System
Encyclopedia
A system is a set of elements (often called 'components' instead) and relationships which are different from relationships of the set or its elements to other elements or sets.
Fields that study the general properties of systems include systems theory
Systems theory
Systems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
, cybernetics
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
, dynamical systems, thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
and complex systems
Complex systems
Complex systems present problems in mathematical modelling.The equations from which complex system models are developed generally derive from statistical physics, information theory and non-linear dynamics, and represent organized but unpredictable behaviors of systems of nature that are considered...
. They investigate the abstract properties of systems' matter and organization, looking for concepts and principles that are independent of domain, substance, type, or temporal scale.
Most systems share common characteristics, including:
- Systems have structureStructureStructure is a fundamental, tangible or intangible notion referring to the recognition, observation, nature, and permanence of patterns and relationships of entities. This notion may itself be an object, such as a built structure, or an attribute, such as the structure of society...
, defined by components/elements and their composition; - Systems have behaviorBehaviorBehavior or behaviour refers to the actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with its environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment...
, which involves inputs, processing and outputs of material, energy, information, or data; - Systems have interconnectivityInterconnectivityInterconnectivity is a concept that is used in numerous fields such as cybernetics, biology, ecology, network theory, and non-linear dynamics. The concept can be summarized as that all parts of a system interact with and rely on one another simply by the fact that they occupy the same system, and...
: the various parts of a system have functional as well as structural relationships to each other. - Systems may have some functions or groups of functions
The term system may also refer to a set of rules that governs structure and/or behavior.
History
The word system in its meaning here, has a long history which can be traced back to PlatoPlato
Plato , was a Classical Greek philosopher, mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the...
(Philebus), Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
(Politics) and Euclid
Euclid
Euclid , fl. 300 BC, also known as Euclid of Alexandria, was a Greek mathematician, often referred to as the "Father of Geometry". He was active in Alexandria during the reign of Ptolemy I...
(Elements). It had meant "total", "crowd" or "union" in even more ancient times, as it derives from the verb sunìstemi, uniting, putting together.
In the 19th century the first to develop the concept of a "system" in the natural sciences was the French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot who studied thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
. In 1824 he studied the system which he called the working substance, i.e. typically a body of water vapor, in steam engines, in regards to the system's ability to do work when heat is applied to it. The working substance could be put in contact with either a boiler, a cold reservoir (a stream of cold water), or a piston (to which the working body could do work by pushing on it). In 1850, the German physicist Rudolf Clausius
Rudolf Clausius
Rudolf Julius Emanuel Clausius , was a German physicist and mathematician and is considered one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics. By his restatement of Sadi Carnot's principle known as the Carnot cycle, he put the theory of heat on a truer and sounder basis...
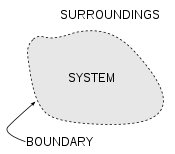
generalized this picture to include the concept of the surroundings
Environment (systems)
In science and engineering, a system is the part of the universe that is being studied, while the environment is the remainder of the universe that lies outside the boundaries of the system. It is also known as the surroundings, and in thermodynamics, as the reservoir...
and began to use the term "working body" when referring to the system.
One of the pioneers of the general systems theory was the biologist Ludwig von Bertalanffy
Ludwig von Bertalanffy
Karl Ludwig von Bertalanffy was an Austrian-born biologist known as one of the founders of general systems theory . GST is an interdisciplinary practice that describes systems with interacting components, applicable to biology, cybernetics, and other fields...
. In 1945 he introduced models, principles, and laws that apply to generalized systems or their subclasses, irrespective of their particular kind, the nature of their component elements, and the relation or 'forces' between them.
Significant development to the concept of a system was done by Norbert Wiener
Norbert Wiener
Norbert Wiener was an American mathematician.A famous child prodigy, Wiener later became an early researcher in stochastic and noise processes, contributing work relevant to electronic engineering, electronic communication, and control systems.Wiener is regarded as the originator of cybernetics, a...
and Ross Ashby who pioneered the use of mathematics to study systems.
In the 1980s the term complex adaptive system
Complex adaptive system
Complex adaptive systems are special cases of complex systems. They are complex in that they are dynamic networks of interactions and relationships not aggregations of static entities...
was coined at the interdisciplinary Santa Fe Institute
Santa Fe Institute
The Santa Fe Institute is an independent, nonprofit theoretical research institute located in Santa Fe and dedicated to the multidisciplinary study of the fundamental principles of complex adaptive systems, including physical, computational, biological, and social systems.The Institute houses a...
by John H. Holland
John Henry Holland
John Henry Holland is an American scientist and Professor of Psychology and Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He is a pioneer in complex systems and nonlinear science. He is known as the father of genetic algorithms. He was awarded...
, Murray Gell-Mann
Murray Gell-Mann
Murray Gell-Mann is an American physicist and linguist who received the 1969 Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the theory of elementary particles...
and others.
System concepts
Environment and boundaries- Systems theorySystems theorySystems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
views the world as a complex system of interconnected parts. We scope a system by defining its boundaryBoundary (topology)In topology and mathematics in general, the boundary of a subset S of a topological space X is the set of points which can be approached both from S and from the outside of S. More precisely, it is the set of points in the closure of S, not belonging to the interior of S. An element of the boundary...
; this means choosing which entities are inside the system and which are outside - part of the environmentEnvironment (systems)In science and engineering, a system is the part of the universe that is being studied, while the environment is the remainder of the universe that lies outside the boundaries of the system. It is also known as the surroundings, and in thermodynamics, as the reservoir...
. We then make simplified representations (modelsScientific modellingScientific modelling is the process of generating abstract, conceptual, graphical and/or mathematical models. Science offers a growing collection of methods, techniques and theory about all kinds of specialized scientific modelling...
) of the system in order to understand it and to predict or impact its future behavior. These models may define the structureStructureStructure is a fundamental, tangible or intangible notion referring to the recognition, observation, nature, and permanence of patterns and relationships of entities. This notion may itself be an object, such as a built structure, or an attribute, such as the structure of society...
and/or the behaviorBehaviorBehavior or behaviour refers to the actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with its environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment...
of the system.
Natural and man-made systems
- There are natural and man-made (designed) systems. Natural systems may not have an apparent objective but their outputs can be interpreted as purposes. Man-made systems are made with purposes that are achieved by the delivery of outputs. Their parts must be related; they must be “designed to work as a coherent entity” - else they would be two or more distinct systems.
Theoretical Framework
- An open system exchanges matter and energy with its surroundings. Most systems are open systems; like a car, coffeemaker, or computer. A closed systemClosed system-In physics:In thermodynamics, a closed system can exchange energy , but not matter, with its surroundings.In contrast, an isolated system cannot exchange any of heat, work, or matter with the surroundings, while an open system can exchange all of heat, work and matter.For a simple system, with...
exchanges energy, but not matter, with its environment; like Earth or the project Biosphere2 or 3. An isolated systemIsolated systemIn the natural sciences an isolated system, as contrasted with an open system, is a physical system without any external exchange. If it has any surroundings, it does not interact with them. It obeys in particular the first of the conservation laws: its total energy - mass stays constant...
exchanges neither matter nor energy with its environment. A theoretical example of such system is the Universe.
Process and transformation process
- A system can also be viewed as a bounded transformation process, that is, a process or collection of processes that transforms inputs into outputs. Inputs are consumed; outputs are produced. The concept of input and output here is very broad. E.g., an output of a passenger ship is the movement of people from departure to destination.
Subsystem
- A subsystem is a set of elements, which is a system itself, and a component of a larger system.
System Model
- A system comprises multiple viewsView modelA view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of views to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architecture, or enterprise architecture. A view is a representation...
. For the man-made systems it may be such views as planning, requirement (analysis), designSystems designSystems design is the process of defining the architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to satisfy specified requirements. One could see it as the application of systems theory to product development...
, implementation, deployment, structureStructureStructure is a fundamental, tangible or intangible notion referring to the recognition, observation, nature, and permanence of patterns and relationships of entities. This notion may itself be an object, such as a built structure, or an attribute, such as the structure of society...
, behaviorBehaviorBehavior or behaviour refers to the actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with its environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment...
, input data, and output data views. A system modelSystem modelA system model is the conceptual model that describes and represents a system. A system comprises multiple views such as planning, requirement , design, implementation, deployment, structure, behavior, input data, and output data views...
is required to describe and represent all these multiple views.
System Architecture
- A system architecture, using one single integrated model for the description of multiple viewsView modelA view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of views to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architecture, or enterprise architecture. A view is a representation...
such as planning, requirement (analysis), designSystems designSystems design is the process of defining the architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to satisfy specified requirements. One could see it as the application of systems theory to product development...
, implementation, deployment, structureStructureStructure is a fundamental, tangible or intangible notion referring to the recognition, observation, nature, and permanence of patterns and relationships of entities. This notion may itself be an object, such as a built structure, or an attribute, such as the structure of society...
, behaviorBehaviorBehavior or behaviour refers to the actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with its environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment...
, input data, and output data views, is a kind of system modelSystem modelA system model is the conceptual model that describes and represents a system. A system comprises multiple views such as planning, requirement , design, implementation, deployment, structure, behavior, input data, and output data views...
.
Elements of System
Following are considered as the elements of a system in terms of Information systems: -- Inputs and Outputs
- Processor
- Control
- Environment
- Feedback
- Boundaries and Interface
Types of systems
Systems are classified in different ways:- Physical or Abstract systems
- Open or Closed systems
- 'Man-made' Information systems
- Formal Information systems
- Informal Information systems
- Computer Based Information systems
Physical systems are tangible entities that may be static or dynamic in operation. For Example, the physical parts of the computer center are the offices , desk and chairs that facilitate operation of the computer. They can be seen and counted as they are static. In contrast, a programmed computer is a dynamic demands or the priority of the information requested changes.
Abstract systems are conceptual or non physical entities.
An open system has many interfaces with its environment. i.e. system that interacts freely with its environment, taking input and returning output. It permits interaction across its boundary; it receives inputs from and delivers outputs to the outside.
A closed system does not interact with the environment; changes in the environment and adaptability are not issues for closed system.
Analysis of systems
Evidently, there are many types of systems that can be analyzed both quantitativeQuantitative property
A quantitative property is one that exists in a range of magnitudes, and can therefore be measured with a number. Measurements of any particular quantitative property are expressed as a specific quantity, referred to as a unit, multiplied by a number. Examples of physical quantities are distance,...
ly and qualitative
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is a method of inquiry employed in many different academic disciplines, traditionally in the social sciences, but also in market research and further contexts. Qualitative researchers aim to gather an in-depth understanding of human behavior and the reasons that govern such...
ly. For example, with an analysis of urban systems dynamics, [A.W. Steiss] defines five intersecting systems, including the physical subsystem and behavioral system. For sociological models influenced by systems theory, where Kenneth D. Bailey
Kenneth D. Bailey
Major Kenneth Dillon Bailey was a United States Marine Corps officer who posthumously received the Medal of Honor for heroic conduct during action during the Battle of Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands...
defines systems in terms of conceptual, concrete
Concrete
Concrete is a composite construction material, composed of cement and other cementitious materials such as fly ash and slag cement, aggregate , water and chemical admixtures.The word concrete comes from the Latin word...
and abstract systems; either isolated
Isolated system
In the natural sciences an isolated system, as contrasted with an open system, is a physical system without any external exchange. If it has any surroundings, it does not interact with them. It obeys in particular the first of the conservation laws: its total energy - mass stays constant...
, closed
Closed system
-In physics:In thermodynamics, a closed system can exchange energy , but not matter, with its surroundings.In contrast, an isolated system cannot exchange any of heat, work, or matter with the surroundings, while an open system can exchange all of heat, work and matter.For a simple system, with...
, or open, Walter F. Buckley
Walter F. Buckley
Walter Frederick Buckley was an American professor of sociology. He was among the first to apply concepts from general systems theory , based on the work of Bertalanffy, to sociology. The sociologist was not specifically aligned to either the cybernetics or the general systems movements.-...
defines social systems in sociology in terms of mechanical
Mechanics
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
, organic
Organic (model)
Organic describes forms, methods and patterns found in living systems such as the organisation of cells, to populations, communities, and ecosystems.Typically organic models stress the interdependence of the component parts, as well as their differentiation...
, and process
Process modeling
The term process model is used in various contexts. For example, in business process modeling the enterprise process model is often referred to as the business process model. Process models are core concepts in the discipline of process engineering....
models. Bela H. Banathy
Béla H. Bánáthy
Béla Heinrich Bánáthy was a Hungarian linguist, systems scientist and a professor at San Jose State University and UC Berkeley. Bánáthy was the founder of the White Stag Leadership Development Program whose leadership model was adopted across the United States...
cautions that with any inquiry into a system that understanding the type of system is crucial and defines Natural and Designed systems.
In offering these more global definitions, the author maintains that it is important not to confuse one for the other. The theorist explains that natural systems include sub-atomic systems, living systems, the solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
, the galactic
Galactic
Galactic is a funk and jazz jam band from New Orleans, Louisiana, United States.-Origins and background:Originally formed in 1994 as an octet and including singer Chris Lane and guitarist Rob Gowen, the group was soon pared down to a sextet of: guitarist Jeff Raines, bassist Robert Mercurio,...
system and the Universe. Designed systems are our creations, our physical structures, hybrid systems which include natural and designed systems, and our conceptual knowledge. The human element of organization and activities are emphasized with their relevant abstract systems and representations. A key consideration in making distinctions among various types of systems is to determine how much freedom the system has to select purpose, goals, methods, tools, etc. and how widely is the freedom to select itself distributed (or concentrated) in the system.
George J. Klir maintains that no "classification is complete and perfect for all purposes," and defines systems in terms of abstract, real
The Real
The Real refers to that which is authentic, the unchangeable truth in reference both to being/the Self and the external dimension of experience, also referred to as the infinite and absolute - as opposed to a reality based on sense perception and the material order.-In psychoanalysis:The Real is a...
, and conceptual
Conceptual system
A conceptual system is a system that is composed of non-physical objects, i.e. ideas or concepts. In this context a system is taken to mean "an interrelated, interworking set of objects".- Overview :...
physical systems, bounded and unbounded system
Unbounded system
In the theory of dynamical systems, an unbounded system is a system that has no bound; i.e. one that can expand forever, with no limit....
s, discrete to continuous, pulse to hybrid system
Hybrid system
A hybrid system is a dynamic system that exhibits both continuous and discrete dynamic behavior – a system that can both flow and jump...
s, et cetera. The interaction between systems and their environments are categorized in terms of relatively closed, and open systems. It seems most unlikely that an absolutely closed system can exist or, if it did, that it could be known by us. Important distinctions have also been made between hard and soft systems. Hard systems are associated with areas such as systems engineering
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
, operations research and quantitative systems analysis. Soft systems are commonly associated with concepts developed by Peter Checkland
Peter Checkland
Peter Checkland is a British management scientist and emeritus professor of Systems at Lancaster University. He is the developer of soft systems methodology : a methodology based on a way of systems thinking.- Biography :...
and Brian Wilson through Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) involving methods such as action research
Action research
Action research or participatory action research – is a reflective process of progressive problem solving led by individuals working with others in teams or as part of a "community of practice" to improve the way they address issues and solve problems. Action research is done simply by action,...
and emphasizing participatory designs. Where hard systems might be identified as more "scientific," the distinction between them is actually often hard to define.
Cultural system
A cultural system may be defined as the interaction of different elements of cultureCulture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
. While a cultural system is quite different from a social system, sometimes both systems together are referred to as the sociocultural system
Sociocultural system
A sociocultural system is a "human population viewed in its ecological context and as one of the many subsystems of a larger ecological system".A sociocultural system may be described as having an infrastructure, a structure, and a superstructure...
. A major concern in the social sciences is the problem of order. One way that social order has been theorized is according to the degree of integration of cultural and social factors.
Economic system
An economic system is a mechanism (social institution) which deals with the production, distributionDistribution (business)
Product distribution is one of the four elements of the marketing mix. An organization or set of organizations involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by a consumer or business user.The other three parts of the marketing mix are product, pricing,...
and consumption
Consumption (economics)
Consumption is a common concept in economics, and gives rise to derived concepts such as consumer debt. Generally, consumption is defined in part by comparison to production. But the precise definition can vary because different schools of economists define production quite differently...
of goods and services in a particular society
Society
A society, or a human society, is a group of people related to each other through persistent relations, or a large social grouping sharing the same geographical or virtual territory, subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations...
. The economic system is composed of people
Person
A person is a human being, or an entity that has certain capacities or attributes strongly associated with being human , for example in a particular moral or legal context...
, institutions and their relationships to resources, such as the convention
Convention (norm)
A convention is a set of agreed, stipulated or generally accepted standards, norms, social norms or criteria, often taking the form of a custom....
of property
Property
Property is any physical or intangible entity that is owned by a person or jointly by a group of people or a legal entity like a corporation...
. It addresses the problems of economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, like the allocation and scarcity of resources.
Application of the system concept
Systems modeling is generally a basic principle in engineering and in social sciences. The system is the representation of the entities under concern. Hence inclusion to or exclusion from system context is dependent of the intention of the modeler.No model of a system will include all features of the real system of concern, and no model of a system must include all entities belonging to a real system of concern.
Systems in information and computer science
In computer scienceComputer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
and information science
Information science
-Introduction:Information science is an interdisciplinary science primarily concerned with the analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval and dissemination of information...
, system is a software system
Software system
A software system is a system based on software forming part of a computer system . The term "software system" is often used as a synonym of computer program or software; is related to the application of systems theory approaches in software engineering context and are used to study large and...
which has components
Component (UML)
A component in the Unified Modeling Language "represents a modular part of a system, that encapsulates its content and whose manifestation is replaceable within its environment. A component defines its behavior in terms of provided and required interfaces".A component may be replaced by another if...
as its structure and observable Inter-process communication
Inter-process communication
In computing, Inter-process communication is a set of methods for the exchange of data among multiple threads in one or more processes. Processes may be running on one or more computers connected by a network. IPC methods are divided into methods for message passing, synchronization, shared...
s as its behavior. Again, an example will illustrate: There are systems of counting, as with Roman numerals
Roman numerals
The numeral system of ancient Rome, or Roman numerals, uses combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet to signify values. The numbers 1 to 10 can be expressed in Roman numerals as:...
, and various systems for filing papers, or catalogues, and various library systems, of which the Dewey Decimal System is an example. This still fits with the definition of components which are connected together (in this case in order to facilitate the flow of information).
System can also be used referring to a framework, be it software or hardware, designed to allow software programs to run, see platform
Platform (computing)
A computing platform includes some sort of hardware architecture and a software framework , where the combination allows software, particularly application software, to run...
.
Systems in engineering and physics
In engineeringEngineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
and physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, a physical system
Physical system
In physics, the word system has a technical meaning, namely, it is the portion of the physical universe chosen for analysis. Everything outside the system is known as the environment, which in analysis is ignored except for its effects on the system. The cut between system and the world is a free...
is the portion of the universe that is being studied (of which a thermodynamic system
Thermodynamic system
A thermodynamic system is a precisely defined macroscopic region of the universe, often called a physical system, that is studied using the principles of thermodynamics....
is one major example). Engineering also has the concept of a system that refers to all of the parts and interactions between parts of a complex project. Systems engineering
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
refers to the branch of engineering that studies how this type of system should be planned, designed, implemented, built, and maintained.
Systems in social and cognitive sciences and management research
Social and cognitive sciences recognize systems in human person models and in human societies. They include human brain functions and human mental processes as well as normative ethics systems and social/cultural behavioral patterns.In management science, operations research
Operations research
Operations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
and organizational development (OD), human organizations are viewed as systems (conceptual systems) of interacting components such as subsystems or system aggregates, which are carriers of numerous complex business processes (organizational behaviors) and organizational structures. Organizational development theorist Peter Senge
Peter Senge
Peter Michael Senge is an American scientist and director of the Center for Organizational Learning at the MIT Sloan School of Management. He is known as author of the book The Fifth Discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization from 1990...
developed the notion of organizations as systems in his book The Fifth Discipline.
Systems thinking
Systems thinking
Systems thinking is the process of understanding how things influence one another within a whole. In nature, systems thinking examples include ecosystems in which various elements such as air, water, movement, plants, and animals work together to survive or perish...
is a style of thinking/reasoning and problem solving. It starts from the recognition of system properties in a given problem. It can be a leadership competency. Some people can think globally while acting locally. Such people consider the potential consequences of their decisions on other parts of larger systems. This is also a basis of systemic coaching in psychology.
Organizational theorists
Organizational studies
Organizational studies, sometimes known as organizational science, encompass the systematic study and careful application of knowledge about how people act within organizations...
such as Margaret Wheatley have also described the workings of organizational systems in new metaphoric contexts, such as quantum physics, chaos theory
Chaos theory
Chaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
, and the self-organization of systems.
Systems applied to strategic thinking
In 1988, military strategist, John A. Warden IIIJohn A. Warden III
John Ashley Warden III is a retired colonel in the United States Air Force. Warden is a graduate of the United States Air Force Academy. His Air Force career spanned 30 years, from 1965 to 1995, and included tours in Vietnam, Germany, Spain, Italy, and Korea, as well as many assignments within...
introduced his Five Ring System model in his book, The Air Campaign contending that any complex system could be broken down into five concentric rings. Each ring—Leadership, Processes, Infrastructure, Population and Action Units—could be used to isolate key elements of any system that needed change. The model was used effectively by Air Force planners in the First Gulf War. In the late 1990s, Warden applied this five ring model to business strategy.
See also
Examples of systems- List of systems (WikiProject)
- physical systemPhysical systemIn physics, the word system has a technical meaning, namely, it is the portion of the physical universe chosen for analysis. Everything outside the system is known as the environment, which in analysis is ignored except for its effects on the system. The cut between system and the world is a free...
- conceptual systemConceptual systemA conceptual system is a system that is composed of non-physical objects, i.e. ideas or concepts. In this context a system is taken to mean "an interrelated, interworking set of objects".- Overview :...
- Complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
- Formal systemFormal systemIn formal logic, a formal system consists of a formal language and a set of inference rules, used to derive an expression from one or more other premises that are antecedently supposed or derived . The axioms and rules may be called a deductive apparatus...
- Information systemInformation systemAn information system - or application landscape - is any combination of information technology and people's activities that support operations, management, and decision making. In a very broad sense, the term information system is frequently used to refer to the interaction between people,...
- Meta-system
- Solar SystemSolar SystemThe Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
- Systems in human anatomyHuman anatomyHuman anatomy is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye...
- MarketMarketA market is one of many varieties of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations and infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services in exchange for money from buyers...
Theories about systems
- Chaos theoryChaos theoryChaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
- CyberneticsCyberneticsCybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
- Systems ecologySystems ecologySystems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
- Systems engineeringSystems engineeringSystems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
- Systems psychologySystems psychologySystems psychology is a branch of applied psychology that studies human behaviour and experience in complex systems. It is inspired by systems theory and systems thinking, and based on the theoretical work of Roger Barker, Gregory Bateson, Humberto Maturana and others. It is an approach in...
- Systems theorySystems theorySystems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
- Thermodynamic systemThermodynamic systemA thermodynamic system is a precisely defined macroscopic region of the universe, often called a physical system, that is studied using the principles of thermodynamics....
s - Control theoryControl theoryControl theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
Related topics
- Glossary of systems theoryGlossary of systems theory-A:* Adaptive capacity: An important part of the resilience of systems in the face of a perturbation, helping to minimise loss of function in individual human, and collective social and biological systems....
- Complexity theory and organizationsComplexity theory and organizationsComplexity theory and organizations, also called complexity strategy or complex adaptive organization, is the use of Complexity theory in the field of strategic management and organizational studies.- Overview :...
- Black boxBlack boxA black box is a device, object, or system whose inner workings are unknown; only the input, transfer, and output are known characteristics.The term black box can also refer to:-In science and technology:*Black box theory, a philosophical theory...
- System of systemsSystem of systemsSystem of systems is a collection of task-oriented or dedicated systems that pool their resources and capabilities together to create a new, more complex system which offers more functionality and performance than simply the sum of the constituent systems...
(engineeringSystem of systems engineeringSystem-of-Systems Engineering is a set of developing processes, tools, and methods for designing, re-designing and deploying solutions to System-of-Systems challenges.- Overview :...
) - Systems artSystems artSystems art is art influenced by cybernetics, and systems theory, which reflects on natural systems, social systems and social signs of the art world itself....
Further reading
- Alexander Backlund (2000). "The definition of system". In: Kybernetes Vol. 29 nr. 4, pp. 444–451.
- Kenneth D. BaileyKenneth D. BaileyMajor Kenneth Dillon Bailey was a United States Marine Corps officer who posthumously received the Medal of Honor for heroic conduct during action during the Battle of Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands...
(1994). Sociology and the New Systems Theory: Toward a Theoretical Synthesis. New York: State of New York Press. - Bela H. BanathyBéla H. BánáthyBéla Heinrich Bánáthy was a Hungarian linguist, systems scientist and a professor at San Jose State University and UC Berkeley. Bánáthy was the founder of the White Stag Leadership Development Program whose leadership model was adopted across the United States...
(1997). "A Taste of Systemics", ISSS The Primer Project. - Walter F. BuckleyWalter F. BuckleyWalter Frederick Buckley was an American professor of sociology. He was among the first to apply concepts from general systems theory , based on the work of Bertalanffy, to sociology. The sociologist was not specifically aligned to either the cybernetics or the general systems movements.-...
(1967). Sociology and Modern Systems Theory, New Jersey: Englewood Cliffs. - Peter ChecklandPeter ChecklandPeter Checkland is a British management scientist and emeritus professor of Systems at Lancaster University. He is the developer of soft systems methodology : a methodology based on a way of systems thinking.- Biography :...
(1997). Systems Thinking, Systems Practice. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. - Robert L. FloodRobert L. FloodRobert Louis Flood , British organizational scientist, and Professor of Management Sciences at the University of Hull, UK. He is a recognized authority on applied systemic thinking in the areas of strategic management, organizational behavior and organizational improvement.- Biography :Flood...
(1999). Rethinking the Fifth Discipline: Learning within the unknowable. London: Routledge. - George J. Klir (1969). Approach to General Systems Theory, 1969.
- Brian Wilson (1980). Systems: Concepts, methodologies and Applications, John Wiley
- Brian Wilson (2001). Soft Systems Methodology—Conceptual model building and its contribution, J.H.Wiley.
- Beynon-Davies P. (2009). Business Information + Systems. Palgrave, Basingstoke. ISBN 978-0-230-20368-6
External links
- Definitions of Systems and Models by Michael Pidwirny, 1999-2007.
- Definitionen von "System" (1572-2002) by Roland Müller, 2001-2007 (most in German).
- Theory and Practical Exercises of System Dynamics by Juan Martin (also in Spanish)

