
Waveform
Encyclopedia
Wave
In physics, a wave is a disturbance that travels through space and time, accompanied by the transfer of energy.Waves travel and the wave motion transfers energy from one point to another, often with no permanent displacement of the particles of the medium—that is, with little or no associated mass...
moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.
In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph of the varying quantity against time or distance. An instrument called an oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
can be used to pictorially represent a wave as a repeating image on a screen
Display device
A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form...
. By extension, the term 'waveform' also describes the shape of the graph of any varying quantity against time.
Examples of waveforms
Common periodicPeriodic function
In mathematics, a periodic function is a function that repeats its values in regular intervals or periods. The most important examples are the trigonometric functions, which repeat over intervals of length 2π radians. Periodic functions are used throughout science to describe oscillations,...
waveforms include (t is time):
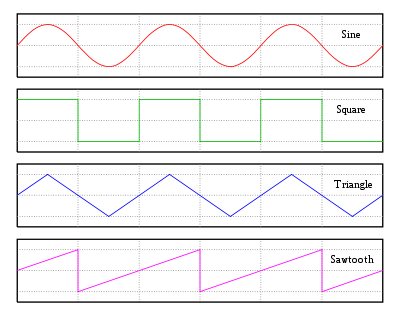
- Sine waveSine waveThe sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
: sin (2 π t). The amplitude of the waveform follows a trigonometricTrigonometryTrigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
sine function with respect to time. - Square waveSquare waveA square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
: saw(t) − saw (t − duty). This waveform is commonly used to represent digital information. A square wave of constant periodFrequencyFrequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
contains odd harmonicHarmonicA harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
s that fall off at −6 dB/octave. - Triangle waveTriangle waveA triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape.Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics...
: (t − 2 floor ((t + 1) /2)) (−1)floor ((t + 1) /2). It contains odd harmonicHarmonicA harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
s that fall off at −12 dB/octave. - Sawtooth waveSawtooth waveThe sawtooth wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is named a sawtooth based on its resemblance to the teeth on the blade of a saw....
: 2 (t − floor(t)) − 1. This looks like the teeth of a saw. Found often in time bases for display scanning. It is used as the starting point for subtractive synthesisSubtractive synthesisSubtractive synthesis is a method of sound synthesis in which partials of an audio signal are attenuated by a filter to alter the timbre of the sound...
, as a sawtooth wave of constant periodFrequencyFrequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
contains odd and even harmonicHarmonicA harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
s that fall off at −6 dBDecibelThe decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
/octave.
Other waveforms are often called composite waveforms and can often be described as a combination of a number of sinusoidal waves or other basis functions added together.
The Fourier series
Fourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
describes the decomposition of periodic waveforms, such that any periodic waveform can be formed by the sum of a (possibly infinite) set of fundamental and harmonic components. Finite-energy non-periodic waveforms can be analyzed into sinusoids by the Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
.
See also
- Electronic tunerElectronic tunerThe term electronic tuner can refer to a number of different things, depending which discipline you wish to study.In the Discipline of radio frequency electronics an electronic tuner is a device which tunes across a part of the radio frequency spectrum by the application of a voltage or appropriate...
s measure waveforms - Pulse wavePulse waveA pulse wave or pulse train is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform that is similar to a square wave, but does not have the symmetrical shape associated with a perfect square wave. It is a term common to synthesizer programming, and is a typical waveform available on many synths. The exact shape of...
- Sawtooth waveSawtooth waveThe sawtooth wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is named a sawtooth based on its resemblance to the teeth on the blade of a saw....
- Shape wavesShape wavesShape waves are excitations propagating along Josephson vortices or fluxons. In the case of two-dimensional Josephson junctions described by the 2D sine-Gordon equation, shape waves are distortions of a Josephson vortex line of an arbitrary profile...
- Sine waveSine waveThe sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
- Spectrum analyzerSpectrum analyzerA spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals...
- Square waveSquare waveA square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
- Triangle waveTriangle waveA triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape.Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics...
- WAVWAVWaveform Audio File Format , is a Microsoft and IBM audio file format standard for storing an audio bitstream on PCs...
, an audio waveform file format - Waveform monitorWaveform monitorA waveform monitor is a special type of oscilloscope used in television production applications. It is typically used to measure and display the level, or voltage, of a video signal with respect to time....
- Waveform viewerWaveform viewerA waveform viewer is a software tool for viewing the signal levels of either a digital or analog circuit design.Waveform viewers comes in two varieties:# simulation waveform viewers for displaying signal levels of simulated design models, and...
External links
- Waveform gallery of vocal sounds, including a stereo track
- Collection of single cycle waveforms sampled from various sources (Wave)

