
United States tropical cyclone rainfall climatology
Encyclopedia

Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
, primarily in the form of rain
Rain
Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
, which occurs during tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s and their extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
remnants across the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. Typically, five tropical cyclones and their remnants impact the country each year, contributing between a tenth and a quarter of the annual rainfall across the southern tier of the country. The highest rainfall amounts appear close to the coast, with lesser amounts falling farther inland. Obstructions to the precipitation pattern, such as the Appalachian mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
, focus higher amounts from northern Georgia through New England. While most impacts occur with systems moving in from the Atlantic ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
or Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
, some emanate from the eastern Pacific ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
, with a few crossing Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
before impacting the Southwest. Those making landfall within the Southeast portion of the country tend to have the greatest potential for heavy rains.
Long term averages
On average, five Atlantic tropical cyclones or their remnants lead to rainfall across the contiguous United States each year, contributing between a tenth and a quarter of the annual rainfall to the southern United States. While many of these storms form in the Atlantic Basin, some systems or their remnants move through Mexico from the Eastern Pacific Basin. Tropical cyclones from the eastern Pacific bring nearly 20 percent of the average annual rainfall to southern California. The average storm total rainfall for a tropical cyclone impacting the lower 48 from the Atlantic Basin is about 16 inches/406 mm, with 70-75 percent of the storm total falling within a 24 hour period.Highest known amounts for the lower 48 since 1962
Below is a list of the top ten highest known storm total rainfall amounts from individual tropical cyclones across the lower 48 since 1962. Four of the wettest systems struck TexasTexas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
, two strongly impacted Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
, while one each made their biggest mark on Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
, Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
, Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
, and Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
.
- 1219 mm/48.00 inches Amelia 1978Tropical Storm Amelia (1978)Tropical Storm Amelia was a weak, poorly-organized tropical storm that caused a severe flooding disaster in Texas during the 1978 Atlantic hurricane season. Amelia developed from a tropical wave on July 30 that entered an area of the Gulf of Mexico that was conductive for tropical cyclogenesis...
- 1143 mm/45.00 inches Claudette 1979Tropical Storm Claudette (1979)Tropical Storm Claudette was a long living tropical storm that produced heavy rain across Puerto Rico and Texas in late July 1979. The storm killed 2 people and left $1.1 billion in damage...
- 1033 mm/40.68 inches Allison 2001
- 977 mm / 38.46 inches Georges 1998Hurricane GeorgesHurricane Georges was a very destructive, powerful and long-lived Cape Verde-type Category 4 hurricane. Georges was the seventh tropical storm, fourth hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 1998 Atlantic hurricane season...
- 932 mm / 36.71 inches Danny 1997Hurricane Danny (1997)Hurricane Danny was the only hurricane to make landfall in the United States during the 1997 Atlantic hurricane season, and the second hurricane and fourth tropical storm of the season...
- 707 mm / 27.85 inches Alberto 1994Tropical Storm Alberto (1994)Tropical Storm Alberto was the first storm of the 1994 Atlantic hurricane season. It hit Florida across the Southeast United States in July, causing a massive flooding disaster while stalling over Georgia and Alabama. Alberto caused $1 billion in damage and 30 deaths.-Meteorological history:A...
- 695 mm / 27.38 inches Beulah 1967Hurricane BeulahHurricane Beulah was the second tropical storm, second hurricane, and only major hurricane during the 1967 Atlantic hurricane season. It tracked through the Caribbean, struck the Yucatán peninsula of Mexico as a major hurricane, and moved west-northwest into the Gulf of Mexico, briefly gaining...
- 686 mm / 27.00 inches Camille 1969Hurricane CamilleHurricane Camille was the third and strongest tropical cyclone and second hurricane during the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season. The second of three catastrophic Category 5 hurricanes to make landfall in the United States during the 20th century , which it did near the mouth of the Mississippi River...
- 652 mm / 25.67 inches Allison 1989Tropical Storm Allison (1989)Tropical Storm Allison was a tropical cyclone that produced severe flooding in the southern United States. The second tropical cyclone and the first named storm of the 1989 Atlantic hurricane season, Allison formed on June 24 in the northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Development of Allison was a result...
- 649 mm / 25.56 inches Dennis 1981Hurricane Dennis (1981)Hurricane Dennis was the most damaging storm of the 1981 Atlantic hurricane season which took twelve and a half days to reach hurricane status. The tropical wave that later would become Dennis moved off the African coastline on August 5. By August 7 a tropical depression developed, which quickly...
Maximum per state for the Lower 48
State maxima relating to tropical cyclones and their remnants are shown on the left, color coded by amount. Tropical cyclones from the Atlantic Basin have the most sway along the Gulf coast and Eastern SeaboardEast Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, refers to the easternmost coastal states in the United States, which touch the Atlantic Ocean and stretch up to Canada. The term includes the U.S...
. The impact of tropical cyclones and their remnants originally from the eastern Pacific stretches as far east as Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
and Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
. Rainfall related to the low pressure area once associated with a tropical cyclone, or its remnants aloft, are included in this sample. No additional rainfall from pre-existing upper lows as seen before cyclones such as Hurricane Fran
Hurricane Fran
Hurricane Fran was a powerful Cape Verde-type hurricane of the 1996 Atlantic hurricane season that made landfall near Cape Fear in North Carolina at Category 3 strength. Throughout the eastern United States, early statistics on Fran reported 27 deaths and $3.2 billion in damage...
of 1996 or from upper cyclones that closed off behind former tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s such as Hurricane Juan
Hurricane Juan
Hurricane Juan was a significant hurricane that struck the southern part of Atlantic Canada in late September 2003. It was the tenth named storm and the sixth hurricane of the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season. Juan formed southeast of Bermuda on September 24, 2003 out of a tropical wave that tracked...
of 1985 was included.
The state of Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
has the highest amounts, followed by Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
, and Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
. This is because over the 31 year sample, the storms that have become quasi-stationary like 2001's Tropical Storm Allison
Tropical Storm Allison
Tropical Storm Allison was a tropical storm that devastated southeast Texas in June of the 2001 Atlantic hurricane season. The first storm of the season, Allison lasted an unusually long period of time for a June storm, remaining tropical or subtropical for 15 days...
, 1978's Tropical Storm Amelia (1978)
Tropical Storm Amelia (1978)
Tropical Storm Amelia was a weak, poorly-organized tropical storm that caused a severe flooding disaster in Texas during the 1978 Atlantic hurricane season. Amelia developed from a tropical wave on July 30 that entered an area of the Gulf of Mexico that was conductive for tropical cyclogenesis...
, and Hurricane Danny (1997)
Hurricane Danny (1997)
Hurricane Danny was the only hurricane to make landfall in the United States during the 1997 Atlantic hurricane season, and the second hurricane and fourth tropical storm of the season...
are dominating the statistics. Out West, the same can be said for Hurricane Kathleen (1976)
Hurricane Kathleen (1976)
Hurricane Kathleen was a hurricane of the 1976 Pacific hurricane season that caused destructive impacts in California. Kathleen caused widespread flooding and damage in northern Mexico and parts of the southwestern United States. It also took an unusual path. On September 7, a tropical depression...
and the remains of Hurricane Olivia of the 1982 Pacific hurricane season
1982 Pacific hurricane season
The 1982 Pacific hurricane season officially started May 15, 1982 in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1982 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1982. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.The...
. Some records across the Midwest occurred during Tropical Storm Candy of 1968.
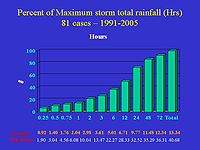
Average and record statistics per time frame for the lower 48
To the right is a graphic showing averages and extremes for a 15 year sample of tropical cyclones and their remnants affecting the contiguous United States. The units of the rainfall amounts are in inches, while the time units are in hours. The bars in the graph express the percent of the storm total rainfall, which is defined to be 100 percent in the final column. Note that, on average, as much as one-fourth of the total occurs in 2–3 hours, while half falls within 12 hours, and almost three-quarters of the storm total falls within a 24 hour period. Cases where a cyclone scraped the coast were not separated out from those that made a more direct landfall. Also, Pacific and Atlantic cases were not separated. This all explains the average storm total of the sample being depressed to 338.8 mm/13.34". On the bottom of the graphic are listed the averages per time frame and the records. The records were mainly set during Tropical Storm Allison (2001) and Hurricane Danny (1997)Hurricane Danny (1997)
Hurricane Danny was the only hurricane to make landfall in the United States during the 1997 Atlantic hurricane season, and the second hurricane and fourth tropical storm of the season...
. This graphic will be updated as the climatology pushes farther back in time.
Kraft rule
During the late 1950s, this rule of thumbRule of thumb
A rule of thumb is a principle with broad application that is not intended to be strictly accurate or reliable for every situation. It is an easily learned and easily applied procedure for approximately calculating or recalling some value, or for making some determination...
came into being, developed by R. H. Kraft. It was noted from rainfall amounts (in imperial units) reported by the first order rainfall network in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
that the storm total rainfall fit a simple equation: 100 divided by the speed of motion in knots. This rule works as long as a tropical cyclone is moving and only the first order or synoptic station network (with observations spaced about 60 miles/100 km apart) are used to derive storm totals. Canada uses a modified version of the Kraft rule which divides the results by a factor of two, which takes into account the lower sea surface temperatures seen around Atlantic Canada and the prevalence of systems undergoing vertical wind shear at their northerly latitudes. The main problem with this rule is that the rainfall observing network is denser than either the synoptic reporting network or the first order station networks, which means the absolute maximum is likely to be underestimated. Another problem is that it does not take the size of the tropical cyclone or topography into account.
Eight inch or 203 mm rule
Rusty Pfost, now the head of the Miami National Weather ServiceNational Weather Service
The National Weather Service , once known as the Weather Bureau, is one of the six scientific agencies that make up the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the United States government...
Forecast Office, did a study in 1999 reviewing rainfall totals from tropical systems affecting Florida between 1960 and 1998. He found that for tropical cyclones moving at greater than 6 knots, the average storm total was normally in the 5–10 inch (127–254 mm) range. Slower moving storms usually forced greater than 15 inches (381 mm) of rain to fall.
Sixteen inch or 406 mm rule

David M. Roth
David M. Roth is an American meteorologist who has done studies focusing on hydrometeorology, hurricanes, and subtropical cyclones. He graduated Florida State University with a Bachelors of Science degree in Meteorology in 1994...
, a forecaster at the Hydrometeorological Prediction Center
Hydrometeorological Prediction Center
The Hydrometeorological Prediction Center is one of nine service centers under the umbrella of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction , a part of the National Weather Service, which in turn is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the U.S. government...
, determined that the average amount for all tropical cyclones impacting the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
was 13.34 inches (339 mm) between 1991 and 2005. When removing the storms that grazed the domain, an average of near 16 inches/406 mm was obtained. Using this latter amount appears to work best for systems that experience little vertical wind shear
Wind shear
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as windshear or wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere...
and are of at least average size. Amounts measured in small/midget tropical cyclones showed storm total amounts closer to 6 inches/152 mm. Operationally, variations to these amounts are introduced if the cyclone encounters mountain zones, interacts with a nearby front, or the storm is significantly sheared.
See also
- List of wettest tropical cyclones in the United States
- Tropical cycloneTropical cycloneA tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
- Tropical cyclone rainfall climatologyTropical cyclone rainfall climatologyA tropical cyclone rainfall climatology is developed to determine rainfall characteristics of past tropical cyclones. A tropical cyclone rainfall climatology can be used to help forecast current or upcoming tropical cyclone impacts. The degree of a tropical cyclone rainfall impact depends upon...
- Tropical cyclone rainfall forecastingTropical cyclone rainfall forecastingTropical cyclone rainfall forecasting involves using scientific models and other tools to predict the precipitation expected in tropical cyclones such as hurricanes and typhoons. Knowledge of tropical cyclone rainfall climatology is helpful in the determination of a tropical cyclone rainfall...

