
John C. Pemberton
Encyclopedia
John Clifford Pemberton (August 10, 1814 – July 13, 1881), was a career United States Army
officer who fought in the Seminole Wars
and with distinction during the Mexican–American War
. He also served as a Confederate
general during the American Civil War
, noted for his defeat and surrender in the critical Siege of Vicksburg in the summer of 1863. After the war he took up farming.
at West Point
in 1833, and graduated four years later, standing 27th out of 50 cadets. He was commissioned a second lieutenant in the 4th U.S. Artillery
Regiment
on July 1, 1837. He participated with the 4th during the U.S. actions against the Seminole
Indians, tribe of native Americans in 1837 and 1838, fighting in Florida
at the Battle of Locha-Hatchee on January 24, 1838.
Pemberton and the 4th Artillery served in garrison
duty at Fort Columbus, New York
, in 1838 and into 1839, and then at the Camp of Instruction located near Trenton, New Jersey
, in 1839. He then served along the northern U.S. frontier during the Canada
Border Disturbances. Pemberton and the 4th were next stationed in Michigan
, serving at Detroit
in 1840, at Fort Mackinac
in 1840 and 1841, and at Fort Bradyin in 1841. He then served in Buffalo, New York
, in 1841 to 1842, and was promoted to first lieutenant on March 19, 1842. Pemberton and the 4th returned to garrison duty at Fort Monroe, Virginia
in 1842, then were stationed at the U.S. Army Cavalry School at Carlisle Barracks
, Pennsylvania
, in 1842 and 1843, and returned to Fort Monroe from 1844 to 1845.
, and then the 4th was sent to Mexico
at the start of the Mexican-American War. He fought at the Battle of Palo Alto
on May 8, 1846, and at the Battle of Resaca de la Palma
the next day. He then fought well at the Battle of Monterrey
in that fall, and was appointed a brevet
captain "for Gallant Conduct in the several Conflicts at [Monterrey]" on September 23.
Pemberton then fought in the Army's 1847 actions in Mexico, including the Siege of Vera Cruz in March, the Battle of Cerro Gordo
in April, the skirmish near Amazoque in May, the capture of San Antonio and the Battle of Churubusco
in August, and most notably in the Battle of Molino del Rey
that September. Pemberton was appointed a brevet major
for his performance at Molino del Rey on September 8. He then was part of the storming of Chapultepec Castle on September 13, and the Battle for Mexico City
that day and the next, where Pemberton was wounded. Pemberton held the position of aide-de-camp
to Brev. Brig. Gen.
William J. Worth
from August 4, 1846, to May 1, 1849.
After the war with Mexico ended, Pemberton and the 4th Artillery served in garrison duty at Fort Pickens
near Pensacola, Florida
, in 1849. He then fought in Florida during hostilities against the Seminoles in 1849 and 1850. The 4th returned to garrison duty at New Orleans Barracks in Louisiana
in 1850, and Pemberton was promoted to captain on September 16. He next served in Fort Washington
, Maryland
, in 1851 and 1852, at Fort Hamilton, New York, in 1852 to 1856. He and the 4th fought again in Florida during hostilities against the Seminoles from 1856 to 1857.
Pemberton and the 4th was then on frontier duty at Fort Leavenworth
, Kansas
, from 1857 to 1858, and participated in the Utah War
in 1858. He was the stationed at Fort Kearny
in the New Mexico Territory
in 1859, at Fort Ridgely in present-day Minnesota
from 1859 to 1861, and in garrison duty at the Washington Arsenal in Washington, D.C.
, in 1861.
, despite his Northern
birth and the fact that his two brothers both fought for the Union. He resigned his commission, effective April 29. His decision was due to the influence of his Virginia
-born wife and many years of service in the southern states before the war. He was appointed a lieutenant colonel
in the Confederate Army
on March 28, and was made assistant adjutant general
of the forces around and in the Southern
capital of Richmond, Virginia
, on April 29. He was promoted to colonel
on May 8, and the next day was assigned to the Virginia Provisional Army Artillery
, with the rank of lieutenant colonel. Pemberton was then appointed a major
in the Confederate Army Artillery on June 15 and quickly promoted to brigadier general two days later. His first brigade
command was in the Department of Norfolk
, leading its 10th Brigade from June to November.
Pemberton was promoted to major general on January 14, 1862, and given command the Confederate Department of South Carolina and Georgia, an assignment lasting from March 14 to August 29, with his headquarters in Charleston
. As a result of Pemberton's abrasive personality, his public statement that if he had to make the choice he would abandon the area rather than risk the loss of his outnumbered army, and the distrust of his Northern birth, the governors of both states in his Department petitioned Confederate President
Jefferson Davis
for his removal. Davis needed a commander for a new department in Mississippi
and also a command for Gen. P.G.T. Beauregard, so he sent Pemberton west and assigned the more popular Beauregard to Charleston.
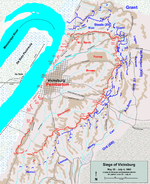
 On October 10, 1862, Pemberton was promoted to the rank of lieutenant general, and assigned to defend the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi
On October 10, 1862, Pemberton was promoted to the rank of lieutenant general, and assigned to defend the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi
, and the Mississippi River
, known as the Department of Mississippi and West Louisiana
. Davis gave him the following instructions regarding his new assignment: "... consider the successful defense of those States as the first and chief object of your command." Pemberton arrived at his new headquarters in Jackson, Mississippi
, on October 14.
His forces consisted of fewer than 50,000 men under the command of Maj. Gens. Earl Van Dorn
and Sterling Price
, with around 24,000 in the permanent garrisons at Vicksburg and Port Hudson, Louisiana
. John D. Winters
described the men under Pemberton as "a beaten and demoralized army, fresh from the defeat
at Corinth
, Mississippi." Pemberton faced his former Mexican War colleague, the aggressive Union
commander Maj. Gen.
Ulysses S. Grant
and over 100,000 Union soldiers in the Vicksburg Campaign
.
In an attempt to carry out his orders from both Davis and Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
, Pemberton and his Army of Mississippi
set out east to combine with Johnston's forces gathering around Jackson, while remaining in contact and covering Vicksburg. Another order from Johnston changing their proposed meeting location caused Pemberton to turn around, and when he did he accidentally collided with Grant's army at the Battle of Champion Hill
on May 16 and suffered a major defeat. Pemberton retreated to the Big Black River
, where he fought and suffered even more heavy losses on May 17. Pemberton resolved to defend Vicksburg and led his defeated men back into its defenses on May 18. Although advised by Johnston to escape with his army, sacrificing the city, Pemberton held firm for over six weeks, while soldiers and civilians were starved into submission. (Pemberton, well aware of his reputation as a Northerner by birth, was probably influenced by his fear of public condemnation as a traitor if he abandoned Vicksburg.)
On the evening of July 2, 1863, Pemberton asked in writing his four division commanders if they believed their men could "make the marches and undergo the fatigues necessary to accomplish a successful evacuation" after 45 days of siege. With four votes of no, the next day Pemberton asked the Federals for an armistice to allow time for the discussion of terms of surrender, and at 10:00 a.m. on July 4 he surrendered the city and his army to Grant. The written terms (which in the first talks were simply unconditional surrender) were negotiated so that the Confederate soldiers would be paroled and:
Pemberton surrendered 2,166 officers and 27,230 men, 172 cannon, and almost 60,000 muskets and rifles to Grant. This, combined with the successful Siege of Port Hudson
on July 9, gave the Union complete control over the Mississippi River, resulting in a major strategic loss for the Confederacy, and cutting off Lt. Gen. Edmund Kirby Smith
's command and the Trans-Mississippi Theater
from the Confederacy for the rest of the war.
After his surrender, Pemberton was exchanged as a prisoner on October 13, 1863, and he returned to Richmond. There he spent some eight months without an assignment. At first Gen. Braxton Bragg
thought he could use Pemberton, but after conferring with his own ranking officers he advised Davis that taking on the discredited lieutenant general "would not be advisable." Pemberton finally wrote Davis directly, asking he be returned to duty "in any capacity in which you think I may be useful." Davis replied that his own personal confidence in him remained unshaken, saying:
 Pemberton resigned as a general officer on May 9, 1864, and Davis offered him a commission as a lieutenant colonel of artillery three days later, which he accepted, a testimonial of his loyalty to the South and the Confederate cause. He commanded the artillery of the defenses of Richmond until January 9, 1865. He was appointed inspector general
Pemberton resigned as a general officer on May 9, 1864, and Davis offered him a commission as a lieutenant colonel of artillery three days later, which he accepted, a testimonial of his loyalty to the South and the Confederate cause. He commanded the artillery of the defenses of Richmond until January 9, 1865. He was appointed inspector general
of the artillery as of January 7, and held this position until he was captured in Salisbury, North Carolina
, on April 12. Along with Pemberton and his 14 remaining guns, the Federals rounded up about 1,300 men and nearly 10,000 small arms. There is no record of his parole after his capture.
, from 1866 to 1876, and then returned to Pennsylvania. He died in the village of Penllyn, Lower Gwynedd Township, Pennsylvania, five years later and is buried in the Laurel Hill Cemetery
in Philadelphia. There were protests against his being buried at Laurel Hill by the families of several famous people, such as General George Meade, Thomas McKean (Signer of the Declarartion of Independence) and Admiral John Adolphus Bernard Dahlgren. It was decided that Pemberton would be interred elsewhere; however, he ended up in an obscure area of the cemetery. Recently, a ground level plate was surreptitiously added noting the fact that he was a 'Confederate General Staff Officer'.
A statue depicting Pemberton was erected in the Vicksburg National Military Park
.
He was also the uncle of John Pemberton
, a Confederate soldier who later invented Coca-Cola
.
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
officer who fought in the Seminole Wars
Seminole Wars
The Seminole Wars, also known as the Florida Wars, were three conflicts in Florida between the Seminole — the collective name given to the amalgamation of various groups of native Americans and Black people who settled in Florida in the early 18th century — and the United States Army...
and with distinction during the Mexican–American War
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known as the First American Intervention, the Mexican War, or the U.S.–Mexican War, was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848 in the wake of the 1845 U.S...
. He also served as a Confederate
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
general during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
, noted for his defeat and surrender in the critical Siege of Vicksburg in the summer of 1863. After the war he took up farming.
Early life and career
Pemberton was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to as the second child of John Pemberton (1783-1847) and Rebecca Clifford (1792-1869). He entered the United States Military AcademyUnited States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy at West Point is a four-year coeducational federal service academy located at West Point, New York. The academy sits on scenic high ground overlooking the Hudson River, north of New York City...
at West Point
West Point, New York
West Point is a federal military reservation established by President of the United States Thomas Jefferson in 1802. It is a census-designated place located in Town of Highlands in Orange County, New York, United States. The population was 7,138 at the 2000 census...
in 1833, and graduated four years later, standing 27th out of 50 cadets. He was commissioned a second lieutenant in the 4th U.S. Artillery
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
Regiment
Regiment
A regiment is a major tactical military unit, composed of variable numbers of batteries, squadrons or battalions, commanded by a colonel or lieutenant colonel...
on July 1, 1837. He participated with the 4th during the U.S. actions against the Seminole
Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people originally of Florida, who now reside primarily in that state and Oklahoma. The Seminole nation emerged in a process of ethnogenesis out of groups of Native Americans, most significantly Creeks from what is now Georgia and Alabama, who settled in Florida in...
Indians, tribe of native Americans in 1837 and 1838, fighting in Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
at the Battle of Locha-Hatchee on January 24, 1838.
Pemberton and the 4th Artillery served in garrison
Garrison
Garrison is the collective term for a body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it, but now often simply using it as a home base....
duty at Fort Columbus, New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, in 1838 and into 1839, and then at the Camp of Instruction located near Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton is the capital of the U.S. state of New Jersey and the county seat of Mercer County. As of the 2010 United States Census, Trenton had a population of 84,913...
, in 1839. He then served along the northern U.S. frontier during the Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
Border Disturbances. Pemberton and the 4th were next stationed in Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
, serving at Detroit
Detroit, Michigan
Detroit is the major city among the primary cultural, financial, and transportation centers in the Metro Detroit area, a region of 5.2 million people. As the seat of Wayne County, the city of Detroit is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan and serves as a major port on the Detroit River...
in 1840, at Fort Mackinac
Fort Mackinac
Fort Mackinac is a former American military outpost garrisoned from the late 18th century to the late 19th century near Michilimackinac, Michigan, on Mackinac Island...
in 1840 and 1841, and at Fort Bradyin in 1841. He then served in Buffalo, New York
Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second most populous city in the state of New York, after New York City. Located in Western New York on the eastern shores of Lake Erie and at the head of the Niagara River across from Fort Erie, Ontario, Buffalo is the seat of Erie County and the principal city of the...
, in 1841 to 1842, and was promoted to first lieutenant on March 19, 1842. Pemberton and the 4th returned to garrison duty at Fort Monroe, Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
in 1842, then were stationed at the U.S. Army Cavalry School at Carlisle Barracks
Carlisle Barracks
Carlisle Barracks is a United States Army facility located in Carlisle, Pennsylvania. It is part of the United States Army Training and Doctrine Command and is the site of the U.S. Army War College...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
, in 1842 and 1843, and returned to Fort Monroe from 1844 to 1845.
Mexican War
From 1845 to 1846, Pemberton and the 4th Artillery were part of the U.S. Military Occupation of TexasTexas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
, and then the 4th was sent to Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
at the start of the Mexican-American War. He fought at the Battle of Palo Alto
Battle of Palo Alto
The Battle of Palo Alto was the first major battle of the Mexican-American War and was fought on May 8, 1846, on disputed ground five miles from the modern-day city of Brownsville, Texas...
on May 8, 1846, and at the Battle of Resaca de la Palma
Battle of Resaca de la Palma
At the Battle of Resaca de la Palma, one of the early engagements of the Mexican-American War,United States General Zachary Taylor engaged the retreating forces of the Mexican Ejército del Norte under General Mariano Arista on May 9, 1846.-Background:During the night of May 8, following...
the next day. He then fought well at the Battle of Monterrey
Battle of Monterrey
In the Battle of Monterrey during the Mexican-American War, General Pedro de Ampudia and the Mexican Army of the North was defeated by U.S...
in that fall, and was appointed a brevet
Brevet (military)
In many of the world's military establishments, brevet referred to a warrant authorizing a commissioned officer to hold a higher rank temporarily, but usually without receiving the pay of that higher rank except when actually serving in that role. An officer so promoted may be referred to as being...
captain "for Gallant Conduct in the several Conflicts at [Monterrey]" on September 23.
Pemberton then fought in the Army's 1847 actions in Mexico, including the Siege of Vera Cruz in March, the Battle of Cerro Gordo
Battle of Cerro Gordo
The Battle of Cerro Gordo, or Battle of Sierra Gordo, in the Mexican-American War saw Winfield Scott's United States troops flank and drive Santa Anna's larger Mexican army from a strong defensive position.-Battle:...
in April, the skirmish near Amazoque in May, the capture of San Antonio and the Battle of Churubusco
Battle of Churubusco
The Battle of Churubusco took place on August 20, 1847, in the immediate aftermath of the Battle of Contreras during the Mexican-American War. After defeating the Mexican army at Churubusco, the U.S. Army was only 5 miles away from Mexico City, the capital of the nation...
in August, and most notably in the Battle of Molino del Rey
Battle of Molino del Rey
The Battle of Molino del Rey was one of the bloodiest engagements of the Mexican-American War. It was fought in September 1847 between Mexican forces under General Antonio Léon against an American force under General Winfield Scott at a hill called El Molino del Rey near Mexico City.-Background:On...
that September. Pemberton was appointed a brevet major
Major (United States)
In the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, major is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of captain and just below the rank of lieutenant colonel...
for his performance at Molino del Rey on September 8. He then was part of the storming of Chapultepec Castle on September 13, and the Battle for Mexico City
Battle for Mexico City
The Battle for Mexico City refers to the series of engagements from September 8 to September 15, 1847, in the general vicinity of Mexico City during the Mexican-American War...
that day and the next, where Pemberton was wounded. Pemberton held the position of aide-de-camp
Aide-de-camp
An aide-de-camp is a personal assistant, secretary, or adjutant to a person of high rank, usually a senior military officer or a head of state...
to Brev. Brig. Gen.
Brigadier general (United States)
A brigadier general in the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, is a one-star general officer, with the pay grade of O-7. Brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below major general. Brigadier general is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral in the other uniformed...
William J. Worth
William J. Worth
William Jenkins Worth was a United States general during the Mexican-American War.-Early life:Worth was born in 1794 in Hudson, New York, to Thomas Worth and Abigail Jenkins. Both of his parents were Quakers, but he rejected the pacifism of their faith...
from August 4, 1846, to May 1, 1849.
After the war with Mexico ended, Pemberton and the 4th Artillery served in garrison duty at Fort Pickens
Fort Pickens
Fort Pickens is a pentagonal historic United States military fort on Santa Rosa Island in the Pensacola, Florida, area. It is named after American Revolutionary War hero Andrew Pickens. The fort was completed in 1834 and remained in use until 1947...
near Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle and the county seat of Escambia County, Florida, United States of America. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 56,255 and as of 2009, the estimated population was 53,752...
, in 1849. He then fought in Florida during hostilities against the Seminoles in 1849 and 1850. The 4th returned to garrison duty at New Orleans Barracks in Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
in 1850, and Pemberton was promoted to captain on September 16. He next served in Fort Washington
Fort Washington, Maryland
Fort Washington, Maryland is an unincorporated area and census-designated place in Prince George's County, Maryland in the suburbs of the capital city of the United States of America, Washington, D.C., south of the downtown district. It is a prosperous community with an African American majority...
, Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
, in 1851 and 1852, at Fort Hamilton, New York, in 1852 to 1856. He and the 4th fought again in Florida during hostilities against the Seminoles from 1856 to 1857.
Pemberton and the 4th was then on frontier duty at Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth is a United States Army facility located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, immediately north of the city of Leavenworth in the upper northeast portion of the state. It is the oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C. and has been in operation for over 180 years...
, Kansas
Kansas
Kansas is a US state located in the Midwestern United States. It is named after the Kansas River which flows through it, which in turn was named after the Kansa Native American tribe, which inhabited the area. The tribe's name is often said to mean "people of the wind" or "people of the south...
, from 1857 to 1858, and participated in the Utah War
Utah War
The Utah War, also known as the Utah Expedition, Buchanan's Blunder, the Mormon War, or the Mormon Rebellion was an armed confrontation between LDS settlers in the Utah Territory and the armed forces of the United States government. The confrontation lasted from May 1857 until July 1858...
in 1858. He was the stationed at Fort Kearny
Fort Kearny
Fort Kearny was a historic outpost of the United States Army founded in 1848 in the western U.S. during the middle and late 19th century. The outpost was located along the Oregon Trail near present-day Kearney, Nebraska, which took its name from the fort .-Origins and various missions of the...
in the New Mexico Territory
New Mexico Territory
thumb|right|240px|Proposed boundaries for State of New Mexico, 1850The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of...
in 1859, at Fort Ridgely in present-day Minnesota
Minnesota
Minnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
from 1859 to 1861, and in garrison duty at the Washington Arsenal in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
, in 1861.
Civil War service
At the start of the American Civil War in 1861, Pemberton chose to resign his commission and join the Confederate causeConfederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
, despite his Northern
Northern United States
Northern United States, also sometimes the North, may refer to:* A particular grouping of states or regions of the United States of America. The United States Census Bureau divides some of the northernmost United States into the Midwest Region and the Northeast Region...
birth and the fact that his two brothers both fought for the Union. He resigned his commission, effective April 29. His decision was due to the influence of his Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
-born wife and many years of service in the southern states before the war. He was appointed a lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant Colonel (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Air Force, and United States Marine Corps, a lieutenant colonel is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of major and just below the rank of colonel. It is equivalent to the naval rank of commander in the other uniformed services.The pay...
in the Confederate Army
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
on March 28, and was made assistant adjutant general
Adjutant general
An Adjutant General is a military chief administrative officer.-Imperial Russia:In Imperial Russia, the General-Adjutant was a Court officer, who was usually an army general. He served as a personal aide to the Tsar and hence was a member of the H. I. M. Retinue...
of the forces around and in the Southern
Southern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
capital of Richmond, Virginia
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
, on April 29. He was promoted to colonel
Colonel
Colonel , abbreviated Col or COL, is a military rank of a senior commissioned officer. It or a corresponding rank exists in most armies and in many air forces; the naval equivalent rank is generally "Captain". It is also used in some police forces and other paramilitary rank structures...
on May 8, and the next day was assigned to the Virginia Provisional Army Artillery
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
, with the rank of lieutenant colonel. Pemberton was then appointed a major
Major
Major is a rank of commissioned officer, with corresponding ranks existing in almost every military in the world.When used unhyphenated, in conjunction with no other indicator of rank, the term refers to the rank just senior to that of an Army captain and just below the rank of lieutenant colonel. ...
in the Confederate Army Artillery on June 15 and quickly promoted to brigadier general two days later. His first brigade
Brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that is typically composed of two to five battalions, plus supporting elements depending on the era and nationality of a given army and could be perceived as an enlarged/reinforced regiment...
command was in the Department of Norfolk
Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. With a population of 242,803 as of the 2010 Census, it is Virginia's second-largest city behind neighboring Virginia Beach....
, leading its 10th Brigade from June to November.
Pemberton was promoted to major general on January 14, 1862, and given command the Confederate Department of South Carolina and Georgia, an assignment lasting from March 14 to August 29, with his headquarters in Charleston
Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the second largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. It was made the county seat of Charleston County in 1901 when Charleston County was founded. The city's original name was Charles Towne in 1670, and it moved to its present location from a location on the west bank of the...
. As a result of Pemberton's abrasive personality, his public statement that if he had to make the choice he would abandon the area rather than risk the loss of his outnumbered army, and the distrust of his Northern birth, the governors of both states in his Department petitioned Confederate President
President of the Confederate States of America
The President of the Confederate States of America was the Head of State and Head of Government of the Confederate States of America, which was formed from the states which declared their secession from the United States, thus precipitating the American Civil War. The only person to hold the...
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Finis Davis , also known as Jeff Davis, was an American statesman and leader of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, serving as President for its entire history. He was born in Kentucky to Samuel and Jane Davis...
for his removal. Davis needed a commander for a new department in Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
and also a command for Gen. P.G.T. Beauregard, so he sent Pemberton west and assigned the more popular Beauregard to Charleston.
Vicksburg


Vicksburg, Mississippi
Vicksburg is a city in Warren County, Mississippi, United States. It is the only city in Warren County. It is located northwest of New Orleans on the Mississippi and Yazoo rivers, and due west of Jackson, the state capital. In 1900, 14,834 people lived in Vicksburg; in 1910, 20,814; in 1920,...
, and the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
, known as the Department of Mississippi and West Louisiana
Louisiana in the American Civil War
Antebellum Louisiana was a leading slave state, where enslaved Africans and African Americans comprised the majority of the population through the eighteenth century. By 1860 47% of the population was enslaved. The state also had one of the largest free black populations in the United States...
. Davis gave him the following instructions regarding his new assignment: "... consider the successful defense of those States as the first and chief object of your command." Pemberton arrived at his new headquarters in Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson is the capital and the most populous city of the US state of Mississippi. It is one of two county seats of Hinds County ,. The population of the city declined from 184,256 at the 2000 census to 173,514 at the 2010 census...
, on October 14.
His forces consisted of fewer than 50,000 men under the command of Maj. Gens. Earl Van Dorn
Earl Van Dorn
Earl Van Dorn was a career United States Army officer, fighting with distinction during the Mexican-American War and against several tribes of Native Americans...
and Sterling Price
Sterling Price
Sterling Price was a lawyer, planter, and politician from the U.S. state of Missouri, who served as the 11th Governor of the state from 1853 to 1857. He also served as a United States Army brigadier general during the Mexican-American War, and a Confederate Army major general in the American Civil...
, with around 24,000 in the permanent garrisons at Vicksburg and Port Hudson, Louisiana
Port Hudson, Louisiana
Port Hudson is a small unincorporated community in East Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, United States. Located about northwest of Baton Rouge, it is most famous for an American Civil War battle known as the Siege of Port Hudson.-Geography:...
. John D. Winters
John D. Winters
John David Winters was a historian at Louisiana Tech University in Ruston, Louisiana, best known for his definitive and award-winning study, The Civil War in Louisiana, still in print, published in 1963 and released in paperback in 1991.-Background:Winters was born to John David Winters, Sr...
described the men under Pemberton as "a beaten and demoralized army, fresh from the defeat
Second Battle of Corinth
The Second Battle of Corinth was fought October 3–4, 1862, in Corinth, Mississippi. For the second time in the Iuka-Corinth Campaign, Union Maj. Gen. William S...
at Corinth
Corinth, Mississippi
Corinth is a city in Alcorn County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 14,054 at the 2000 census. It is the county seat of Alcorn County. Its ZIP codes are 38834 and 38835.- History :...
, Mississippi." Pemberton faced his former Mexican War colleague, the aggressive Union
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
commander Maj. Gen.
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th President of the United States as well as military commander during the Civil War and post-war Reconstruction periods. Under Grant's command, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and ended the Confederate States of America...
and over 100,000 Union soldiers in the Vicksburg Campaign
Vicksburg Campaign
The Vicksburg Campaign was a series of maneuvers and battles in the Western Theater of the American Civil War directed against Vicksburg, Mississippi, a fortress city that dominated the last Confederate-controlled section of the Mississippi River. The Union Army of the Tennessee under Maj. Gen....
.
In an attempt to carry out his orders from both Davis and Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston was a career U.S. Army officer, serving with distinction in the Mexican-American War and Seminole Wars, and was also one of the most senior general officers in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War...
, Pemberton and his Army of Mississippi
Army of Mississippi
There were three organizations known as the Army of Mississippi in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. -Army of Mississippi :This army, at times known by the names Army of the West or Army of the...
set out east to combine with Johnston's forces gathering around Jackson, while remaining in contact and covering Vicksburg. Another order from Johnston changing their proposed meeting location caused Pemberton to turn around, and when he did he accidentally collided with Grant's army at the Battle of Champion Hill
Battle of Champion Hill
The Battle of Champion Hill, or Bakers Creek, fought May 16, 1863, was the pivotal battle in the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. Union commander Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee pursued the retreating Confederate Lt. Gen. John C...
on May 16 and suffered a major defeat. Pemberton retreated to the Big Black River
Battle of Big Black River Bridge
The Battle of Big Black River Bridge, or Big Black, fought May 17, 1863, was part of the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. Union commander Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee pursued the retreating Confederate Lt. Gen. John C...
, where he fought and suffered even more heavy losses on May 17. Pemberton resolved to defend Vicksburg and led his defeated men back into its defenses on May 18. Although advised by Johnston to escape with his army, sacrificing the city, Pemberton held firm for over six weeks, while soldiers and civilians were starved into submission. (Pemberton, well aware of his reputation as a Northerner by birth, was probably influenced by his fear of public condemnation as a traitor if he abandoned Vicksburg.)
On the evening of July 2, 1863, Pemberton asked in writing his four division commanders if they believed their men could "make the marches and undergo the fatigues necessary to accomplish a successful evacuation" after 45 days of siege. With four votes of no, the next day Pemberton asked the Federals for an armistice to allow time for the discussion of terms of surrender, and at 10:00 a.m. on July 4 he surrendered the city and his army to Grant. The written terms (which in the first talks were simply unconditional surrender) were negotiated so that the Confederate soldiers would be paroled and:
Pemberton surrendered 2,166 officers and 27,230 men, 172 cannon, and almost 60,000 muskets and rifles to Grant. This, combined with the successful Siege of Port Hudson
Siege of Port Hudson
The Siege of Port Hudson occurred from May 22 to July 9, 1863, when Union Army troops assaulted and then surrounded the Mississippi River town of Port Hudson, Louisiana, during the American Civil War....
on July 9, gave the Union complete control over the Mississippi River, resulting in a major strategic loss for the Confederacy, and cutting off Lt. Gen. Edmund Kirby Smith
Edmund Kirby Smith
Edmund Kirby Smith was a career United States Army officer and educator. He served as a general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War, notable for his command of the Trans-Mississippi Department of the Confederacy after the fall of Vicksburg.After the conflict ended Smith...
's command and the Trans-Mississippi Theater
Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War
The Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War was the major military and naval operations west of the Mississippi River. The area excluded the states and territories bordering the Pacific Ocean, which formed the Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War.The campaign classification...
from the Confederacy for the rest of the war.
After his surrender, Pemberton was exchanged as a prisoner on October 13, 1863, and he returned to Richmond. There he spent some eight months without an assignment. At first Gen. Braxton Bragg
Braxton Bragg
Braxton Bragg was a career United States Army officer, and then a general in the Confederate States Army—a principal commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War and later the military adviser to Confederate President Jefferson Davis.Bragg, a native of North Carolina, was...
thought he could use Pemberton, but after conferring with his own ranking officers he advised Davis that taking on the discredited lieutenant general "would not be advisable." Pemberton finally wrote Davis directly, asking he be returned to duty "in any capacity in which you think I may be useful." Davis replied that his own personal confidence in him remained unshaken, saying:

Inspector General
An Inspector General is an investigative official in a civil or military organization. The plural of the term is Inspectors General.-Bangladesh:...
of the artillery as of January 7, and held this position until he was captured in Salisbury, North Carolina
Salisbury, North Carolina
Salisbury is a city in Rowan County in North Carolina, a state of the United States of America. The population was 33,663 in the 2010 Census . It is the county seat of Rowan County...
, on April 12. Along with Pemberton and his 14 remaining guns, the Federals rounded up about 1,300 men and nearly 10,000 small arms. There is no record of his parole after his capture.
Postbellum life
After the war, John Pemberton lived on his farm near Warrenton, VirginiaWarrenton, Virginia
Warrenton is a town in Fauquier County, Virginia, United States. The population was 6,670 at the 2000 census, and 14,634 at the 2010 estimate. It is the county seat of Fauquier County. Public schools in the town include Fauquier High School, Warrenton Middle School, Taylor Middle School and two...
, from 1866 to 1876, and then returned to Pennsylvania. He died in the village of Penllyn, Lower Gwynedd Township, Pennsylvania, five years later and is buried in the Laurel Hill Cemetery
Laurel Hill Cemetery
Laurel Hill Cemetery, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, is the second major garden or rural cemetery in the United States. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1998, one of only a few cemeteries to receive the distinction....
in Philadelphia. There were protests against his being buried at Laurel Hill by the families of several famous people, such as General George Meade, Thomas McKean (Signer of the Declarartion of Independence) and Admiral John Adolphus Bernard Dahlgren. It was decided that Pemberton would be interred elsewhere; however, he ended up in an obscure area of the cemetery. Recently, a ground level plate was surreptitiously added noting the fact that he was a 'Confederate General Staff Officer'.
A statue depicting Pemberton was erected in the Vicksburg National Military Park
Vicksburg National Military Park
Vicksburg National Military Park preserves the site of the American Civil War Battle of Vicksburg, waged from May 18 to July 4, 1863. The park, in Vicksburg, Mississippi, and Delta, Louisiana, also commemorates the greater Vicksburg Campaign, which preceded the battle. Reconstructed forts and...
.
He was also the uncle of John Pemberton
John Pemberton
John Stith Pemberton was a Confederate veteran and an American druggist, and is best known for being the inventor of Coca-Cola.-Early life:...
, a Confederate soldier who later invented Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola is a carbonated soft drink sold in stores, restaurants, and vending machines in more than 200 countries. It is produced by The Coca-Cola Company of Atlanta, Georgia, and is often referred to simply as Coke...
.
See also
- List of American Civil War generals
Further reading
- Ballard, Michael B. Vicksburg, The Campaign that Opened the Mississippi. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2004. ISBN 0-8078-2893-9.
- Bearss, Edwin C.Ed BearssEdwin Cole Bearss , a United States Marine Corps veteran of World War II, is a military historian and author known for his work on the American Civil War and World War II eras and is a popular tour guide of historic battlefields...
The Campaign for Vicksburg. 3 vols. Dayton, OH: Morningside House, 1985. ISBN 978-0-89029-312-6. - Groom, WinstonWinston GroomWinston F. Groom, Jr. is an American novelist and non-fiction writer, best known for his book Forrest Gump, which was adapted into a film in 1994.- Life :...
. Vicksburg, 1863. New York: Knopf, 2009. ISBN 978-0-307-26425-1. - Winschel, Terrence J. Triumph & Defeat: The Vicksburg Campaign. Campbell, CA: Savas Publishing Company, 1999. ISBN 1-882810-31-7.
- Woodworth, Steven E. Jefferson Davis and His Generals: The Failure of Confederate Command in the West. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1990. ISBN 0-7006-0461-8.

