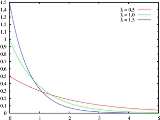
Failure rate
Encyclopedia
Failure rate is the frequency
with which an engineered system or component
fails, expressed for example in failures per hour. It is often denoted by the Greek letter
λ (lambda) and is important in reliability engineering
.
The failure rate of a system usually depends on time, with the rate varying over the life cycle of the system. For example, an automobile's failure rate in its fifth year of service may be many times greater than its failure rate during its first year of service. One does not expect to replace an exhaust pipe, overhaul the brakes, or have major transmission
problems in a new vehicle.
In practice, the mean time between failures (MTBF, 1/λ) is often used instead of the failure rate. This is valid if the failure rate is constant (general agreement in some reliability standards (Military and Aerospace) - part of the flat region of the bathtub curve
, also called the "useful life period". The MTBF is an important system parameter in systems where failure rate needs to be managed, in particular for safety systems. The MTBF appears frequently in the engineering
design requirements, and governs frequency of required system maintenance and inspections. In special processes called renewal processes, where the time to recover from failure can be neglected and the likelihood of failure remains constant with respect to time, the failure rate is simply the multiplicative inverse of the MTBF (1/λ).
A similar ratio used in the transport industries, especially in railways and trucking
is 'mean distance between failures', a variation which attempts to correlate
actual loaded distances to similar reliability needs and practices.
Failure rates are important factors in the insurance, finance, commerce and regulatory industries and fundamental to the design of safe systems in a wide variety of applications.
Although the failure rate,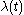 , is often thought of as the probability
, is often thought of as the probability
that a failure occurs in a specified interval given no failure before time , it is not actually a probability because it can exceed 1. Erroneous expression of the failure rate in % could result in incorrect perception of the measure, specially if it would be measured from repairable systems and multiple systems with non-constant failure rates or different operation times. It can be defined with the aid of the reliability function or survival function
, it is not actually a probability because it can exceed 1. Erroneous expression of the failure rate in % could result in incorrect perception of the measure, specially if it would be measured from repairable systems and multiple systems with non-constant failure rates or different operation times. It can be defined with the aid of the reliability function or survival function  , the probability of no failure before time
, the probability of no failure before time  .
.
Failure_rate(t)= f(t)/R(t), where f(t) is the time to (first) failure distribution and R(t) is 1 - F(t):
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
with which an engineered system or component
Component
-Usage:Component may refer to:* System components, the constituents of a system* Electronic components, the constituents of electronic circuits* Component ingredient, the main ingredient in a dish...
fails, expressed for example in failures per hour. It is often denoted by the Greek letter
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
λ (lambda) and is important in reliability engineering
Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is an engineering field, that deals with the study, evaluation, and life-cycle management of reliability: the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time. It is often measured as a probability of...
.
The failure rate of a system usually depends on time, with the rate varying over the life cycle of the system. For example, an automobile's failure rate in its fifth year of service may be many times greater than its failure rate during its first year of service. One does not expect to replace an exhaust pipe, overhaul the brakes, or have major transmission
Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
problems in a new vehicle.
In practice, the mean time between failures (MTBF, 1/λ) is often used instead of the failure rate. This is valid if the failure rate is constant (general agreement in some reliability standards (Military and Aerospace) - part of the flat region of the bathtub curve
Bathtub curve
The bathtub curve is widely used in reliability engineering. It describes a particular form of the hazard function which comprises three parts:*The first part is a decreasing failure rate, known as early failures....
, also called the "useful life period". The MTBF is an important system parameter in systems where failure rate needs to be managed, in particular for safety systems. The MTBF appears frequently in the engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
design requirements, and governs frequency of required system maintenance and inspections. In special processes called renewal processes, where the time to recover from failure can be neglected and the likelihood of failure remains constant with respect to time, the failure rate is simply the multiplicative inverse of the MTBF (1/λ).
A similar ratio used in the transport industries, especially in railways and trucking
Truck driver
A truck driver , is a person who earns a living as the driver of a truck, usually a semi truck, box truck, or dump truck.Truck drivers provide an essential service to...
is 'mean distance between failures', a variation which attempts to correlate
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
actual loaded distances to similar reliability needs and practices.
Failure rates are important factors in the insurance, finance, commerce and regulatory industries and fundamental to the design of safe systems in a wide variety of applications.
Failure rate in the discrete sense
The failure rate can be defined as the following:- The total number of failures within an item populationStatistical populationA statistical population is a set of entities concerning which statistical inferences are to be drawn, often based on a random sample taken from the population. For example, if we were interested in generalizations about crows, then we would describe the set of crows that is of interest...
, divided by the total time expended by that population, during a particular measurement interval under stated conditions. (MacDiarmid, et al.)
Although the failure rate,
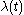 , is often thought of as the probability
, is often thought of as the probabilityProbability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
that a failure occurs in a specified interval given no failure before time
 , it is not actually a probability because it can exceed 1. Erroneous expression of the failure rate in % could result in incorrect perception of the measure, specially if it would be measured from repairable systems and multiple systems with non-constant failure rates or different operation times. It can be defined with the aid of the reliability function or survival function
, it is not actually a probability because it can exceed 1. Erroneous expression of the failure rate in % could result in incorrect perception of the measure, specially if it would be measured from repairable systems and multiple systems with non-constant failure rates or different operation times. It can be defined with the aid of the reliability function or survival function  , the probability of no failure before time
, the probability of no failure before time  .
.Failure_rate(t)= f(t)/R(t), where f(t) is the time to (first) failure distribution and R(t) is 1 - F(t):
-
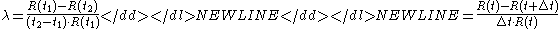
over a time interval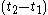 from
from 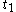 (or
(or  ) to
) to 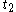 and
and 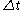 is defined as
is defined as 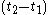 . Note that this is a conditional probabilityConditional probabilityIn probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
. Note that this is a conditional probabilityConditional probabilityIn probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
, hence the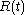 in the denominator.
in the denominator.
The failure_rate (t) function is a CONDITIONAL probability of failure DENSITY function. The condition is that the failure has not occurred at time t.
Hazard rate and ROCOF (rate of occurrence of failures) is often incorrectly seen as the same and equal to the failure rate. And literature is even contaminated with inconsistent definitions. The hazard rate is in contrast to the ROCOF the same a failure rate. ROCOF is used for repairable systems only. In practice not many serious errors are made due to this confusion (although this statement is hard to validate...).
Failure rate in the continuous sense
Calculating the failure rate for ever smaller intervals of time, results in the (or hazard rate),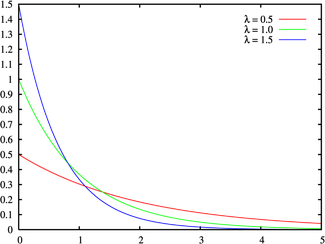
 . This becomes the instantaneous failure rate as
. This becomes the instantaneous failure rate as 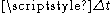 tends to zero:
tends to zero:
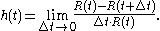
A continuous failure rate depends on the existence of a failure distribution,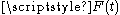 , which is a cumulative distribution functionCumulative distribution functionIn probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
, which is a cumulative distribution functionCumulative distribution functionIn probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
that describes the probability of failure (at least) up to and including time t,

where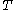 is the failure time.
is the failure time.
The failure distribution function is the integral of the failure density functionProbability density functionIn probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
, f(t),

The hazard function can be defined now as
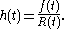
Many probability distributions can be used to model the failure distribution (see List of important probability distributions). A common model is the exponential failure distribution,
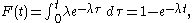
which is based on the exponential density functionExponential distributionIn probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions. It describes the time between events in a Poisson process, i.e...
. The hazard rate function for this is:
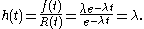
Thus, for an exponential failure distribution, the hazard rate is a constant with respect to time (that is, the distribution is "memory-less"). For other distributions, such as a Weibull distribution or a log-normal distribution, the hazard function may not be constant with respect to time. For some such as the deterministic distribution it is monotonic increasing (analogous to "wearing out"Wear and tearWear and tear is damage that naturally and inevitably occurs as a result of normal wear or aging. It is used in a legal context for such areas as warranty contracts from manufacturers, which usually stipulate that damage due to wear and tear will not be covered.Wear and tear is a form of...
), for others such as the Pareto distribution it is monotonic decreasing (analogous to "burning in"), while for many it is not monotonic.
Failure rate data
Failure rate dataDataThe term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
can be obtained in several ways. The most common means are:- Historical data about the device or system under consideration.
-
- Many organizations maintain internal databases of failure information on the devices or systems that they produce, which can be used to calculate failure rates for those devices or systems. For new devices or systems, the historical data for similar devices or systems can serve as a useful estimate.
- Government and commercial failure rate data.
- Handbooks of failure rate data for various components are available from government and commercial sources. MIL-HDBK-217F, Reliability Prediction of Electronic Equipment, is a military standard that provides failure rate data for many military electronic components. Several failure rate data sources are available commercially that focus on commercial components, including some non-electronic components.
- Testing.
- The most accurate source of data is to test samples of the actual devices or systems in order to generate failure data. This is often prohibitively expensive or impractical, so that the previous data sources are often used instead.
- Many organizations maintain internal databases of failure information on the devices or systems that they produce, which can be used to calculate failure rates for those devices or systems. For new devices or systems, the historical data for similar devices or systems can serve as a useful estimate.
Units
Failure rates can be expressed using any measure of time, but hours is the most common unit in practice. Other units, such as miles, revolutions, etc., can also be used in place of "time" units.
Failure rates are often expressed in engineering notationEngineering notationEngineering notation is a version of scientific notation in which the powers of ten must be multiples of three...
as failures per million, or 10−6, especially for individual components, since their failure rates are often very low.
The Failures In Time (FIT) rate of a device is the number of failures that can be expected in one billion1000000000 (number)1,000,000,000 is the natural number following 999,999,999 and preceding 1,000,000,001.In scientific notation, it is written as 109....
(109) device-hours of operation. (E.g. 1000 devices for 1 million hours, or 1 million devices for 1000 hours each, or some other combination.) This term is used particularly by the semiconductorSemiconductorA semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
industry.
The relationship of FIT to MTBF may be expressed as: MTBF = 1,000,000,000 x 1/FIT.
Additivity
Under certain engineeringEngineeringEngineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
assumptions (e.g. besides the above assumptions for a constant failure rate, the assumption that the considered system has no relevant redundanciesRedundancy (engineering)In engineering, redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system, usually in the case of a backup or fail-safe....
), the failure rate for a complex systemSystemSystem is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
is simply the sum of the individual failure rates of its components, as long as the units are consistent, e.g. failures per million hours. This permits testing of individual components or subsystems, whose failure rates are then added to obtain the total system failure rate.
Example
Suppose it is desired to estimate the failure rate of a certain component. A test can be performed to estimate its failure rate. Ten identical components are each tested until they either fail or reach 1000 hours, at which time the test is terminated for that component. (The level of statistical confidenceConfidence intervalIn statistics, a confidence interval is a particular kind of interval estimate of a population parameter and is used to indicate the reliability of an estimate. It is an observed interval , in principle different from sample to sample, that frequently includes the parameter of interest, if the...
is not considered in this example.) The results are as follows:
Estimated failure rate is
or 799.8 failures for every million hours of operation.
Estimation
The Nelson–Aalen estimatorNelson–Aalen estimatorThe Nelson–Aalen estimator is a non-parametric estimator of the cumulative hazard rate function in case of censored data or incomplete data. It is used in survival theory, reliability engineering and life insurance to estimate the cumulative number of expected events. An event can be a failure of a...
can be used to estimate the cumulative hazard rate function.
Print
- Blanchard, Benjamin S. (1992), Logistics Engineering and Management, Fourth Ed., pp 26–32, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
- Ebeling, Charles E., (1997), An Introduction to Reliability and Maintainability Engineering, pp 23–32, McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., Boston.
- Federal Standard 1037CFederal Standard 1037CFederal Standard 1037C, titled Telecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunication Terms is a United States Federal Standard, issued by the General Services Administration pursuant to the Federal Property and Administrative Services Act of 1949, as amended....
- Kapur, K.C., and Lamberson, L.R., (1977), Reliability in Engineering Design, pp 8–30, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
- Knowles, D.I.,(1995), Should We Move Away From "Acceptable Failure Rate", Communications in Reliability Maintainability and Supportability, Vol. 2, No. 1, P. 23, International RMS Committee, USA
- MacDiarmid, Preston; Morris, Seymour; et al., (no date), Reliability Toolkit: Commercial Practices Edition, pp 35–39, Reliability Analysis Center and Rome Laboratory, Rome, New York.
- Rausand, M. and Hoyland, A., (2004), System Reliability Theory; Models, Statistical methods, and Applications, John Wuiley & Sons, New York. NTNU.no
- Turner, T., Hockley, C., and Burdaky, R., (1997), The Customer Needs A Maintenance-Free Operating Period, 1997 Avionics Conference and Exhibition, No. 97-0819, P. 2.2, ERA Technology Ltd., Leatherhead, Surrey, UK
Online
- Mondro, Mitchell J, (June 2002), "Approximation of Mean Time Between Failure When a System has Periodic Maintenance", IEEE Transactions on Reliability, v 51, no 2. (available from MITRE Corp.)
- Reliability Prediction of Electronic Equipment, MIL-HDBK-217F(2), (DOD download site.)
- Bathtub curve issues by ASQC.
- Fault Tolerant Computing in Industrial Automation by Hubert Kirrmann, ABB Research Center, Switzerland
External links


