
Tsushima Strait
Encyclopedia
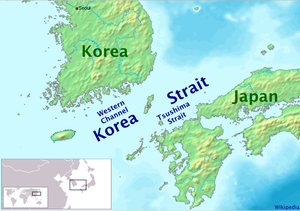
Korea Strait
The Korea Strait is a sea passage between South Korea and Japan, connecting the East China Sea and the Sea of Japan in the northwest Pacific Ocean...
, which lies between Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, connecting the Sea of Japan
Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific...
and the East China Sea
East China Sea
The East China Sea is a marginal sea east of China. It is a part of the Pacific Ocean and covers an area of 1,249,000 km² or 750,000 square miles.-Geography:...
.
The Tsushima Strait is the broader eastern channel to the east and southeast of Tsushima Island
Tsushima Island
Tsushima Island is an island of the Japanese Archipelago situated in the middle of the Tsushima Strait at 34°25'N and 129°20'E. The main island of Tsushima was once a single island, but the island was divided into two in 1671 by the Ōfunakosiseto canal and into three in 1900 by the Manzekiseto canal...
, with the Japanese islands of Honshū
Honshu
is the largest island of Japan. The nation's main island, it is south of Hokkaido across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyushu across the Kanmon Strait...
to the east and northeast, and Kyūshū
Kyushu
is the third largest island of Japan and most southwesterly of its four main islands. Its alternate ancient names include , , and . The historical regional name is referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands....
and the Gotō Islands
Goto Islands
The are Japanese islands in the East China Sea, off the western coast of Kyūshū. The islands are a part of Nagasaki Prefecture.- Geography :There are 140 islands in total, including five main islands:,,,, and....
to the south and southeast. It is narrowest south-east of Shimono-shima
Shimono-shima
or is the southern end of Tsushima Island, which lies in the Korea / Tsushima Straits between the East China Sea to the south and the Sea of Japan to the north, and Korea to the west and mainland Japan to the east....
, the south end of Tsushima Island proper, constricted there by nearby Iki Island
Iki Island
Iki Island is an island lying between the island of Kyūshū and the Tsushima islands in the Tsushima Strait, the eastern channel of the Korea Strait. It is currently part of Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan. The city of Iki is the centre of the local government. The island has three ports.The island’s...
, which lies wholly in the strait near the tip of Honshū. South of that point Japan's Inland Sea mingles its waters through the narrow Kanmon Strait between Honshū
Honshu
is the largest island of Japan. The nation's main island, it is south of Hokkaido across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyushu across the Kanmon Strait...
and Kyūshū
Kyushu
is the third largest island of Japan and most southwesterly of its four main islands. Its alternate ancient names include , , and . The historical regional name is referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands....
, with the those of the Tsushima Strait, making for some of the busiest sea lanes in the world.
Geography
The strait measures approximately 100 kilometres along Tsushima Island and is about 65 kilometres wide at its narrowest. The strait has a depth of about 90 metres and is bounded by the Tsushima Islands to the west through north (of Gotō Islands). Nearby Iki IslandIki Island
Iki Island is an island lying between the island of Kyūshū and the Tsushima islands in the Tsushima Strait, the eastern channel of the Korea Strait. It is currently part of Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan. The city of Iki is the centre of the local government. The island has three ports.The island’s...
lies in the strait about 50 kilometres towards Kyūshū from the southern tip of Kamino-shima (South Island).
The Tsushima Current, a warm branch of the Kuroshio
Kuroshio Current
The Kuroshio is a north-flowing ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean. It is similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic and is part of the North Pacific ocean gyre...
(Japan Current) passes through the strait. Originating along the Japanese islands, this current passes through the Sea of Japan
Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific...
then a branch eventually flowing into the Pacific
Northern Pacific Ocean via the Tsugaru Strait
Tsugaru Strait
is a channel between Honshu and Hokkaido in northern Japan connecting the Sea of Japan with the Pacific Ocean. It was named after the western part of Aomori Prefecture...
south of Hokkaidō
Hokkaido
, formerly known as Ezo, Yezo, Yeso, or Yesso, is Japan's second largest island; it is also the largest and northernmost of Japan's 47 prefectural-level subdivisions. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaido from Honshu, although the two islands are connected by the underwater railway Seikan Tunnel...
. Another branch continues far northward and divides along either shore of Sakhalin Island
Sakhalin
Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast...
; eventually flowing into the Sea of Okhotsk
Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and...
via the La Perouse Strait
La Perouse Strait
La Pérouse Strait is a strait dividing the southern part of the Russian island of Sakhalin from the northern part of the Japanese island of Hokkaidō, and connecting the Sea of Japan on the west with the Sea of Okhotsk on the east....
north of Hokkaidō
Hokkaido
, formerly known as Ezo, Yezo, Yeso, or Yesso, is Japan's second largest island; it is also the largest and northernmost of Japan's 47 prefectural-level subdivisions. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaido from Honshu, although the two islands are connected by the underwater railway Seikan Tunnel...
and via the Strait of Tartary
Strait of Tartary
Strait of Tartary is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia , connecting the Sea of Okhotsk on the north with...
into the Sea of Okhotsk
Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and...
north of Sakhalin Island
Sakhalin
Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast...
near Vladivostok
Vladivostok
The city is located in the southern extremity of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, which is about 30 km long and approximately 12 km wide.The highest point is Mount Kholodilnik, the height of which is 257 m...
.
The Tsushima Current brings rich fisheries resources from the East China Sea into the Sea of Japan, like Japanese amberjack
Japanese amberjack
The Japanese amberjack or yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata, is a fish in the family Carangidae. It is native to the northwest Pacific, from Japan to Hawaii....
, Japanese horse mackerel, but these days also brings disaster like mass aggregation of gigantic Nomura's jellyfish
Nomura's jellyfish
is a very large jellyfish, in the same size class as the lion's mane jellyfish, the largest cnidarian in the world. The diameter of one fully grown is slightly greater than the height of an average fully grown man. The species was named in tribute to Mr...
and waste
Waste
Waste is unwanted or useless materials. In biology, waste is any of the many unwanted substances or toxins that are expelled from living organisms, metabolic waste; such as urea, sweat or feces. Litter is waste which has been disposed of improperly...
from countries along the course of the current.
A commercial ferry service operates between Shimonoseki at the western tip of Honshū and Busan (aka Pusan), South Korea. Another operates between Shimonoseki and Tsushima Island
Tsushima Island
Tsushima Island is an island of the Japanese Archipelago situated in the middle of the Tsushima Strait at 34°25'N and 129°20'E. The main island of Tsushima was once a single island, but the island was divided into two in 1671 by the Ōfunakosiseto canal and into three in 1900 by the Manzekiseto canal...
. The Cities of Kitakyushu (Kyūshū) and Shimonoseki (Honshū) are joined by an ocean-spanning bridge across the Kanmon Strait joining those cities with Nagasaki, which latter city serves as prefecture-level capital and administers both Tsushima and Iki Island. Kanmon Strait lies approximately 85 miles (135 km) due east of the center of Tsushima Island
Tsushima Island
Tsushima Island is an island of the Japanese Archipelago situated in the middle of the Tsushima Strait at 34°25'N and 129°20'E. The main island of Tsushima was once a single island, but the island was divided into two in 1671 by the Ōfunakosiseto canal and into three in 1900 by the Manzekiseto canal...
, while Nagasaki city proper lies about 100 miles (165 km) to the south-south-east of the southern tip of the island.
Historical impact
The earliest settlement of Japan by people most resembling modern Japanese in litoral northern Kyūshū next to the Tsushima Strait is supported by legendary, historical, and archeological evidence, and is undisputed. Exactly who and when is a matter of intense debate and national pride, for Japanese, Koreans, and Chinese alike. Historians have suggested a range of dates when immigration began from what is modern day Korea to north Kyūshū from the fall of Four Commanderies of HanFour Commanderies of Han
The Four Commanderies of Han are Lelang, Lintun, Xuantu and Zhenfan commanderies in northern Korean Peninsula and part of the Liaodong Peninsula. set up by Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty in early 2nd century BC after his conquest of Wiman Joseon...
(108 BC) to the 4th Century AD. Historically these narrows (i.e., the whole Korea/Tsushima Strait) served as a highway for high-risk voyages (Korea to the Tsushima Islands to Iki Island to the western tip of Honshū
Honshu
is the largest island of Japan. The nation's main island, it is south of Hokkaido across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyushu across the Kanmon Strait...
) for cultural exchange between Japan and Korea.
The straits also served as a migration or an invasion path, in both directions. For example, archeologists believe the first Mesolithic
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
migrations (Jōmon) traveled across to Honshū around the 10th century BC, supplanting Paleolithic
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic Age, Era or Period, is a prehistoric period of human history distinguished by the development of the most primitive stone tools discovered , and covers roughly 99% of human technological prehistory...
people that walked from Asia to Japan overland over 100,000 years ago when the sea level was lower during the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. Immigrants from Goguryeo
Goguryeo
Goguryeo or Koguryŏ was an ancient Korean kingdom located in present day northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula, southern Manchuria, and southern Russian Maritime province....
, Gaya Confederacy
Gaya confederacy
Gaya was a confederacy of territorial polities in the Nakdong River basin of southern Korea, growing out of the Byeonhan confederacy of the Samhan period.The traditional period used by historians for Gaya chronology is 42–532 CE...
, and Baekje
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche was a kingdom located in southwest Korea. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla....
also contributed to waves of immigrants arriving in Kyūshū, although who, when, and how many exactly is a matter of intense debate. Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, along with Chinese writing, was initially transmitted from Baekje
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche was a kingdom located in southwest Korea. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla....
to Japan in the 5th century by way of the straits as well. Iki to Kamino-shima, the southern end of the large island of Tsushima, is about 50 kilometres. Busan
Busan
Busan , formerly spelled Pusan is South Korea's second largest metropolis after Seoul, with a population of around 3.6 million. The Metropolitan area population is 4,399,515 as of 2010. It is the largest port city in South Korea and the fifth largest port in the world...
(Korea), to the Northern tip of Tsushima, about the same across the Korea Strait. These were tremendous distances to attempt in small boats over open seas.
The Mongolian invasion of Japan crossed this sea and ravaged the Tsushima Islands before the kamikaze
Kamikaze
The were suicide attacks by military aviators from the Empire of Japan against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign of World War II, designed to destroy as many warships as possible....
(神風) – translated as "divine wind" – a typhoon that is said to have saved Japan from a Mongol invasion fleet led by Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan , born Kublai and also known by the temple name Shizu , was the fifth Great Khan of the Mongol Empire from 1260 to 1294 and the founder of the Yuan Dynasty in China...
in 1281. Military commander Toyotomi Hideyoshi
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
was a daimyo warrior, general and politician of the Sengoku period. He unified the political factions of Japan. He succeeded his former liege lord, Oda Nobunaga, and brought an end to the Sengoku period. The period of his rule is often called the Momoyama period, named after Hideyoshi's castle...
and loyal allies of Western Japan (but not the East) led an invasion of Korea by way of the straits in the late 16th century, and more recently, the Japanese Imperial Army had attacked Korea and beyond.
But the reason the strait is famous is that one of the most decisive naval battles of modern times, the Battle of Tsushima
Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima , commonly known as the “Sea of Japan Naval Battle” in Japan and the “Battle of Tsushima Strait”, was the major naval battle fought between Russia and Japan during the Russo-Japanese War...
, fought on May 27 and May 28, 1905 took place there due east of the north part of Tsushima
Tsushima Island
Tsushima Island is an island of the Japanese Archipelago situated in the middle of the Tsushima Strait at 34°25'N and 129°20'E. The main island of Tsushima was once a single island, but the island was divided into two in 1671 by the Ōfunakosiseto canal and into three in 1900 by the Manzekiseto canal...
and due north of Iki Island
Iki Island
Iki Island is an island lying between the island of Kyūshū and the Tsushima islands in the Tsushima Strait, the eastern channel of the Korea Strait. It is currently part of Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan. The city of Iki is the centre of the local government. The island has three ports.The island’s...
(shown in red on the second map) between the Japanese and Russian navies in 1905; the Russian fleet was virtually destroyed by the Japanese. This decisive result was to affect Naval planners and Fleet Admirals for the next forty years with a type of tunnel vision such that national and naval leaders were continually looking for the chance or to create that set of circumstances which would lead to a similar decisive major fleet engagement— while ignoring objective realities such as the new and eventually overwhelming ability of air power to devastate and neutralize the big gun ship. Even brilliant strategists such as Britain's Admiral Sir John Jellicoe
John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe
Admiral of the Fleet John Rushworth Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, GCB, OM, GCVO was a British Royal Navy admiral who commanded the Grand Fleet at the Battle of Jutland in World War I...
(Battle of Jutland
Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland was a naval battle between the British Royal Navy's Grand Fleet and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet during the First World War. The battle was fought on 31 May and 1 June 1916 in the North Sea near Jutland, Denmark. It was the largest naval battle and the only...
) and air power enthusiastists and supporters like Japan's Combined Fleet Commanding Fleet Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto
Isoroku Yamamoto
was a Japanese Naval Marshal General and the commander-in-chief of the Combined Fleet during World War II, a graduate of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy and a student of Harvard University ....
(Battle of Midway
Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway is widely regarded as the most important naval battle of the Pacific Campaign of World War II. Between 4 and 7 June 1942, approximately one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea and six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States Navy decisively defeated...
), or a tactician like American Vice-Admiral William 'Bull' Halsey
William Halsey, Jr.
Fleet Admiral William Frederick Halsey, Jr., United States Navy, , was a U.S. Naval officer. He commanded the South Pacific Area during the early stages of the Pacific War against Japan...
(Battle of Leyte Gulf
Battle of Leyte Gulf
The Battle of Leyte Gulf, also called the "Battles for Leyte Gulf", and formerly known as the "Second Battle of the Philippine Sea", is generally considered to be the largest naval battle of World War II and, by some criteria, possibly the largest naval battle in history.It was fought in waters...
) fell prey to the 'Big Fleet Battle Theory', consequently ignoring other tactical realities with an over focus on 'The Big Score'; an idealization which eluded all.
Japan's territorial waters extend to three nautical miles (5.6 km) into the strait instead of the usual twelve, reportedly to allow nuclear
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
-armed United States Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
warships and submarines to transit the strait without violating Japan's prohibition against nuclear weapons in its territory.
See also
- List of Korea-related topics
- List of Japan-related topics
- Geography of Korea
- Geography of JapanGeography of JapanJapan is an island nation in East Asia comprising a stratovolcanic archipelago extending along the Pacific coast of Asia. Measured from the geographic coordinate system, Japan stretches from 24° to 46° north latitude and from 123° to 146° east longitude...
- Busan Strait
- Russo-Japanese WarRusso-Japanese WarThe Russo-Japanese War was "the first great war of the 20th century." It grew out of rival imperial ambitions of the Russian Empire and Japanese Empire over Manchuria and Korea...
- Battle of TsushimaBattle of TsushimaThe Battle of Tsushima , commonly known as the “Sea of Japan Naval Battle” in Japan and the “Battle of Tsushima Strait”, was the major naval battle fought between Russia and Japan during the Russo-Japanese War...
- Tsushima CityTsushima, Nagasakiis a city governed by Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. It is the only city of Tsushima Subprefecture and it encompasses all of Tsushima Island Archipelago, which lies in the Tsushima Strait north of Nagasaki on the western side of Kyūshū, the southernmost mainland island of Japan. the city has an...
- Kanmon Strait
- Nagasaki PrefectureNagasaki Prefectureis a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyūshū. The capital is the city of Nagasaki.- History :Nagasaki Prefecture was created by merging of the western half of the former province of Hizen with the island provinces of Tsushima and Iki...

