Limb darkening
Encyclopedia

- The density of the star diminishes as the distance from the center increases
- The temperature of the star diminishes as the distance from the center increases.
Crucial to understanding limb darkening is the idea of optical depth
Optical depth
Optical depth, or optical thickness, is a measure of transparency. Optical depth is defined by the negative logarithm of the fraction of radiation that is not scattered or absorbed on a path...
. An optical
depth of unity is that thickness of absorbing gas from which a fraction of 1/e
E (mathematical constant)
The mathematical constant ' is the unique real number such that the value of the derivative of the function at the point is equal to 1. The function so defined is called the exponential function, and its inverse is the natural logarithm, or logarithm to base...
photons can escape. This is what defines the visible edge of a star since it is at an optical depth of unity that the star becomes opaque. The radiation reaching us is closely approximated by the sum of all the emission along the entire line of sight, up to that point where the optical depth is unity. When we look near the edge of a star, we cannot "see" to the same depth as when we look at the center because the line of sight must travel at an oblique angle through the stellar gas when looking near the limb. In other words, the solar radius at which we see the optical depth as being unity increases as we move our line of sight towards the limb.
The second effect is the fact that the effective temperature
Effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation...
of the stellar atmosphere is (usually) decreasing for an increasing distance from the center of the star. The radiation emitted from a gas is a strongly increasing function of temperature. For a black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
, for example, the spectrally integrated intensity is proportional to the fourth power of the temperature (Stefan-Boltzmann law). Since when we look at a star, at first approximation the radiation comes from the point at which the optical depth is unity, and that point is deeper in when looking at the center, the temperature will be higher, and the intensity will be greater, than when we look at the limb.
In fact, the temperature in the atmosphere of a star does not always decrease with increasing height, and for certain spectral line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
s, the optical depth is unity in a region of increasing temperature. In this case we see the phenomenon of "limb brightening".
At very long (IR to radio) and very short (EUV to X-ray) wavelengths the situation becomes much more complicated.
A coronal emission such as soft X-radiation will be optically thin
Optical depth
Optical depth, or optical thickness, is a measure of transparency. Optical depth is defined by the negative logarithm of the fraction of radiation that is not scattered or absorbed on a path...
and thus be characteristically limb-brightened.
Further complication comes from the existence of rough (three-dimensional) structure.
The classical analysis of stellar limb darkening, as described below, assumes the existence of a smooth hydrostatic equilibrium, and at some level of precision this assumption must fail (most obviously in sunspots and faculae, but generally everywhere).
The analysis of these effects is presently in its infancy because of its computational difficulty [1].
Calculation of limb darkening
In the figure on the right, as long as the observer at point P is outside the stellar atmosphere,the intensity seen in the direction θ will be a function only of the angle of incidence
ψ. This is most conveniently approximated as a polynomial in cos(ψ)
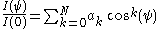
where I(ψ) is the intensity seen at P along a line of sight forming angle
ψ with respect to the stellar radius, and I(0) is the central intensity.
It can be seen that in order that the ratio be unity for ψ=0, we must have:
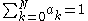
For example, for a Lambertian
Lambert's cosine law
In optics, Lambert's cosine law says that the radiant intensity observed from a Lambertian surface or a Lambertian radiator is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle θ between the observer's line of sight and the surface normal. A Lambertian surface is also known as an ideal diffusely...
radiator (no limb darkening) we will have all ak=0 except a0=1. As another example, for the sun at 550 nm, the limb darkening is well expressed by N=2 and
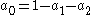
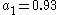

(See Cox, 2000). Note - the equation for limb darkening is sometimes more conveniently written as:
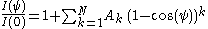
which now has N independent coefficients rather than N+1 coefficients which must sum to unity.
We can convert from ψ to θ using the relationship:
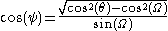
where Ω is the angle from the observer to the limb of the star.
The above approximation can be used to derive an analytic expression for the ratio of
the mean intensity to the central intensity. The mean intensity Im is the integral of the intensity over the disk of the star divided by the solid angle subtended by the disk:
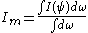
where dω=sin(θ)dθdφ is a solid angle element and the integrals are
over the disk: 0≤φ≤2π and 0≤θ≤Ω. Although this equation
can be solved analytically, it is rather cumbersome. However, for an observer at infinite distance from the star, the above equation simplifies to: