
Tired light
Encyclopedia
Tired light is a class of hypothetical redshift
mechanisms that was proposed as an alternative explanation for the redshift-distance relationship
. These models have been proposed as alternatives to the metric expansion of space
of which the Big Bang
and the Steady State
cosmologies
are the most famous examples. The concept was first proposed in 1929 by Fritz Zwicky
, who suggested that if photons lost energy over time through collisions with other particles in a regular way, the more distant objects would appear redder than more nearby ones. Zwicky himself acknowledged that any sort of scattering
of light would blur the images of distant objects more than what is seen. Additionally, the surface brightness of galaxies evolves with time
, time dilation
of cosmological sources, and a thermal spectrum of the cosmic microwave background have been observed — these effects that should not be present if the cosmological redshift was due to any tired light scattering mechanism. Despite periodic re-examination of the concept, tired light has not been supported by observational tests and has lately been consigned to consideration only in the fringes of astrophysics.
was an idea that came about due to the observation made by Edwin Hubble
that distant galaxies
have redshift
s proportional to their distance
. Redshift is a shift in the spectrum
of the emitted electromagnetic radiation
from an object toward lower energies and frequencies, associated with the phenomenon of the Doppler Effect
. Observers of spiral nebulae such as Vesto Slipher
observed that regardless of their position in the sky, these objects (now known to be separate galaxies
) generally exhibited redshift rather than blueshifts independent of where they were located. Since the relation holds in all directions it cannot be attributed to normal movement with respect to a background which would show an assortment of redshifts and blueshifts. Everything is moving away from the Milky Way galaxy. Hubble's contribution was to show that the magnitude of the redshift correlated strongly with the distance to the galaxies.
Immediately upon publishing these results, Willem de Sitter
who was working with Einstein's Theory of General Relativity recognized that these observations fit a set of solutions to Einstein equations now collectively known as the FRW metric. The universal redshift-distance relation in this solution is attributable to the effect an expanding universe has on a photon traveling on a null spacetime interval (also known as a "light-like" geodesic
). In this formulation, there was still an analogous effect to the Doppler Effect
, though relative velocities need to be handled with more care since distances
can be defined in different ways in expanding metrics
.
At the same time, other explanations were proposed that did not concord with general relativity. Edward Milne
proposed an explanation compatible with special relativity
but not general relativity that there was a giant explosion that could explain redshifts (see Milne universe). Others proposed that systematic effects
could explain the redshift-distance correlation. Along this line, Fritz Zwicky
proposed a "tired light" mechanism in 1929. Zwicky suggested that photon
s might slowly lose energy
as they travel vast distance
s through a static universe
by interaction with matter or other photons, or by some novel physical mechanism. Since a decrease in energy
corresponds to an increase in light's wavelength
, this effect would produce a redshift
in spectral line
s that increase proportionally
with the distance of the source. The term "tired light" was coined by Richard Tolman in the early 1930s as a way to refer to this idea.
Tired light mechanisms were among the proposed alternatives to the Big Bang
and the Steady State
cosmologies
, both of which relied on the general relativistic expansion of the universe of the FRW metric. Through the middle of the twentieth century, most cosmologists supported one of these two paradigm
s, but there were a few scientists, especially those who were working on alternatives to general relativity, who worked with the tired light alternative. As the discipline of observational cosmology
developed in the late twentieth century and the associated data became more numerous and accurate, the Big Bang emerged as the cosmological theory most supported by the observational evidence, and it remains the accepted consensus model
with a current parametrization
that precisely specifies the state and evolution of the universe. Although the proposals of "tired light cosmologies" are now more-or-less relegated to the dustbin of history, as a completely alternative proposal tired-light cosmologies were considered a remote possibility worthy of some consideration in cosmology texts well into the 1980s, though it was dismissed as an unlikely and ad hoc proposal by mainstream astrophysicists.
By the 1990s and on into the twenty-first century, a number of falsifying observations have shown that "tired light" hypotheses are not viable explanations for cosmological redshifts. For example, in a static universe with tired light mechanisms, the surface brightness of stars and galaxies should be constant, that is, the farther an object is, the less light we receive, but its apparent area diminishes as well, so the light received divided by the apparent area should be constant. In an expanding universe, the surface brightness diminishes with distance. As the observed object recedes, photons are emitted at a reduced rate because each photon has to travel a distance that is a little longer than the previous one, while its energy is reduced a little because of increasing redshift at a larger distance. On the other hand, in an expanding universe, the object appears to be larger than it really is, because it was closer to us when the photons started their travel. This causes a difference in surface brilliance of objects between a static and an expanding Universe. This is known as the Tolman surface brightness test
that in those studies favors the expanding universe hypothesis and rules out static tired light models.
Redshift is directly observable and used by cosmologists as a direct measure of lookback time. They often refer to age and distance to objects in terms of redshift rather than years or light-years. In such a scale, the Big Bang
corresponds to a redshift of infinity. Alternative theories of gravity that do not have an expanding universe in them need an alternative to explain the correspondence between redshift and distance that is sui generis
to the expanding metrics
of general relativity. Such theories are sometimes referred to as "tired-light cosmologies", though not all authors are necessarily aware of the historical antecedents.
 In general, any "tired light" mechanism must solve some basic problems, in that the observed redshift must:
In general, any "tired light" mechanism must solve some basic problems, in that the observed redshift must:
A number of tired light mechanisms have been suggested over the years. Fritz Zwicky
, in his paper proposing these models investigated a number of redshift explanations, ruling out some himself. The simplest form of a tired light theory assumes an exponential decrease in photon energy with distance traveled:
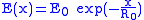
where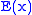 is the energy of the photon at distance
is the energy of the photon at distance  from the source of light,
from the source of light, 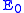 is the energy of the photon at the source of light, and
is the energy of the photon at the source of light, and 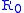 is a large constant characterizing the "resistance of the space". To correspond to Hubble's law
is a large constant characterizing the "resistance of the space". To correspond to Hubble's law
, the constant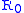 must be several gigaparsec
must be several gigaparsec
s. For example, Zwicky considered whether an integrated Compton Effect could account for the scale normalization of the above model:
This expected "blurring" of cosmologically distant objects is not seen in the observational evidence, though it would take much larger telescopes than those available at that time to show this with certainty. Alternatively, Zwicky proposed a kind of Sachs-Wolfe Effect
explanation for the redshift distance relation:
Zwicky's proposals were carefully presented as falsifiable according to later observations:
Such broadening of absorption lines is not seen in high-redshift objects, thus falsifying this particular hypothesis.
Zwicky also notes, in the same paper, that according to a tired light model a distance-redshift relationship would necessarily be present in the light from sources within our own galaxy (even if the redshift would be so small that it would be hard to measure), that do not appear under a recessional-velocity based theory. He writes, referring to sources of light within our galaxy: "It is especially desirable to determine the redshift independent of the proper velocities of the objects observed". Subsequent to this, astronomers have patiently mapped out the three-dimensional velocity-position phase space
for the galaxy and found the redshifts and blueshifts of galactic objects to accord well with the statistical distribution of a spiral galaxy, eliminating the intrinsic redshift component as an effect.
Following after Zwicky in 1935, Edwin Hubble
and Richard Tolman compared recessional redshift with a non-recessional one, writing that they:
These conditions became almost impossible to meet and the overall success of general relativistic explanations for the redshift-distance relation is one of the core reasons that the Big Bang model of the universe remains the cosmology preferred by researchers.
In the early 1950s, Erwin Finlay-Freundlich
proposed a redshift as "the result of loss of energy by observed photons traversing a radiation field." which was cited and argued for as an explanation for the redshift-distance relation in a 1962 astrophysics theory Nature
paper by University of Manchester
physics professor P. F. Browne. The pre-eminent cosmologist Ralph Asher Alpher
wrote a letter to Nature three months later in response to this suggestion heavily criticizing the approach, "No generally accepted physical mechanism has been proposed for this loss," Still, until the so-called "Age of Precision Cosmology" was ushered in with results from the WMAP space probe and modern redshift survey
s, tired light models could occasionally get published in the mainstream journals, including one that was published in the February 1979 edition of Nature proposing "photon decay" in a curved spacetime that was five months later criticized in the same journal as being wholly inconsistent with observations of the gravitational redshift
observed in the solar limb
.. In 1986 a paper claiming tired light theories explained redshift better than cosmic expansion was published in the Astrophysical Journal. As cosmological measurements became more precise and the statistics in cosmological data sets improved, tired light proposals ended up being falsified, to the extent that the theory was described in 2001 by science writer Charles Seife
as being "firmly on the fringe of physics 30 years ago", however tired light theories still appear occasionally in speculative journals.
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
mechanisms that was proposed as an alternative explanation for the redshift-distance relationship
Hubble's law
Hubble's law is the name for the astronomical observation in physical cosmology that: all objects observed in deep space are found to have a doppler shift observable relative velocity to Earth, and to each other; and that this doppler-shift-measured velocity, of various galaxies receding from...
. These models have been proposed as alternatives to the metric expansion of space
Metric expansion of space
The metric expansion of space is the increase of distance between distant parts of the universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion—that is, it is defined by the relative separation of parts of the universe and not by motion "outward" into preexisting space...
of which the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
and the Steady State
Steady State theory
In cosmology, the Steady State theory is a model developed in 1948 by Fred Hoyle, Thomas Gold, Hermann Bondi and others as an alternative to the Big Bang theory...
cosmologies
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
are the most famous examples. The concept was first proposed in 1929 by Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky was a Swiss astronomer. He worked most of his life at the California Institute of Technology in the United States of America, where he made many important contributions in theoretical and observational astronomy.- Biography :Fritz Zwicky was born in Varna, Bulgaria to a Swiss father....
, who suggested that if photons lost energy over time through collisions with other particles in a regular way, the more distant objects would appear redder than more nearby ones. Zwicky himself acknowledged that any sort of scattering
Scattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
of light would blur the images of distant objects more than what is seen. Additionally, the surface brightness of galaxies evolves with time
Tolman surface brightness test
The Tolman surface brightness test is one out of a half-dozen cosmological tests that was conceived in the 1930s to check the viability of and compare new cosmological models. Tolman's test compares the surface brightness of galaxies as a function of their redshift . Such a comparison was first...
, time dilation
Time dilation
In the theory of relativity, time dilation is an observed difference of elapsed time between two events as measured by observers either moving relative to each other or differently situated from gravitational masses. An accurate clock at rest with respect to one observer may be measured to tick at...
of cosmological sources, and a thermal spectrum of the cosmic microwave background have been observed — these effects that should not be present if the cosmological redshift was due to any tired light scattering mechanism. Despite periodic re-examination of the concept, tired light has not been supported by observational tests and has lately been consigned to consideration only in the fringes of astrophysics.
History and reception
Tired lightLight
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
was an idea that came about due to the observation made by Edwin Hubble
Edwin Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble was an American astronomer who profoundly changed the understanding of the universe by confirming the existence of galaxies other than the Milky Way - our own galaxy...
that distant galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
have redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
s proportional to their distance
Distance measures (cosmology)
Distance measures are used in physical cosmology to give a natural notion of the distance between two objects or events in the universe. They are often used to tie some observable quantity to another quantity that is not directly...
. Redshift is a shift in the spectrum
Astronomical spectroscopy
Astronomical spectroscopy is the technique of spectroscopy used in astronomy. The object of study is the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other celestial objects...
of the emitted electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
from an object toward lower energies and frequencies, associated with the phenomenon of the Doppler Effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
. Observers of spiral nebulae such as Vesto Slipher
Vesto Slipher
Vesto Melvin Slipher was an American astronomer. His brother Earl C. Slipher was also an astronomer and a director at the Lowell Observatory....
observed that regardless of their position in the sky, these objects (now known to be separate galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
) generally exhibited redshift rather than blueshifts independent of where they were located. Since the relation holds in all directions it cannot be attributed to normal movement with respect to a background which would show an assortment of redshifts and blueshifts. Everything is moving away from the Milky Way galaxy. Hubble's contribution was to show that the magnitude of the redshift correlated strongly with the distance to the galaxies.
Immediately upon publishing these results, Willem de Sitter
Willem de Sitter
Willem de Sitter was a Dutch mathematician, physicist and astronomer.-Life and work:Born in Sneek, De Sitter studied mathematics at the University of Groningen and then joined the Groningen astronomical laboratory. He worked at the Cape Observatory in South Africa...
who was working with Einstein's Theory of General Relativity recognized that these observations fit a set of solutions to Einstein equations now collectively known as the FRW metric. The universal redshift-distance relation in this solution is attributable to the effect an expanding universe has on a photon traveling on a null spacetime interval (also known as a "light-like" geodesic
Geodesic
In mathematics, a geodesic is a generalization of the notion of a "straight line" to "curved spaces". In the presence of a Riemannian metric, geodesics are defined to be the shortest path between points in the space...
). In this formulation, there was still an analogous effect to the Doppler Effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
, though relative velocities need to be handled with more care since distances
Comoving distance
In standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects...
can be defined in different ways in expanding metrics
Metric expansion of space
The metric expansion of space is the increase of distance between distant parts of the universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion—that is, it is defined by the relative separation of parts of the universe and not by motion "outward" into preexisting space...
.
At the same time, other explanations were proposed that did not concord with general relativity. Edward Milne
Edward Milne
Edward Milne may refer to:*Edward Arthur Milne , British mathematician and astrophysicist*Eddie Milne , British Labour Party Member of Parliament for Blyth, afterwards re-elected as an independent...
proposed an explanation compatible with special relativity
Special relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
but not general relativity that there was a giant explosion that could explain redshifts (see Milne universe). Others proposed that systematic effects
Systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of terrestrial life, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees...
could explain the redshift-distance correlation. Along this line, Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky was a Swiss astronomer. He worked most of his life at the California Institute of Technology in the United States of America, where he made many important contributions in theoretical and observational astronomy.- Biography :Fritz Zwicky was born in Varna, Bulgaria to a Swiss father....
proposed a "tired light" mechanism in 1929. Zwicky suggested that photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s might slowly lose energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
as they travel vast distance
Distance
Distance is a numerical description of how far apart objects are. In physics or everyday discussion, distance may refer to a physical length, or an estimation based on other criteria . In mathematics, a distance function or metric is a generalization of the concept of physical distance...
s through a static universe
Static universe
A static universe, also referred to as a "stationary" or "Einstein" universe, is a model in which space is neither expanding nor contracting. Albert Einstein proposed such a model as his preferred cosmology in 1917...
by interaction with matter or other photons, or by some novel physical mechanism. Since a decrease in energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
corresponds to an increase in light's wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
, this effect would produce a redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
in spectral line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
s that increase proportionally
Proportionality (mathematics)
In mathematics, two variable quantities are proportional if one of them is always the product of the other and a constant quantity, called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. In other words, are proportional if the ratio \tfrac yx is constant. We also say that one...
with the distance of the source. The term "tired light" was coined by Richard Tolman in the early 1930s as a way to refer to this idea.
Tired light mechanisms were among the proposed alternatives to the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
and the Steady State
Steady State theory
In cosmology, the Steady State theory is a model developed in 1948 by Fred Hoyle, Thomas Gold, Hermann Bondi and others as an alternative to the Big Bang theory...
cosmologies
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
, both of which relied on the general relativistic expansion of the universe of the FRW metric. Through the middle of the twentieth century, most cosmologists supported one of these two paradigm
Paradigm
The word paradigm has been used in science to describe distinct concepts. It comes from Greek "παράδειγμα" , "pattern, example, sample" from the verb "παραδείκνυμι" , "exhibit, represent, expose" and that from "παρά" , "beside, beyond" + "δείκνυμι" , "to show, to point out".The original Greek...
s, but there were a few scientists, especially those who were working on alternatives to general relativity, who worked with the tired light alternative. As the discipline of observational cosmology
Observational cosmology
Observational cosmology is the study of the structure, the evolution and the origin of the universe through observation, using instruments such as telescopes and cosmic ray detectors.-Early observations:...
developed in the late twentieth century and the associated data became more numerous and accurate, the Big Bang emerged as the cosmological theory most supported by the observational evidence, and it remains the accepted consensus model
Scientific consensus
Scientific consensus is the collective judgment, position, and opinion of the community of scientists in a particular field of study. Consensus implies general agreement, though not necessarily unanimity. Scientific consensus is not by itself a scientific argument, and it is not part of the...
with a current parametrization
Lambda-CDM model
ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM is an abbreviation for Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, which is also known as the cold dark matter model with dark energy...
that precisely specifies the state and evolution of the universe. Although the proposals of "tired light cosmologies" are now more-or-less relegated to the dustbin of history, as a completely alternative proposal tired-light cosmologies were considered a remote possibility worthy of some consideration in cosmology texts well into the 1980s, though it was dismissed as an unlikely and ad hoc proposal by mainstream astrophysicists.
By the 1990s and on into the twenty-first century, a number of falsifying observations have shown that "tired light" hypotheses are not viable explanations for cosmological redshifts. For example, in a static universe with tired light mechanisms, the surface brightness of stars and galaxies should be constant, that is, the farther an object is, the less light we receive, but its apparent area diminishes as well, so the light received divided by the apparent area should be constant. In an expanding universe, the surface brightness diminishes with distance. As the observed object recedes, photons are emitted at a reduced rate because each photon has to travel a distance that is a little longer than the previous one, while its energy is reduced a little because of increasing redshift at a larger distance. On the other hand, in an expanding universe, the object appears to be larger than it really is, because it was closer to us when the photons started their travel. This causes a difference in surface brilliance of objects between a static and an expanding Universe. This is known as the Tolman surface brightness test
Tolman surface brightness test
The Tolman surface brightness test is one out of a half-dozen cosmological tests that was conceived in the 1930s to check the viability of and compare new cosmological models. Tolman's test compares the surface brightness of galaxies as a function of their redshift . Such a comparison was first...
that in those studies favors the expanding universe hypothesis and rules out static tired light models.
Redshift is directly observable and used by cosmologists as a direct measure of lookback time. They often refer to age and distance to objects in terms of redshift rather than years or light-years. In such a scale, the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
corresponds to a redshift of infinity. Alternative theories of gravity that do not have an expanding universe in them need an alternative to explain the correspondence between redshift and distance that is sui generis
Sui generis
Sui generis is a Latin expression, literally meaning of its own kind/genus or unique in its characteristics. The expression is often used in analytic philosophy to indicate an idea, an entity, or a reality which cannot be included in a wider concept....
to the expanding metrics
Metric expansion of space
The metric expansion of space is the increase of distance between distant parts of the universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion—that is, it is defined by the relative separation of parts of the universe and not by motion "outward" into preexisting space...
of general relativity. Such theories are sometimes referred to as "tired-light cosmologies", though not all authors are necessarily aware of the historical antecedents.
Specific falsified models

- admit the same measurement in any wavelength-band
- not exhibit blurring
- follow the detailed Hubble relation observed with supernovaSupernovaA supernova is a stellar explosion that is more energetic than a nova. It is pronounced with the plural supernovae or supernovas. Supernovae are extremely luminous and cause a burst of radiation that often briefly outshines an entire galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months...
data (see accelerating universeAccelerating universeThe accelerating universe is the observation that the universe appears to be expanding at an increasing rate, which in formal terms means that the cosmic scale factor a has a positive second derivative, implying that the velocity at which a given galaxy is receding from us should be continually...
) - explain associated time dilationTime dilationIn the theory of relativity, time dilation is an observed difference of elapsed time between two events as measured by observers either moving relative to each other or differently situated from gravitational masses. An accurate clock at rest with respect to one observer may be measured to tick at...
of cosmologically distant events.
A number of tired light mechanisms have been suggested over the years. Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky was a Swiss astronomer. He worked most of his life at the California Institute of Technology in the United States of America, where he made many important contributions in theoretical and observational astronomy.- Biography :Fritz Zwicky was born in Varna, Bulgaria to a Swiss father....
, in his paper proposing these models investigated a number of redshift explanations, ruling out some himself. The simplest form of a tired light theory assumes an exponential decrease in photon energy with distance traveled:
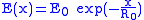
where
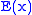 is the energy of the photon at distance
is the energy of the photon at distance  from the source of light,
from the source of light, 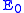 is the energy of the photon at the source of light, and
is the energy of the photon at the source of light, and 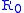 is a large constant characterizing the "resistance of the space". To correspond to Hubble's law
is a large constant characterizing the "resistance of the space". To correspond to Hubble's lawHubble's law
Hubble's law is the name for the astronomical observation in physical cosmology that: all objects observed in deep space are found to have a doppler shift observable relative velocity to Earth, and to each other; and that this doppler-shift-measured velocity, of various galaxies receding from...
, the constant
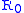 must be several gigaparsec
must be several gigaparsecParsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
s. For example, Zwicky considered whether an integrated Compton Effect could account for the scale normalization of the above model:
This expected "blurring" of cosmologically distant objects is not seen in the observational evidence, though it would take much larger telescopes than those available at that time to show this with certainty. Alternatively, Zwicky proposed a kind of Sachs-Wolfe Effect
Sachs-Wolfe effect
The Sachs–Wolfe effect, named after Rainer Kurt Sachs and Arthur Michael Wolfe, is a property of the cosmic microwave background radiation , in which photons from the CMB are gravitationally redshifted, causing the CMB spectrum to appear uneven...
explanation for the redshift distance relation:
Zwicky's proposals were carefully presented as falsifiable according to later observations:
Such broadening of absorption lines is not seen in high-redshift objects, thus falsifying this particular hypothesis.
Zwicky also notes, in the same paper, that according to a tired light model a distance-redshift relationship would necessarily be present in the light from sources within our own galaxy (even if the redshift would be so small that it would be hard to measure), that do not appear under a recessional-velocity based theory. He writes, referring to sources of light within our galaxy: "It is especially desirable to determine the redshift independent of the proper velocities of the objects observed". Subsequent to this, astronomers have patiently mapped out the three-dimensional velocity-position phase space
Phase space
In mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
for the galaxy and found the redshifts and blueshifts of galactic objects to accord well with the statistical distribution of a spiral galaxy, eliminating the intrinsic redshift component as an effect.
Following after Zwicky in 1935, Edwin Hubble
Edwin Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble was an American astronomer who profoundly changed the understanding of the universe by confirming the existence of galaxies other than the Milky Way - our own galaxy...
and Richard Tolman compared recessional redshift with a non-recessional one, writing that they:
These conditions became almost impossible to meet and the overall success of general relativistic explanations for the redshift-distance relation is one of the core reasons that the Big Bang model of the universe remains the cosmology preferred by researchers.
In the early 1950s, Erwin Finlay-Freundlich
Erwin Finlay-Freundlich
Erwin Finlay-Freundlich was a German astronomer, a pupil of Felix Klein. He was born in Biebrich, Germany. Freundlich was a working associate of Albert Einstein and introduced experiments for which the general theory of relativity could be tested by astronomical observations based on the...
proposed a redshift as "the result of loss of energy by observed photons traversing a radiation field." which was cited and argued for as an explanation for the redshift-distance relation in a 1962 astrophysics theory Nature
Nature (journal)
Nature, first published on 4 November 1869, is ranked the world's most cited interdisciplinary scientific journal by the Science Edition of the 2010 Journal Citation Reports...
paper by University of Manchester
University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public research university located in Manchester, United Kingdom. It is a "red brick" university and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive British universities and the N8 Group...
physics professor P. F. Browne. The pre-eminent cosmologist Ralph Asher Alpher
Ralph Asher Alpher
Ralph Asher Alpher was an American cosmologist.- Childhood and education :Alpher was the son of a Russian Jewish immigrant, Samuel Alpher, from Vitebsk, Russia. His mother, Rose, died of stomach cancer in 1938 and his father later remarried...
wrote a letter to Nature three months later in response to this suggestion heavily criticizing the approach, "No generally accepted physical mechanism has been proposed for this loss," Still, until the so-called "Age of Precision Cosmology" was ushered in with results from the WMAP space probe and modern redshift survey
Redshift survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey, or galaxy survey, is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to calculate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift...
s, tired light models could occasionally get published in the mainstream journals, including one that was published in the February 1979 edition of Nature proposing "photon decay" in a curved spacetime that was five months later criticized in the same journal as being wholly inconsistent with observations of the gravitational redshift
Gravitational redshift
In astrophysics, gravitational redshift or Einstein shift describes light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation of certain wavelengths that originate from a source that is in a region of a stronger gravitational field that appear to be of longer wavelength, or redshifted, when seen or...
observed in the solar limb
Limb darkening
Limb darkening refers to the diminishing of intensity in the image of a star as one moves from the center of the image to the edge or "limb" of the image...
.. In 1986 a paper claiming tired light theories explained redshift better than cosmic expansion was published in the Astrophysical Journal. As cosmological measurements became more precise and the statistics in cosmological data sets improved, tired light proposals ended up being falsified, to the extent that the theory was described in 2001 by science writer Charles Seife
Charles Seife
Charles Seife is an American author, journalist and professor.His first published book was Zero: The Biography of a Dangerous Idea. He had written within the scientific community for years before this, having done freelance work for New Scientist, Scientific American, The Economist, Science, Wired...
as being "firmly on the fringe of physics 30 years ago", however tired light theories still appear occasionally in speculative journals.

