
Rogowski coil
Encyclopedia
A Rogowski coil, named after Walter Rogowski
, is an electrical device for measuring
alternating current
(AC) or high speed current pulses. It consists of a helical
coil
of wire
with the lead
from one end returning through the centre of the coil to the other end, so that both terminal
s are at the same end of the coil. The whole assembly is then wrapped around the straight conductor whose current is to be measured. Since the voltage
that is induced in the coil is proportional to the rate of change (derivative
) of current in the straight conductor, the output of the Rogowski coil is usually connected to an electrical (or electronic) integrator
circuit in order to provide an output signal that is proportional to the current.
This type of coil has many advantages over other types of current transformer
s, the most notable being that it is not a closed loop, because the second terminal is passed back through the center of the toroid core (commonly a plastic or rubber tube) and connected along the first terminal. This allows the coil to be open-ended and flexible, allowing it to be wrapped around a live conductor without disturbing it.
Furthermore, since a Rogowski coil has an air core rather than an iron
core, it has a low inductance
and can respond to fast-changing currents. Also, because it has no iron core to saturate, it is highly linear even when subjected to large currents, such as those used in electric power transmission
, welding
, or pulsed power
applications. A correctly formed Rogowski coil, with equally spaced windings, is largely immune to electromagnetic interference
.
A good set of traditional and more recent designs of Rogowski coils can be found in US patent 6313623. In this patent there is a mention to an added purpose of the second wire returning through the center of the toroid, claiming that it helps reject interference from electrical fields present in the environment.
A device similar to the Rogowski coil was described by Arthur Prince Chattock
of Bristol University in 1887. Chattock used it to measure magnetic field
s rather than currents. The definitive description was given by Walter Rogowski and W. Steinhaus in 1912.
More recently, low-cost current sensors based on the principle of a Rogowski coil have been developed. These sensors share the principles of a Rogowski coil, measuring the rate of change of current using a transformer with no magnetic core. The difference from the traditional Rogowski coil is that the sensor can be manufactured using a planar coil rather than a toroidal coil. In order to reject the influence of conductors outside the sensor's measurement region, these planar Rogowski current sensors use a concentric coil geometry instead of a toroidal geometry to limit the response to external fields. The main advantage of the planar Rogowski current sensor is that the coil winding precision that is a requirement for accuracy can be achieved using low-cost printed circuit board
manufacturing.
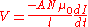 ,
,
where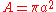 is the area of one of the small loops, N is the number of turns, and
is the area of one of the small loops, N is the number of turns, and 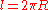 is the length of the winding.
is the length of the winding.  is the rate of change of the current threading the loop. This formula assumes the turns are evenly spaced and that these turns are small relative to the radius of the coil itself. At high frequencies, the Rogowski coil's inductance
is the rate of change of the current threading the loop. This formula assumes the turns are evenly spaced and that these turns are small relative to the radius of the coil itself. At high frequencies, the Rogowski coil's inductance
will decrease its output. The inductance of a toroid is

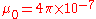 is the magnetic constant,
is the magnetic constant,  is the major radius of the toroid, and
is the major radius of the toroid, and  is its minor radius.
is its minor radius.
Walter Rogowski
Walter Rogowski was a German physicist who bridged the gap between theoretical physics and applied technology in numerous areas of electronics; the Rogowski coil was named after him....
, is an electrical device for measuring
Electrical measurements
Electrical measurements are the methods, devices and calculations used to measure electrical quantities. Measurement of electrical quantities may be done to measure electrical parameters of a system...
alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC) or high speed current pulses. It consists of a helical
Helix
A helix is a type of smooth space curve, i.e. a curve in three-dimensional space. It has the property that the tangent line at any point makes a constant angle with a fixed line called the axis. Examples of helixes are coil springs and the handrails of spiral staircases. A "filled-in" helix – for...
coil
Coil
A coil is a series of loops. A coiled coil is a structure in which the coil itself is in turn also looping.-Electromagnetic coils:An electromagnetic coil is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet...
of wire
Wire
A wire is a single, usually cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads and to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Standard sizes are determined by various...
with the lead
Lead (electronics)
In electronics, a lead is an electrical connection consisting of a length of wire or soldering pad that comes from a device. Leads are used for physical support, to transfer power, to probe circuits , and to transmit information...
from one end returning through the centre of the coil to the other end, so that both terminal
Terminal (electronics)
A terminal is the point at which a conductor from an electrical component, device or network comes to an end and provides a point of connection to external circuits. A terminal may simply be the end of a wire or it may be fitted with a connector or fastener...
s are at the same end of the coil. The whole assembly is then wrapped around the straight conductor whose current is to be measured. Since the voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
that is induced in the coil is proportional to the rate of change (derivative
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
) of current in the straight conductor, the output of the Rogowski coil is usually connected to an electrical (or electronic) integrator
Integrator
An integrator is a device to perform the mathematical operation known as integration, a fundamental operation in calculus.The integration function is often part of engineering, physics, mechanical, chemical and scientific calculations....
circuit in order to provide an output signal that is proportional to the current.
This type of coil has many advantages over other types of current transformer
Current transformer
In electrical engineering, a current transformer is used for measurement of electric currents. Current transformers, together with voltage transformers , are known as instrument transformers...
s, the most notable being that it is not a closed loop, because the second terminal is passed back through the center of the toroid core (commonly a plastic or rubber tube) and connected along the first terminal. This allows the coil to be open-ended and flexible, allowing it to be wrapped around a live conductor without disturbing it.
Furthermore, since a Rogowski coil has an air core rather than an iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
core, it has a low inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
and can respond to fast-changing currents. Also, because it has no iron core to saturate, it is highly linear even when subjected to large currents, such as those used in electric power transmission
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
, welding
Welding
Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes...
, or pulsed power
Pulsed power
Pulsed power is the term used to describe the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it very quickly thus increasing the instantaneous power.-Overview:...
applications. A correctly formed Rogowski coil, with equally spaced windings, is largely immune to electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
.
A good set of traditional and more recent designs of Rogowski coils can be found in US patent 6313623. In this patent there is a mention to an added purpose of the second wire returning through the center of the toroid, claiming that it helps reject interference from electrical fields present in the environment.
A device similar to the Rogowski coil was described by Arthur Prince Chattock
Arthur Prince Chattock
Arthur Prince Chattock, FRS was a British physicist.Chattock was educated at University College School and University College, London. After a short time as an electrical engineer for Siemens he returned to University College, London to study under George Carey Foster.In 1885 he succeeded Silvanus P...
of Bristol University in 1887. Chattock used it to measure magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s rather than currents. The definitive description was given by Walter Rogowski and W. Steinhaus in 1912.
More recently, low-cost current sensors based on the principle of a Rogowski coil have been developed. These sensors share the principles of a Rogowski coil, measuring the rate of change of current using a transformer with no magnetic core. The difference from the traditional Rogowski coil is that the sensor can be manufactured using a planar coil rather than a toroidal coil. In order to reject the influence of conductors outside the sensor's measurement region, these planar Rogowski current sensors use a concentric coil geometry instead of a toroidal geometry to limit the response to external fields. The main advantage of the planar Rogowski current sensor is that the coil winding precision that is a requirement for accuracy can be achieved using low-cost printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
manufacturing.
Formulae
The voltage produced by a Rogowski coil is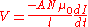 ,
,where
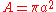 is the area of one of the small loops, N is the number of turns, and
is the area of one of the small loops, N is the number of turns, and 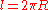 is the length of the winding.
is the length of the winding.  is the rate of change of the current threading the loop. This formula assumes the turns are evenly spaced and that these turns are small relative to the radius of the coil itself. At high frequencies, the Rogowski coil's inductance
is the rate of change of the current threading the loop. This formula assumes the turns are evenly spaced and that these turns are small relative to the radius of the coil itself. At high frequencies, the Rogowski coil's inductanceInductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
will decrease its output. The inductance of a toroid is

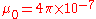 is the magnetic constant,
is the magnetic constant,  is the major radius of the toroid, and
is the major radius of the toroid, and  is its minor radius.
is its minor radius.See also
- Current
- Current transformerCurrent transformerIn electrical engineering, a current transformer is used for measurement of electric currents. Current transformers, together with voltage transformers , are known as instrument transformers...
- List of electronics topics
- Pulsed powerPulsed powerPulsed power is the term used to describe the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it very quickly thus increasing the instantaneous power.-Overview:...
- Toroidal inductors and transformersToroidal inductors and transformersToroidal inductors and transformers are electronic components, typically consisting of a circular ring-shaped magnetic core of iron powder, ferrite, or other material around which wire is coiled to make an inductor. Toroidal coils are used in a broad range of applications, such as high-frequency...
External links
- Miniature Wideband Current Probe sensor using this principle
- ABB Middle Voltage CSG/RMU uses Rogowski coil sensors
- PEM UK Rogowski current transducer theory

