Exponential distribution
Overview
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the exponential distribution (a.k.a. negative exponential distribution) is a family of continuous probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
s. It describes the time between events in a Poisson process
Poisson process
A Poisson process, named after the French mathematician Siméon-Denis Poisson , is a stochastic process in which events occur continuously and independently of one another...
, i.e. a process in which events occur continuously and independently
Memorylessness
In probability and statistics, memorylessness is a property of certain probability distributions: the exponential distributions of non-negative real numbers and the geometric distributions of non-negative integers....
at a constant average rate.
Note that the exponential distribution is not the same as the class of exponential families
Exponential family
In probability and statistics, an exponential family is an important class of probability distributions sharing a certain form, specified below. This special form is chosen for mathematical convenience, on account of some useful algebraic properties, as well as for generality, as exponential...
of distributions, which is a large class of probability distributions that includes the exponential distribution as one of its members, but also includes the normal distribution, binomial distribution, gamma distribution, Poisson
Poisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
, and many others.
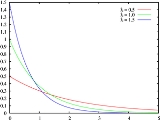
The probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
(pdf) of an exponential distribution is
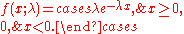
Alternatively, this can be defined using the Heaviside step function
Heaviside step function
The Heaviside step function, or the unit step function, usually denoted by H , is a discontinuous function whose value is zero for negative argument and one for positive argument....
, H(x).
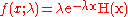
Here λ > 0 is the parameter of the distribution, often called the rate parameter.

