
Reward dependence
Encyclopedia
In psychology
, Reward Dependence (RD) is a moderately heritable personality trait which is stable throughout life. It is an inherited neurophysiological mechanism that drives our perception of the environment and society. Even though we are born with these personality traits, the full expression of them can be modulated during development with the right approach.
 RD is characterized as a tendency to respond intensely to signals of reward
RD is characterized as a tendency to respond intensely to signals of reward
, particularly to verbal signals of social approval, sentiment, and social support , and learning to maintain and pursue behaviors which were previously associated with such rewards . When Reward Dependence levels deviate from normal we see the rise of several personality and addictive disorders.
dimensions from the “tridimensional personality theory”
, which was proposed by C. Robert Cloninger
as part of his “unified bio-social theory of personality” . His personality theory suggested the hypothesis that specific neurochemical transmitters
determine specific stimulus–response characteristics.
These innate personality traits can play a significant role not only in an individuals' predisposition to certain disorders, but also in their maintenance of those disorders.
By understanding the specific temperamental traits that are common among individuals with specific disorders, clinicians can form a more targeted, informed approach to treatment and look to newer psychotherapies for guidance. The relationship between temperament and individual clusters of DSM
personality disorders is often investigated. According to the DSM-IV , the tridimensional structure allows up to nine major personality disorders
to be identified, the theory thereby making a great contribution to the understanding of psychiatric disorders.
 Cloninger’s tridimensional personality theory offered three independent “temperament” dimensions by which individual differences in how people feel, act or behave can be measured. RD is one of the three temperament dimensions, the other two being “Harm Avoidance (HA)”
Cloninger’s tridimensional personality theory offered three independent “temperament” dimensions by which individual differences in how people feel, act or behave can be measured. RD is one of the three temperament dimensions, the other two being “Harm Avoidance (HA)”
and “Novelty Seeking (NS)”
. A temperament, according to Cloninger, is the automatic emotional response to experience .
Cloninger suggested that RD is influenced by a single monoamine neurotransmitter
system: the noradrenergic
system and reward dependence is correlated with low basal noradrenergic activity. This suggestion has led to several research experiments that have investigated and supported his hypothesis, that reward dependence traits are indeed in part determined by norepinephrine.
Measure of the Reward Dependence dimension, as suggested by Cloninger, is used to assess the Altruistic-warm versus detached-tough mindedness components of our personalities. The RD dimension reflects on the highs and lows of the positive-gratifying pleasure valence.
According to Cloninger’s theory, individuals high in Reward Dependence and low in norepinephrine levels are ambitious, warm, sentimental, pleasant, sociable, sensitive, sympathetic and socially dependent. One of the major adaptive advantages of high RD is the sensitivity to social cues which facilitates affectionate social relations, genuine care for others and communication. The disadvantage is related to suggestibility
and loss of objectivity frequently encountered with people who are excessively socially dependent. These individuals also exhibit persistent behaviors and are easily influenced by emotional appeals.
Individuals low in Reward Dependence and high in norepinephrine levels are hypothesized to be typically independent, non-conformist, practical, tough-minded, cynical, unwilling to share their intimate feelings with others, socially detached, irresolute, insensitive to social cues and pressures, and content to be alone. They are also minimally motivated to please others and act for immediate gratification. So being low in RD is related to social withdrawal, with aggressive anti-social behavior, detachment, and coldness in social attitudes.
The Reward Dependence temperament interacts with other temperaments and characters inherent in us enabling us to adapt to life experiences and influence susceptibility to emotional and behavioral disorders
(TPQ) personality test and by the newer and refined version of the personality test called Temperament and Character Inventory
(TCI) and its revised version (TCI-R). Owing to the limitations encountered in the TPQ, in that the three dimensions’ clinical utility was not readily apparent to many clinicians, Cloninger revamped the questionnaire and produced the TCI scale, which incorporates four dimensions of “temperament” and three dimensions of “character”.
The so-called subscales of reward dependence in TCI-R are
maintenance System (BMS) . Norepinephrine
(NE), apart from producing alertness and arousal, is seen as influencing the brain reward system. Norepinephrine aids in the learning of new paired associations.
According to Cloninger, the norepinephrine neurotransmitter has its major ascending pathways arising in the locus coeruleus in the pons
, projecting onward to the hypothalamic
and limbic structures
, and then branching upwards to the neocortex
.
Reward dependence has been linked to "dissociable connectivity streams" in the brain. Striatal projections
and Tracts between prefrontal cortex
predict the individual differences in reward processing, reward dependence and reward-guided behaviors . These findings suggest that personality traits may be affected by the strength of limbic-striatal connectivity. High RD is characterized by learning from reward signals, persisting repetition of actions that are associated with rewards, increased sociability and a need for social approval. The striatum, especially the dorsal regions
, is necessary to carry out these functions. .
Using Positron Emission Tomography
(PET) researchers have shown that Reward dependence is the only temperament dimension strongly correlated with opiate receptor binding (the endorphine system) and that positive correlation is restricted to the bilateral ventral striatum
, which is considered the key area of the human reward system and of the development of addictive behavior
. This correlation means that people with high reward dependence have a high concentration of opiate receptors present in that area, while people with low dependence have fewer receptors. The subjects who felt a high need for social approval were also those with the highest uptake of opiates in the reward system. This finding demonstrates that elevated opiate receptors in the ventral striatum could be a biologic link between personality traits and dependence
risk. According to the researchers, this novel finding will provide a deeper understanding of the functional relationship between human personality, neurobiology, and substance abuse
and other addictive behaviors.
 fMRI studies have shown that individuals with less developed inferior part of the frontal lobe
fMRI studies have shown that individuals with less developed inferior part of the frontal lobe
around the midline inner surface of the brain, showed greater reward dependence. People with social reward dependence personalities were also seen to have brains with far less tissue in the fronto-striatal
section of the brain (e.g. damage to the fronto-striatal area is often linked to autism
and schizophrenia
). Relationship between concentration of grey matter
(brain-cell containing tissue) in different brain regions and social reward dependence was also studied. It was found that the greater the concentration of tissue in the orbitofrontal cortex
(the outer strip of the brain just above the eyes), and in the ventral striatum (a deep structure in the centre of the brain), the higher they tended to score on the social RD measure. The researchers warn that these studies are only correlational and cross-sectional
and none of this research is definitive in proving that brain structure determines personality but it could be that personality, through experience, may help in determining the structure of the brain.
Social Reward Dependence has also been associated with temporal lobes
, the caudate
Grey Matter Density (GMD) in the orbitofrontal cortex and the basal ganglia
of the ventral striatum : structures, which are rich in dopamine
receptors, already known to play a crucial role in reward receipt, Incentive anticipation
and error in prediction of simple and discrete primary and secondary rewards. These significant findings showed a correlation between primary reward processing regions and reward dependence, keeping with the fMRI research studies that demonstrate that the striatum is activated following the experience of complex rewards.
Primary reward processing has also been associated with the orbitofrontal cortex and the grey matter density in the ventral striatum, whereas higher reward dependence scores were associated with the interactions between dopamine projections, neuropeptides and opiates in the ventral striatum. It is demonstrated here, then, that there is evidence for a structural disposition of the brain towards social interactions, and that both primary reward processing and sensitivity to social reward cues share the same brain systems.
In addition to these findings, the bilateral temporal poles were also identified in which gray matter density correlated with RD. The orbitofrontal cortex and medial prefrontal cortex, in addition to other temporal structures, project to the temporal pole, enabling these regions to integrate reward-related information between frontal and temporal regions. In an fMRI study, the temporal poles and the ventral striatal areas have been shown to be activated in response to social rewards (such as humor) and also in looking forward to simpler rewards (such as money).
of the RD temperament could cause psychiatric illnesses, such as addictive behaviors
, sociopathies
, and personality disorders
.
Low levels of norepinephrine cause an increase in Reward Dependence. When produced in normal levels, norepinephrine creates a sense of well-being, but low levels of norepinephrine cause symptoms of depression
, lack of arousal
and lack of motivation
. In humans, this leads to then a negative feedback
mechanism whereby we seek out pleasurable activities to remove the negative affect
caused by the low levels of norepinephrine, therefore increasing our Reward Dependence.
An increase in the Reward Dependence temperament leads us to seek out those behaviors or substances that will allow us to remain in a pleasant physical and/or mental state, based on the hedonistic
principle that people seek pleasure and avoid pain . Our pleasure and reward systems in the brain are hyper-activated, which makes us display continuous approach behaviors to the reward in question. Our neuro-circuity is as such that when we stop having access to such pleasurable objects of desire, we then experience negative consequences (withdrawal
symptoms). Addictive behaviors then arise to alleviate such negative consequences and the cycle continues.
. Knowing that someone has such a predisposition could help them to adopt preventive strategies and avoid situations where they might seek rewards which could be potentially harmful. Reward dependence drives behavior maintenance systems, and in addictive behaviors, maintenance of behaviors occurs despite adverse consequences.
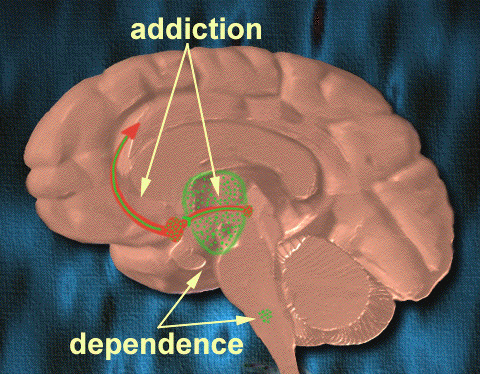 According to researchers the biological purpose of the human reward system is to initiate behavior essential for the maintenance of the individual - for example, food intake - or maintenance of the species - for example, reproduction. Therefore, food or sexual stimuli lead to an opioid
According to researchers the biological purpose of the human reward system is to initiate behavior essential for the maintenance of the individual - for example, food intake - or maintenance of the species - for example, reproduction. Therefore, food or sexual stimuli lead to an opioid
-modulated dopamine release in core structures of the reward system and subsequently induce the sensation of craving
. Modern addiction research maintains that genetic or acquired abuses of the reward system are the central basis for the development of addictive behavior. This latest finding suggests that individuals suffering from a relative endorphin deficit in their reward system show increased reward dependence and are probably more at risk for developing addictions.
Adolescents
low in reward dependence may find conventional sources of reward unfulfilling (e.g., academic achievement or activities involving social affiliation), and eventually turn to unconventional reward sources (e.g., smoking
and other forms of substance misuse) to derive satisfaction and pleasure. A study conducted using adolescents with Excessive Internet video Game Play (EIGP) showed that such addictive behaviors were correlated with higher RD scores on the TCI , whereas both low and high scores of RD were implicated in specific alcoholic and drug addictions.
and attachment as a personality dimension. It is suggested that the brain substrates that are involved in learning and signaling about simple primary rewards are also implicated in the brain’s response to more complex social rewards. The RD sub-scale from the TCI inventory measures how sensitive individuals are to social rewards. High RD scores on the test correlate to increased attachment and an increased need for social relationships. Low RD scores show a movement towards social detachment and insensitivity.
At the 2010 Annual meeting of the American Psychological Association
(APA), a study looking at treatment methods of personality disorders was presented in which it was found, that panic disorder patients with higher Reward Dependence scores were more resistant to Escitalopram
treatment. Since long-term pharmacotherapy
is needed for treatment of panic disorder, the present results suggest that development of therapeutic strategy for panic patients with high reward dependence is needed.
, individuals with high reward dependence are susceptible to compensatory noradrenergic hyperactivity. Hence acute or recurrent states of agitated dysphoria
associated with reward-seeking behaviors, such as overeating and increased sexual activity, are prevalent in these individuals.
Individuals with higher reward dependence also look for more social approval, and are more inclined to succumb to peer-pressure. They often become overly concerned about their body image
and maybe prone to eating disorders, such a Bulimia nervosa
. Whereas restricting anorexia
, in particular, tends to reflect low reward dependence.
Reward dependence is not consistently associated with diagnosis but can significantly affect treatment issues, such as Therapeutic alliance. Persistence in completing weight-loss programs
were related to pretreatment high reward dependence scores. Thus showing that, having a tendency toward being sociable, dedicated and highly responsive to social pressure reduced the risk of dropout in this behavioral weight-loss program.
(CSF) levels of the norepinephrine (NE) metabolite 3-methoq-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MI-IPG). This could suggest a relationship between gambling and norepinephrine, and so gambling could be viewed as a reward-dependent behavior, although Cloninger’s theory would predict that CSF MHPG should have been low, not high. Cloninger speculated that these gamblers might have shown a reduction of NE and its metabolites if they had been reexamined after a period of abstinence from gambling . A study of alcoholics showed a significant negative correlation of the level of MHPG in CSF to a score of alcohol-dependent drinking patterns. This correlation is consistent with a relationship between NE and reward dependence.
Several genes have also been found to express the Reward dependence dimension. Specifically, the gene MAOA-uVNTR has been highly implicated in evoking the RD personality trait.
Psychology
Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society...
, Reward Dependence (RD) is a moderately heritable personality trait which is stable throughout life. It is an inherited neurophysiological mechanism that drives our perception of the environment and society. Even though we are born with these personality traits, the full expression of them can be modulated during development with the right approach.

Reward system
In neuroscience, the reward system is a collection of brain structures which attempts to regulate and control behavior by inducing pleasurable effects...
, particularly to verbal signals of social approval, sentiment, and social support , and learning to maintain and pursue behaviors which were previously associated with such rewards . When Reward Dependence levels deviate from normal we see the rise of several personality and addictive disorders.
History
Reward Dependence is one of the temperamentTemperament
In psychology, temperament refers to those aspects of an individual's personality, such as introversion or extroversion, that are often regarded as innate rather than learned...
dimensions from the “tridimensional personality theory”
Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire
Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire is a personality test.It was devised by C. Robert Cloninger.A newer version of the questionnaire is called Temperament and Character Inventory....
, which was proposed by C. Robert Cloninger
C. Robert Cloninger
Claude Robert Cloninger, M.D. is a psychiatrist and geneticist noted for his pioneering research on the biological, psychological, social, and spiritual foundation of both mental health and mental illness. He is Wallace Renard Professor of Psychiatry, Professor of Psychology and of Genetics, and...
as part of his “unified bio-social theory of personality” . His personality theory suggested the hypothesis that specific neurochemical transmitters
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
determine specific stimulus–response characteristics.
These innate personality traits can play a significant role not only in an individuals' predisposition to certain disorders, but also in their maintenance of those disorders.
By understanding the specific temperamental traits that are common among individuals with specific disorders, clinicians can form a more targeted, informed approach to treatment and look to newer psychotherapies for guidance. The relationship between temperament and individual clusters of DSM
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is published by the American Psychiatric Association and provides a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders...
personality disorders is often investigated. According to the DSM-IV , the tridimensional structure allows up to nine major personality disorders
Personality disorder
Personality disorders, formerly referred to as character disorders, are a class of personality types and behaviors. Personality disorders are noted on Axis II of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders or DSM-IV-TR of the American Psychiatric Association.Personality disorders are...
to be identified, the theory thereby making a great contribution to the understanding of psychiatric disorders.
Cloninger’s Tridemension Personality Theory and Reward Dependence

Harm avoidance
In psychology, harm avoidance is a personality trait characterized by excessive worrying; pessimism; shyness; and being fearful, doubtful, and easily fatigued...
and “Novelty Seeking (NS)”
Novelty seeking
In psychology, novelty seeking is a personality trait.It is measured in the Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire as well as the later version Temperament and Character Inventory.NS has been suggested to be related to low dopaminergic activity....
. A temperament, according to Cloninger, is the automatic emotional response to experience .
Cloninger suggested that RD is influenced by a single monoamine neurotransmitter
Monoamine neurotransmitter
thumb|right|350px| A phylogenetic tree showing how a number of monoamine receptors are related to each other.Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group that is connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain...
system: the noradrenergic
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
system and reward dependence is correlated with low basal noradrenergic activity. This suggestion has led to several research experiments that have investigated and supported his hypothesis, that reward dependence traits are indeed in part determined by norepinephrine.
Measure of the Reward Dependence dimension, as suggested by Cloninger, is used to assess the Altruistic-warm versus detached-tough mindedness components of our personalities. The RD dimension reflects on the highs and lows of the positive-gratifying pleasure valence.
According to Cloninger’s theory, individuals high in Reward Dependence and low in norepinephrine levels are ambitious, warm, sentimental, pleasant, sociable, sensitive, sympathetic and socially dependent. One of the major adaptive advantages of high RD is the sensitivity to social cues which facilitates affectionate social relations, genuine care for others and communication. The disadvantage is related to suggestibility
Suggestibility
Suggestibility is the quality of being inclined to accept and act on the suggestions of others.A person experiencing intense emotions tends to be more receptive to ideas and therefore more suggestible. Generally, suggestibility decreases as age increases...
and loss of objectivity frequently encountered with people who are excessively socially dependent. These individuals also exhibit persistent behaviors and are easily influenced by emotional appeals.
Individuals low in Reward Dependence and high in norepinephrine levels are hypothesized to be typically independent, non-conformist, practical, tough-minded, cynical, unwilling to share their intimate feelings with others, socially detached, irresolute, insensitive to social cues and pressures, and content to be alone. They are also minimally motivated to please others and act for immediate gratification. So being low in RD is related to social withdrawal, with aggressive anti-social behavior, detachment, and coldness in social attitudes.
The Reward Dependence temperament interacts with other temperaments and characters inherent in us enabling us to adapt to life experiences and influence susceptibility to emotional and behavioral disorders
Quantifying Reward Dependence
Two questionnaires were devised by Cloninger to measure the temperaments and characters of individuals. RD can be measured using both the Tridimensional Personality QuestionnaireTridimensional Personality Questionnaire
Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire is a personality test.It was devised by C. Robert Cloninger.A newer version of the questionnaire is called Temperament and Character Inventory....
(TPQ) personality test and by the newer and refined version of the personality test called Temperament and Character Inventory
Temperament and Character Inventory
Temperament and Character Inventory is an inventory for personality traits devised by Cloninger et al.It is closely related to and an outgrowth of Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire ,...
(TCI) and its revised version (TCI-R). Owing to the limitations encountered in the TPQ, in that the three dimensions’ clinical utility was not readily apparent to many clinicians, Cloninger revamped the questionnaire and produced the TCI scale, which incorporates four dimensions of “temperament” and three dimensions of “character”.
The so-called subscales of reward dependence in TCI-R are
- SentimentalitySentimentalitySentimentality originally indicated the reliance on feelings as a guide to truth, but current usage defines it as an appeal to shallow, uncomplicated emotions at the expense of reason....
(RD1) - Openness to warm communication or social sensitivitySensitivity (human)The sensitivity or insensitivity of a human, often considered with regard to a particular kind of stimulus, is the strength of the feeling it results in, in comparison with the strength of the stimulus...
(RD2) - AttachmentAttachment theoryAttachment theory describes the dynamics of long-term relationships between humans. Its most important tenet is that an infant needs to develop a relationship with at least one primary caregiver for social and emotional development to occur normally. Attachment theory is an interdisciplinary study...
(RD3) - Dependence on approval by others (RD4)
Brain Physiology
Cloninger describes RD as being a prime component of the BehaviorBehaviorism
Behaviorism , also called the learning perspective , is a philosophy of psychology based on the proposition that all things that organisms do—including acting, thinking, and feeling—can and should be regarded as behaviors, and that psychological disorders are best treated by altering behavior...
maintenance System (BMS) . Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
(NE), apart from producing alertness and arousal, is seen as influencing the brain reward system. Norepinephrine aids in the learning of new paired associations.
According to Cloninger, the norepinephrine neurotransmitter has its major ascending pathways arising in the locus coeruleus in the pons
Pons
The pons is a structure located on the brain stem, named after the Latin word for "bridge" or the 16th-century Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio . It is superior to the medulla oblongata, inferior to the midbrain, and ventral to the cerebellum. In humans and other bipeds this means it...
, projecting onward to the hypothalamic
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions...
and limbic structures
Limbic system
The limbic system is a set of brain structures including the hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, septum, limbic cortex and fornix, which seemingly support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long term memory, and olfaction. The term "limbic" comes from the Latin...
, and then branching upwards to the neocortex
Neocortex
The neocortex , also called the neopallium and isocortex , is a part of the brain of mammals. It is the outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres, and made up of six layers, labelled I to VI...
.
Reward dependence has been linked to "dissociable connectivity streams" in the brain. Striatal projections
Striatum
The striatum, also known as the neostriatum or striate nucleus, is a subcortical part of the forebrain. It is the major input station of the basal ganglia system. The striatum, in turn, gets input from the cerebral cortex...
and Tracts between prefrontal cortex
Prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex is the anterior part of the frontal lobes of the brain, lying in front of the motor and premotor areas.This brain region has been implicated in planning complex cognitive behaviors, personality expression, decision making and moderating correct social behavior...
predict the individual differences in reward processing, reward dependence and reward-guided behaviors . These findings suggest that personality traits may be affected by the strength of limbic-striatal connectivity. High RD is characterized by learning from reward signals, persisting repetition of actions that are associated with rewards, increased sociability and a need for social approval. The striatum, especially the dorsal regions
Dorsal striatum
The dorsal striatum, corpus striatum or striated body is a compound structure consisting of the caudate nucleus, and the lentiform nucleus...
, is necessary to carry out these functions. .
Using Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
(PET) researchers have shown that Reward dependence is the only temperament dimension strongly correlated with opiate receptor binding (the endorphine system) and that positive correlation is restricted to the bilateral ventral striatum
Ventral striatum
The ventral striatum is generally considered that part of the striatum that is connectionally associated with limbic structures, such as the amygdala, hippocampus, midline thalamus, and certain regions of the prefrontal cortex...
, which is considered the key area of the human reward system and of the development of addictive behavior
Addictive behavior
Addictive behavior is any activity, substance, object, or behavior that becomes the major focus of a person's life, during which they withdraw from other activities. Along with this, there are often other signs of having an addiction either physically, mentally, or socially.A person can become...
. This correlation means that people with high reward dependence have a high concentration of opiate receptors present in that area, while people with low dependence have fewer receptors. The subjects who felt a high need for social approval were also those with the highest uptake of opiates in the reward system. This finding demonstrates that elevated opiate receptors in the ventral striatum could be a biologic link between personality traits and dependence
Behavioral addiction
Behavioral addiction is a form of addiction which does not rely on drugs or alcohol. Increasingly referred to as process addiction or non-substance-related addiction ) behavioral addiction includes a compulsion to repeatedly engage in an action until said action causes serious negative consequences...
risk. According to the researchers, this novel finding will provide a deeper understanding of the functional relationship between human personality, neurobiology, and substance abuse
Substance abuse
A substance-related disorder is an umbrella term used to describe several different conditions associated with several different substances .A substance related disorder is a condition in which an individual uses or abuses a...
and other addictive behaviors.

Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is an area in the brain of humans and other mammals, located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned anterior to the parietal lobe and superior and anterior to the temporal lobes...
around the midline inner surface of the brain, showed greater reward dependence. People with social reward dependence personalities were also seen to have brains with far less tissue in the fronto-striatal
Frontostriatal circuit
Frontostriatal circuits are neural pathways that connect frontal lobe regions with the basal ganglia that mediate motor, cognitive, and behavioural programs within the brain and receive inputs from dopaminergic, serotonergic, noradrenergic, and cholinergic cell groups that modulate information...
section of the brain (e.g. damage to the fronto-striatal area is often linked to autism
Autism
Autism is a disorder of neural development characterized by impaired social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism affects information processing in the brain by altering how nerve cells and their...
and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
). Relationship between concentration of grey matter
Grey matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil , glial cells and capillaries. Grey matter contains neural cell bodies, in contrast to white matter, which does not and mostly contains myelinated axon tracts...
(brain-cell containing tissue) in different brain regions and social reward dependence was also studied. It was found that the greater the concentration of tissue in the orbitofrontal cortex
Orbitofrontal cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes in the brain which is involved in the cognitive processing of decision-making...
(the outer strip of the brain just above the eyes), and in the ventral striatum (a deep structure in the centre of the brain), the higher they tended to score on the social RD measure. The researchers warn that these studies are only correlational and cross-sectional
Cross-sectional study
Cross-sectional studies form a class of research methods that involve observation of all of a population, or a representative subset, at one specific point in time...
and none of this research is definitive in proving that brain structure determines personality but it could be that personality, through experience, may help in determining the structure of the brain.
Social Reward Dependence has also been associated with temporal lobes
Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is a region of the cerebral cortex that is located beneath the Sylvian fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain....
, the caudate
Caudate nucleus
The caudate nucleus is a nucleus located within the basal ganglia of the brains of many animal species. The caudate nucleus is an important part of the brain's learning and memory system.-Anatomy:...
Grey Matter Density (GMD) in the orbitofrontal cortex and the basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
of the ventral striatum : structures, which are rich in dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
receptors, already known to play a crucial role in reward receipt, Incentive anticipation
Incentive
In economics and sociology, an incentive is any factor that enables or motivates a particular course of action, or counts as a reason for preferring one choice to the alternatives. It is an expectation that encourages people to behave in a certain way...
and error in prediction of simple and discrete primary and secondary rewards. These significant findings showed a correlation between primary reward processing regions and reward dependence, keeping with the fMRI research studies that demonstrate that the striatum is activated following the experience of complex rewards.
Primary reward processing has also been associated with the orbitofrontal cortex and the grey matter density in the ventral striatum, whereas higher reward dependence scores were associated with the interactions between dopamine projections, neuropeptides and opiates in the ventral striatum. It is demonstrated here, then, that there is evidence for a structural disposition of the brain towards social interactions, and that both primary reward processing and sensitivity to social reward cues share the same brain systems.
In addition to these findings, the bilateral temporal poles were also identified in which gray matter density correlated with RD. The orbitofrontal cortex and medial prefrontal cortex, in addition to other temporal structures, project to the temporal pole, enabling these regions to integrate reward-related information between frontal and temporal regions. In an fMRI study, the temporal poles and the ventral striatal areas have been shown to be activated in response to social rewards (such as humor) and also in looking forward to simpler rewards (such as money).
Reward Dependence and Clinical disorders
Cloninger’s theory suggests that over expressionGene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
of the RD temperament could cause psychiatric illnesses, such as addictive behaviors
Addictive behavior
Addictive behavior is any activity, substance, object, or behavior that becomes the major focus of a person's life, during which they withdraw from other activities. Along with this, there are often other signs of having an addiction either physically, mentally, or socially.A person can become...
, sociopathies
Psychopathy
Psychopathy is a mental disorder characterized primarily by a lack of empathy and remorse, shallow emotions, egocentricity, and deceptiveness. Psychopaths are highly prone to antisocial behavior and abusive treatment of others, and are very disproportionately responsible for violent crime...
, and personality disorders
Personality disorder
Personality disorders, formerly referred to as character disorders, are a class of personality types and behaviors. Personality disorders are noted on Axis II of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders or DSM-IV-TR of the American Psychiatric Association.Personality disorders are...
.
Low levels of norepinephrine cause an increase in Reward Dependence. When produced in normal levels, norepinephrine creates a sense of well-being, but low levels of norepinephrine cause symptoms of depression
Depression (mood)
Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
, lack of arousal
Arousal
Arousal is a physiological and psychological state of being awake or reactive to stimuli. It involves the activation of the reticular activating system in the brain stem, the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure and a condition of...
and lack of motivation
Motivation
Motivation is the driving force by which humans achieve their goals. Motivation is said to be intrinsic or extrinsic. The term is generally used for humans but it can also be used to describe the causes for animal behavior as well. This article refers to human motivation...
. In humans, this leads to then a negative feedback
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when the output of a system acts to oppose changes to the input of the system, with the result that the changes are attenuated. If the overall feedback of the system is negative, then the system will tend to be stable.- Overview :...
mechanism whereby we seek out pleasurable activities to remove the negative affect
Affect (psychology)
Affect refers to the experience of feeling or emotion. Affect is a key part of the process of an organism's interaction with stimuli. The word also refers sometimes to affect display, which is "a facial, vocal, or gestural behavior that serves as an indicator of affect" .The affective domain...
caused by the low levels of norepinephrine, therefore increasing our Reward Dependence.
An increase in the Reward Dependence temperament leads us to seek out those behaviors or substances that will allow us to remain in a pleasant physical and/or mental state, based on the hedonistic
Hedonism
Hedonism is a school of thought which argues that pleasure is the only intrinsic good. In very simple terms, a hedonist strives to maximize net pleasure .-Etymology:The name derives from the Greek word for "delight" ....
principle that people seek pleasure and avoid pain . Our pleasure and reward systems in the brain are hyper-activated, which makes us display continuous approach behaviors to the reward in question. Our neuro-circuity is as such that when we stop having access to such pleasurable objects of desire, we then experience negative consequences (withdrawal
Withdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
symptoms). Addictive behaviors then arise to alleviate such negative consequences and the cycle continues.
Addictive Behaviors and Reward Dependence
People who have a high reward dependent personality but find themselves in an environment where they do not find reward through family support or other types, will seek reward through other means e.g. food or drugsDRUGS
Destroy Rebuild Until God Shows are an American post-hardcore band formed in 2010. They released their debut self-titled album on February 22, 2011.- Formation :...
. Knowing that someone has such a predisposition could help them to adopt preventive strategies and avoid situations where they might seek rewards which could be potentially harmful. Reward dependence drives behavior maintenance systems, and in addictive behaviors, maintenance of behaviors occurs despite adverse consequences.

Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
-modulated dopamine release in core structures of the reward system and subsequently induce the sensation of craving
Craving (withdrawal)
When going through withdrawal, craving is a psychological urge to administer a discontinued medication or recreational drug.-Duration:The duration that cravings last after discontinuation varies substantially between different addictive drugs...
. Modern addiction research maintains that genetic or acquired abuses of the reward system are the central basis for the development of addictive behavior. This latest finding suggests that individuals suffering from a relative endorphin deficit in their reward system show increased reward dependence and are probably more at risk for developing addictions.
Adolescents
Adolescence
Adolescence is a transitional stage of physical and mental human development generally occurring between puberty and legal adulthood , but largely characterized as beginning and ending with the teenage stage...
low in reward dependence may find conventional sources of reward unfulfilling (e.g., academic achievement or activities involving social affiliation), and eventually turn to unconventional reward sources (e.g., smoking
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance, most commonly tobacco or cannabis, is burned and the smoke is tasted or inhaled. This is primarily practised as a route of administration for recreational drug use, as combustion releases the active substances in drugs such as nicotine and makes them...
and other forms of substance misuse) to derive satisfaction and pleasure. A study conducted using adolescents with Excessive Internet video Game Play (EIGP) showed that such addictive behaviors were correlated with higher RD scores on the TCI , whereas both low and high scores of RD were implicated in specific alcoholic and drug addictions.
- Proposed Type 1 AlcoholismAlcoholismAlcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
is clinically characterized by a late onset (after the age of 25) of alcohol-related problems(usually after an extended period of drinking that is socially encouraged), strong psychological dependence (loss of control) with guilt and fear about alcohol dependence, and rare occurrence of fighting and arrests after drinking. Psychologically, it is proposed to be characterized by high reward-dependence (in both males and females).
- Low reward-dependence is then hypothesized to fit the psychological profile of Type 2 Alcoholism (predominantly in males). Type 2 Alcoholism is clinically characterized by an early onset of alcohol-related problems before the age of 25 (independent of external circumstances), drinking often associated with antisocial behaviorAnti-social behaviourAnti-social behaviour is behaviour that lacks consideration for others and that may cause damage to society, whether intentionally or through negligence, as opposed to pro-social behaviour, behaviour that helps or benefits society...
, spontaneous alcohol-seeking behavior (inability to abstain), low associated guilt and fear, and frequent fighting and arrests after drinking. This combination of traits also describes people with Antisocial Personality DisorderAntisocial personality disorderAntisocial personality disorder is described by the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, fourth edition , as an Axis II personality disorder characterized by "...a pervasive pattern of disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others that begins in childhood...
(ASPD) and is consistent with findings that type 2 alcoholics frequently suffer from ASPD. Since the inception of these theories they have been tested in several investigations and the results have been consistent with the theories.
- The likelihood of becoming a smoker has also been linked to Reward Dependence. Both males and females were seen to score low in the Sentimentality-Dependence-Attachment subscale of RD, possibly accounting for indifference towards social pressures to quit. Whereas they scored high on the PersistencePersistence (psychology)In psychology, persistence is a personality trait.It is measured in the Temperament and Character Inventory.The subscales of PS in TCI-R consist of# Eagerness of effort # Work hardened # Ambitious # Perfectionist...
sub scale of RD, representing resistance to extinctionExtinction (psychology)Extinction is the conditioning phenomenon in which a previously learned response to a cue is reduced when the cue is presented in the absence of the previously paired aversive or appetitive stimulus.-Fear conditioning:...
of previously rewarded behavior thereby reengaging in the addictive behavior.
- Craving has increasingly received attention as a critical phenomenon in addictive psychopathologyPsychopathologyPsychopathology is the study of mental illness, mental distress, and abnormal/maladaptive behavior. The term is most commonly used within psychiatry where pathology refers to disease processes...
. Craving has been defined as the desire or the memory of a pleasant experience superimposed on a negative affective state. Hence, conceptually, craving combines elements of desireDesire (emotion)Desire is a sense of longing for a person or object or hoping for an outcome. Desire is the fire that sets action aflame. The same sense is expressed by emotions such as "craving" or "hankering". When a person desires something or someone, their sense of longing is excited by the enjoyment or the...
/motivationMotivationMotivation is the driving force by which humans achieve their goals. Motivation is said to be intrinsic or extrinsic. The term is generally used for humans but it can also be used to describe the causes for animal behavior as well. This article refers to human motivation...
and emotions. Pathologic gamblers with an addictive personality have been linked to high reward dependence scores. Pathological gambling disorder (PGD) is characterized by persistent and recurrent gambling behaviors that cause significant disruption in a person’s life. The positive relation of gambling craving to depressionDepression (mood)Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
and negative relation to reward dependence suggests that, individuals who have a lesser propensity to experience positive emotions are the ones who most miss gambling when abstaining. Meanwhile, pathologic gamblers seem to turn to gambling as a way to cope with depressive feelings and lack of positive experiences in life. Pathologic gamblers would potentially benefit from interventions targeting early relief of depression symptoms and replacement of the activity and joy once prompted by gambling.
- fMRI studies also show that brain systems involved in primary reward processing may also be critical for the processing of social reward information. Since higher RD scores are also correlated to the basal ganglia of the ventral striatum, this explains why Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients on medications indulge in impulsive gambling behaviors. Pathologic gamblers were shown to experience stronger cravings than did Alcohol-DependentAlcohol dependenceAlcohol dependence, as described in the DSM-IV, is a psychiatric diagnosis describing an entity in which an individual uses alcohol despite significant areas of dysfunction, evidence of physical dependence, and/or related hardship.-Definition and diagnosis:According to the DSM-IV criteria for...
Subjects (ADS). This may be a disturbing experience for pathologic gamblers and a potential cause for relapseRelapseRelapse, in relation to drug misuse, is resuming the use of a drug or a dependent substance after one or more periods of abstinence. The term is a landmark feature of both substance dependence and substance abuse, which are learned behaviors, and is maintained by neuronal adaptations that mediate...
.
Personality Disorders and Reward Dependence
Social reward dependence (RD) in humans is hypothesized to be associated with behaviors and attitudes that represent a disposition towards social relationshipsSocial relation
In social science, a social relation or social interaction refers to a relationship between two , three or more individuals . Social relations, derived from individual agency, form the basis of the social structure. To this extent social relations are always the basic object of analysis for social...
and attachment as a personality dimension. It is suggested that the brain substrates that are involved in learning and signaling about simple primary rewards are also implicated in the brain’s response to more complex social rewards. The RD sub-scale from the TCI inventory measures how sensitive individuals are to social rewards. High RD scores on the test correlate to increased attachment and an increased need for social relationships. Low RD scores show a movement towards social detachment and insensitivity.
- Antisocial Personality DisorderAntisocial personality disorderAntisocial personality disorder is described by the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, fourth edition , as an Axis II personality disorder characterized by "...a pervasive pattern of disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others that begins in childhood...
(ASPD) is characterized in behavioral terms by childhood or adolescent onset of recurrent antisocial behavior affecting school, work, family, and social life. Cloninger had predicted from his biosocial theoryBiosocial theoryBiosocial Theory is a theory in behavioral and social science that suggests the attribution of disorders of personality and conditions of mind to the reaction of biologically determined personality traits to environmental stimuli.-Biosocial theory in DBT:...
that individuals most at risk of aggressive, antisocial behavior, will be those with lower reward dependence scores and these individuals are equated with the primary psychopaths who show aloofness and social detachment. Particular research conducted on childhood behavior has tested this theory and researchers have shown that children with lower RD scores have more of an anti-social profile as defined in the DSM, and are at highest risk for early onset of frequent delinquent behavior.
- Lower scores of RD were also shown in Obsessional Personality, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and in Borderline Personality DisorderBorderline personality disorderBorderline personality disorder is a personality disorder described as a prolonged disturbance of personality function in a person , characterized by depth and variability of moods.The disorder typically involves unusual levels of instability in mood; black and white thinking, or splitting; the...
(BPD) individuals, who exhibit symptoms leading to self-harm due to social detachment and feelings of rejectionSocial rejectionSocial rejection occurs when an individual is deliberately excluded from a social relationship or social interaction. The topic includes both interpersonal rejection and romantic rejection. A person can be rejected on an individual basis or by an entire group of people...
, whereas higher scores of RD were shown in Histrionic Personality DisorderHistrionic personality disorderHistrionic personality disorder is defined by the American Psychiatric Association as a personality disorder characterized by a pattern of excessive emotionality and attention-seeking, including an excessive need for approval and inappropriately seductive behavior, usually beginning in early...
(HPD) and Dependent Personality DisorderDependent personality disorderDependent personality disorder , formerly known as asthenic personality disorder, is a personality disorder that is characterized by a pervasive psychological dependence on other people...
individuals who exhibit behavioral instability and poor emotional control.
- According to Cloninger’s model, the early life onset of neuropsychiatricNeuropsychiatryNeuropsychiatry is the branch of medicine dealing with mental disorders attributable to diseases of the nervous system. It preceded the current disciplines of psychiatry and neurology, in as much as psychiatrists and neurologists had a common training....
disorders lead to personality disorders, with a "typical ADHD temperament" corresponding to the low reward dependence scores associated with explosive/borderline type personalities, or a "typical autism temperament", also with low reward dependence scores. Studies in Autistic disorder and Asperger syndromeAsperger syndromeAsperger's syndrome that is characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction, alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. It differs from other autism spectrum disorders by its relative preservation of linguistic and cognitive development...
have also shown similar results, where lower oxytocinOxytocinOxytocin is a mammalian hormone that acts primarily as a neuromodulator in the brain.Oxytocin is best known for its roles in sexual reproduction, in particular during and after childbirth...
levels and lower RD scores were reported in these children leading to their abnormal social behaviors. The direction of the effect i.e. whether reduced oxytocin leads to decreased affiliation or vice versa has not been clearly established. Recent animal studies would, however, suggest that changes to oxytocin lead to changes in behavior.
- Also a significant positive correlation between plasma oxytocin levels and reward dependence personality dimension was found by researchers in New Zealand. Considerable evidence from animal studies has shown oxytocin to be involved in the processing of social informationSocial Information Processing (Cognition)Social information processing refers to a theory of how individuals, especially children, establish successful relationships with society....
and the regulation of social affiliative behavior. Results from studies measuring plasma oxytocin levels in patients with a diagnosis of major depressive episode according to DSM III-R has shown decreased oxytocin levels in these patients and lower reward dependence scores on the TCI, leading to an assumption that lower reward dependence leads to depression.
- Lower Reward Dependence scores have also typically been associated with paranoidParanoiaParanoia [] is a thought process believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of irrationality and delusion. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concerning a perceived threat towards oneself...
, schizoidSchizoid personality disorderSchizoid personality disorder is a personality disorder characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency towards a solitary lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldness, and sometimes apathy, with a simultaneous rich, elaborate, and exclusively internal fantasy world...
and schizotypal personality disordersSchizotypal personality disorderSchizotypal personality disorder, or simply schizotypal disorder, is a personality disorder that is characterized by a need for social isolation, anxiety in social situations, odd behavior and thinking, and often unconventional beliefs.-Genetic:...
in the DSM, and these patients also showed decreased plasma oxytocin levels.
- In another study conducted with patients with Above-normal Plasma Vasopression (AVP) depression, it was found that these patients had lower RD scores than controls and other patients with depression disorders . In this case a directional relationship was found in which the low Reward Dependence is a state-dependent characteristic of patients with AVP depression, and not vice versa.
- Research has also found that low expression of RD is seen in suicideSuicideSuicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Suicide is often committed out of despair or attributed to some underlying mental disorder, such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, or drug abuse...
attempters. The findings of lower reward dependence scores in suicide attempters and the negative correlation with the number of suicide attempts may imply the relationship between the noradrenergic pathway and suicide behaviors. Low scores of RD have also been implicated in showing criminality in adult age.
At the 2010 Annual meeting of the American Psychological Association
American Psychological Association
The American Psychological Association is the largest scientific and professional organization of psychologists in the United States. It is the world's largest association of psychologists with around 154,000 members including scientists, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. The APA...
(APA), a study looking at treatment methods of personality disorders was presented in which it was found, that panic disorder patients with higher Reward Dependence scores were more resistant to Escitalopram
Escitalopram
Escitalopram is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor class. It is approved by the U.S...
treatment. Since long-term pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy is the treatment of disease through the administration of drugs. As such, it is considered part of the larger category of therapy....
is needed for treatment of panic disorder, the present results suggest that development of therapeutic strategy for panic patients with high reward dependence is needed.
Other Clinical Disorders
In response to frustrative non-rewardFrustration
This article concerns the field of psychology. The term frustration does, however, also concern physics. In this context, the term is treated in a different article, geometric frustration....
, individuals with high reward dependence are susceptible to compensatory noradrenergic hyperactivity. Hence acute or recurrent states of agitated dysphoria
Dysphoria
Dysphoria is medically recognized as a mental and emotional condition in which a person experiences intense feelings of depression, discontent and indifference to the world around them.Mood disorders can induce dysphoria, often with a heightened risk of suicide, especially in...
associated with reward-seeking behaviors, such as overeating and increased sexual activity, are prevalent in these individuals.
Individuals with higher reward dependence also look for more social approval, and are more inclined to succumb to peer-pressure. They often become overly concerned about their body image
Body image
Body image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
and maybe prone to eating disorders, such a Bulimia nervosa
Bulimia nervosa
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating and purging or consuming a large amount of food in a short amount of time, followed by an attempt to rid oneself of the food consumed, usually by purging and/or by laxative, diuretics or excessive exercise. Bulimia nervosa is...
. Whereas restricting anorexia
Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by refusal to maintain a healthy body weight and an obsessive fear of gaining weight. Although commonly called "anorexia", that term on its own denotes any symptomatic loss of appetite and is not strictly accurate...
, in particular, tends to reflect low reward dependence.
Reward dependence is not consistently associated with diagnosis but can significantly affect treatment issues, such as Therapeutic alliance. Persistence in completing weight-loss programs
Dieting
Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated fashion to achieve or maintain a controlled weight. In most cases dieting is used in combination with physical exercise to lose weight in those who are overweight or obese. Some athletes, however, follow a diet to gain weight...
were related to pretreatment high reward dependence scores. Thus showing that, having a tendency toward being sociable, dedicated and highly responsive to social pressure reduced the risk of dropout in this behavioral weight-loss program.
Miscellaneous Research and Reward Dependence
A study of gamblers found elevated Cerebrospinal fluidCerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
(CSF) levels of the norepinephrine (NE) metabolite 3-methoq-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MI-IPG). This could suggest a relationship between gambling and norepinephrine, and so gambling could be viewed as a reward-dependent behavior, although Cloninger’s theory would predict that CSF MHPG should have been low, not high. Cloninger speculated that these gamblers might have shown a reduction of NE and its metabolites if they had been reexamined after a period of abstinence from gambling . A study of alcoholics showed a significant negative correlation of the level of MHPG in CSF to a score of alcohol-dependent drinking patterns. This correlation is consistent with a relationship between NE and reward dependence.
Several genes have also been found to express the Reward dependence dimension. Specifically, the gene MAOA-uVNTR has been highly implicated in evoking the RD personality trait.
See also
- Substance dependenceSubstance dependenceThe section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
- DopamineDopamineDopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
- Reward systemReward systemIn neuroscience, the reward system is a collection of brain structures which attempts to regulate and control behavior by inducing pleasurable effects...
- DSMDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental DisordersThe Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is published by the American Psychiatric Association and provides a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders...
- Personality disorderPersonality disorderPersonality disorders, formerly referred to as character disorders, are a class of personality types and behaviors. Personality disorders are noted on Axis II of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders or DSM-IV-TR of the American Psychiatric Association.Personality disorders are...
- Harm avoidanceHarm avoidanceIn psychology, harm avoidance is a personality trait characterized by excessive worrying; pessimism; shyness; and being fearful, doubtful, and easily fatigued...
- Novelty seekingNovelty seekingIn psychology, novelty seeking is a personality trait.It is measured in the Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire as well as the later version Temperament and Character Inventory.NS has been suggested to be related to low dopaminergic activity....
- C. Robert CloningerC. Robert CloningerClaude Robert Cloninger, M.D. is a psychiatrist and geneticist noted for his pioneering research on the biological, psychological, social, and spiritual foundation of both mental health and mental illness. He is Wallace Renard Professor of Psychiatry, Professor of Psychology and of Genetics, and...

