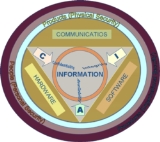
Information security
Encyclopedia
Information security means protecting information and information system
s from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, perusal, inspection, recording or destruction.
The terms information security, computer security
and information assurance
are
frequently incorrectly used interchangeably. These fields are interrelated often and share the common goals of
protecting the confidentiality
, integrity
and availability
of information; however, there are some subtle differences between them.
These differences lie primarily in the approach to the subject, the methodologies used, and the areas of concentration.
Information security is concerned with the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data
regardless of the form the data may take: electronic, print, or other forms. Computer security can focus on ensuring the availability and correct operation of a computer system without concern for the information stored or processed by the computer.
Governments, military
, corporations, financial institutions, hospitals, and private businesses amass a great deal of confidential information about their employees, customers, products, research, and financial status. Most of this information is now collected, processed and stored on electronic computers and transmitted across network
s to other computers.
Should confidential information about a business' customers or finances or new product line fall into the hands of a competitor, such a breach of security could lead to lost business, law suits or even bankruptcy
of the business. Protecting confidential information is a business requirement, and in many cases also an ethical and legal requirement.
For the individual, information security has a significant effect on privacy
, which is viewed very differently in different cultures.
The field of information security has grown and evolved significantly in recent years. There are many ways of gaining entry into the field as a career. It offers many areas for specialization including: securing network(s) and allied infrastructure
, securing applications
and database
s, security testing
, information systems audit
ing, business continuity planning
and digital forensics
science, etc.
This article presents a general overview of information security and its core concepts.
and military commanders understood that it was necessary to provide some mechanism to protect the confidentiality of written correspondence and to have some means of detecting tampering
.
Julius Caesar
is credited with the invention of the Caesar cipher
ca. 50 B.C., which was created in order to prevent his secret messages from being read should a message fall into the wrong hands.
World War II
brought about many advancements in information security and marked the beginning of the professional field of information security.
The end of the 20th century and early years of the 21st century saw rapid advancements in telecommunications, computing hardware
and software, and data encryption
. The availability of smaller, more powerful and less expensive computing equipment made electronic data processing
within the reach of small business
and the home user. These computers quickly became interconnected through a network generically called the Internet or World Wide Web.
The rapid growth and widespread use of electronic data processing and electronic business
conducted through the Internet, along with numerous occurrences of international terrorism
, fueled the need for better methods of protecting the computers and the information they store, process and transmit. The academic disciplines of computer security
, information security and information assurance
emerged along with numerous professional organizations – all sharing the common goals of ensuring the security and reliability of information systems.
There is continuous debate about extending this classic trio. Other principles such as Accountability have sometimes been proposed for addition – it has been pointed out that issues such as Non-Repudiation
do not fit well within the three core concepts, and as regulation of computer systems has increased (particularly amongst the Western nations) Legality is becoming a key consideration for practical security installations.
In 1992 and revised in 2002 the OECD's Guidelines for the Security of Information Systems and Networks proposed the nine generally accepted principles: Awareness, Responsibility, Response, Ethics, Democracy, Risk Assessment, Security Design and Implementation, Security Management, and Reassessment. Building upon those, in 2004 the NIST's Engineering Principles for Information Technology Security proposed 33 principles. From each of these derived guidelines and practices.
In 2002, Donn Parker proposed an alternative model for the classic CIA triad that he called the six atomic elements of information
. The elements are confidentiality
, possession
, integrity
, authenticity
, availability
, and utility
. The merits of the Parkerian hexad
are a subject of debate amongst security professionals.
is the term used to prevent the disclosure of information to unauthorized individuals or systems. For example, a credit card
transaction
on the Internet requires the credit card number to be transmitted from the buyer to the merchant and from the merchant to a transaction processing
network. The system attempts to enforce confidentiality by encrypting the card number during transmission, by limiting the places where it might appear (in databases, log files, backups, printed receipts, and so on), and by restricting access to the places where it is stored. If an unauthorized party obtains the card number in any way, a breach of confidentiality has occurred.
Breaches of confidentiality take many forms. Permitting someone to look over your shoulder at your computer screen while you have confidential data displayed on it could be a breach of confidentiality. If a laptop computer containing sensitive information about a company's employees is stolen or sold, it could result in a breach of confidentiality. Giving out confidential information over the telephone is a breach of confidentiality if the caller is not authorized to have the information.
Confidentiality is necessary (but not sufficient) for maintaining the privacy
of the people whose personal information a system holds.
in databases, although it can be viewed as a special case of Consistency as understood in the classic ACID
model of transaction processing
. Integrity is violated when a message is actively modified in transit. Information security systems typically provide message integrity in addition to data confidentiality.
when it is needed. This means that the computing systems used to store and process the information, the security controls
used to protect it, and the communication channels used to access it must be functioning correctly. High availability
systems aim to remain available at all times, preventing service disruptions due to power outages, hardware failures, and system upgrades. Ensuring availability also involves preventing denial-of-service attack
s.
implies one's intention to fulfill their obligations to a contract. It also implies that one party of a transaction cannot deny having received a transaction nor can the other party deny having sent a transaction.
Electronic commerce
uses technology such as digital signature
s and public key encryption to establish authenticity and non-repudiation.
is beyond the scope of this article. However, a useful definition of risk management will be provided as well as some basic terminology and a commonly used process for risk management.
The CISA Review Manual 2006 provides the following definition of risk management: "Risk management is the process of identifying vulnerabilities
and threats
to the information resources used by an organization in achieving business objectives, and deciding what countermeasures
, if any, to take in reducing risk to an acceptable level, based on the value of the information resource to the organization."
There are two things in this definition that may need some clarification. First, the process of risk management is an ongoing iterative process
. It must be repeated indefinitely. The business environment is constantly changing and new threats
and vulnerability
emerge every day. Second, the choice of countermeasures
(controls
) used to manage risks must strike a balance between productivity, cost, effectiveness of the countermeasure, and the value of the informational asset being protected.
Risk is the likelihood that something bad will happen that causes harm to an informational asset (or the loss of the asset). A vulnerability is a weakness that could be used to endanger or cause harm to an informational asset. A threat is anything (man made or act of nature
) that has the potential to cause harm.
The likelihood that a threat will use a vulnerability to cause harm creates a risk. When a threat does use a vulnerability to inflict harm, it has an impact. In the context of information security, the impact is a loss of availability, integrity, and confidentiality, and possibly other losses (lost income, loss of life, loss of real property). It should be pointed out that it is not possible to identify all risks, nor is it possible to eliminate all risk. The remaining risk is called residual risk.
A risk assessment
is carried out by a team of people who have knowledge of specific areas of the business. Membership of the team may vary over time as different parts of the business are assessed. The assessment may use a subjective qualitative analysis based on informed opinion, or where reliable dollar figures and historical information is available, the analysis may use quantitative
analysis.
The research has shown that the most vulnerable point in most information systems is the human user, operator, designer, or other human
The ISO/IEC 27002:2005 Code of practice for information security management
recommends the following be examined during a risk assessment:
In broad terms, the risk management process consists of:
For any given risk, Executive Management can choose to accept the risk based upon the relative low value of the asset, the relative low frequency of occurrence, and the relative low impact on the business. Or, leadership may choose to mitigate the risk by selecting and implementing appropriate control measures to reduce the risk. In some cases, the risk can be transferred to another business by buying insurance or out-sourcing to another business. The reality of some risks may be disputed. In such cases leadership may choose to deny the risk.
and Master Card
is such an example. Other examples of administrative controls include the corporate security policy, password policy
, hiring policies, and disciplinary policies.
Administrative controls form the basis for the selection and implementation of logical and physical controls. Logical and physical controls are manifestations of administrative controls. Administrative controls are of paramount importance.
systems, access control list
s, and data encryption are
logical controls.
An important logical control that is frequently overlooked is the principle of least privilege. The principle of least privilege
requires that an individual, program or system process is not granted any more access privileges than are necessary to perform the task. A blatant example of the failure to adhere to the principle of least privilege is logging into Windows as user Administrator to read Email and surf the Web. Violations of this principle can also occur when an individual
collects additional access privileges over time. This happens when employees' job duties change, or they are promoted to a new position, or they transfer to another department. The access privileges required by their new duties are frequently added onto their already existing access privileges which may no longer be necessary or appropriate.
place into functional areas are also physical controls.
An important physical control that is frequently overlooked is the separation of duties. Separation of duties ensures that an individual can not complete a critical task by himself. For example: an employee who submits a request for reimbursement should not also be able to authorize payment or print the check. An applications programmer should not also be the server administrator
or the database administrator
– these roles and responsibilities must be separated from one another.
 Information security must protect information throughout the life span of the information, from the initial creation of the information on through to the final disposal of the information. The information must be protected while in motion and while at rest. During its lifetime, information may pass through many different information processing systems and through many different parts of information processing systems. There are many different ways the information and information systems can be threatened. To fully protect the information during its lifetime, each component of the information processing system must have its own protection mechanisms. The building up, layering on and overlapping of security measures is called defense in depth. The strength of any system is no greater than its weakest link. Using a defence in depth strategy, should one defensive measure fail there are other defensive measures in place that continue to provide protection.
Information security must protect information throughout the life span of the information, from the initial creation of the information on through to the final disposal of the information. The information must be protected while in motion and while at rest. During its lifetime, information may pass through many different information processing systems and through many different parts of information processing systems. There are many different ways the information and information systems can be threatened. To fully protect the information during its lifetime, each component of the information processing system must have its own protection mechanisms. The building up, layering on and overlapping of security measures is called defense in depth. The strength of any system is no greater than its weakest link. Using a defence in depth strategy, should one defensive measure fail there are other defensive measures in place that continue to provide protection.
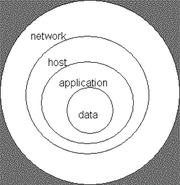
Recall the earlier discussion about administrative controls, logical controls, and physical controls. The three types of controls can be used to form the basis upon which to build a defense-in-depth strategy. With this approach, defense-in-depth can be conceptualized as three distinct layers or planes laid one on top of the other. Additional insight into defense-in- depth can be gained by thinking of it as forming the layers of an onion, with data at the core of the onion, people the next outer layer of the onion, and network security
, host-based security and application security
forming the outermost layers of the onion. Both perspectives are equally valid and each provides valuable insight into the implementation of a good defense-in-depth strategy.
The first step in information classification is to identify a member of senior management as the owner of the particular information to be classified. Next, develop a classification policy. The policy should describe the different classification labels, define the criteria for information to be assigned a particular label, and list the required security controls
for each classification.
Some factors that influence which classification information should be assigned include how much value that information has to the organization, how old the information is and whether or not the information has become obsolete. Laws and other regulatory requirements are also important considerations when classifying information.
The type of information security classification labels selected and used will depend on the nature of the organisation, with examples being:
All employees in the organization, as well as business partners, must be trained on the classification schema and understand the required security controls and handling procedures for each classification. The classification of a particular information asset has been assigned should be reviewed periodically to ensure the classification is still appropriate for the information and to ensure the security controls required by the classification are in place.
.
Identification is an assertion of who someone is or what something is. If a person makes the statement "Hello, my name is John Doe" they are making a claim of who they are. However, their claim may or may not be true. Before John Doe can be granted access to protected information it will be necessary to verify that the person claiming to be John Doe really is John Doe.
Authentication is the act of verifying a claim of identity. When John Doe goes into a bank to make a withdrawal, he tells the bank teller he is John Doe (a claim of identity). The bank teller asks to see a photo ID, so he hands the teller his driver's license. The bank teller checks the license to make sure it has John Doe printed on it and compares the photograph on the license against the person claiming to be John Doe. If the photo and name match the person, then the teller has authenticated that John Doe is who he claimed to be.
There are three different types of information that can be used for authentication: something you know, something you have, or something you are. Examples of something you know include such things as a PIN, a password, or your mother's maiden name. Examples of something you have include a driver's license or a magnetic swipe card. Something you are refers to biometrics. Examples of biometrics include palm prints, finger prints, voice prints and retina (eye) scans. Strong authentication requires providing information from two of the three different types of authentication information. For example, something you know plus something you have. This is called two factor authentication.
On computer systems in use today, the Username is the most common form of identification and the Password is the most common form of authentication. Usernames and passwords have served their purpose but in our modern world they are no longer adequate. Usernames and passwords are slowly being replaced with more sophisticated authentication mechanisms.
After a person, program or computer has successfully been identified and authenticated then it must be determined what informational resources they are permitted to access and what actions they will be allowed to perform (run, view, create, delete, or change). This is called authorization
.
Authorization to access information and other computing services begins with administrative policies and procedures. The policies prescribe what information and computing services can be accessed, by whom, and under what conditions. The access control mechanisms are then configured to enforce these policies.
Different computing systems are equipped with different kinds of access control mechanisms - some may even offer a choice of different access control mechanisms. The access control mechanism a system offers will be based upon one of three approaches to access control or it may be derived from a combination of the three approaches.
The non-discretionary approach consolidates all access control under a centralized administration. The access to information and other resources is usually based on the individuals function (role) in the organization or the tasks the individual must perform. The discretionary approach gives the creator or owner of the information resource the ability to control access to those resources. In the Mandatory access control approach, access is granted or denied basing upon the security classification assigned to the information resource.
Examples of common access control mechanisms in use today include Role-based
access control
available in many advanced Database Management Systems, simple file permissions
provided in the UNIX and Windows operating systems, Group Policy Objects provided in Windows network systems, Kerberos, RADIUS
, TACACS
, and the simple access lists used in many firewalls and routers.
To be effective, policies and other security controls must be enforceable and upheld. Effective policies ensure that people are held accountable for their actions. All failed and successful authentication attempts must be logged, and all access to information must leave some type of audit trail.
to transform usable information into a form that renders it unusable by anyone other than an authorized user; this process is called encryption
. Information that has been encrypted (rendered unusable) can be transformed back into its original usable form by an authorized user, who possesses the cryptographic key
, through the process of decryption. Cryptography is used in information security to protect information from unauthorized or accidental disclosure while the information
is in transit (either electronically or physically) and while information is in storage.
Cryptography provides information security with other useful applications as well including improved authentication methods, message digests, digital signatures, non-repudiation
, and encrypted network communications. Older less secure application such as telnet and ftp are slowly being replaced with more secure applications such as ssh
that use encrypted network communications. Wireless communications can be encrypted using protocols such as WPA/WPA2
or the older (and less secure) WEP
. Wired communications (such as ITU-T
G.hn
) are secured using AES
for encryption and X.1035
for authentication and key exchange. Software applications such as GnuPG or PGP
can be used to encrypt data files and Email.
Cryptography can introduce security problems when it is not implemented correctly. Cryptographic solutions need to be implemented using industry accepted solutions that have undergone rigorous peer review by independent experts in cryptography. The length and strength
of the encryption key is also an important consideration. A key that is weak
or too short will produce weak encryption. The keys used for encryption and decryption must be protected with the same degree of rigor as any other confidential information. They must be protected from unauthorized disclosure and destruction and they must be available when needed. PKI
solutions address many of the problems that surround key management
.
now make it possible to hold corporate officers liable for failing to exercise due care and due diligence in the management of their information systems.
In the business world, stockholders, customers, business partners and governments have the expectation that corporate officers will run the business in accordance with accepted business practices and in compliance with laws and other regulatory requirements. This is often described as the "reasonable and prudent person" rule. A prudent person takes due care to ensure that everything necessary is done to operate the business by sound business principles and in a legal ethical manner. A prudent person is also diligent (mindful, attentive, and ongoing) in their due care of the business.
In the field of Information Security, Harris
offers the following definitions of due care and due diligence:
Attention should be made to two important points in these definitions. First, in due care, steps are taken to show - this means that the steps can be verified, measured, or even produce tangible artifacts. Second, in due diligence, there are continual activities - this means that people are actually doing things to monitor and maintain the protection mechanisms, and these activities are ongoing.
at Carnegie Mellon University
, in a publication titled "Governing for Enterprise Security (GES)", defines characteristics of effective security governance. These include:
processing environment as changes are made. It is not the objective of change management to prevent or hinder necessary changes from being implemented.
Any change to the information processing environment introduces an element of risk. Even apparently simple changes can have unexpected effects. One of Managements many responsibilities is the management of risk. Change management is a tool for managing the risks introduced by changes to the information processing environment. Part of the change management process ensures that changes are not implemented at inopportune times when they may disrupt critical business processes or interfere with other changes being implemented.
Not every change needs to be managed. Some kinds of changes are a part of the everyday routine of information processing and adhere to a predefined procedure, which reduces the overall level of risk to the processing environment. Creating a new user account or deploying a new desktop computer are examples of changes that do not generally require change management. However, relocating user file shares, or upgrading the Email server pose a much higher level of risk to the processing environment and are not a normal everyday activity. The critical first steps in change management are (a) defining change (and communicating that definition) and (b) defining the scope of the change system.
Change management is usually overseen by a Change Review Board composed of representatives from key business areas, security, networking, systems administrators, Database administration, applications development, desktop support and the help desk. The tasks of the Change Review Board can be facilitated with the use of automated work flow application. The responsibility of the Change Review Board is to ensure the organizations documented change management procedures are followed. The change management process is as follows:
Change management procedures that are simple to follow and easy to use can greatly reduce the overall risks created when changes are made to the information processing environment. Good change management procedures improve the over all quality and success of changes as they are implemented. This is accomplished through planning, peer review, documentation and communication.
ISO/IEC 20000, The Visible OPS Handbook: Implementing ITIL in 4 Practical and Auditable Steps (Full book summary), and Information Technology Infrastructure Library
all provide valuable guidance on implementing an efficient and effective change management program information security.
Unlike what most people think business continuity is not necessarily an IT system or process, simply because it is about the business. Today disasters or disruptions to business are a reality. Whether the disaster is natural or man-made, it affects normal life and so business. So why is planning so important? Let us face reality that "all businesses recover", whether they planned for recovery or not, simply because business is about earning money for survival.
The planning is merely getting better prepared to face it, knowing fully well that the best plans may fail. Planning helps to reduce cost of recovery, operational overheads and most importantly sail through some smaller ones effortlessly.
For businesses to create effective plans they need to focus upon the following key questions. Most of these are common knowledge, and anyone can do a BCP.
(ISO) is a consortium of national standards
institutes from 157 countries, coordinated through a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland. ISO is
the world's largest developer of standards. ISO 15443: "Information technology - Security techniques - A framework
for IT security assurance", ISO/IEC 27002
: "Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice for information security management", ISO-20000
: "Information technology - Service management", and ISO/IEC27001
: "Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems - Requirements" are of particular interest to information security professionals.
The USA National Institute of Standards and Technology
(NIST) is a non-regulatory federal agency
within the U.S. Department of Commerce. The NIST Computer Security Division
develops standards, metrics, tests and validation programs as well as publishes standards and guidelines to
increase secure IT planning, implementation, management and operation. NIST is also the custodian of the USA Federal Information Processing Standard
publications (FIPS).
The Internet Society is a professional membership society with more than 100 organization
and over 20,000 individual members in over 180 countries. It provides leadership in addressing issues that confront the
future of the Internet, and is the organization home for the groups responsible for Internet infrastructure standards,
including the Internet Engineering Task Force
(IETF) and the Internet Architecture Board
(IAB). The ISOC hosts the Requests for Comments (RFCs) which includes the Official Internet Protocol Standards
and the RFC-2196 Site Security Handbook
.
The Information Security Forum
is a global nonprofit organization of several hundred leading organizations in financial services, manufacturing, telecommunications, consumer goods, government, and other areas. It undertakes research into information security practices and offers advice in its biannual Standard of Good Practice
and more detailed advisories for members.
The IT Baseline Protection Catalogs
, or IT-Grundschutz Catalogs, ("IT Baseline Protection
Manual" before 2005) are a collection of documents from the German Federal Office for Security in Information Technology (FSI), useful for detecting and combating security-relevant weak points in the IT environment (IT cluster). The collection encompasses over 3000 pages with the introduction and catalogs.
information systems, from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, destruction, modification, or disruption or distribution.
The never ending process of information security involves ongoing training, assessment, protection, monitoring & detection,
incident response & repair, documentation, and review. This makes information security an indispensable part of all the business operations across different domains.
Information system
An information system - or application landscape - is any combination of information technology and people's activities that support operations, management, and decision making. In a very broad sense, the term information system is frequently used to refer to the interaction between people,...
s from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, perusal, inspection, recording or destruction.
The terms information security, computer security
Computer security
Computer security is a branch of computer technology known as information security as applied to computers and networks. The objective of computer security includes protection of information and property from theft, corruption, or natural disaster, while allowing the information and property to...
and information assurance
Information Assurance
Information assurance is the practice of managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information or data and the systems and processes used for those purposes...
are
frequently incorrectly used interchangeably. These fields are interrelated often and share the common goals of
protecting the confidentiality
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is an ethical principle associated with several professions . In ethics, and in law and alternative forms of legal resolution such as mediation, some types of communication between a person and one of these professionals are "privileged" and may not be discussed or divulged to...
, integrity
Data integrity
Data Integrity in its broadest meaning refers to the trustworthiness of system resources over their entire life cycle. In more analytic terms, it is "the representational faithfulness of information to the true state of the object that the information represents, where representational faithfulness...
and availability
Availability
In telecommunications and reliability theory, the term availability has the following meanings:* The degree to which a system, subsystem, or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at an unknown, i.e., a random, time...
of information; however, there are some subtle differences between them.
These differences lie primarily in the approach to the subject, the methodologies used, and the areas of concentration.
Information security is concerned with the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
regardless of the form the data may take: electronic, print, or other forms. Computer security can focus on ensuring the availability and correct operation of a computer system without concern for the information stored or processed by the computer.
Governments, military
Military
A military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
, corporations, financial institutions, hospitals, and private businesses amass a great deal of confidential information about their employees, customers, products, research, and financial status. Most of this information is now collected, processed and stored on electronic computers and transmitted across network
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
s to other computers.
Should confidential information about a business' customers or finances or new product line fall into the hands of a competitor, such a breach of security could lead to lost business, law suits or even bankruptcy
Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal status of an insolvent person or an organisation, that is, one that cannot repay the debts owed to creditors. In most jurisdictions bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor....
of the business. Protecting confidential information is a business requirement, and in many cases also an ethical and legal requirement.
For the individual, information security has a significant effect on privacy
Privacy
Privacy is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves and thereby reveal themselves selectively...
, which is viewed very differently in different cultures.
The field of information security has grown and evolved significantly in recent years. There are many ways of gaining entry into the field as a career. It offers many areas for specialization including: securing network(s) and allied infrastructure
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
, securing applications
Application software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
and database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
s, security testing
Security Testing
Security testing is a process to determine that an information system protects data and maintains functionality as intended.The six basic security concepts that need to be covered by security testing are: confidentiality, integrity, authentication, availability, authorization and non-repudiation...
, information systems audit
Audit
The general definition of an audit is an evaluation of a person, organization, system, process, enterprise, project or product. The term most commonly refers to audits in accounting, but similar concepts also exist in project management, quality management, and energy conservation.- Accounting...
ing, business continuity planning
Business continuity planning
Business continuity planning “identifies [an] organization's exposure to internal and external threats and synthesizes hard and soft assets to provide effective prevention and recovery for the organization, whilst maintaining competitive advantage and value system integrity”. It is also called...
and digital forensics
Digital forensics
Digital forensics is a branch of forensic science encompassing the recovery and investigation of material found in digital devices, often in relation to computer crime...
science, etc.
This article presents a general overview of information security and its core concepts.
History
Since the early days of writing, heads of stateHead of State
A head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
and military commanders understood that it was necessary to provide some mechanism to protect the confidentiality of written correspondence and to have some means of detecting tampering
Tamper-evident
Tamper-evident describes a device or process that makes unauthorized access to the protected object easily detected. Seals, markings or other techniques may be tamper indicating.-Tampering:...
.
Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
is credited with the invention of the Caesar cipher
Caesar cipher
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as a Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number...
ca. 50 B.C., which was created in order to prevent his secret messages from being read should a message fall into the wrong hands.
World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
brought about many advancements in information security and marked the beginning of the professional field of information security.
The end of the 20th century and early years of the 21st century saw rapid advancements in telecommunications, computing hardware
Hardware
Hardware is a general term for equipment such as keys, locks, hinges, latches, handles, wire, chains, plumbing supplies, tools, utensils, cutlery and machine parts. Household hardware is typically sold in hardware stores....
and software, and data encryption
Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of transforming information using an algorithm to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special knowledge, usually referred to as a key. The result of the process is encrypted information...
. The availability of smaller, more powerful and less expensive computing equipment made electronic data processing
Data processing
Computer data processing is any process that a computer program does to enter data and summarise, analyse or otherwise convert data into usable information. The process may be automated and run on a computer. It involves recording, analysing, sorting, summarising, calculating, disseminating and...
within the reach of small business
Small business
A small business is a business that is privately owned and operated, with a small number of employees and relatively low volume of sales. Small businesses are normally privately owned corporations, partnerships, or sole proprietorships...
and the home user. These computers quickly became interconnected through a network generically called the Internet or World Wide Web.
The rapid growth and widespread use of electronic data processing and electronic business
Electronic business
Electronic business, commonly referred to as "eBusiness" or "e-business", or an internet business, may be defined as the application of information and communication technologies in support of all the activities of business...
conducted through the Internet, along with numerous occurrences of international terrorism
Terrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
, fueled the need for better methods of protecting the computers and the information they store, process and transmit. The academic disciplines of computer security
Computer security
Computer security is a branch of computer technology known as information security as applied to computers and networks. The objective of computer security includes protection of information and property from theft, corruption, or natural disaster, while allowing the information and property to...
, information security and information assurance
Information Assurance
Information assurance is the practice of managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information or data and the systems and processes used for those purposes...
emerged along with numerous professional organizations – all sharing the common goals of ensuring the security and reliability of information systems.
Key concepts
For over twenty years, information security has held confidentiality, integrity and availability (known as the CIA triad) to be the core principles of information security.There is continuous debate about extending this classic trio. Other principles such as Accountability have sometimes been proposed for addition – it has been pointed out that issues such as Non-Repudiation
Non-repudiation
Non-repudiation refers to a state of affairs where the purported maker of a statement will not be able to successfully challenge the validity of the statement or contract. The term is often seen in a legal setting wherein the authenticity of a signature is being challenged...
do not fit well within the three core concepts, and as regulation of computer systems has increased (particularly amongst the Western nations) Legality is becoming a key consideration for practical security installations.
In 1992 and revised in 2002 the OECD's Guidelines for the Security of Information Systems and Networks proposed the nine generally accepted principles: Awareness, Responsibility, Response, Ethics, Democracy, Risk Assessment, Security Design and Implementation, Security Management, and Reassessment. Building upon those, in 2004 the NIST's Engineering Principles for Information Technology Security proposed 33 principles. From each of these derived guidelines and practices.
In 2002, Donn Parker proposed an alternative model for the classic CIA triad that he called the six atomic elements of information
Parkerian hexad
The Parkerian hexad is a set of six elements of information security proposed by Donn B. Parker in 2002. The term was coined by M. E. Kabay. The Parkerian hexad adds three additional attributes to the three classic security attributes of the CIA triad .The Parkerian Hexad attributes are the...
. The elements are confidentiality
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is an ethical principle associated with several professions . In ethics, and in law and alternative forms of legal resolution such as mediation, some types of communication between a person and one of these professionals are "privileged" and may not be discussed or divulged to...
, possession
Ownership
Ownership is the state or fact of exclusive rights and control over property, which may be an object, land/real estate or intellectual property. Ownership involves multiple rights, collectively referred to as title, which may be separated and held by different parties. The concept of ownership has...
, integrity
Integrity
Integrity is a concept of consistency of actions, values, methods, measures, principles, expectations, and outcomes. In ethics, integrity is regarded as the honesty and truthfulness or accuracy of one's actions...
, authenticity
Authentication
Authentication is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a datum or entity...
, availability
Availability
In telecommunications and reliability theory, the term availability has the following meanings:* The degree to which a system, subsystem, or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at an unknown, i.e., a random, time...
, and utility
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of customer satisfaction, referring to the total satisfaction received by a consumer from consuming a good or service....
. The merits of the Parkerian hexad
Parkerian hexad
The Parkerian hexad is a set of six elements of information security proposed by Donn B. Parker in 2002. The term was coined by M. E. Kabay. The Parkerian hexad adds three additional attributes to the three classic security attributes of the CIA triad .The Parkerian Hexad attributes are the...
are a subject of debate amongst security professionals.
Confidentiality
ConfidentialityConfidentiality
Confidentiality is an ethical principle associated with several professions . In ethics, and in law and alternative forms of legal resolution such as mediation, some types of communication between a person and one of these professionals are "privileged" and may not be discussed or divulged to...
is the term used to prevent the disclosure of information to unauthorized individuals or systems. For example, a credit card
Credit card
A credit card is a small plastic card issued to users as a system of payment. It allows its holder to buy goods and services based on the holder's promise to pay for these goods and services...
transaction
Financial transaction
A financial transaction is an event or condition under the contract between a buyer and a seller to exchange an asset for payment. It involves a change in the status of the finances of two or more businesses or individuals.-History:...
on the Internet requires the credit card number to be transmitted from the buyer to the merchant and from the merchant to a transaction processing
Transaction processing
In computer science, transaction processing is information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations, called transactions. Each transaction must succeed or fail as a complete unit; it cannot remain in an intermediate state...
network. The system attempts to enforce confidentiality by encrypting the card number during transmission, by limiting the places where it might appear (in databases, log files, backups, printed receipts, and so on), and by restricting access to the places where it is stored. If an unauthorized party obtains the card number in any way, a breach of confidentiality has occurred.
Breaches of confidentiality take many forms. Permitting someone to look over your shoulder at your computer screen while you have confidential data displayed on it could be a breach of confidentiality. If a laptop computer containing sensitive information about a company's employees is stolen or sold, it could result in a breach of confidentiality. Giving out confidential information over the telephone is a breach of confidentiality if the caller is not authorized to have the information.
Confidentiality is necessary (but not sufficient) for maintaining the privacy
Privacy
Privacy is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves and thereby reveal themselves selectively...
of the people whose personal information a system holds.
Integrity
In information security, integrity means that data cannot be modified undetectably. This is not the same thing as referential integrityReferential integrity
Referential integrity is a property of data which, when satisfied, requires every value of one attribute of a relation to exist as a value of another attribute in a different relation ....
in databases, although it can be viewed as a special case of Consistency as understood in the classic ACID
ACID
In computer science, ACID is a set of properties that guarantee database transactions are processed reliably. In the context of databases, a single logical operation on the data is called a transaction...
model of transaction processing
Transaction processing
In computer science, transaction processing is information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations, called transactions. Each transaction must succeed or fail as a complete unit; it cannot remain in an intermediate state...
. Integrity is violated when a message is actively modified in transit. Information security systems typically provide message integrity in addition to data confidentiality.
Availability
For any information system to serve its purpose, the information must be availableAvailability
In telecommunications and reliability theory, the term availability has the following meanings:* The degree to which a system, subsystem, or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at an unknown, i.e., a random, time...
when it is needed. This means that the computing systems used to store and process the information, the security controls
Security controls
Security controls are safeguards or countermeasures to avoid, counteract or minimize security risks.To help review or design security controls, they can be classified by several criteria, for example according to the time that they act, relative to a security incident:*Before the event, preventive...
used to protect it, and the communication channels used to access it must be functioning correctly. High availability
High availability
High availability is a system design approach and associated service implementation that ensures a prearranged level of operational performance will be met during a contractual measurement period....
systems aim to remain available at all times, preventing service disruptions due to power outages, hardware failures, and system upgrades. Ensuring availability also involves preventing denial-of-service attack
Denial-of-service attack
A denial-of-service attack or distributed denial-of-service attack is an attempt to make a computer resource unavailable to its intended users...
s.
Authenticity
In computing, e-Business and information security it is necessary to ensure that the data, transactions, communications or documents (electronic or physical) are genuine. It is also important for authenticity to validate that both parties involved are who they claim they are.Non-repudiation
In law, non-repudiationNon-repudiation
Non-repudiation refers to a state of affairs where the purported maker of a statement will not be able to successfully challenge the validity of the statement or contract. The term is often seen in a legal setting wherein the authenticity of a signature is being challenged...
implies one's intention to fulfill their obligations to a contract. It also implies that one party of a transaction cannot deny having received a transaction nor can the other party deny having sent a transaction.
Electronic commerce
Electronic commerce
Electronic commerce, commonly known as e-commerce, eCommerce or e-comm, refers to the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. However, the term may refer to more than just buying and selling products online...
uses technology such as digital signature
Digital signature
A digital signature or digital signature scheme is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit...
s and public key encryption to establish authenticity and non-repudiation.
Risk management
A comprehensive treatment of the topic of risk managementRisk management
Risk management is the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability and/or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities...
is beyond the scope of this article. However, a useful definition of risk management will be provided as well as some basic terminology and a commonly used process for risk management.
The CISA Review Manual 2006 provides the following definition of risk management: "Risk management is the process of identifying vulnerabilities
Vulnerability (computing)
In computer security, a vulnerability is a weakness which allows an attacker to reduce a system's information assurance.Vulnerability is the intersection of three elements: a system susceptibility or flaw, attacker access to the flaw, and attacker capability to exploit the flaw...
and threats
Threat (computer)
In Computer security a threat is a possible danger that might exploit a vulnerability to breach security and thus cause possible harm.A threat can be either "intentional" or "accidental" In Computer security a threat is a possible danger that might exploit a vulnerability to breach security and...
to the information resources used by an organization in achieving business objectives, and deciding what countermeasures
Countermeasure (computer)
In Computer Security a countermeasure is an action, device, procedure, or technique that reduces a threat, a vulnerability, or an attack by eliminating or preventing it, by minimizing the harm it can cause, or by discovering and reporting it so that corrective action can be taken.The definition is...
, if any, to take in reducing risk to an acceptable level, based on the value of the information resource to the organization."
There are two things in this definition that may need some clarification. First, the process of risk management is an ongoing iterative process
Business process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
. It must be repeated indefinitely. The business environment is constantly changing and new threats
Threat (computer)
In Computer security a threat is a possible danger that might exploit a vulnerability to breach security and thus cause possible harm.A threat can be either "intentional" or "accidental" In Computer security a threat is a possible danger that might exploit a vulnerability to breach security and...
and vulnerability
Vulnerability (computing)
In computer security, a vulnerability is a weakness which allows an attacker to reduce a system's information assurance.Vulnerability is the intersection of three elements: a system susceptibility or flaw, attacker access to the flaw, and attacker capability to exploit the flaw...
emerge every day. Second, the choice of countermeasures
Countermeasure (computer)
In Computer Security a countermeasure is an action, device, procedure, or technique that reduces a threat, a vulnerability, or an attack by eliminating or preventing it, by minimizing the harm it can cause, or by discovering and reporting it so that corrective action can be taken.The definition is...
(controls
Security controls
Security controls are safeguards or countermeasures to avoid, counteract or minimize security risks.To help review or design security controls, they can be classified by several criteria, for example according to the time that they act, relative to a security incident:*Before the event, preventive...
) used to manage risks must strike a balance between productivity, cost, effectiveness of the countermeasure, and the value of the informational asset being protected.
Risk is the likelihood that something bad will happen that causes harm to an informational asset (or the loss of the asset). A vulnerability is a weakness that could be used to endanger or cause harm to an informational asset. A threat is anything (man made or act of nature
Natural disaster
A natural disaster is the effect of a natural hazard . It leads to financial, environmental or human losses...
) that has the potential to cause harm.
The likelihood that a threat will use a vulnerability to cause harm creates a risk. When a threat does use a vulnerability to inflict harm, it has an impact. In the context of information security, the impact is a loss of availability, integrity, and confidentiality, and possibly other losses (lost income, loss of life, loss of real property). It should be pointed out that it is not possible to identify all risks, nor is it possible to eliminate all risk. The remaining risk is called residual risk.
A risk assessment
Risk assessment
Risk assessment is a step in a risk management procedure. Risk assessment is the determination of quantitative or qualitative value of risk related to a concrete situation and a recognized threat...
is carried out by a team of people who have knowledge of specific areas of the business. Membership of the team may vary over time as different parts of the business are assessed. The assessment may use a subjective qualitative analysis based on informed opinion, or where reliable dollar figures and historical information is available, the analysis may use quantitative
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
analysis.
The research has shown that the most vulnerable point in most information systems is the human user, operator, designer, or other human
The ISO/IEC 27002:2005 Code of practice for information security management
Information Security Management
Information security describes activities that relate to the protection of information and information infrastructure assets against the risks of loss, misuse, disclosure or damage...
recommends the following be examined during a risk assessment:
- security policySecurity policySecurity policy is a definition of what it means to be secure for a system, organization or other entity. For an organization, it addresses the constraints on behavior of its members as well as constraints imposed on adversaries by mechanisms such as doors, locks, keys and walls...
, - organizationOrganizationAn organization is a social group which distributes tasks for a collective goal. The word itself is derived from the Greek word organon, itself derived from the better-known word ergon - as we know `organ` - and it means a compartment for a particular job.There are a variety of legal types of...
of information security, - asset management,
- human resourcesHuman resourcesHuman resources is a term used to describe the individuals who make up the workforce of an organization, although it is also applied in labor economics to, for example, business sectors or even whole nations...
security, - physical and environmental securityEnvironmental securityEnvironmental security examines the threat posed by environmental events and trends to national power, as well as the impact of human conflict and international relations on the environment....
, - communications and operations management,
- access controlAccess controlAccess control refers to exerting control over who can interact with a resource. Often but not always, this involves an authority, who does the controlling. The resource can be a given building, group of buildings, or computer-based information system...
, - information systems acquisition, development and maintenance,
- information security incident managementIncident managementIncident Management refers to the activities of an organization to identify, analyze and correct hazards. For instance, a fire in a factory would be a risk that realized, or an incident that happened...
, - business continuity management, and
- regulatory compliance.
In broad terms, the risk management process consists of:
- Identification of assets and estimating their value. Include: people, buildings, hardware, software, data (electronic, print, other), supplies.
- Conduct a threat assessment. Include: Acts of nature, acts of warActs of WarTom Clancy's Op-Center: Acts of War is a technothriller by Tom Clancy- Plot introduction :The mobile Regional Operations Center in Turkey investigates a dam blown up by Kurdish terrorists...
, accidents, malicious acts originating from inside or outside the organization. - Conduct a vulnerability assessmentVulnerability assessmentA vulnerability assessment is the process of identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing the vulnerabilities in a system. Examples of systems for which vulnerability assessments are performed include, but are not limited to, information technology systems, energy supply systems, water supply...
, and for each vulnerability, calculate the probability that it will be exploited. Evaluate policies, procedures, standards, training, physical securityPhysical securityPhysical security describes measures that are designed to deny access to unauthorized personnel from physically accessing a building, facility, resource, or stored information; and guidance on how to design structures to resist potentially hostile acts...
, quality controlQuality controlQuality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
, technical security. - Calculate the impact that each threat would have on each asset. Use qualitative analysis or quantitative analysis.
- Identify, select and implement appropriate controls. Provide a proportional response. Consider productivity, cost effectiveness, and value of the asset.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the control measures. Ensure the controls provide the required cost effective protection without discernible loss of productivity.
For any given risk, Executive Management can choose to accept the risk based upon the relative low value of the asset, the relative low frequency of occurrence, and the relative low impact on the business. Or, leadership may choose to mitigate the risk by selecting and implementing appropriate control measures to reduce the risk. In some cases, the risk can be transferred to another business by buying insurance or out-sourcing to another business. The reality of some risks may be disputed. In such cases leadership may choose to deny the risk.
Controls
When Management chooses to mitigate a risk, they will do so by implementing one or more of three different types of controls.Administrative
Administrative controls (also called procedural controls) consist of approved written policies, procedures, standards and guidelines. Administrative controls form the framework for running the business and managing people. They inform people on how the business is to be run and how day to day operations are to be conducted. Laws and regulations created by government bodies are also a type of administrative control because they inform the business. Some industry sectors have policies, procedures, standards and guidelines that must be followed – the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard required by VisaVisa
Visa or VISA may refer to:* Visa , a document issued by a country's government allowing the holder to enter or to leave that country...
and Master Card
MasterCard
Mastercard Incorporated or MasterCard Worldwide is an American multinational financial services corporation with its headquarters in the MasterCard International Global Headquarters, Purchase, Harrison, New York, United States...
is such an example. Other examples of administrative controls include the corporate security policy, password policy
Password policy
A password policy is a set of rules designed to enhance computer security by encouraging users to employ strong passwords and use them properly. A password policy is often part of an organization's official regulations and may be taught as part of security awareness training...
, hiring policies, and disciplinary policies.
Administrative controls form the basis for the selection and implementation of logical and physical controls. Logical and physical controls are manifestations of administrative controls. Administrative controls are of paramount importance.
Logical
Logical controls (also called technical controls) use software and data to monitor and control access to information and computing systems. For example: passwords, network and host based firewalls, network intrusion detectionIntrusion detection
In Information Security, intrusion detection is the act of detecting actions that attempt to compromise the confidentiality, integrity or availability of a resource. When Intrusion detection takes a preventive measure without direct human intervention, then it becomes an Intrusion-prevention...
systems, access control list
Access control list
An access control list , with respect to a computer file system, is a list of permissions attached to an object. An ACL specifies which users or system processes are granted access to objects, as well as what operations are allowed on given objects. Each entry in a typical ACL specifies a subject...
s, and data encryption are
logical controls.
An important logical control that is frequently overlooked is the principle of least privilege. The principle of least privilege
Principle of least privilege
In information security, computer science, and other fields, the principle of least privilege, also known as the principle of minimal privilege or just least privilege, requires that in a particular abstraction layer of a computing environment, every module must be able to access only the...
requires that an individual, program or system process is not granted any more access privileges than are necessary to perform the task. A blatant example of the failure to adhere to the principle of least privilege is logging into Windows as user Administrator to read Email and surf the Web. Violations of this principle can also occur when an individual
collects additional access privileges over time. This happens when employees' job duties change, or they are promoted to a new position, or they transfer to another department. The access privileges required by their new duties are frequently added onto their already existing access privileges which may no longer be necessary or appropriate.
Physical
Physical controls monitor and control the environment of the work place and computing facilities. They also monitor and control access to and from such facilities. For example: doors, locks, heating and air conditioning, smoke and fire alarms, fire suppression systems, cameras, barricades, fencing, security guards, cable locks, etc. Separating the network and workplace into functional areas are also physical controls.
An important physical control that is frequently overlooked is the separation of duties. Separation of duties ensures that an individual can not complete a critical task by himself. For example: an employee who submits a request for reimbursement should not also be able to authorize payment or print the check. An applications programmer should not also be the server administrator
System administrator
A system administrator, IT systems administrator, systems administrator, or sysadmin is a person employed to maintain and operate a computer system and/or network...
or the database administrator
Database administrator
A database administrator is a person responsible for the design, implementation, maintenance and repair of an organization's database. They are also known by the titles Database Coordinator or Database Programmer, and is closely related to the Database Analyst, Database Modeller, Programmer...
– these roles and responsibilities must be separated from one another.
Defense in depth

Recall the earlier discussion about administrative controls, logical controls, and physical controls. The three types of controls can be used to form the basis upon which to build a defense-in-depth strategy. With this approach, defense-in-depth can be conceptualized as three distinct layers or planes laid one on top of the other. Additional insight into defense-in- depth can be gained by thinking of it as forming the layers of an onion, with data at the core of the onion, people the next outer layer of the onion, and network security
Network security
In the field of networking, the area of network security consists of the provisions and policies adopted by the network administrator to prevent and monitor unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of the computer network and network-accessible resources...
, host-based security and application security
Application security
Application security encompasses measures taken throughout the application's life-cycle to prevent exceptions in the security policy of an application or the underlying system through flaws in the design, development, deployment, upgrade, or maintenance of the application.Applications only...
forming the outermost layers of the onion. Both perspectives are equally valid and each provides valuable insight into the implementation of a good defense-in-depth strategy.
Security classification for information
An important aspect of information security and risk management is recognizing the value of information and defining appropriate procedures and protection requirements for the information. Not all information is equal and so not all information requires the same degree of protection. This requires information to be assigned a security classification.The first step in information classification is to identify a member of senior management as the owner of the particular information to be classified. Next, develop a classification policy. The policy should describe the different classification labels, define the criteria for information to be assigned a particular label, and list the required security controls
Security controls
Security controls are safeguards or countermeasures to avoid, counteract or minimize security risks.To help review or design security controls, they can be classified by several criteria, for example according to the time that they act, relative to a security incident:*Before the event, preventive...
for each classification.
Some factors that influence which classification information should be assigned include how much value that information has to the organization, how old the information is and whether or not the information has become obsolete. Laws and other regulatory requirements are also important considerations when classifying information.
The type of information security classification labels selected and used will depend on the nature of the organisation, with examples being:
- In the business sector, labels such as: Public, Sensitive, Private, Confidential.
- In the government sector, labels such as: Unclassified, Sensitive But Unclassified, Restricted, Confidential, Secret, Top Secret and their non-English equivalents.
- In cross-sectoral formations, the Traffic Light ProtocolTraffic Light ProtocolThis document relates to areas of classified information and document classification.The Traffic Light Protocol was created to encourage greater sharing of sensitive information. The originator signals how widely they want their information to be circulated beyond the immediate recipient.The TLP...
, which consists of: White, Green, Amber and Red.
All employees in the organization, as well as business partners, must be trained on the classification schema and understand the required security controls and handling procedures for each classification. The classification of a particular information asset has been assigned should be reviewed periodically to ensure the classification is still appropriate for the information and to ensure the security controls required by the classification are in place.
Access control
Access to protected information must be restricted to people who are authorized to access the information. The computer programs, and in many cases the computers that process the information, must also be authorized. This requires that mechanisms be in place to control the access to protected information. The sophistication of the access control mechanisms should be in parity with the value of the information being protected – the more sensitive or valuable the information the stronger the control mechanisms need to be. The foundation on which access control mechanisms are built start with identification and authenticationAuthentication
Authentication is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a datum or entity...
.
Identification is an assertion of who someone is or what something is. If a person makes the statement "Hello, my name is John Doe" they are making a claim of who they are. However, their claim may or may not be true. Before John Doe can be granted access to protected information it will be necessary to verify that the person claiming to be John Doe really is John Doe.
Authentication is the act of verifying a claim of identity. When John Doe goes into a bank to make a withdrawal, he tells the bank teller he is John Doe (a claim of identity). The bank teller asks to see a photo ID, so he hands the teller his driver's license. The bank teller checks the license to make sure it has John Doe printed on it and compares the photograph on the license against the person claiming to be John Doe. If the photo and name match the person, then the teller has authenticated that John Doe is who he claimed to be.
There are three different types of information that can be used for authentication: something you know, something you have, or something you are. Examples of something you know include such things as a PIN, a password, or your mother's maiden name. Examples of something you have include a driver's license or a magnetic swipe card. Something you are refers to biometrics. Examples of biometrics include palm prints, finger prints, voice prints and retina (eye) scans. Strong authentication requires providing information from two of the three different types of authentication information. For example, something you know plus something you have. This is called two factor authentication.
On computer systems in use today, the Username is the most common form of identification and the Password is the most common form of authentication. Usernames and passwords have served their purpose but in our modern world they are no longer adequate. Usernames and passwords are slowly being replaced with more sophisticated authentication mechanisms.
After a person, program or computer has successfully been identified and authenticated then it must be determined what informational resources they are permitted to access and what actions they will be allowed to perform (run, view, create, delete, or change). This is called authorization
Authorization
Authorization is the function of specifying access rights to resources, which is related to information security and computer security in general and to access control in particular. More formally, "to authorize" is to define access policy...
.
Authorization to access information and other computing services begins with administrative policies and procedures. The policies prescribe what information and computing services can be accessed, by whom, and under what conditions. The access control mechanisms are then configured to enforce these policies.
Different computing systems are equipped with different kinds of access control mechanisms - some may even offer a choice of different access control mechanisms. The access control mechanism a system offers will be based upon one of three approaches to access control or it may be derived from a combination of the three approaches.
The non-discretionary approach consolidates all access control under a centralized administration. The access to information and other resources is usually based on the individuals function (role) in the organization or the tasks the individual must perform. The discretionary approach gives the creator or owner of the information resource the ability to control access to those resources. In the Mandatory access control approach, access is granted or denied basing upon the security classification assigned to the information resource.
Examples of common access control mechanisms in use today include Role-based
Role-Based Access Control
In computer systems security, role-based access control is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users. It is used by the majority of enterprises with more than 500 employees, and can be implemented via mandatory access control or discretionary access control...
access control
available in many advanced Database Management Systems, simple file permissions
File system permissions
Most current file systems have methods of administering permissions or access rights to specific users and groups of users. These systems control the ability of the users to view or make changes to the contents of the filesystem....
provided in the UNIX and Windows operating systems, Group Policy Objects provided in Windows network systems, Kerberos, RADIUS
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service is a networking protocol that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting management for computers to connect and use a network service...
, TACACS
TACACS
Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System is a remote authentication protocol that is used to communicate with an authentication server commonly used in UNIX networks. TACACS allows a remote access server to communicate with an authentication server in order to determine if the user has...
, and the simple access lists used in many firewalls and routers.
To be effective, policies and other security controls must be enforceable and upheld. Effective policies ensure that people are held accountable for their actions. All failed and successful authentication attempts must be logged, and all access to information must leave some type of audit trail.
Cryptography
Information security uses cryptographyCryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties...
to transform usable information into a form that renders it unusable by anyone other than an authorized user; this process is called encryption
Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of transforming information using an algorithm to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special knowledge, usually referred to as a key. The result of the process is encrypted information...
. Information that has been encrypted (rendered unusable) can be transformed back into its original usable form by an authorized user, who possesses the cryptographic key
Key (cryptography)
In cryptography, a key is a piece of information that determines the functional output of a cryptographic algorithm or cipher. Without a key, the algorithm would produce no useful result. In encryption, a key specifies the particular transformation of plaintext into ciphertext, or vice versa...
, through the process of decryption. Cryptography is used in information security to protect information from unauthorized or accidental disclosure while the information
Information
Information in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
is in transit (either electronically or physically) and while information is in storage.
Cryptography provides information security with other useful applications as well including improved authentication methods, message digests, digital signatures, non-repudiation
Non-repudiation
Non-repudiation refers to a state of affairs where the purported maker of a statement will not be able to successfully challenge the validity of the statement or contract. The term is often seen in a legal setting wherein the authenticity of a signature is being challenged...
, and encrypted network communications. Older less secure application such as telnet and ftp are slowly being replaced with more secure applications such as ssh
Secure Shell
Secure Shell is a network protocol for secure data communication, remote shell services or command execution and other secure network services between two networked computers that it connects via a secure channel over an insecure network: a server and a client...
that use encrypted network communications. Wireless communications can be encrypted using protocols such as WPA/WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access
Wi-Fi Protected Access and Wi-Fi Protected Access II are two security protocols and security certification programs developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks...
or the older (and less secure) WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy
Wired Equivalent Privacy is a weak security algorithm for IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. Introduced as part of the original 802.11 standard ratified in September 1999, its intention was to provide data confidentiality comparable to that of a traditional wired network...
. Wired communications (such as ITU-T
ITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union ; it coordinates standards for telecommunications....
G.hn
G.hn
G.hn is the common name for a home network technology family of standards developed under the International Telecommunication Union's Standardization arm and promoted by the HomeGrid Forum...
) are secured using AES
Advanced Encryption Standard
Advanced Encryption Standard is a specification for the encryption of electronic data. It has been adopted by the U.S. government and is now used worldwide. It supersedes DES...
for encryption and X.1035
X.1035
ITU-T Recommendation X.1035 specifies a password-authenticated key agreement protocol that ensures mutual authentication of two parties by using a Diffie–Hellman key exchange to establish a symmetric cryptographic key...
for authentication and key exchange. Software applications such as GnuPG or PGP
Pretty Good Privacy
Pretty Good Privacy is a data encryption and decryption computer program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP is often used for signing, encrypting and decrypting texts, E-mails, files, directories and whole disk partitions to increase the security...
can be used to encrypt data files and Email.
Cryptography can introduce security problems when it is not implemented correctly. Cryptographic solutions need to be implemented using industry accepted solutions that have undergone rigorous peer review by independent experts in cryptography. The length and strength
Key size
In cryptography, key size or key length is the size measured in bits of the key used in a cryptographic algorithm . An algorithm's key length is distinct from its cryptographic security, which is a logarithmic measure of the fastest known computational attack on the algorithm, also measured in bits...
of the encryption key is also an important consideration. A key that is weak
Weak key
In cryptography, a weak key is a key, which, used with a specific cipher, makes the cipher behave in some undesirable way. Weak keys usually represent a very small fraction of the overall keyspace, which usually means that, if one generates a random key to encrypt a message, weak keys are very...
or too short will produce weak encryption. The keys used for encryption and decryption must be protected with the same degree of rigor as any other confidential information. They must be protected from unauthorized disclosure and destruction and they must be available when needed. PKI
Public key infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure is a set of hardware, software, people, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates. In cryptography, a PKI is an arrangement that binds public keys with respective user identities by means of a certificate...
solutions address many of the problems that surround key management
Key management
Key management is the provisions made in a cryptography system design that are related to generation, exchange, storage, safeguarding, use, vetting, and replacement of keys. It includes cryptographic protocol design, key servers, user procedures, and other relevant protocols.Key management concerns...
.
Process
The terms reasonable and prudent person, due care and due diligence have been used in the fields of Finance, Securities, and Law for many years. In recent years these terms have found their way into the fields of computing and information security. U.S.A. Federal Sentencing GuidelinesFederal Sentencing Guidelines
The Federal Sentencing Guidelines are rules that set out a uniform sentencing policy for individuals and organizations convicted of felonies and serious misdemeanors in the United States federal courts system...
now make it possible to hold corporate officers liable for failing to exercise due care and due diligence in the management of their information systems.
In the business world, stockholders, customers, business partners and governments have the expectation that corporate officers will run the business in accordance with accepted business practices and in compliance with laws and other regulatory requirements. This is often described as the "reasonable and prudent person" rule. A prudent person takes due care to ensure that everything necessary is done to operate the business by sound business principles and in a legal ethical manner. A prudent person is also diligent (mindful, attentive, and ongoing) in their due care of the business.
In the field of Information Security, Harris
offers the following definitions of due care and due diligence:
"Due care are steps that are taken to show that a company has taken responsibility for the activities that take place within the corporation and has taken the necessary steps to help protect the company, its resources, and employees." And,[Due diligence are the] "continual activities that make sure the protection mechanisms are continually maintained and operational."
Attention should be made to two important points in these definitions. First, in due care, steps are taken to show - this means that the steps can be verified, measured, or even produce tangible artifacts. Second, in due diligence, there are continual activities - this means that people are actually doing things to monitor and maintain the protection mechanisms, and these activities are ongoing.
Security governance
The Software Engineering InstituteSoftware Engineering Institute
The Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute is a federally funded research and development center headquartered on the campus of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. SEI also has offices in Arlington, Virginia, and Frankfurt, Germany. The SEI operates...
at Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States....
, in a publication titled "Governing for Enterprise Security (GES)", defines characteristics of effective security governance. These include:
- An enterprise-wide issue
- Leaders are accountable
- Viewed as a business requirement
- Risk-based
- Roles, responsibilities, and segregation of duties defined
- Addressed and enforced in policy
- Adequate resources committed
- Staff aware and trained
- A development life cycle requirement
- Planned, managed, measurable, and measured
- Reviewed and audited
Incident response plans
1 to 3 paragraphs (non technical) that discuss:- Selecting team members
- Define roles, responsibilities and lines of authority
- Define a security incident
- Define a reportable incident
- Training
- Detection
- Classification
- Escalation
- Containment
- Eradication
- Documentation
Change management
Change management is a formal process for directing and controlling alterations to the information processing environment. This includes alterations to desktop computers, the network, servers and software. The objectives of change management are to reduce the risks posed by changes to the information processing environment and improve the stability and reliability of theprocessing environment as changes are made. It is not the objective of change management to prevent or hinder necessary changes from being implemented.
Any change to the information processing environment introduces an element of risk. Even apparently simple changes can have unexpected effects. One of Managements many responsibilities is the management of risk. Change management is a tool for managing the risks introduced by changes to the information processing environment. Part of the change management process ensures that changes are not implemented at inopportune times when they may disrupt critical business processes or interfere with other changes being implemented.
Not every change needs to be managed. Some kinds of changes are a part of the everyday routine of information processing and adhere to a predefined procedure, which reduces the overall level of risk to the processing environment. Creating a new user account or deploying a new desktop computer are examples of changes that do not generally require change management. However, relocating user file shares, or upgrading the Email server pose a much higher level of risk to the processing environment and are not a normal everyday activity. The critical first steps in change management are (a) defining change (and communicating that definition) and (b) defining the scope of the change system.
Change management is usually overseen by a Change Review Board composed of representatives from key business areas, security, networking, systems administrators, Database administration, applications development, desktop support and the help desk. The tasks of the Change Review Board can be facilitated with the use of automated work flow application. The responsibility of the Change Review Board is to ensure the organizations documented change management procedures are followed. The change management process is as follows:
- Requested: Anyone can request a change. The person making the change request may or may not be the same person that performs the analysis or implements the change. When a request for change is received, it may undergo a preliminary review to determine if the requested change is compatible with the organizations business modelBusiness modelA business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
and practices, and to determine the amount of resources needed to implement the change.
- Approved: Management runs the business and controls the allocation of resources therefore, Management must approve requests for changes and assign a priority for every change. Management might choose to reject a change request if the change is not compatible with the business model, industry standards or best practices. Management might also choose to reject a change request if the change requires more resources than can be allocated for the change.
- Planned: Planning a change involves discovering the scope and impact of the proposed change; analyzing the complexity of the change; allocation of resources and, developing, testing and documenting both implementation and backout plans. Need to define the criteria on which a decision to back out will be made.
- Tested: Every change must be tested in a safe test environment, which closely reflects the actual production environment, before the change is applied to the production environment. The backout plan must also be tested.
- Scheduled: Part of the change review board's responsibility is to assist in the scheduling of changes by reviewing the proposed implementation date for potential conflicts with other scheduled changes or critical business activities.
- Communicated: Once a change has been scheduled it must be communicated. The communication is to give others the opportunity to remind the change review board about other changes or critical business activities that might have been overlooked when scheduling the change. The communication also serves to make the Help Desk and users aware that a change is about to occur. Another responsibility of the change review board is to ensure that scheduled changes have been properly communicated to those who will be affected by the change or otherwise have an interest in the change.
- Implemented: At the appointed date and time, the changes must be implemented. Part of the planning process was to develop an implementation plan, testing plan and, a back out plan. If the implementation of the change should fail or, the post implementation testing fails or, other "drop dead" criteria have been met, the back out plan should be implemented.
- Documented: All changes must be documented. The documentation includes the initial request for change, its approval, the priority assigned to it, the implementation, testing and back out plans, the results of the change review board critique, the date/time the change was implemented, who implemented it, and whether the change was implemented successfully, failed or postponed.
- Post change review: The change review board should hold a post implementation review of changes. It is particularly important to review failed and backed out changes. The review board should try to understand the problems that were encountered, and look for areas for improvement.
Change management procedures that are simple to follow and easy to use can greatly reduce the overall risks created when changes are made to the information processing environment. Good change management procedures improve the over all quality and success of changes as they are implemented. This is accomplished through planning, peer review, documentation and communication.
ISO/IEC 20000, The Visible OPS Handbook: Implementing ITIL in 4 Practical and Auditable Steps (Full book summary), and Information Technology Infrastructure Library
Information Technology Infrastructure Library
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library , is a set of good practices for IT service management that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. In its current form , ITIL is published in a series of five core publications, each of which covers an ITSM lifecycle stage...
all provide valuable guidance on implementing an efficient and effective change management program information security.
Business continuity
Business continuity is the mechanism by which an organization continues to operate its critical business units, during planned or unplanned disruptions that affect normal business operations, by invoking planned and managed procedures.Unlike what most people think business continuity is not necessarily an IT system or process, simply because it is about the business. Today disasters or disruptions to business are a reality. Whether the disaster is natural or man-made, it affects normal life and so business. So why is planning so important? Let us face reality that "all businesses recover", whether they planned for recovery or not, simply because business is about earning money for survival.
The planning is merely getting better prepared to face it, knowing fully well that the best plans may fail. Planning helps to reduce cost of recovery, operational overheads and most importantly sail through some smaller ones effortlessly.
For businesses to create effective plans they need to focus upon the following key questions. Most of these are common knowledge, and anyone can do a BCP.
- Should a disaster strike, what are the first few things that I should do? Should I call people to find if they are OK or call up the bank to figure out my money is safe? This is Emergencey Response. Emergency Response services help take the first hit when the disaster strikes and if the disaster is serious enough the Emergency Response teams need to quickly get a Crisis Management team in place.
- What parts of my business should I recover first? The one that brings me most money or the one where I spend the most, or the one that will ensure I shall be able to get sustained future growth? The identified sections are the critical business units. There is no magic bullet here, no one answer satisfies all. Businesses need to find answers that meet business requirements.
- How soon should I target to recover my critical business units? In BCP technical jargon this is called Recovery Time Objective, or RTORecovery Time ObjectiveThe recovery time objective is the duration of time and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster in order to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity....
. This objective will define what costs the business will need to spend to recover from a disruption. For example, it is cheaper to recover a business in 1 day than in 1 hour. - What all do I need to recover the business? IT, machinery, records...food, water, people...So many aspects to dwell upon. The cost factor becomes clearer now...Business leaders need to drive business continuity. Hold on. My IT manager spent $200000 last month and created a DRP (Disaster Recovery PlanDisaster recoveryDisaster recovery is the process, policies and procedures related to preparing for recovery or continuation of technology infrastructure critical to an organization after a natural or human-induced disaster. Disaster recovery is a subset of business continuity...
), whatever happened to that? a DRP is about continuing an IT system, and is one of the sections of a comprehensive Business Continuity Plan. Look below for more on this. - And where do I recover my business from... Will the business center give me space to work, or would it be flooded by many people queuing up for the same reasons that I am.
- But once I do recover from the disaster and work in reduced production capacity, since my main operational sites are unavailable, how long can this go on. How long can I do without my original sites, systems, people? this defines the amount of business resilience a business may have.
- Now that I know how to recover my business. How do I make sure my plan works? Most BCP pundits would recommend testing the plan at least once a year, reviewing it for adequacy and rewriting or updating the plans either annually or when businesses change.
Disaster recovery planning
While a business continuity plan (BCP) takes a broad approach to dealing with organizational-wide effects of a disaster, a disaster recovery plan (DRP), which is a subset of the business continuity plan, is instead focused on taking the necessary steps to resume normal business operations as quickly as possible. A disaster recovery plan is executed immediately after the disaster occurs and details what steps are to be taken in order to recover critical information technology infrastructure.Laws and regulations
Below is a partial listing of European, United Kingdom, Canadian and USA governmental laws and regulations that have, or will have, a significant effect on data processing and information security. Important industry sector regulations have also been included when they have a significant impact on information security.- UK Data Protection Act 1998Data Protection Act 1984The Data Protection Act 1998 is a United Kingdom Act of Parliament which defines UK law on the processing of data on identifiable living people. It is the main piece of legislation that governs the protection of personal data in the UK...
makes new provisions for the regulation of the processing of information relating to individuals, including the obtaining, holding, use or disclosure of such information. The European Union Data Protection Directive (EUDPD) requires that all EU member must adopt national regulations to standardize the protection of data privacy for citizens throughout the EU.
- The Computer Misuse Act 1990 is an Act of the UK ParliamentParliament of the United KingdomThe Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
making computer crime (e.g. cracking - sometimes incorrectly referred to as hacking) a criminal offence. The Act has become a model upon which several other countries including CanadaCanadaCanada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
and the Republic of IrelandRepublic of IrelandIreland , described as the Republic of Ireland , is a sovereign state in Europe occupying approximately five-sixths of the island of the same name. Its capital is Dublin. Ireland, which had a population of 4.58 million in 2011, is a constitutional republic governed as a parliamentary democracy,...
have drawn inspiration when subsequently drafting their own information security laws. - EU Data Retention laws requires Internet service providers and phone companies to keep data on every electronic message sent and phone call made for between six months and two years.
- The Family Educational Rights and Privacy ActFamily Educational Rights and Privacy ActThe Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act of 1974 is a United States federal law.It allows students with access to their education records, an opportunity to seek to have the records amended, and some control over the disclosure of information from the records...
(FERPA) ( g; 34 CFR Part 99) is a USA Federal law that protects the privacy of student education records. The law applies to all schools that receive funds under an applicable program of the U.S. Department of Education. Generally, schools must have written permission from the parent or eligible student in order to release any information from a student's education record. - Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 requires the adoption of national standards for electronic health care transactions and national identifiers for providers, health insurance plans, and employers. And, it requires health care providers, insurance providers and employers to safeguard the security and privacy of health data.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley ActGramm-Leach-Bliley ActThe Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act , also known as the Financial Services Modernization Act of 1999, is an act of the 106th United States Congress...
of 1999 (GLBA), also known as the Financial Services Modernization Act of 1999, protects the privacy and security of private financial information that financial institutions collect, hold, and process. - Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX)Sarbanes-Oxley ActThe Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002 , also known as the 'Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act' and 'Corporate and Auditing Accountability and Responsibility Act' and commonly called Sarbanes–Oxley, Sarbox or SOX, is a United States federal law enacted on July 30, 2002, which...
. Section 404 of the act requires publicly traded companies to assess the effectiveness of their internal controls for financial reporting in annual reports they submit at the end of each fiscal year. Chief information officers are responsible for the security, accuracy and the reliability of the systems that manage and report the financial data. The act also requires publicly traded companies to engage independent auditors who must attest to, and report on, the validity of their assessments. - Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)PCI DSSThe Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard is an information security standard for organizations that handle cardholder information for the major debit, credit, prepaid, e-purse, ATM, and POS cards....
establishes comprehensive requirements for enhancing payment account data security. It was developed by the founding payment brands of the PCI Security Standards Council, including American ExpressAmerican ExpressAmerican Express Company or AmEx, is an American multinational financial services corporation headquartered in Three World Financial Center, Manhattan, New York City, New York, United States. Founded in 1850, it is one of the 30 components of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. The company is best...
, Discover Financial ServicesDiscover CardThe Discover Card is a major credit card, issued primarily in the United States. It was originally introduced by Sears in 1985, and was part of Dean Witter, and then Morgan Stanley, until 2007, when Discover Financial Services became an independent company. Novus, a major processing center, used to...
, JCB, MasterCard Worldwide and Visa InternationalVISA (credit card)Visa Inc. is an American multinational financial services corporation headquartered on 595 Market Street, Financial District in San Francisco, California, United States, although much of the company's staff is based in Foster City, California. It facilitates electronic funds transfers throughout...
, to help facilitate the broad adoption of consistent data security measures on a global basis. The PCI DSS is a multifaceted security standard that includes requirements for security management, policies, procedures, network architectureNetwork architectureNetwork architecture is the design of a communications network. It is a framework for the specification of a network's physical components and their functional organization and configuration, its operational principles and procedures, as well as data formats used in its operation.In...
, software design and other critical protective measures. - State Security Breach Notification LawsSecurity Breach Notification LawsSecurity breach notification laws have been enacted in most U.S. states since 2002. These laws were enacted in response to an escalating number of breaches of consumer databases containing personally identifiable information....
(California and many others) require businesses, nonprofits, and state institutions to notify consumers when unencrypted "personal information" may have been compromised, lost, or stolen. - Personal Information Protection and Electronics Document Act (PIPEDAPersonal Information Protection and Electronic Documents ActThe Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act is a Canadian law relating to data privacy. It governs how private sector organizations collect, use and disclose personal information in the course of commercial business. In addition, the Act contains various provisions to...
) – An Act to support and promote electronic commerce by protecting personal information that is collected, used or disclosed in certain circumstances, by providing for the use of electronic means to communicate or record information or transactions and by amending the Canada Evidence ActCanada Evidence ActThe Canada Evidence Act is an Act of the Parliament of Canada, first passed in 1893, that regulates the rules of evidence in court proceedings under federal law. As law of evidence is largely set by common law, the Act is not comprehensive....
, the Statutory Instruments Act and the Statute Revision Act.
Sources of standards
International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) is a consortium of national standards
institutes from 157 countries, coordinated through a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland. ISO is
the world's largest developer of standards. ISO 15443: "Information technology - Security techniques - A framework
for IT security assurance", ISO/IEC 27002
ISO/IEC 27002
ISO/IEC 27002 is an information security standard published by the International Organization for Standardization and by the International Electrotechnical Commission , entitled Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice for information security management.ISO/IEC 27002:2005...
: "Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice for information security management", ISO-20000
ISO 20000
ISO/IEC 20000 is the first international standard for IT service management. It was developed in 2005, by ISO/IEC JTC1 SC7 and revised in 2011. It is based on and intended to supersede the earlier BS 15000 that was developed by BSI Group....
: "Information technology - Service management", and ISO/IEC27001
ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001, part of the growing ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards, is an Information Security Management System standard published in October 2005 by the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission...
: "Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems - Requirements" are of particular interest to information security professionals.
The USA National Institute of Standards and Technology
National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology , known between 1901 and 1988 as the National Bureau of Standards , is a measurement standards laboratory, otherwise known as a National Metrological Institute , which is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce...
(NIST) is a non-regulatory federal agency
within the U.S. Department of Commerce. The NIST Computer Security Division
develops standards, metrics, tests and validation programs as well as publishes standards and guidelines to
increase secure IT planning, implementation, management and operation. NIST is also the custodian of the USA Federal Information Processing Standard
Federal Information Processing Standard
A Federal Information Processing Standard is a publicly announced standardization developed by the United States federal government for use in computer systems by all non-military government agencies and by government contractors, when properly invoked and tailored on a contract...
publications (FIPS).
The Internet Society is a professional membership society with more than 100 organization
and over 20,000 individual members in over 180 countries. It provides leadership in addressing issues that confront the
future of the Internet, and is the organization home for the groups responsible for Internet infrastructure standards,
including the Internet Engineering Task Force
Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force develops and promotes Internet standards, cooperating closely with the W3C and ISO/IEC standards bodies and dealing in particular with standards of the TCP/IP and Internet protocol suite...
(IETF) and the Internet Architecture Board
Internet Architecture Board
The Internet Architecture Board is the committee charged with oversight of the technical and engineering development of the Internet by the Internet Society ....
(IAB). The ISOC hosts the Requests for Comments (RFCs) which includes the Official Internet Protocol Standards
and the RFC-2196 Site Security Handbook
Site Security Handbook
The Site Security Handbook, RFC 2196, is a guide on setting computer security policies and procedures for sites that have systems on the Internet . The guide lists issues and factors that a site must consider when setting their own policies...
.
The Information Security Forum
Information Security Forum
The Information Security Forum is an independent, not-for-profit association of leading organizations from around the world. It is dedicated to investigating, clarifying and resolving key issues in information security, and developing best practice methodologies, processes and solutions that meet...
is a global nonprofit organization of several hundred leading organizations in financial services, manufacturing, telecommunications, consumer goods, government, and other areas. It undertakes research into information security practices and offers advice in its biannual Standard of Good Practice
Standard of Good Practice
The Standard of Good Practice for Information Security, published by the Information Security Forum , is a business-focused, practical and comprehensive guide to identifying and managing information security risks in organizations and their supply chains....
and more detailed advisories for members.
The IT Baseline Protection Catalogs
IT Baseline Protection Catalogs
The IT Baseline Protection Catalogs, or IT-Grundschutz-Kataloge, are a collection of documents from the German Federal Office for Security in Information Technology that provide useful information for detecting weaknesses and combating attacks in the information technology environment...
, or IT-Grundschutz Catalogs, ("IT Baseline Protection
IT baseline protection
- Overview :The term baseline security is used in various contexts with somewhat different meanings. For example:* Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer: Software tool focused on Microsoft operating system and services security...
Manual" before 2005) are a collection of documents from the German Federal Office for Security in Information Technology (FSI), useful for detecting and combating security-relevant weak points in the IT environment (IT cluster). The collection encompasses over 3000 pages with the introduction and catalogs.
Professionalism
Conclusion
Information security is the ongoing process of exercising due care and due diligence to protect information, andinformation systems, from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, destruction, modification, or disruption or distribution.
The never ending process of information security involves ongoing training, assessment, protection, monitoring & detection,
incident response & repair, documentation, and review. This makes information security an indispensable part of all the business operations across different domains.
See also
- Enterprise information security architectureEnterprise Information Security ArchitectureEnterprise information security architecture is a part of enterprise architecture focusing on information security throughout the enterprise.- Overview :...
- Information security audit
- Information security management systemInformation security management systemAn information security management system is a set of policies concerned with information security management or IT related risks. The idioms arose primarily out of ISO 27001....
- Information security policies
- Information security standardsInformation security standardsThe term "standard" is sometimes used within the context of information security policies to distinguish between written policies, standards and procedures. Organizations should maintain all three levels of documentation to help secure their environment. Information security policies are...
- Information technology security audit
- IntypediaIntypediaIntypedia is an educational non-profit project developed by the Technical University of Madrid. It’s a visual encyclopedia on information security. The aim of this Project is to spread knowledge of this topic through a series of videos created by renowned experts, while using a language that is...
- ISO/IEC 27001ISO/IEC 27001ISO/IEC 27001, part of the growing ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards, is an Information Security Management System standard published in October 2005 by the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission...
- IT riskIT riskInformation technology risk, or IT risk, IT-related risk, is a risk related to information technology. This relatively new term due to an increasing awareness that information security is simply one facet of a multitude of risks that are relevant to IT and the real world processes it...
- ITIL security managementITIL Security ManagementThe ITIL security management process describes the structured fitting of security in the management organization. ITIL security management is based on the ISO 27001 standard. According to "ISO/IEC 27001:2005 covers all types of organizations...
- Network Security ServicesNetwork Security ServicesIn computing, Network Security Services comprises a set of libraries designed to support cross-platform development of security-enabled client and server applications. NSS provides a complete open-source implementation of crypto libraries supporting SSL and S/MIME...
- Physical information securityPhysical Information SecurityPhysical information security is concerned with physically protecting data and means to access that data . Many individuals and companies place importance in protecting their information from a software and/or network perspective, but fewer devote resources to protecting data physically...
- Privacy softwarePrivacy softwarePrivacy software is software built to protect the privacy of its users. The software typically works in conjunction with Internet usage to control or limit the amount of information made available to third-parties. The software can apply encryption or filtering of various kinds.Privacy software can...
- Privacy-enhancing technologies
- Security bugSecurity bugA security bug is a software bug that benefits someone other than intended beneficiaries in the intended ways.Security bugs introduce security vulnerabilities by compromising one or more of:* Authentication of users and other entities...
- Security information managementSecurity Information ManagementSecurity information management is the industry-specific term in computer security referring to the collection of data into a central repository for trend analysis...
- Security of Information ActSecurity of Information ActIn Canada, the Security of Information Act is part of the Canadian Anti-Terrorism Act which received Royal Assent on December 18, 2001 and came into effect on December 24, 2001. This Act renamed and replaced Official Secrets Act 1981...
- Security level managementSecurity level managementSecurity Level Management comprises a quality assurance system for electronic information security.The aim of SLM is to display the IT security status transparently across a company at any time, and to make IT security a measurable quantity...
- Security service (telecommunication)Security service (telecommunication)Security service is a service, provided by a layer of communicating open systems, which ensures adequate security of the systems or of data transfers as defined by ITU-T X.800 Recommendation....
- Single sign-onSingle sign-onSingle sign-on is a property of access control of multiple related, but independent software systems. With this property a user logs in once and gains access to all systems without being prompted to log in again at each of them...
- Verification and validationVerification and ValidationIn software project management, software testing, and software engineering, verification and validation is the process of checking that a software system meets specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose...
Scholars working in the field
- Ross J. Anderson
- Adam BackAdam BackAdam Back is a British cryptographer and crypto-hacker.He is the inventor of hashcash, a proof-of-work system for protecting against email spam and other denial-of-service attacks. He wrote credlib...
- Stefan BrandsStefan BrandsStefan Brands is an entrepreneur and former cryptography researcher whose work has focused on digital identity, electronic money, and information privacy. He obtained his doctorate from Eindhoven University of Technology while at CWI in Amsterdam. In 2002 Stefan founded Credentica to advance his...
- Lance CottrellLance CottrellLance Cottrell develops Internet privacy systems. Cottrell launched the first commercial privacy service, Anonymizer.com, in 1995 while studying towards a PhD in Astrophysics at the University of California, San Diego. Cottrell was the original coder for the Mixmaster anonymous remailer and...
- Ian GoldbergIan GoldbergIan Avrum Goldberg is a cryptographer and cypherpunk. He is best known for breaking Netscape's implementation of SSL , and for his role as Chief Scientist of Radialpoint , a Canadian software company...
- Peter GutmannPeter Gutmann (computer scientist)Peter Gutmann is a computer scientist in the Department of Computer Science at the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand. He has a Ph.D. in computer science from the University of Auckland. His Ph.D. thesis and a book based on the thesis were about a cryptographic security architecture...
- Bruce SchneierBruce SchneierBruce Schneier is an American cryptographer, computer security specialist, and writer. He is the author of several books on general security topics, computer security and cryptography, and is the founder and chief technology officer of BT Managed Security Solutions, formerly Counterpane Internet...
- Gene SpaffordGene SpaffordEugene Howard Spafford , commonly known as Spaf, is a professor of computer science at Purdue University and a leading computer security expert....
Further reading
- Anderson, K., "IT Security Professionals Must Evolve for Changing Market", SC Magazine, October 12, 2006.
- Aceituno, V., "On Information Security Paradigms",ISSA Journal, September, 2005.
- Dhillon, G., "Principles of Information Systems Security: text and cases", John Wiley & SonsJohn Wiley & SonsJohn Wiley & Sons, Inc., also referred to as Wiley, is a global publishing company that specializes in academic publishing and markets its products to professionals and consumers, students and instructors in higher education, and researchers and practitioners in scientific, technical, medical, and...
, 2007. - Easttom, C., "Computer Security Fundamentals (2nd Edition)" Pearson Press, 2011.
- Lambo, T."ISO/IEC 27001: The future of infosec certification",ISSA Journal, November, 2006.
External links
- DoD IA Policy Chart on the DoD Information Assurance Technology Analysis Center web site.
- patterns & practices Security Engineering Explained
- Open Security Architecture- Controls and patterns to secure IT systems
- An Introduction to Information Security
- IWS - Information Security Chapter
- Information Security News .com

