
Timeline of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season
Encyclopedia
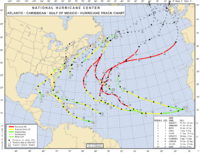
2006 Atlantic hurricane season
The 2006 Atlantic hurricane season was significantly less active than the record previous season. It marked the first since 2001 in which no hurricanes made landfall in the United States, and was the first since 1994 that no tropical cyclones formed during October. Following the intense activity of...
was the first since 2001
2001 Atlantic hurricane season
The 2001 Atlantic hurricane season was a fairly active Atlantic hurricane season that produced 17 tropical cyclones, 15 named storms, nine hurricanes, and four major hurricanes. The season officially lasted from June 1, 2001, to November 30, 2001, dates which by convention limit the period of each...
in which no hurricanes made landfall in the United States, and the first since 1994
1994 Atlantic hurricane season
The 1994 Atlantic hurricane seasonofficially began June 1, 1994, and officially ended November 30, 1994. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin....
that no tropical cyclones formed during October. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. The season officially began on June 1, 2006, and lasted until November 30. The timeline includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
, such as information about a storm that was not operationally warned on,To be warned on operationally means that storms were tracked at the time of their existence have been included.
The 2006 Atlantic hurricane season was significantly less active than the previous year
2005 Atlantic hurricane season
The 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season in recorded history, repeatedly shattering numerous records. The impact of the season was widespread and ruinous with an estimated 3,913 deaths and record damage of about $159.2 billion...
's Atlantic hurricane season
Atlantic hurricane season
The Atlantic hurricane season is the period in a year when hurricanes usually form in the Atlantic Ocean. Tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic are called hurricanes, tropical storms, or tropical depressions. In addition, there have been several storms over the years that have not been fully...
. Following the intense activity of 2005, forecasts predicted that the 2006 season would be only slightly less active. However, activity was slowed by a rapidly forming El Niño event in 2006, the presence of the Saharan Air Layer
Saharan Air Layer
The Saharan Air Layer is an intensely dry, warm and sometimes dust-laden layer of the atmosphere which often overlies the cooler, more-humid surface air of the Atlantic Ocean. In the Sahara Desert region of North Africa, where it originates, it is the prevalent atmosphere, extending from the...
over the tropical Atlantic, and the steady presence of a robust secondary high pressure area to the Azores high
Azores High
The Azores High is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure found near the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse latitudes...
centered around Bermuda. There were no tropical cyclones after October 2. The calendar year 2006 also saw Tropical Storm Zeta
Tropical Storm Zeta (2005)
Tropical Storm Zeta was a late-developing tropical storm over the central Atlantic which formed after the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season had officially ended , and continued into January 2006...
, which arose in December 2005 and persisted until early January, only the second event on record that a storm spanned two calendar years in the Atlantic. The storm can be considered a part of the 2005 and 2006 seasons, although it occurred outside the June 1 – November 30 windows during which most Atlantic basin
Atlantic Basin
The Atlantic Basin is the Atlantic Ocean.Atlantic Basin may also refer to:* Atlantic Basin Iron Works, an ironworks that operated in Brooklyn, New York, in the early to mid-20th century...
tropical cyclones form.
January
January 1- 0000 UTCCoordinated Universal TimeCoordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose...
– The year 2006 begins with Tropical Storm ZetaTropical Storm Zeta (2005)Tropical Storm Zeta was a late-developing tropical storm over the central Atlantic which formed after the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season had officially ended , and continued into January 2006...
still active from the previous season, making Zeta only the second cross-season North Atlantic tropical cyclone ever recorded.
January 6
- 2 a.m. ASTAtlantic Standard Time ZoneThe Atlantic Standard Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps time by subtracting four hours from either Coordinated Universal Time or Greenwich Mean Time , resulting in UTC-4 or GMT-4...
(0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Zeta weakens into a tropical depression. - 5 p.m. AST (2100 UTC) – Tropical Depression Zeta dissipates, finally ending the 2005 season2005 Atlantic hurricane seasonThe 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season in recorded history, repeatedly shattering numerous records. The impact of the season was widespread and ruinous with an estimated 3,913 deaths and record damage of about $159.2 billion...
.
June

- The 2006 Atlantic hurricane season officially begins.
June 10
- 1 a.m. CDTCentral Time zoneIn North America, the Central Time Zone refers to national time zones which observe standard time by subtracting six hours from UTC , and daylight saving, or summer time by subtracting five hours...
(0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression One forms 120 nautical miles (140 miles, 220 km) south of the western tip of CubaCubaThe Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
. - 7 p.m. CDT (0000 UTC June 11) – Tropical Depression One strengthens into Tropical Storm AlbertoTropical Storm Alberto (2006)Tropical Storm Alberto was the first tropical storm of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season. Forming on June 10 in the northwestern Caribbean, the storm moved generally to the north, reaching a maximum intensity of 70 mph before weakening and moving ashore in the Big Bend area of Florida on...
.
June 13
- 12:30 p.m. EDTNorth American Eastern Time ZoneThe Eastern Time Zone of the United States and Canada is a time zone that falls mostly along the east coast of North America. Its UTC time offset is −5 hrs during standard time and −4 hrs during daylight saving time...
(1630 UTC) – Tropical Storm Alberto makes landfall near Adams Beach, FloridaFloridaFlorida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, with 45 mph (70 km/h) winds.The figures for maximum sustained windMaximum sustained windThe maximum sustained winds associated with a tropical cyclone are a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, they are found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are...
s and position estimates are rounded to the nearest 5 units (knots, miles, or kilometers), following the convention used in the National Hurricane CenterNational Hurricane CenterThe National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
's operational products for each storm. All other units are rounded to the nearest digit. June 14 - 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Alberto weakens into a tropical depression.
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – The remnants of Alberto become extratropical.
July
July 17- 0600 UTC – A previously extratropical low pressure area becomes a tropical depression about 210 nautical miles (245 miles, 390 km) southeast of Nantucket, MassachusettsMassachusettsThe Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
. However, this depression is not assigned a number operationally, or warned on, by the National Hurricane CenterNational Hurricane CenterThe National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
. - 1200 UTC – The tropical depression near Nantucket strengthens into a tropical stormUnnamed Tropical Storm (2006)The 2006 Nova Scotia tropical storm was a short-lived tropical cyclone that was unnamed operationally during the season but was recognized during post-season analysis and designated AL022006...
, but is not operationally named.
July 18
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Two forms 250 nautical miles (290 miles, 645 km) east-southeast of Wilmington, North CarolinaWilmington, North CarolinaWilmington is a port city in and is the county seat of New Hanover County, North Carolina, United States. The population is 106,476 according to the 2010 Census, making it the eighth most populous city in the state of North Carolina...
. - 1200 UTC – The unnamed tropical storm degenerates into a remnant low.
- 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Two strengthens into Tropical Storm BerylTropical Storm Beryl (2006)Tropical Storm Beryl was the third tropical storm of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season. Developing from a tropical disturbance on July 18, it tracked generally northward, and strengthened to attain peak winds of 60 mph under generally favorable conditions. After turning to the northeast,...
.
July 21
- 2:45 a.m. EDT (0645 UTC) – Tropical Storm Beryl makes landfall on the island of Nantucket, MassachusettsMassachusettsThe Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
, with 50 mph (80.5 km/h) winds. - 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Tropical Storm Beryl becomes extratropical.
July 31
- 8 p.m. EDT (0000 UTC August 1) – Tropical Depression Three forms 205 nautical miles (235 miles, 380 km) east-southeast of BarbudaBarbudaBarbuda is an island in the Eastern Caribbean, and forms part of the state of Antigua and Barbuda. It has a population of about 1,500, most of whom live in the town of Codrington.-Location:...
.
August

- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Three strengthens into Tropical Storm ChrisTropical Storm Chris (2006)Tropical Storm Chris was the fourth tropical storm of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season. Forming on July 31 in the Atlantic Ocean east of the Leeward Islands from a tropical wave, Chris moved generally to the west-northwest, skirting the northern fringes of the Caribbean islands...
.
August 3
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Tropical Storm Chris weakens to a tropical depression.
August 4
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Chris weakens into a remnant lowLow pressure areaA low-pressure area, or "low", is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence which occur in upper levels of the troposphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as...
.
August 21
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Four forms 225 nautical miles (260 miles, 415 km) south-southeast of PraiaPraiaPraia , is the capital and largest city of Cape Verde, an island nation in the Atlantic Ocean west of Senegal. It lies on the southern coast of Santiago island in the Sotavento Islands group. It is the island's ferry port and is home to one of the nation’s four international airports...
, Cape VerdeCape VerdeThe Republic of Cape Verde is an island country, spanning an archipelago of 10 islands located in the central Atlantic Ocean, 570 kilometres off the coast of Western Africa...
.
August 22
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC August 23) – Tropical Depression Four strengthens into Tropical Storm DebbyTropical Storm Debby (2006)Tropical Storm Debby was the fifth tropical storm of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season. Debby formed just off the coast of Africa on August 21 from a tropical wave. After passing near the Cape Verde islands, Debby moved generally northwestward for much of its life, reaching a peak intensity of...
.
August 24
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Five forms in the Caribbean SeaCaribbean SeaThe Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located in the tropics of the Western hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles, and to the east by the Lesser Antilles....
about 40 nautical miles (45 miles, 75 km) north-northwest of GrenadaGrenadaGrenada is an island country and Commonwealth Realm consisting of the island of Grenada and six smaller islands at the southern end of the Grenadines in the southeastern Caribbean Sea...
.
August 25
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Five strengthens into Tropical Storm Ernesto.
August 26
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Debby weakens to a tropical depression.
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Debby weakens into a low.
August 27
- 2 a.m EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Ernesto strengthens into Hurricane ErnestoHurricane Ernesto (2006)Hurricane Ernesto was the costliest tropical cyclone of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season. The sixth tropical storm and first hurricane of the season, Ernesto developed from a tropical wave on August 24 in the eastern Caribbean Sea...
.

- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Hurricane Ernesto weakens to a tropical storm.
August 28
- 7:15 a.m. EDT (1115 UTC) – Tropical Storm Ernesto makes a first landfall in CubaCubaThe Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
at Playa Cazonal with 40 mph (65 km/h) winds.
August 29
- 11 p.m. EDT (0300 UTC) – Tropical Storm Ernesto makes a second landfall at Plantation KeyPlantation KeyPlantation Key is an island in Monroe County, Florida, United States. It is located in the upper Florida Keys on U.S. 1 , between Key Largo and Windley Key....
, FloridaFloridaFlorida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, with 45 mph (70 km/h) winds.
August 30
- 1 a.m. EDT (0500 UTC) – Tropical Storm Ernesto makes a third landfall in southwestern Miami-Dade County, FloridaMiami-Dade County, FloridaMiami-Dade County is a county located in the southeastern part of the state of Florida. As of 2010 U.S. Census, the county had a population of 2,496,435, making it the most populous county in Florida and the eighth-most populous county in the United States...
with 45 mph (70 km/h).
August 31
- 11:40 p.m. EDT (0340 UTC September 1) – Tropical Storm Ernesto makes a fourth landfall at Oak IslandOak Island, North CarolinaOak Island, North Carolina is a seaside town located mostly on the barrier island of Oak Island , in Brunswick County, North Carolina, United States. A small part of the town extends onto the mainland north of the island's bridge. The population was 6,571 at the 2000 census...
, North CarolinaNorth CarolinaNorth Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
, with 70 mph (112.7 km/h).
September
September 1- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Storm Ernesto weakens to a tropical depression.
- 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Ernesto becomes extratropical.
September 3
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Six forms 855 nautical miles (990 miles, 1585 km) west of the Cape Verde Islands.
September 5
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Six strengthens into Tropical Storm Florence.
September 10
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Florence strengthens into Hurricane FlorenceHurricane Florence (2006)Hurricane Florence was the first Atlantic hurricane to produce hurricane force winds on Bermuda since Hurricane Fabian hit the island in September 2003. The seventh tropical storm and second hurricane of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season, Florence developed from a tropical wave in the tropical...
. - 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Seven forms 470 nautical miles (545 miles, 870 km) east-northeast of the Leeward IslandsLeeward IslandsThe Leeward Islands are a group of islands in the West Indies. They are the northern islands of the Lesser Antilles chain. As a group they start east of Puerto Rico and reach southward to Dominica. They are situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean...
.
September 11
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Seven strengthens into Tropical Storm Gordon.
September 12
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Eight forms 200 nautical miles (230 miles, 370 km) south-southeast of the Cape Verde Islands.
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 13) – Hurricane Florence becomes extratropical.
- 8 p.m. EDT (0000 UTC September 13) – Tropical Storm Gordon strengthens into Hurricane GordonHurricane Gordon (2006)Hurricane Gordon was the first tropical cyclone since 1992 to affect the Azores while retaining tropical characteristics. The eighth tropical storm, third hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season, Gordon formed on September 10 in the tropical Atlantic Ocean...
.
September 13
- 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Hurricane Gordon reaches Category 2 intensity.
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 14) – Hurricane Gordon reaches Category 3 intensity, becoming the first major hurricane of the season.
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 14) – Tropical Depression Eight strengthens into Tropical Storm Helene.
September 16
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Storm Helene strengthens into Hurricane Helene.
September 17
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Hurricane Helene reaches Category 2 intensity.

- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 18) – Hurricane Helene reaches to Category 3 intensity, becoming the second major hurricane of the season.
September 20
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 21) – Hurricane Gordon becomes extratropical.
September 24
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Hurricane Helene becomes extratropical.
September 27
- 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Nine forms 810 nautical miles (940 miles, 1500 km) east-southeast of BermudaBermudaBermuda is a British overseas territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. Located off the east coast of the United States, its nearest landmass is Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, about to the west-northwest. It is about south of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, and northeast of Miami, Florida...
.
September 28
- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Nine strengthens into Tropical Storm Isaac.
September 30
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Storm Isaac strengthens into Hurricane Isaac.
October
October 2- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Hurricane Isaac weakens to a tropical storm.
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC October 3) – Tropical Storm Isaac becomes extratropical.
See also
- 2006 Atlantic hurricane season2006 Atlantic hurricane seasonThe 2006 Atlantic hurricane season was significantly less active than the record previous season. It marked the first since 2001 in which no hurricanes made landfall in the United States, and was the first since 1994 that no tropical cyclones formed during October. Following the intense activity of...
- List of Atlantic hurricane seasons
- Timeline of the 2006 Pacific hurricane seasonTimeline of the 2006 Pacific hurricane seasonThe 2006 Pacific hurricane season was the most active since the 2000 season, producing produced 21 tropical depressions; 19 of which became tropical storms or hurricanes...
- Timeline of the 2006 Pacific typhoon seasonTimeline of the 2006 Pacific typhoon seasonThe 2006 Pacific typhoon season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 2006, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December...

