
Slurry ice
Encyclopedia
Phase transition
A phase transition is the transformation of a thermodynamic system from one phase or state of matter to another.A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties....
refrigerant
Refrigerant
A refrigerant is a substance used in a heat cycle usually including, for enhanced efficiency, a reversible phase change from a liquid to a gas. Traditionally, fluorocarbons, especially chlorofluorocarbons, were used as refrigerants, but they are being phased out because of their ozone depletion...
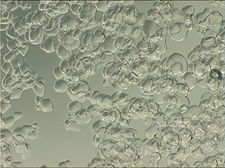
made up of millions of ice “micro-crystals” (typically 0.1 to 1 mm in diameter) formed and suspended within a solution of water and a freezing point depressant
Freezing-point depression
Freezing-point depression describes the phenomenon in which the freezing point of a liquid is depressed when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a lower freezing point than a pure solvent. This happens whenever a non-volatile solute is added to a pure solvent, such as water...
. Some compounds used in the field are salt (sodium chloride
Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms...
), ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol is an organic compound widely used as an automotive antifreeze and a precursor to polymers. In its pure form, it is an odorless, colorless, syrupy, sweet-tasting liquid...
, propylene glycol
Propylene glycol
Propylene glycol, also called 1,2-propanediol or propane-1,2-diol, is an organic compound with formula C3H8O2 or HO-CH2-CHOH-CH3...
, various alcohols (Isobutyl, ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
) and sugar (sucrose
Sucrose
Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. A white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste, it is best known for its role in human nutrition. The molecule is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose with the molecular formula...
, glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
). Slurry Ice has greater heat absorption compared with single phase refrigerants (Brine
Brine
Brine is water, saturated or nearly saturated with salt .Brine is used to preserve vegetables, fruit, fish, and meat, in a process known as brining . Brine is also commonly used to age Halloumi and Feta cheeses, or for pickling foodstuffs, as a means of preserving them...
) because the melting enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
(latent heat
Latent heat
Latent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a chemical substance or a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature. A typical example is a change of state of matter, meaning a phase transition such as the melting of ice or the boiling of water. The term was...
) of the ice is also used.
Characteristics
The small ice particle size results in greater heat transferHeat transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the exchange of thermal energy from one physical system to another. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as heat conduction, convection, thermal radiation, and phase-change transfer...
area than other types of ice for a given weight. It can be packed inside a container as dense as 700 kg/m3, the highest ice-packing factor among all usable industrial ice.
The spherical crystals have good flow properties, making them easy to distribute through conventional pumps and piping and over product in direct contact chilling applications, allowing them to flow into crevices and provide greater surface contact and faster cooling than other traditional forms of ice (flake, block, shell, etc.).
Its flow properties, high cooling capacity and flexibility in application make a slurry ice system a substitute for conventional ice generators and refrigeration
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is a process in which work is done to move heat from one location to another. This work is traditionally done by mechanical work, but can also be done by magnetism, laser or other means...
systems, and offers improvements in efficiency
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
: energy efficiency of 70%, compared to around 45% in standard systems, lower freon consumption per ton of ice and lower operating costs.
Application fields
Slurry ice is commonly used in a wide range of air conditioningAir conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
, packaging, and industrial cooling processes, supermarkets, and cooling and storage of fish, produce, poultry and other perishable products.

Heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact...
, pipes, valves), and reduce the amount of energy consumption
Energy consumption
Energy consumption is the consumption of energy or power. It is covered in the following articles and categories:* World energy consumption* Domestic energy consumption* Fuel efficiency in transportation* Electric energy consumption* Electricity generation...
used for pumping.
Advantages of slurry ice
Slurry ice is also used in direct contact cooling of products in food processing applications in water resistant shipping containerShipping container
A shipping container is a container with strength suitable to withstand shipment, storage, and handling. Shipping containers range from large reusable steel boxes used for intermodal shipments to the ubiquitous corrugated boxes...
s. It provides the following advantages:
- Product is cooled faster - the smooth round shape of the small crystals ensures maximum surface area contact with the product and as a result, faster heat transfer.
- Better product protection - the smooth, round crystals do not damage product, unlike other forms of sharp, jagged ice (flake, block, shell, etc.).
- Even cooling - unlike other irregular shaped ice which mostly conductsHeat conductionIn heat transfer, conduction is a mode of transfer of energy within and between bodies of matter, due to a temperature gradient. Conduction means collisional and diffusive transfer of kinetic energy of particles of ponderable matter . Conduction takes place in all forms of ponderable matter, viz....
heat through the air, the round shape of the slurry crystals enables them to flow freely around the entire product, filling all air pockets to uniformly maintain direct contact and the desired low temperature.
Slurry ice generators
Slurry ice is generated using a unique type of ice-making technology. Conventional ice generators produce sharp edged, dry ice fragments, not the small, spherical crystals found in slurry ice. In traditional brine chiller systems, crystals forming inside the solution would block or damage the system.Scraped surface generators
The world’s first patentPatent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
for a slurry ice generator was filed by Sunwell Technologies Inc. of Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
in 1976. Sunwell Technologies Inc. introduced slurry ice under the trade name deepchill ice, in the late 1970’s. Slurry ice is created through a process of forming spherical ice crystals within a liquid. The slurry ice generator is a scraped-surface vertical shell and tube heat exchanger
Shell and tube heat exchanger
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger designs. It is the most common type of heat exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes, and is suited for higher-pressure applications. As its name implies, this type of heat exchanger consists of a shell with a...
. It consists of concentric
Concentric
Concentric objects share the same center, axis or origin with one inside the other. Circles, tubes, cylindrical shafts, disks, and spheres may be concentric to one another...
tubes with refrigerant flowing between them and the water/freezing point depressant solution in the inner tube. The inner surface of the inner tube is wiped using a wiping mechanism which in the original Sunwell design consists of a central shaft, spring-loaded plastic blades, bearings
Bearing (mechanical)
A bearing is a device to allow constrained relative motion between two or more parts, typically rotation or linear movement. Bearings may be classified broadly according to the motions they allow and according to their principle of operation as well as by the directions of applied loads they can...
and seals
Seal (mechanical)
A mechanical seal is a device which helps join systems or mechanisms together by preventing leakage , containing pressure, or excluding contamination...
. The small ice crystals formed in the solution near the tube surface are wiped away from the surface and mixed with unfrozen water, forming the slurry.
Other Ice Slurry Generators adapted the first idea of the scraped surface wiping the surface by using an auger
Auger
An auger is a drilling device, or drill bit, that usually includes a rotating helical screw blade called a "flighting" to act as a screw conveyor to remove the drilled out material...
originally designed to create flake ice. Wipers can be also brushes or fluidized bed
Fluidized bed
A fluidized bed is formed when a quantity of a solid particulate substance is placed under appropriate conditions to cause the solid/fluid mixture to behave as a fluid. This is usually achieved by the introduction of pressurized fluid through the particulate medium...
heat exchanger for ice crystallization. In this heat exchangers steel particles circulate with the fluid mechanically removing the crystals from the surface. At the outlet steel particles and Slurry ice are separated.
Direct contact generators
An immiscible primary refrigerant evaporates to supersaturate the water and form small smooth crystals. With direct contact chilling, there is no physical boundary between the brine and the refrigerant, increasing the rate of heat transfer. However, the major disadvantage of this system is that a small amount of refrigerant stays in the brine, trapped in the crystals. This refrigerant is pumped with the slurry out of the generator and into the environment.Supercooling generators
Pure water is supercooledSupercooling
Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its freezing point without it becoming a solid....
in a chiller to -2°C and released through a nozzle into a storage tank. On release it undergoes a phase change forming small ice particles within 2.5% ice fraction. In the storage tank it is separated by the difference in density between ice and water. The cold water is supercooled and released again increasing the ice fraction in the storage tank.
However a small crystal in the supercooled water or a nucleation cell on the surface may act as a seed for ice crystals and block the generator.

