an equivalent ferrite core.
Planar transformer


Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
to form the "windings" of a planar transformer.
(Manufacturers literally wind pieces of wire on some core or bobbin to form the windings of other kinds of transformers).
Some planar transformers are commercially sold as discrete components—the transformer is the only thing on that printed circuit board.
Other planar transformers are one of many components on one large printed circuit board.
- much thinner than other transformers, for low-profile applications (even when several PCBs are stacked)
- almost all use a ferrite planar core
Oil cooled transformer
For large transformers used in power distribution or electrical substations, the core and coils of the transformer are immersed in oilTransformer oil
Transformer oil or insulating oil is usually a highly-refined mineral oil that is stable at high temperatures and has excellent electrical insulating properties. It is used in oil-filled transformers, some types of high voltage capacitors, fluorescent lamp ballasts, and some types of high voltage...
which cools and insulates. Oil circulates through ducts in the coil and around the coil and core assembly, moved by convection. The oil is cooled by the outside of the tank in small ratings, and in larger ratings an air-cooled radiator is used. Where a higher rating is required, or where the transformer is used in a building or underground, oil pumps are used to circulate the oil and an oil-to-water heat exchanger may also be used. Formerly, indoor transformers required to be fire-resistant used PCB
Polychlorinated biphenyl
Polychlorinated biphenyls are a class of organic compounds with 2 to 10 chlorine atoms attached to biphenyl, which is a molecule composed of two benzene rings. The chemical formula for PCBs is C12H10-xClx...
liquids; since these are now banned, substitute fire-resistant liquids such as silicone
Silicone
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications , cookware, and insulation....
oils are instead used.
Cast resin transformers
Cast-resin power transformers encase the windings in epoxy resin. These transformers simplify installation since they are dry, without cooling oil, and so require no fire-proof vault for indoor installations. The epoxy protects the windings from dust and corrosive atmospheres. However, because the molds for casting the coils are only available in fixed sizes, the design of the transformers is less flexible, which may make them more costly if customized features (voltage, turns ratio, taps) are required.Isolating Transformer
Most transformers isolate, meaning the secondary winding is not connected to the primary. But this isn't true of all transformers.However the term 'isolating transformer' is normally applied to mains transformers providing isolation rather than voltage transformation. They are simply 1:1 laminated core transformers. Extra voltage tappings are sometimes included, but to earn the name 'isolating transformer' it is expected that they will usually be used at 1:1 ratio.
Current transformers

Electricity meter
An electricity meter or energy meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, business, or an electrically powered device....
and protective relay
Protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a complex electromechanical apparatus, often with more than one coil, designed to calculate operating conditions on an electrical circuit and trip circuit breakers when a fault is detected...
s in the electrical power industry
Electrical power industry
The electric power industry provides the production and delivery of electric energy, often known as power, or electricity, in sufficient quantities to areas that need electricity through a grid connection. The grid distributes electrical energy to customers...
where they allow safe measurement of large currents, often in the presence of high voltage
High voltage
The term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements...
s. The current transformer safely isolates measurement and control circuitry from the high voltages typically present on the circuit being measured.
Current transformers are often constructed by passing a single primary turn (either an insulated
Electrical insulation
thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation...
cable or an uninsulated bus bar) through a well-insulated toroidal
Torus
In geometry, a torus is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle...
core wrapped with many turns of wire. The CT is typically described by its current ratio from primary to secondary. For example, a 4000:5 CT would provide an output current of 5 amperes when the primary was passing 4000 amperes. The secondary winding can be single ratio or have several tap
Tap (transformer)
A transformer tap is a connection point along a transformer winding that allows a certain number of turns to be selected. This means, a transformer with a variable turns ratio is produced, enabling voltage regulation of the output...
points to provide a range of ratios. Care must be taken that the secondary winding is not disconnected from its load while current flows in the primary, as this will produce a dangerously high voltage across the open secondary and may permanently affect the accuracy of the transformer.
Specially constructed wideband
Wideband
In communications, wideband is a relative term used to describe a wide range of frequencies in a spectrum. A system is typically described as wideband if the message bandwidth significantly exceeds the channel's coherence bandwidth....
CTs are also used, usually with an oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
, to measure high frequency
High frequency
High frequency radio frequencies are between 3 and 30 MHz. Also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decameters . Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted Medium-frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Very high frequency...
waveform
Waveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
s or pulsed currents within pulsed power
Pulsed power
Pulsed power is the term used to describe the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it very quickly thus increasing the instantaneous power.-Overview:...
systems. One type provides a voltage output that is proportional to the measured current; another, called a Rogowski coil
Rogowski coil
A Rogowski coil, named after Walter Rogowski, is an electrical device for measuring alternating current or high speed current pulses. It consists of a helical coil of wire with the lead from one end returning through the centre of the coil to the other end, so that both terminals are at the same...
, requires an external integrator
Integrator
An integrator is a device to perform the mathematical operation known as integration, a fundamental operation in calculus.The integration function is often part of engineering, physics, mechanical, chemical and scientific calculations....
in order to provide a proportional output.
Voltage transformers
Voltage transformers (VT) or potential transformers (PT) are another type of instrument transformer, used for metering and protection in high-voltage circuits. They are designed to present negligible load to the supply being measured and to have a precise voltage ratio to accurately step down high voltages so that metering and protective relayProtective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a complex electromechanical apparatus, often with more than one coil, designed to calculate operating conditions on an electrical circuit and trip circuit breakers when a fault is detected...
equipment can be operated at a lower potential. Typically the secondary of a voltage transformer is rated for 69 V or 120 V at rated primary voltage, to match the input ratings of protective relays.
The transformer winding high-voltage connection points are typically labeled as H1, H2 (sometimes H0 if it is internally grounded) and X1, X2 and sometimes an X3 tap may be present. Sometimes a second isolated winding (Y1, Y2, Y3) may also be available on the same voltage transformer. The high side (primary) may be connected phase to ground or phase to phase. The low side (secondary) is usually phase to ground.
The terminal identifications (H1, X1, Y1, etc.) are often referred to as polarity. This applies to current transformers as well. At any instant terminals with the same suffix numeral have the same polarity and phase. Correct identification of terminals and wiring is essential for proper operation of metering and protective relays.
Some meters operate directly on the secondary service voltages at or below 600 V. VTs are typically used for higher voltages (for example, 765 kV for power transmission
Power transmission
Power transmission is the movement of energy from its place of generation to a location where it is applied to performing useful work.Power is defined formally as units of energy per unit time...
) , or where isolation is desired between the meter and the measured circuit.
Pulse transformers
A pulse transformer is a transformer that is optimised for transmitting rectangular electrical pulses (that is, pulses with fast rise and fall times and a relatively constant amplitudeAmplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
). Small versions called signal types are used in digital logic and telecommunications circuits, often for matching logic drivers to transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
s. Medium-sized power versions are used in power-control circuits such as camera flash controllers. Larger power versions are used in the electrical power distribution industry to interface low-voltage control circuitry to the high-voltage gates of power semiconductor
Power semiconductor device
Power semiconductor devices are semiconductor devices used as switches or rectifiers in power electronic circuits . They are also called power devices or when used in integrated circuits, called power ICs....
s. Special high voltage
High voltage
The term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements...
pulse transformers are also used to generate high power pulses for radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
, particle accelerators, or other high energy pulsed power
Pulsed power
Pulsed power is the term used to describe the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it very quickly thus increasing the instantaneous power.-Overview:...
applications.
To minimise distortion of the pulse shape, a pulse transformer needs to have low values of leakage inductance and distributed capacitance, and a high open-circuit inductance. In power-type pulse transformers, a low coupling capacitance (between the primary and secondary) is important to protect the circuitry on the primary side from high-powered transients created by the load. For the same reason, high insulation resistance and high breakdown voltage are required. A good transient response is necessary to maintain the rectangular pulse shape at the secondary, because a pulse with slow edges would create switching losses in the power semiconductors.
The product of the peak pulse voltage and the duration of the pulse (or more accurately, the voltage-time integral) is often used to characterise pulse transformers. Generally speaking, the larger this product, the larger and more expensive the transformer.
Pulse transformers by definition have a duty cycle of less than 0.5, whatever energy stored in the coil during the pulse must be "dumped" out before the pulse is fired again.
RF transformers
There are several types of transformer used in radio frequencyRadio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
(RF) work. Steel laminations are not suitable for RF.
Air-core transformers
These are used for high frequency work. The lack of a core means very low inductanceInductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
. Such transformers may be nothing more than a few turns of wire soldered onto a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
.
Ferrite-core transformers
Widely used in intermediate frequencyIntermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency is a frequency to which a carrier frequency is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called...
(IF) stages in superheterodyne radio receivers. are mostly tuned transformers, containing a threaded ferrite slug that is screwed in or out to adjust IF tuning. The transformers are usually canned for stability and to reduce interference.
Transmission-line transformers
For radio frequencyRadio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
use, transformers are sometimes made from configurations of transmission line, sometimes bifilar or coaxial
Coaxial
In geometry, coaxial means that two or more forms share a common axis; it is the three-dimensional linear analogue of concentric.Coaxial cable, as a common example, has a wire conductor in the centre a circumferential outer conductor and an insulating medium called the dielectric separating...
cable, wound around ferrite
Ferrite (magnet)
Ferrites are chemical compounds consisting of ceramic materials with iron oxide as their principal component. Many of them are magnetic materials and they are used to make permanent magnets, ferrite cores for transformers, and in various other applications.Many ferrites are spinels with the...
or other types of core. This style of transformer gives an extremely wide bandwidth but only a limited number of ratios (such as 1:9, 1:4 or 1:2) can be achieved with this technique.
The core material increases the inductance dramatically, thereby raising its Q factor
Q factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
. The cores of such transformers help improve performance at the lower frequency end of the band.
RF transformers sometimes used a third coil (called a tickler winding) to inject feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
into an earlier (detector
Detector (radio)
A detector is a device that recovers information of interest contained in a modulated wave. The term dates from the early days of radio when all transmissions were in Morse code, and it was only necessary to detect the presence of a radio wave using a device such as a coherer without necessarily...
) stage in antique
Antique radio
An antique radio is a radio receiving set that is collectible because of its age and rarity. Although collectors may differ on the cutoff dates, most would use 50 years old, or the pre-World War II Era, for vacuum tube sets and the first five years of transistor sets.-Morse only sets:The first...
regenerative
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit or "autodyne" allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same vacuum tube or other active component such as a field effect transistor. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback...
radio receivers
Antique radio
An antique radio is a radio receiving set that is collectible because of its age and rarity. Although collectors may differ on the cutoff dates, most would use 50 years old, or the pre-World War II Era, for vacuum tube sets and the first five years of transistor sets.-Morse only sets:The first...
.
Baluns
Baluns are transformers designed specifically to connect between balanced and unbalancedUnbalanced
Unbalanced may refer to:* Unbalanced line or network in electrical circuits, where the impedance of the two conductor paths are not equal* An unbalanced formation in American football* Unbalanced chemical equations...
circuits. These are sometimes made from configurations of transmission line and sometimes bifilar or coaxial
Coaxial
In geometry, coaxial means that two or more forms share a common axis; it is the three-dimensional linear analogue of concentric.Coaxial cable, as a common example, has a wire conductor in the centre a circumferential outer conductor and an insulating medium called the dielectric separating...
cable and are similar to transmission line transformers in construction and operation.
Audio transformers

Frequency response
Frequency response is the quantitative measure of the output spectrum of a system or device in response to a stimulus, and is used to characterize the dynamics of the system. It is a measure of magnitude and phase of the output as a function of frequency, in comparison to the input...
and low distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
are relatively simple to design.
Transformers are also used in DI boxes to convert high-impedance instrument signals (e.g. bass guitar
Bass guitar
The bass guitar is a stringed instrument played primarily with the fingers or thumb , or by using a pick....
) to low impedance signals to enable them to be connected to a microphone input on the mixing console
Mixing console
In professional audio, a mixing console, or audio mixer, also called a sound board, mixing desk, or mixer is an electronic device for combining , routing, and changing the level, timbre and/or dynamics of audio signals. A mixer can mix analog or digital signals, depending on the type of mixer...
.
A particularly critical component is the output transformer of an audio
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
power amplifier. Valve circuits for quality reproduction have long been produced with no other (inter-stage) audio transformers, but an output transformer is needed to couple
Coupling (electronics)
In electronics and telecommunication, coupling is the desirable or undesirable transfer of energy from one medium, such as a metallic wire or an optical fiber, to another medium, including fortuitous transfer....
the relatively high impedance (up to a few hundred ohms depending upon configuration) of the output valve(s) to the low impedance of a loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
. (The valves can deliver a low current at a high voltage; the speakers require high current at low voltage.) Most solid-state power amplifiers need no output transformer at all.
For good low-frequency response a relatively large iron core
Magnetic core
A magnetic core is a piece of magnetic material with a high permeability used to confine and guide magnetic fields in electrical, electromechanical and magnetic devices such as electromagnets, transformers, electric motors, inductors and magnetic assemblies. It is made of ferromagnetic metal such...
is required; high power handling increases the required core size. Good high-frequency response requires carefully designed and implemented windings without excessive leakage inductance
Leakage inductance
Leakage inductance is the property of an electrical transformer that causes a winding to appear to have some inductance in series with the mutually-coupled transformer windings...
or stray capacitance. All this makes for an expensive component.
Early transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
audio power amplifiers often had output transformers, but they were eliminated as designers discovered how to design amplifiers without them.
Loudspeaker transformers
In the same way that transformers are used to create high voltage power transmission circuits that minimize transmission losses, loudspeakerLoudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
transformers can be used to allow many individual loudspeakers to be powered from a single audio circuit operated at higher-than normal loudspeaker voltages. This application is common in industrial public address
Public address
A public address system is an electronic amplification system with a mixer, amplifier and loudspeakers, used to reinforce a sound source, e.g., a person giving a speech, a DJ playing prerecorded music, and distributing the sound throughout a venue or building.Simple PA systems are often used in...
applications. Such circuits are commonly referred to as constant voltage speaker system
Constant voltage speaker system
Constant voltage speaker systems refer to networks of loudspeakers which are connected to an audio amplifier using step-up and step-down transformers to simplify impedance calculations and to minimize power loss over the speaker cables. They are more appropriately called high-voltage audio...
s, although the audio waveform is a changing voltage. Such systems are also known by other terms such as 25-, 70- and 100-volt speaker systems, referring to the nominal voltage of the loudspeaker line.
At the audio amplifier, a large audio transformer may be used to step-up the low impedance, low-voltage output of the amplifier to the designed line voltage of the loudspeaker circuit. At the distant loudspeaker location, a smaller step-down transformer returns the voltage and impedance to ordinary loudspeaker levels. The loudspeaker transformers commonly have multiple primary taps, allowing the volume at each speaker to be adjusted in discrete steps.
Output transformer
Valve (tube) amplifiers almost always use an output transformer to match the high load impedance requirement of the valves (several kilohms) to a low impedance speaker.Small signal transformers
Moving coil phonograph cartridges produce a very small voltage. In order for this to be amplified with a reasonable signal-noise ratio, a transformer is usually used to convert the voltage to the range of the more common moving-magnet cartridges.Microphones may also be matched to their load with a small transformer, which is mumetal shielded to minimise noise pickup. These transformers are less widely used today, as transistorized buffers are now cheaper.
Interstage and coupling transformers
In a push-pull amplifier, an inverted signal is required and is obtained from a transformer with a center-tapped winding, used to drive two active devices in opposite phase. These phase splitting transformers are not much used today.Transformer kits
Transformers may be wound at home using commercial transformer kits, which contain laminations & bobbin. Alternatively, ready made transformers may be disassembled and rewound. These approaches are occasionally used by home constructors but are usually avoided where possible due to the number of hours required to hand wind a transformer.Firm clamping of laminations and varnish help to avoid buzz.
100% homemade
It is possible to make the transformer laminations by hand too. Such transformers are encountered at times in 3rd world countries, using laminations cut from scrap sheet steel, paper slips between the laminations, and string to tie the assembly together. The result works, but is usually noisy due to poor clamping of laminations.Hedgehog
Hedgehog transformers are occasionally encountered in homemade 1920s radios. They are homemade audio interstage coupling transformers.Enamelled copper wire is wound round the central half of the length of a bundle of insulated iron wire (eg florists' wire), to make the windings. The ends of the iron wires are then bent around the electrical winding to complete the magnetic circuit, and the whole is wrapped with tape or string to hold it together.
Variocouplers
Variocouplers (sometimes called variometers) are RF transformers with two windings and variable coupling between the windings. They were standard equipment in 1920s radio sets.Pancake coil variocouplers were common in 1920s radios for variable RF coupling. The two planar coils were arranged to swing away from each other and for the angle between them to increase to 90 degrees, thus giving wide variation in coupling. No core was used. These were mostly used to control reaction. The pancake structure was a means to minimize stray capacitance.
In another design of variocoupler, two coils were wound on two circular bands, and housed one inside the other, with provision for rotating the inner coil. Coupling varies as one coil is rotated between 0 and 90 degrees from the other. These had higher stray capacitance than the pancake type.
Not transformers
Items which may be mistaken for transformers, but which are not always transformers.Wall wart
Wall wart
The AC adapter, AC/DC adapter or AC/DC converter is a type of external power supply, often enclosed in what looks like an over-sized AC plug. Other names include plug pack, plug-in adapter, adapter block, domestic mains adapter, line power adapter, or power adapter...
s: small power supplies with integral mains plug. These can contain a transformer and other circuitry. Most use a laminated iron transformer, but an increasing number now contain a small switched-mode power supply
Switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
. These are smaller and much lighter.
Halogen lighting transformers: Toroidal transformers are sometimes used for this task, but most halogen 'transformers' are switched-mode power supplies.
Transformers rely on a linear relationship between the currents in primary and secondary circuits. Interesting and useful power control devices such as the saturable reactor
Saturable reactor
A saturable reactor in electrical engineering is a special form of inductor where the magnetic core can be deliberately saturated by means of a direct electric current in a control winding...
and the magnetic amplifier
Magnetic amplifier
The magnetic amplifier is an electromagnetic device for amplifying electrical signals. The magnetic amplifier was invented early in the 20th century, and was used as an alternative to vacuum tube amplifiers where robustness and high current capacity were required...
rely on controlled saturation of a ferromagnetic core. Such devices can provide considerable power amplification without use of transistors or vacuum tubes. Although they resemble transformers with cores and sets of windings, the operating principles and purposes are different.
See also
- Polyphase systemPolyphase systemA polyphase system is a means of distributing alternating current electrical power. Polyphase systems have three or more energized electrical conductors carrying alternating currents with a definite time offset between the voltage waves in each conductor. Polyphase systems are particularly useful...
- Three-phaseThree-phaseIn electrical engineering, three-phase electric power systems have at least three conductors carrying voltage waveforms that are radians offset in time...
- Three-phase electric powerThree-phase electric powerThree-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads...
- Buck–boost transformer
- TransformerTransformerA transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
- Motor-generatorMotor-generatorA motor-generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor-generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line...

