
Poland in the Middle Ages
Encyclopedia
Poland in the Middle Ages is a period of Polish history
covering roughly a millennium
in the 5th century through to the 16th century. It is commonly dated from the fall of the Western Roman Empire
, and contrasted with a later Early Modern Period
; the time during which the rise of humanism
in the Italian Renaissance
and the Reformation
unfolded, are generally associated with the transition out of the Middle Ages, with European overseas expansion as a succeeding process, but such dates are approximate and based upon nuanced arguments.
migration settled the area of the upper Vistula River and elsewhere in the lands of present-day southeastern Poland
and southern Masovia, coming from the upper and middle regions of the Dnieper River
. Results of a genetic study by researchers from Gdańsk Medical University "support hypothesis placing the earliest known homeland of Slavs in the middle Dnieper basin". The West Slavs
came primarily from the more western early Slavic branch called the Sclaveni
by the Byzantine
historian Jordanes
in Getica
, the eastern branch being the Antes
. The Slavs had first migrated into Poland in the second half of the 5th century, some half century after these territories had been vacated by Germanic
tribes (after a period during which settlements were absent or rare).. According to the references given in this and Poland in the Early Middle Ages
article, many scholars now believe that the Slavic tribes had not been present in Poland before the earliest medieval period, though the opposite view, predominant in Polish prehistory
and protohistory
in the past, is still represented.
From there, over the 6th century, the new population dispersed north and west. The Slavs lived mostly by cultivating crops but also engaged in hunting and gathering
. Their migrations took place while Eastern
and Central Europe
were being invaded from the east by waves of peoples and armies such as the Huns
, Avars
and Magyars.
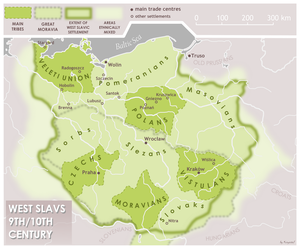 A number of West Slavic
A number of West Slavic
Polish tribes
formed small states, beginning in the 8th century, some of which later coalesced into larger states. Among these tribes were the Vistulans
(Wiślanie) in southern Poland, with Kraków
and Wiślica
as their main centers (major fortified centers were built in their country in the 9th century), but later the tribe(s) referred to as the Polans
(Polanie—literally, "people of the fields") would prove of decisive historic importance. At the end of the 9th century Vistulans were part of the Great Moravia
, according to some theories.
The tribal states built many gords – fortified structures with earthen and wooden walls and embankments – from the 7th century onward. Some of these were developed and inhabited; others featured a large empty space and may have served primarily as refuges in times of trouble. The Polans settled the plains around Giecz
, Poznań
and Gniezno
that would become the early center of Poland and lent their name to the country. They went through a period of accelerated building of gord-type fortified settlements and of territorial expansion, beginning in the first half of the 10th century, and the Polish state developed from their tribal polities in the second half of the 10th century.
of the Piast dynasty
in the second half of the 10th century. Mieszko chose to be baptized
in the Western Latin Rite in 966. Following its emergence, the Polish nation
was led by a series of rulers who converted the population to Christianity
, created a strong kingdom and integrated Poland into the European culture
. Mieszko's son Bolesław I Chrobry established a Polish Church province, pursued territorial conquests and was officially crowned, becoming the first King of Poland. This was followed by a collapse of the monarchy and restoration under Casimir I. Casimir's son Bolesław II the Bold became fatally involved in a conflict with the ecclesiastical authority
, and was expelled from the country. After Bolesław III divided the country among his sons, internal fragmentation eroded the initial Piast monarchy structure in the 12th and 13th centuries. One of the regional Piast dukes
invited the Teutonic Knights
to help him fight the Baltic
Prussian
pagans, which caused centuries of Poland's warfare with the Knights and then with the German Prussian state. The Kingdom was restored under Władysław I the Elbow-high, strengthened and expanded by his son Casimir III the Great. The western provinces of Silesia
and Pomerania
were lost after the fragmentation, and Poland began expanding to the east. The consolidation in the 14th century laid the base for, after the reigns of two members of the Angevin dynasty
, the new powerful Kingdom of Poland
that was to follow.
(Władysław II Jagiełło), the Jagiellon dynasty
(1385–1569) formed the Polish–Lithuanian union. The partnership brought vast Lithuania
-controlled Rus' areas
into Poland's sphere of influence and proved beneficial for the Poles and Lithuanians
, who coexisted and cooperated in one of the largest political entities
in Europe
for the next four centuries. In the Baltic Sea
region Poland's struggle with the Teutonic Knights continued and included the milestone Peace of Thorn under King Casimir IV Jagiellon
; the treaty created the future Duchy of Prussia. In the south Poland confronted the Ottoman Empire
and the Crimean Tatars
, and in the east helped Lithuania fight the Grand Duchy of Moscow
. Poland was developing as a feudal
state, with predominantly agricultural economy and an increasingly dominant landed nobility
component. The Nihil novi
act adopted by the Polish Sejm
(parliament
) in 1505, transferred most of the legislative power
from the monarch
to the Sejm. This event marked the beginning of the period known as "Golden Liberty
", when the state was ruled by the "free and equal" Polish nobility
. Protestant Reformation
movements made deep inroads into the Polish Christianity, which resulted in unique at that time in Europe policies of religious tolerance
. The European Renaissance
currents evoked in late Jagiellon Poland (kings Sigismund I the Old
and Sigismund II Augustus
) an immense cultural flowering
. Poland's and Lithuania's territorial expansion included the far north region of Livonia
.
History of Poland
The History of Poland is rooted in the arrival of the Slavs, who gave rise to permanent settlement and historic development on Polish lands. During the Piast dynasty Christianity was adopted in 966 and medieval monarchy established...
covering roughly a millennium
Millennium
A millennium is a period of time equal to one thousand years —from the Latin phrase , thousand, and , year—often but not necessarily related numerically to a particular dating system....
in the 5th century through to the 16th century. It is commonly dated from the fall of the Western Roman Empire
Decline of the Roman Empire
The decline of the Roman Empire refers to the gradual societal collapse of the Western Roman Empire. Many theories of causality prevail, but most concern the disintegration of political, economic, military, and other social institutions, in tandem with foreign invasions and usurpers from within the...
, and contrasted with a later Early Modern Period
Early modern period
In history, the early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the Middle Ages through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions...
; the time during which the rise of humanism
Humanism
Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism....
in the Italian Renaissance
Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance began the opening phase of the Renaissance, a period of great cultural change and achievement in Europe that spanned the period from the end of the 13th century to about 1600, marking the transition between Medieval and Early Modern Europe...
and the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
unfolded, are generally associated with the transition out of the Middle Ages, with European overseas expansion as a succeeding process, but such dates are approximate and based upon nuanced arguments.
Early Middle Ages
The first waves of SlavicSlavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
migration settled the area of the upper Vistula River and elsewhere in the lands of present-day southeastern Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
and southern Masovia, coming from the upper and middle regions of the Dnieper River
Dnieper River
The Dnieper River is one of the major rivers of Europe that flows from Russia, through Belarus and Ukraine, to the Black Sea.The total length is and has a drainage basin of .The river is noted for its dams and hydroelectric stations...
. Results of a genetic study by researchers from Gdańsk Medical University "support hypothesis placing the earliest known homeland of Slavs in the middle Dnieper basin". The West Slavs
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples speaking West Slavic languages. They include Poles , Czechs, Slovaks, Lusatian Sorbs and the historical Polabians. The northern or Lechitic group includes, along with Polish, the extinct Polabian and Pomeranian languages...
came primarily from the more western early Slavic branch called the Sclaveni
Sclaveni (military)
The name Sklaveni was generally used to describe all Slavic peoples that the Byzantine Empire came into contact with. The Sklaveni are the basis of the nation-building of the South Slavs....
by the Byzantine
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
historian Jordanes
Jordanes
Jordanes, also written Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th century Roman bureaucrat, who turned his hand to history later in life....
in Getica
Getica (Jordanes)
De origine actibusque Getarum , or the Getica, written in Late Latin by Jordanes in 551, claims to be a summary of a voluminous account by Cassiodorus of the origin and history of the Gothic people, which may have had the title "Origo Gothica" and which is now lost...
, the eastern branch being the Antes
Antes (people)
The Antes or Antae were an ancient Slavic-Iranian tribal union in Eastern Europe who lived north of the lower Danube and the Black Sea in the 6th and 7th century AD and who are associated with the archaeological Penkovka culture.- Historiography :Procopius and Jordanes mention the Antes as one of...
. The Slavs had first migrated into Poland in the second half of the 5th century, some half century after these territories had been vacated by Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
tribes (after a period during which settlements were absent or rare).. According to the references given in this and Poland in the Early Middle Ages
Poland in the Early Middle Ages
The ancient Roman scholars new nothing about the impenetrable forest north of Dacia and the Carpathian Mountains, between the migrating Celts and Germanic tribes to the west, and the Sarmatians to the east. Augustian historian Strabo only assumed the presence of a different tribe reaching north to...
article, many scholars now believe that the Slavic tribes had not been present in Poland before the earliest medieval period, though the opposite view, predominant in Polish prehistory
Prehistory
Prehistory is the span of time before recorded history. Prehistory can refer to the period of human existence before the availability of those written records with which recorded history begins. More broadly, it refers to all the time preceding human existence and the invention of writing...
and protohistory
Protohistory
Protohistory refers to a period between prehistory and history, during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures have already noted its existence in their own writings...
in the past, is still represented.
From there, over the 6th century, the new population dispersed north and west. The Slavs lived mostly by cultivating crops but also engaged in hunting and gathering
Hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forage society is one in which most or all food is obtained from wild plants and animals, in contrast to agricultural societies which rely mainly on domesticated species. Hunting and gathering was the ancestral subsistence mode of Homo, and all modern humans were...
. Their migrations took place while Eastern
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
and Central Europe
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
were being invaded from the east by waves of peoples and armies such as the Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
, Avars
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
and Magyars.

West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples speaking West Slavic languages. They include Poles , Czechs, Slovaks, Lusatian Sorbs and the historical Polabians. The northern or Lechitic group includes, along with Polish, the extinct Polabian and Pomeranian languages...
Polish tribes
Polish tribes
Polish tribes - a term used sometimes to describe the tribes of West Slavs that lived in the territories that became Polish from around the mid-7th century to the creation of Polish state by the Piast dynasty...
formed small states, beginning in the 8th century, some of which later coalesced into larger states. Among these tribes were the Vistulans
Vistulans
Vistulans were an early medieval West Slavic tribe inhabiting the land of modern Lesser Poland.From the 1st century and possibly earlier, the Vistulans , were part of the Carpian Tribe, which got its name from the area that they lived in, which was beside the Carpathian Mountain Range...
(Wiślanie) in southern Poland, with Kraków
Kraków
Kraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life...
and Wiślica
Wislica
Wiślica is a village in Busko County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina called Gmina Wiślica. It lies on the Nida River, approximately south of Busko-Zdrój and south of the regional capital Kielce...
as their main centers (major fortified centers were built in their country in the 9th century), but later the tribe(s) referred to as the Polans
Polans (western)
The Polans were a West Slavic tribe, part of the Lechitic group, inhabiting the Warta river basin of the historic Greater Poland region in the 8th century.During the reign of King Svatopluk I of Great Moravia , who subdued the tribes of the Vistulans and Ślężanie...
(Polanie—literally, "people of the fields") would prove of decisive historic importance. At the end of the 9th century Vistulans were part of the Great Moravia
Great Moravia
Great Moravia was a Slavic state that existed in Central Europe and lasted for nearly seventy years in the 9th century whose creators were the ancestors of the Czechs and Slovaks. It was a vassal state of the Germanic Frankish kingdom and paid an annual tribute to it. There is some controversy as...
, according to some theories.
The tribal states built many gords – fortified structures with earthen and wooden walls and embankments – from the 7th century onward. Some of these were developed and inhabited; others featured a large empty space and may have served primarily as refuges in times of trouble. The Polans settled the plains around Giecz
Giecz
Giecz is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Dominowo, within Środa Wielkopolska County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately north of Dominowo, north-east of Środa Wielkopolska, and east of the regional capital Poznań...
, Poznań
Poznan
Poznań is a city on the Warta river in west-central Poland, with a population of 556,022 in June 2009. It is among the oldest cities in Poland, and was one of the most important centres in the early Polish state, whose first rulers were buried at Poznań's cathedral. It is sometimes claimed to be...
and Gniezno
Gniezno
Gniezno is a city in central-western Poland, some 50 km east of Poznań, inhabited by about 70,000 people. One of the Piasts' chief cities, it was mentioned by 10th century A.D. sources as the capital of Piast Poland however the first capital of Piast realm was most likely Giecz built around...
that would become the early center of Poland and lent their name to the country. They went through a period of accelerated building of gord-type fortified settlements and of territorial expansion, beginning in the first half of the 10th century, and the Polish state developed from their tribal polities in the second half of the 10th century.
High Middle Ages
The historically recorded Polish state begins with the rule of Mieszko IMieszko I of Poland
Mieszko I , was a Duke of the Polans from about 960 until his death. A member of the Piast dynasty, he was son of Siemomysł; grandchild of Lestek; father of Bolesław I the Brave, the first crowned King of Poland; likely father of Świętosława , a Nordic Queen; and grandfather of her son, Cnut the...
of the Piast dynasty
Piast dynasty
The Piast dynasty was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. It began with the semi-legendary Piast Kołodziej . The first historical ruler was Duke Mieszko I . The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir the Great...
in the second half of the 10th century. Mieszko chose to be baptized
Baptism of Poland
The Baptism of Poland was the event in 966 that signified the beginning of the Christianization of Poland, commencing with the baptism of Mieszko I, who was the first ruler of the Polish state. The next significant step in Poland's adoption of Christianity was the establishment of various...
in the Western Latin Rite in 966. Following its emergence, the Polish nation
Poles
thumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe...
was led by a series of rulers who converted the population to Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
, created a strong kingdom and integrated Poland into the European culture
Culture of Europe
The culture of Europe might better be described as a series of overlapping cultures. Whether it is a question of North as opposed to South; West as opposed to East; Orthodoxism as opposed to Protestantism as opposed to Catholicism as opposed to Secularism; many have claimed to identify cultural...
. Mieszko's son Bolesław I Chrobry established a Polish Church province, pursued territorial conquests and was officially crowned, becoming the first King of Poland. This was followed by a collapse of the monarchy and restoration under Casimir I. Casimir's son Bolesław II the Bold became fatally involved in a conflict with the ecclesiastical authority
Stanislaus of Szczepanów
Stanislaus of Szczepanów, or Stanisław Szczepanowski, was a Bishop of Kraków known chiefly for having been martyred by the Polish king Bolesław II the Bold...
, and was expelled from the country. After Bolesław III divided the country among his sons, internal fragmentation eroded the initial Piast monarchy structure in the 12th and 13th centuries. One of the regional Piast dukes
Konrad I of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia , from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia from 1194 until his death and High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232.-Life:...
invited the Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
to help him fight the Baltic
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
Prussian
Old Prussians
The Old Prussians or Baltic Prussians were an ethnic group, autochthonous Baltic tribes that inhabited Prussia, the lands of the southeastern Baltic Sea in the area around the Vistula and Curonian Lagoons...
pagans, which caused centuries of Poland's warfare with the Knights and then with the German Prussian state. The Kingdom was restored under Władysław I the Elbow-high, strengthened and expanded by his son Casimir III the Great. The western provinces of Silesia
Silesia
Silesia is a historical region of Central Europe located mostly in Poland, with smaller parts also in the Czech Republic, and Germany.Silesia is rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. Silesia's largest city and historical capital is Wrocław...
and Pomerania
Pomerania
Pomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
were lost after the fragmentation, and Poland began expanding to the east. The consolidation in the 14th century laid the base for, after the reigns of two members of the Angevin dynasty
Capetian House of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou, also known as the House of Anjou-Sicily and House of Anjou-Naples, was a royal house and cadet branch of the direct House of Capet. Founded by Charles I of Sicily, a son of Louis VIII of France, the Capetian king first ruled the Kingdom of Sicily during the 13th century...
, the new powerful Kingdom of Poland
Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons was the Polish state created by the accession of Jogaila , Grand Duke of Lithuania, to the Polish throne in 1386. The Union of Krewo or Krėva Act, united Poland and Lithuania under the rule of a single monarch...
that was to follow.
Late Middle Ages
Beginning with the Lithuanian Grand Duke JogailaJogaila
Jogaila, later 'He is known under a number of names: ; ; . See also: Jogaila : names and titles. was Grand Duke of Lithuania , king consort of Kingdom of Poland , and sole King of Poland . He ruled in Lithuania from 1377, at first with his uncle Kęstutis...
(Władysław II Jagiełło), the Jagiellon dynasty
Jagiellon dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty was a royal dynasty originating from the Lithuanian House of Gediminas dynasty that reigned in Central European countries between the 14th and 16th century...
(1385–1569) formed the Polish–Lithuanian union. The partnership brought vast Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
-controlled Rus' areas
Rus' (people)
The Rus' were a group of Varangians . According to the Primary Chronicle of Rus, compiled in about 1113 AD, the Rus had relocated from the Baltic region , first to Northeastern Europe, creating an early polity which finally came under the leadership of Rurik...
into Poland's sphere of influence and proved beneficial for the Poles and Lithuanians
Lithuanians
Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language...
, who coexisted and cooperated in one of the largest political entities
Personal union
A personal union is the combination by which two or more different states have the same monarch while their boundaries, their laws and their interests remain distinct. It should not be confused with a federation which is internationally considered a single state...
in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
for the next four centuries. In the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
region Poland's struggle with the Teutonic Knights continued and included the milestone Peace of Thorn under King Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV KG of the House of Jagiellon was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440, and King of Poland from 1447, until his death.Casimir was the second son of King Władysław II Jagiełło , and the younger brother of Władysław III of Varna....
; the treaty created the future Duchy of Prussia. In the south Poland confronted the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
and the Crimean Tatars
Crimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate, or Khanate of Crimea , was a state ruled by Crimean Tatars from 1441 to 1783. Its native name was . Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan...
, and in the east helped Lithuania fight the Grand Duchy of Moscow
Grand Duchy of Moscow
The Grand Duchy of Moscow or Grand Principality of Moscow, also known in English simply as Muscovy , was a late medieval Rus' principality centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the early modern Tsardom of Russia....
. Poland was developing as a feudal
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
state, with predominantly agricultural economy and an increasingly dominant landed nobility
Landed nobility
Landed nobility is a category of nobility in various countries over the history, for which landownership was part of their noble privileges. Their character depends on the country.*Landed gentry is the landed nobility in the United Kingdom and Ireland....
component. The Nihil novi
Nihil novi
Nihil novi nisi commune consensu is the original Latin title of a 1505 act adopted by the Polish Sejm , meeting in the royal castle at Radom.-History:...
act adopted by the Polish Sejm
General sejm
The general sejm was the parliament of Poland for four centuries from the late 15th until the late 18th century.-Genesis:The power of early sejms grew during the period of Poland's fragmentation , when the power of individual rulers waned and that of various councils and wiece grew...
(parliament
Parliament
A parliament is a legislature, especially in those countries whose system of government is based on the Westminster system modeled after that of the United Kingdom. The name is derived from the French , the action of parler : a parlement is a discussion. The term came to mean a meeting at which...
) in 1505, transferred most of the legislative power
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
from the monarch
Monarch
A monarch is the person who heads a monarchy. This is a form of government in which a state or polity is ruled or controlled by an individual who typically inherits the throne by birth and occasionally rules for life or until abdication...
to the Sejm. This event marked the beginning of the period known as "Golden Liberty
Golden Liberty
Golden Liberty , sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth refers to a unique aristocratic political system in the Kingdom of Poland and later, after the Union of Lublin , in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth...
", when the state was ruled by the "free and equal" Polish nobility
Szlachta
The szlachta was a legally privileged noble class with origins in the Kingdom of Poland. It gained considerable institutional privileges during the 1333-1370 reign of Casimir the Great. In 1413, following a series of tentative personal unions between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of...
. Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
movements made deep inroads into the Polish Christianity, which resulted in unique at that time in Europe policies of religious tolerance
Religious toleration
Toleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
. The European Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
currents evoked in late Jagiellon Poland (kings Sigismund I the Old
Sigismund I the Old
Sigismund I of Poland , of the Jagiellon dynasty, reigned as King of Poland and also as the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until 1548...
and Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus I was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the only son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548...
) an immense cultural flowering
Renaissance in Poland
The Renaissance in Poland lasted from the late 15th to the late 16th century and is widely considered to have been the Golden Age of Polish culture. Ruled by the Jagiellon dynasty, the Kingdom of Poland actively participated in the broad European Renaissance...
. Poland's and Lithuania's territorial expansion included the far north region of Livonia
Livonia
Livonia is a historic region along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It was once the land of the Finnic Livonians inhabiting the principal ancient Livonian County Metsepole with its center at Turaida...
.
See also
- Culture of medieval PolandCulture of medieval PolandThe culture of medieval Poland was closely linked to the Catholic Church in Poland and its involvement in the country's affairs, especially during the first centuries of the Polish state's history...
- ObotritesObotritesThe Obotrites , also commonly known as the Obodrites, Abotrites, or Abodrites, were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany . For decades they were allies of Charlemagne in his wars against Germanic Saxons and Slavic...
- Principality of NitraPrincipality of NitraThe Principality of Nitra also Nitrian Principality or Slovak Principality is the name for a polity of Nitra Sloviens, centered on large agglomeration, a multi-tribal centre around Nitra, Slovakia. The initially independent Principality of Nitra came into existence in the early 9th century...

