
German town law
Encyclopedia
German town law or German municipal concerns (Deutsches Städtewesen) concerns town privileges
used by many cities, towns, and villages throughout Central
and Eastern Europe
during the Middle Ages
.
 As Germans
As Germans
began establishing towns throughout northern Europe as early as the 10th century, they often received town privileges
granting them autonomy from local secular or religious rulers. Such privileges often included the right to self-governance, economic autonomy, criminal courts, and militia
. Town laws were more or less entirely copied from neighboring towns, such as the Westphalia
n towns of Soest
, Dortmund
, Minden
, and Münster
. As Germans began settling eastward, the colonists modelled their town laws on the pre-existing 12th century laws of Cologne
, Lübeck
in the north (Lübeck law
), Magdeburg
roughly in the center (Magdeburg rights
), and either Nuremberg
or Vienna
in the south (South German law).
Because many larger cities such as Braunschweig
and Hildesheim
grew through the agglomeration
of neighboring towns, some previously self-contained settlements were split between regions utilizing differing town rights variants.
The granting of German city rights modelled after an established town to a new town regarded the original model as a Rechtsvorort, or roughly a legal sponsor of the newly-chartered town. For instance, Magdeburg became the sponsor of towns using Magdeburg Rights, and its lay judges could rule in ambiguous legal cases in towns using such rights. Certain city rights became known under different names, although they originally came from the same source; the name of some city variants designates the Rechtsvorort they became famous from, not necessarily that that specific style of rights originated from the Rechtsvorort.
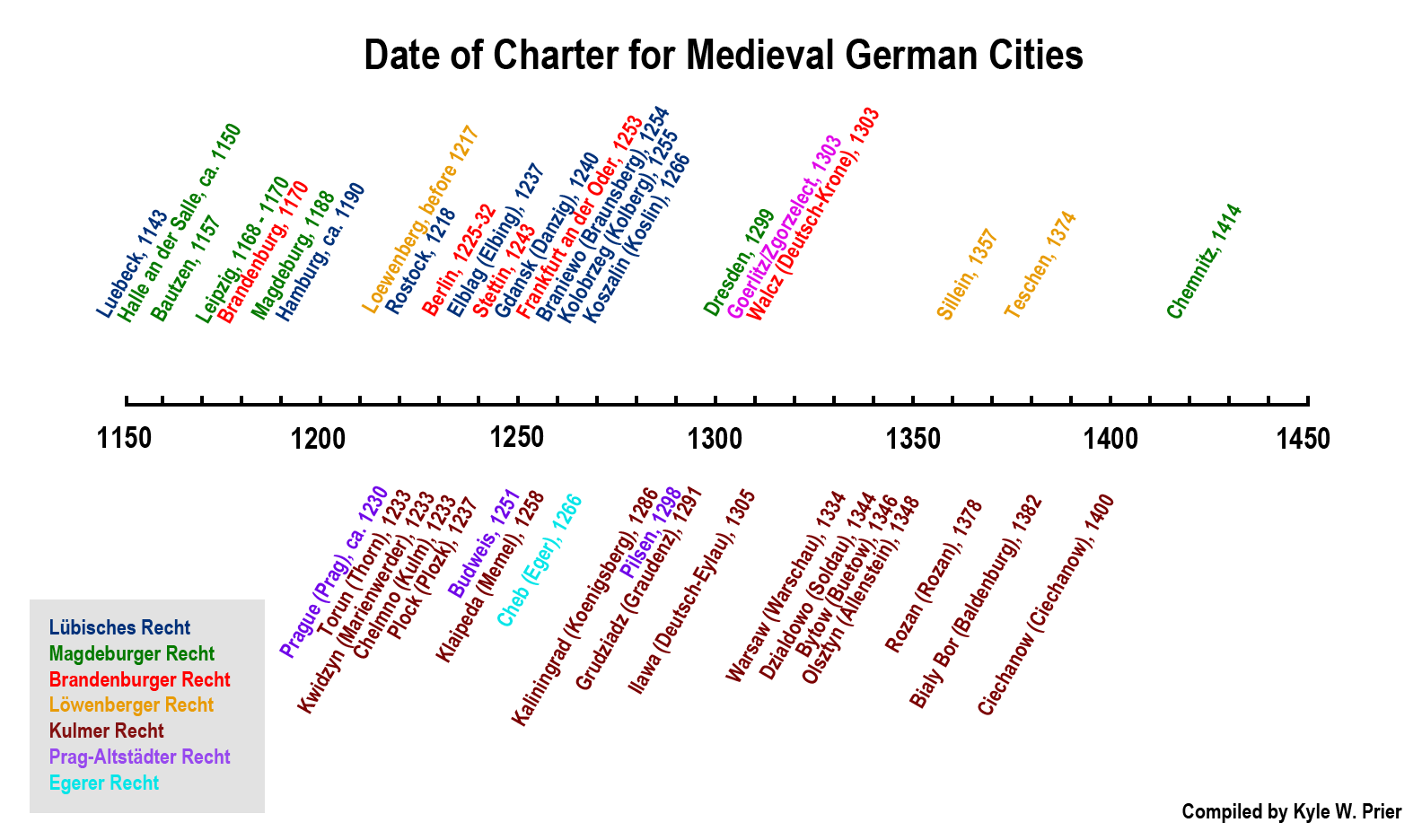 As territorial borders changed through the passage of time, changes to German city rights were inevitable. During the course of the 15th, 16th, and 17th centuries, the town laws of many places were modified with aspects of Roman law
As territorial borders changed through the passage of time, changes to German city rights were inevitable. During the course of the 15th, 16th, and 17th centuries, the town laws of many places were modified with aspects of Roman law
by legal experts. Ultimately, the older towns' laws, along with local autonomy and jurisdiction, gave way to landed territorial rulers. With the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss of 1803, almost all of the 51 reichsfrei cities of the Holy Roman Empire
were mediatised
by the territorial princes; the remaining imperial free cities of Frankfurt
, Bremen
, Hamburg
, and Lübeck became sovereign states. The only remnants of medieval town rights (statutes) included in the Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch
of 1 January 1900 were single articles concerning family and inheritance laws. The cities of Hamburg, Bremen, and Berlin
are currently administered under Landesrechte, or laws of the federal states
of Germany
.
Cities with German city rights often had similar layouts. Somewhat isolated was part of the city containing the residence and castle of the regional ruler, along with a cathedral
. The city proper was centered around a market square
which featured a church for wealthy merchants and artisans. Streets led out from the market in a planned grid system or concentric circles in which less wealthy citizens lived; riverfront sections of a city were designed with semicircles. The perimeter of the city was guarded by defensive wall
s, gate
s, and moat
s. If the city had already existed as a settlement, pre-existing defenses were sometimes incorporated into the fortifications. Cities whose layouts depict this type of urban planning
include Wrocław, Kraków
, Vienna
, Brno
, and Prague
.
Towns with German law developed in differing density depending on their locations. In much of northern Europe, the regular positioning of many smaller cities was planned. In the middle region, towns were compactly located near another as a continuation of the dense cities of middle Germany
. In the south the town density was meager, although there existed many market
s which lacked town charters.
of Central and Eastern Europe by German colonists beginning in the early 13th century. Because many areas were underpopulated or underdeveloped, local rulers offered urban privileges to peasants from western Germany to induce them to immigrate eastward. Some towns which received a German law charter were based on pre-existing settlements, while others were constructed anew by colonists. Many towns were formed in conjunction with the settlement of nearby rural communities, but the towns' urban rights were jealously guarded. Initially German town law was applied only to ethnic Germans, but gradually in most localities all town-dwellers were regarded as citizens, regardless of ethnic origin.
Lübeck law
spread rapidly among the maritime settlements along the southern shore of the Baltic Sea
and was used in northern Mecklenburg
, Western Pomerania, and parts of Pomerelia
and Warmia
. It formed the basis of Riga law in Riga
, used in the lands of the Livonian Order
in Livonia
, Estonia
, and Courland
.
Magdeburg law was popular around the March of Meißen and Upper Saxony
and was the source of several variants, including Neumarkt-Magdeburg law (Środa Śląska
), used extensively in Upper Silesia
, and Kulm law, used in the territory of the Teutonic Knights
in Prussia
and along the lower Vistula
in Eastern Pomerania. Other variants included Brandenburg, Litoměřice, and Olomouc law.
Litoměřice law and codes based on that of Nuremberg
, such as Old Prague and Cheb law, were introduced into Bohemia
during the reign of King Wenceslaus I, while German colonists introduced Brünn (Brno) and Olmütz (Olomouc) law in Moravia
. South German law, broadly referring to the codes of Nuremberg and Vienna
, was used in Bavaria
, Austria
, and Slovenia
, and was introduced into the Kingdom of Hungary
during the rule of King Béla IV
. Jihlava law was a variant used frequently by mining
communities in Bohemia, Moravia, the mountains of Slovakia
, and Transylvania
. Other town laws were only suitable for or were modified to fit local conditions, such as Głubczyce, Görlitz, Goslar, Lüneburg, Lwówek Śląski, Nysa, Spiš, and Székesfehérvár laws.
Resulting from the reign of King Casimir III of Poland
, numerous towns were chartered with Neumarkter law throughout the Kingdom of Poland in the 14th century, especially in Masovia, Galicia, and Volhynia
. Many Transylvanian Saxon
settlements in Transylvania, especially in the regions of Altland, Burzenland
, and Nösnerland
, received South German law in the 14th century.
In the 15th century, many towns in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
were chartered with the Neumarkter law used in much of Poland, although this was done through the duplication of Polish administrative methods instead of German colonization. In the 16th century Muscovy granted or reaffirmed Magdeburg rights to various towns along the Dnieper acquired from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
. After the Partitions of Poland
, Magdeburg law continued to be used in western Imperial Russia until the 1830s.
It is important to keep in mind that although many towns outside of the Holy Roman Empire
had significant German populations, in some cases a town being a "German city" referred to its legal system based on German law, not necessarily meaning it had a German population. Especially in Eastern Europe, most towns had minimal German populations, if any at all.
Town privileges
Town privileges or city rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium.Judicially, a town was distinguished from the surrounding land by means of a charter from the ruling monarch that defined its privileges and laws. Common privileges were related to trading...
used by many cities, towns, and villages throughout Central
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
during the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
.
Town law in Germany

Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
began establishing towns throughout northern Europe as early as the 10th century, they often received town privileges
Town privileges
Town privileges or city rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium.Judicially, a town was distinguished from the surrounding land by means of a charter from the ruling monarch that defined its privileges and laws. Common privileges were related to trading...
granting them autonomy from local secular or religious rulers. Such privileges often included the right to self-governance, economic autonomy, criminal courts, and militia
Militia
The term militia is commonly used today to refer to a military force composed of ordinary citizens to provide defense, emergency law enforcement, or paramilitary service, in times of emergency without being paid a regular salary or committed to a fixed term of service. It is a polyseme with...
. Town laws were more or less entirely copied from neighboring towns, such as the Westphalia
Westphalia
Westphalia is a region in Germany, centred on the cities of Arnsberg, Bielefeld, Dortmund, Minden and Münster.Westphalia is roughly the region between the rivers Rhine and Weser, located north and south of the Ruhr River. No exact definition of borders can be given, because the name "Westphalia"...
n towns of Soest
Soest, Germany
Soest is a town in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Soest district. After Lippstadt, a neighbouring town, Soest is the second biggest town in its district.-Geography:...
, Dortmund
Dortmund
Dortmund is a city in Germany. It is located in the Bundesland of North Rhine-Westphalia, in the Ruhr area. Its population of 585,045 makes it the 7th largest city in Germany and the 34th largest in the European Union....
, Minden
Minden
Minden is a town of about 83,000 inhabitants in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The town extends along both sides of the river Weser. It is the capital of the Kreis of Minden-Lübbecke, which is part of the region of Detmold. Minden is the historic political centre of the...
, and Münster
Münster
Münster is an independent city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also capital of the local government region Münsterland...
. As Germans began settling eastward, the colonists modelled their town laws on the pre-existing 12th century laws of Cologne
Cologne
Cologne is Germany's fourth-largest city , and is the largest city both in the Germany Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia and within the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area, one of the major European metropolitan areas with more than ten million inhabitants.Cologne is located on both sides of the...
, Lübeck
Lübeck
The Hanseatic City of Lübeck is the second-largest city in Schleswig-Holstein, in northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany. It was for several centuries the "capital" of the Hanseatic League and, because of its Brick Gothic architectural heritage, is listed by UNESCO as a World...
in the north (Lübeck law
Lübeck law
The Lübeck law was the constitution of a municipal form of government developed at Lübeck in Schleswig-Holstein after it was made a free city in 1226. The law provides for self-government. It replaced the personal rule of tribal monarchs descending from ancient times or the rule of the regional...
), Magdeburg
Magdeburg
Magdeburg , is the largest city and the capital city of the Bundesland of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Magdeburg is situated on the Elbe River and was one of the most important medieval cities of Europe....
roughly in the center (Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg Rights or Magdeburg Law were a set of German town laws regulating the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by a local ruler. Modelled and named after the laws of the German city of Magdeburg and developed during many centuries of the Holy Roman Empire, it was...
), and either Nuremberg
Nuremberg
Nuremberg[p] is a city in the German state of Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Situated on the Pegnitz river and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it is located about north of Munich and is Franconia's largest city. The population is 505,664...
or Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
in the south (South German law).
Because many larger cities such as Braunschweig
Braunschweig
Braunschweig , is a city of 247,400 people, located in the federal-state of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located north of the Harz mountains at the farthest navigable point of the Oker river, which connects to the North Sea via the rivers Aller and Weser....
and Hildesheim
Hildesheim
Hildesheim is a city in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located in the district of Hildesheim, about 30 km southeast of Hanover on the banks of the Innerste river, which is a small tributary of the Leine river...
grew through the agglomeration
Agglomeration
In the study of human settlements, an urban agglomeration is an extended city or town area comprising the built-up area of a central place and any suburbs linked by continuous urban area. In France, INSEE the French Statistical Institute, translate it as "Unité urbaine" which means continuous...
of neighboring towns, some previously self-contained settlements were split between regions utilizing differing town rights variants.
The granting of German city rights modelled after an established town to a new town regarded the original model as a Rechtsvorort, or roughly a legal sponsor of the newly-chartered town. For instance, Magdeburg became the sponsor of towns using Magdeburg Rights, and its lay judges could rule in ambiguous legal cases in towns using such rights. Certain city rights became known under different names, although they originally came from the same source; the name of some city variants designates the Rechtsvorort they became famous from, not necessarily that that specific style of rights originated from the Rechtsvorort.

Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, and the legal developments which occurred before the 7th century AD — when the Roman–Byzantine state adopted Greek as the language of government. The development of Roman law comprises more than a thousand years of jurisprudence — from the Twelve...
by legal experts. Ultimately, the older towns' laws, along with local autonomy and jurisdiction, gave way to landed territorial rulers. With the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss of 1803, almost all of the 51 reichsfrei cities of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
were mediatised
German Mediatisation
The German Mediatisation was the series of mediatisations and secularisations that occurred in Germany between 1795 and 1814, during the latter part of the era of the French Revolution and then the Napoleonic Era....
by the territorial princes; the remaining imperial free cities of Frankfurt
Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main , commonly known simply as Frankfurt, is the largest city in the German state of Hesse and the fifth-largest city in Germany, with a 2010 population of 688,249. The urban area had an estimated population of 2,300,000 in 2010...
, Bremen
Bremen
The City Municipality of Bremen is a Hanseatic city in northwestern Germany. A commercial and industrial city with a major port on the river Weser, Bremen is part of the Bremen-Oldenburg metropolitan area . Bremen is the second most populous city in North Germany and tenth in Germany.Bremen is...
, Hamburg
Hamburg
-History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808...
, and Lübeck became sovereign states. The only remnants of medieval town rights (statutes) included in the Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch
Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch
The Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch is the civil code of Germany. In development since 1881, it became effective on January 1, 1900, and was considered a massive and groundbreaking project....
of 1 January 1900 were single articles concerning family and inheritance laws. The cities of Hamburg, Bremen, and Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
are currently administered under Landesrechte, or laws of the federal states
States of Germany
Germany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries...
of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
.
Town layout
Many towns granted German city rights had already existed for some time, but the granting of town law codified the legal status of the settlement. Many European localities date their foundation to their reception of a town charter, even though they had existed as a settlement beforehand.Cities with German city rights often had similar layouts. Somewhat isolated was part of the city containing the residence and castle of the regional ruler, along with a cathedral
Cathedral
A cathedral is a Christian church that contains the seat of a bishop...
. The city proper was centered around a market square
Market square
The market square is a feature of many European and colonial towns. It is an open area where market stalls are traditionally set out for trading, commonly on one particular day of the week known as market day....
which featured a church for wealthy merchants and artisans. Streets led out from the market in a planned grid system or concentric circles in which less wealthy citizens lived; riverfront sections of a city were designed with semicircles. The perimeter of the city was guarded by defensive wall
Defensive wall
A defensive wall is a fortification used to protect a city or settlement from potential aggressors. In ancient to modern times, they were used to enclose settlements...
s, gate
Gate
A gate is a point of entry to a space enclosed by walls, or a moderately sized opening in a fence. Gates may prevent or control entry or exit, or they may be merely decorative. Other terms for gate include yett and port...
s, and moat
Moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that surrounds a castle, other building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive water defences, including natural or artificial lakes, dams and sluices...
s. If the city had already existed as a settlement, pre-existing defenses were sometimes incorporated into the fortifications. Cities whose layouts depict this type of urban planning
Urban planning
Urban planning incorporates areas such as economics, design, ecology, sociology, geography, law, political science, and statistics to guide and ensure the orderly development of settlements and communities....
include Wrocław, Kraków
Kraków
Kraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life...
, Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
, Brno
Brno
Brno by population and area is the second largest city in the Czech Republic, the largest Moravian city, and the historical capital city of the Margraviate of Moravia. Brno is the administrative centre of the South Moravian Region where it forms a separate district Brno-City District...
, and Prague
Prague
Prague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million...
.
Towns with German law developed in differing density depending on their locations. In much of northern Europe, the regular positioning of many smaller cities was planned. In the middle region, towns were compactly located near another as a continuation of the dense cities of middle Germany
Middle Germany
Central Germany is an economic and cultural region in Germany. Its exact borders depend on context, but it is often defined as being a region within the federal states of Saxony, Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, or a smaller part of this region .The name dates from the German Empire, when the region...
. In the south the town density was meager, although there existed many market
Market
A market is one of many varieties of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations and infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services in exchange for money from buyers...
s which lacked town charters.
Eastward colonization
German town law was frequently applied during the OstsiedlungOstsiedlung
Ostsiedlung , also called German eastward expansion, was the medieval eastward migration and settlement of Germans from modern day western and central Germany into less-populated regions and countries of eastern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The affected area roughly stretched from Slovenia...
of Central and Eastern Europe by German colonists beginning in the early 13th century. Because many areas were underpopulated or underdeveloped, local rulers offered urban privileges to peasants from western Germany to induce them to immigrate eastward. Some towns which received a German law charter were based on pre-existing settlements, while others were constructed anew by colonists. Many towns were formed in conjunction with the settlement of nearby rural communities, but the towns' urban rights were jealously guarded. Initially German town law was applied only to ethnic Germans, but gradually in most localities all town-dwellers were regarded as citizens, regardless of ethnic origin.
Lübeck law
Lübeck law
The Lübeck law was the constitution of a municipal form of government developed at Lübeck in Schleswig-Holstein after it was made a free city in 1226. The law provides for self-government. It replaced the personal rule of tribal monarchs descending from ancient times or the rule of the regional...
spread rapidly among the maritime settlements along the southern shore of the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
and was used in northern Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern...
, Western Pomerania, and parts of Pomerelia
Pomerelia
Pomerelia is a historical region in northern Poland. Pomerelia lay in eastern Pomerania: on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea and west of the Vistula and its delta. The area centered on the city of Gdańsk at the mouth of the Vistula...
and Warmia
Warmia
Warmia or Ermland is a region between Pomerelia and Masuria in northeastern Poland. Together with Masuria, it forms the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship....
. It formed the basis of Riga law in Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
, used in the lands of the Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
in Livonia
Livonia
Livonia is a historic region along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It was once the land of the Finnic Livonians inhabiting the principal ancient Livonian County Metsepole with its center at Turaida...
, Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
, and Courland
Courland
Courland is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland.- Geography and climate :...
.
Magdeburg law was popular around the March of Meißen and Upper Saxony
Upper Saxony
Upper Saxony was a name given to the majority of the German lands held by the House of Wettin, in what is now called Mitteldeutschland....
and was the source of several variants, including Neumarkt-Magdeburg law (Środa Śląska
Sroda Slaska
Środa Śląska is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of Środa Śląska County, and of the smaller administrative district called Gmina Środa Śląska. Prior to 1945 it was in Germany...
), used extensively in Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia. Since the 9th century, Upper Silesia has been part of Greater Moravia, the Duchy of Bohemia, the Piast Kingdom of Poland, again of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown and the Holy Roman Empire, as well as of...
, and Kulm law, used in the territory of the Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
in Prussia
Prussia (region)
Prussia is a historical region in Central Europe extending from the south-eastern coast of the Baltic Sea to the Masurian Lake District. It is now divided between Poland, Russia, and Lithuania...
and along the lower Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
in Eastern Pomerania. Other variants included Brandenburg, Litoměřice, and Olomouc law.
Litoměřice law and codes based on that of Nuremberg
Nuremberg
Nuremberg[p] is a city in the German state of Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Situated on the Pegnitz river and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it is located about north of Munich and is Franconia's largest city. The population is 505,664...
, such as Old Prague and Cheb law, were introduced into Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
during the reign of King Wenceslaus I, while German colonists introduced Brünn (Brno) and Olmütz (Olomouc) law in Moravia
Moravia
Moravia is a historical region in Central Europe in the east of the Czech Republic, and one of the former Czech lands, together with Bohemia and Silesia. It takes its name from the Morava River which rises in the northwest of the region...
. South German law, broadly referring to the codes of Nuremberg and Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
, was used in Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, and Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
, and was introduced into the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
during the rule of King Béla IV
Béla IV of Hungary
Béla IV , King of Hungary and of Croatia , duke of Styria 1254–58. One of the most famous kings of Hungary, he distinguished himself through his policy of strengthening of the royal power following the example of his grandfather Bela III, and by the rebuilding Hungary after the catastrophe of the...
. Jihlava law was a variant used frequently by mining
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
communities in Bohemia, Moravia, the mountains of Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, and Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
. Other town laws were only suitable for or were modified to fit local conditions, such as Głubczyce, Görlitz, Goslar, Lüneburg, Lwówek Śląski, Nysa, Spiš, and Székesfehérvár laws.
Resulting from the reign of King Casimir III of Poland
Casimir III of Poland
Casimir III the Great , last King of Poland from the Piast dynasty , was the son of King Władysław I the Elbow-high and Hedwig of Kalisz.-Biography:...
, numerous towns were chartered with Neumarkter law throughout the Kingdom of Poland in the 14th century, especially in Masovia, Galicia, and Volhynia
Volhynia
Volhynia, Volynia, or Volyn is a historic region in western Ukraine located between the rivers Prypiat and Southern Bug River, to the north of Galicia and Podolia; the region is named for the former city of Volyn or Velyn, said to have been located on the Southern Bug River, whose name may come...
. Many Transylvanian Saxon
Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania from the 12th century onwards.The colonization of Transylvania by Germans was begun by King Géza II of Hungary . For decades, the main task of the German settlers was to defend the southeastern border of the...
settlements in Transylvania, especially in the regions of Altland, Burzenland
Burzenland
The Burzenland is a historic and ethnographic area in southeastern Transylvania, Romania with a mixed population...
, and Nösnerland
Nösnerland
The Nösnerland is an historic region of northeastern Transylvania in present-day Romania centered between the Bistriţa and Mureş rivers.Beginning in the 12th century and increasingly in the 13th-14th centuries, Hungarian kings invited German colonists to settle in the eastern lands of the Kingdom...
, received South German law in the 14th century.
In the 15th century, many towns in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
were chartered with the Neumarkter law used in much of Poland, although this was done through the duplication of Polish administrative methods instead of German colonization. In the 16th century Muscovy granted or reaffirmed Magdeburg rights to various towns along the Dnieper acquired from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
. After the Partitions of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
, Magdeburg law continued to be used in western Imperial Russia until the 1830s.
It is important to keep in mind that although many towns outside of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
had significant German populations, in some cases a town being a "German city" referred to its legal system based on German law, not necessarily meaning it had a German population. Especially in Eastern Europe, most towns had minimal German populations, if any at all.
See also
- List of towns with German town law
- Kulm law
- Lübeck lawLübeck lawThe Lübeck law was the constitution of a municipal form of government developed at Lübeck in Schleswig-Holstein after it was made a free city in 1226. The law provides for self-government. It replaced the personal rule of tribal monarchs descending from ancient times or the rule of the regional...
- Magdeburg rightsMagdeburg rightsMagdeburg Rights or Magdeburg Law were a set of German town laws regulating the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by a local ruler. Modelled and named after the laws of the German city of Magdeburg and developed during many centuries of the Holy Roman Empire, it was...
- OstsiedlungOstsiedlungOstsiedlung , also called German eastward expansion, was the medieval eastward migration and settlement of Germans from modern day western and central Germany into less-populated regions and countries of eastern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The affected area roughly stretched from Slovenia...
- Town privilegesTown privilegesTown privileges or city rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium.Judicially, a town was distinguished from the surrounding land by means of a charter from the ruling monarch that defined its privileges and laws. Common privileges were related to trading...
- BurgrechtBurgrechtA Burgrecht was a medieval agreement, most commonly in southern Germany and northern German-speaking Switzerland. It came to refer to an agreement between a town and surrounding settlements or to include the specific rights held by a city or town.The word Burgrecht is first used by the St...

