
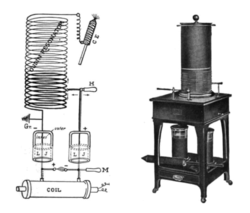
Oudin coil
Encyclopedia
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
designed to produce high voltage
High voltage
The term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements...
arcs and discharges
Corona discharge
In electricity, a corona discharge is an electrical discharge brought on by the ionization of a fluid surrounding a conductor that is electrically energized...
, similar to a Tesla coil
Tesla coil
A Tesla coil is a type of resonant transformer circuit invented by Nikola Tesla around 1891. It is used to produce high voltage, low current, high frequency alternating current electricity. Tesla coils produce higher current than the other source of high voltage discharges, electrostatic machines...
. It was invented by French physician Paul Marie Oudin
Paul Oudin
Paul Marie Oudin was a French doctor. He was born, and later died, in Épinal. He developed the "Oudin coil", which is an autotransforming resonator.-External links:*...
and physicist Jacques d'Arsonval around 1899.
The device is a high frequency
High frequency
High frequency radio frequencies are between 3 and 30 MHz. Also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decameters . Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted Medium-frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Very high frequency...
current generator
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
which uses the principles of resonant electrical circuits
Electrical resonance
Electrical resonance occurs in an electric circuit at a particular resonance frequency where the imaginary parts of circuit element impedances or admittances cancel each other...
. It produces an antinode
Node (physics)
A node is a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimal amplitude. For instance, in a vibrating guitar string, the ends of the string are nodes. By changing the position of the end node through frets, the guitarist changes the effective length of the vibrating string and thereby the...
of high potential
Potential
*In linguistics, the potential mood*The mathematical study of potentials is known as potential theory; it is the study of harmonic functions on manifolds...
. The high-voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
, self-regenerative
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit or "autodyne" allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same vacuum tube or other active component such as a field effect transistor. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback...
resonant transformer has the bottom ends of the primary and secondary coils connected together and to ground.
Oudin coils generate high voltages
High voltage
The term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements...
at high frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, but produce lower currents than other disruptive discharge coils (such as the later version of the Tesla coil
Tesla coil
A Tesla coil is a type of resonant transformer circuit invented by Nikola Tesla around 1891. It is used to produce high voltage, low current, high frequency alternating current electricity. Tesla coils produce higher current than the other source of high voltage discharges, electrostatic machines...
). The Oudin coil is modified for greater safety
Safety
Safety is the state of being "safe" , the condition of being protected against physical, social, spiritual, financial, political, emotional, occupational, psychological, educational or other types or consequences of failure, damage, error, accidents, harm or any other event which could be...
.
See also
- Violet wandViolet wandViolet wands are modern electrical sexual or kink stimulation toys. They are used for the application of low current, high voltage , high-frequency, electricity to the body...
- Tesla coilTesla coilA Tesla coil is a type of resonant transformer circuit invented by Nikola Tesla around 1891. It is used to produce high voltage, low current, high frequency alternating current electricity. Tesla coils produce higher current than the other source of high voltage discharges, electrostatic machines...
- Van de Graaff generatorVan de Graaff generatorA Van de Graaff generator is an electrostatic generator which uses a moving belt to accumulate very high voltages on a hollow metal globe on the top of the stand. It was invented in 1929 by American physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff. The potential differences achieved in modern Van de Graaff...
- Wimshurst machineWimshurst machineThe Wimshurst influence machine is an electrostatic generator, a machine for generating high voltages developed between 1880 and 1883 by British inventor James Wimshurst ....
- Static electricityStatic electricityStatic electricity refers to the build-up of electric charge on the surface of objects. The static charges remain on an object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge. Static electricity can be contrasted with current electricity, which can be delivered...
External articles
- Circuit diagram of demonstration device (Glasgow University)
- de Queiroz, Antonio Carlos M., "Oudin coil". coe.ufrj.br (image)

