
Petroleum industry in Iran
Encyclopedia
In 2004 Iran
produced 5.1 percent of the world’s total crude oil (3.9 Moilbbl per day), which generated revenues of US$25 billion to US$30 billion and was the country’s primary source of foreign currency. At 2006 levels of production, oil proceeds represented about 18.7 percent of gross domestic product
(GDP). However, the importance of the hydrocarbon
sector to Iran’s economy
has been far greater. The oil and gas industry has been the engine of economic growth, directly affecting public development projects, the government’s annual budget, and most foreign exchange sources.
In FY 2009, for example, the sector accounted for 60 percent of total government revenues and 80 percent of the total annual value of both exports and foreign currency earnings. However, oil and gas revenues are affected by the value of crude oil on the international market. It has been estimated that at the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) quota level (December 2004), a one-dollar change in the price of crude oil on the international market would alter Iran’s oil revenues by US$1 billion. Iran plans to invest $500 billion in the oil sector until 2025. Officials in Iran estimate that Iran's annual oil and gas revenues could reach $250 billion by 2015.
speculator William D’Arcy
received a concession from Iran to explore and develop southern Iran’s oil resources. The discovery of oil in 1908 led to the formation in 1909 of the London-based Anglo-Persian Oil Company (APOC). By purchasing a majority of the company’s shares in 1914, the British government gained direct control of the Iranian oil industry, which it would not relinquish for 37 years. After 1935 the APOC was called the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company (AIOC). A 60-year agreement signed in 1933 established a flat payment to Iran of four British pounds for every ton of crude oil exported and denied Iran any right to control oil exports.
In 1950 ongoing popular demand prompted a vote in the Majlis
to nationalize the petroleum industry. A year later, the government of Prime Minister Mohammad Mossadeq formed the National Iranian Oil Company
(NIOC). A 1953 coup d’état led by British
and U.S. intelligence
agencies ousted the Mossadeq government and paved the way for a new oil agreement. In 1954 a new agreement divided profits equally between the NIOC and a multinational consortium that had replaced the AIOC. In 1973 Iran signed a new 20-year concession with the consortium.
Beginning in the late 1950s, many of Iran’s international oil agreements did not produce the expected outcomes; even those oil companies that managed to extract oil in their designated areas contributed very little to the country’s total oil production. By the time of the Islamic Revolution of 1978–79, the five largest international companies that had agreements with the NIOC accounted for only 10.4 percent of total oil production. During this period, Iran’s oil industry remained disconnected from other industries, particularly manufacturing. This separation promoted inefficiencies in the country’s overall industrial economy
.
export of oil were delegated to the Ministry of Petroleum. Initially Iran’s post-revolutionary oil policy was based on foreign currency requirements and the long-term preservation of the natural resource
. Following the Iran–Iraq War, however, this policy was replaced by a more aggressive approach: maximizing exports and accelerating economic growth
. From 1979 until 1998, Iran did not sign any oil agreements with foreign oil companies. Early in the first administration of President Mohammad Khatami
(in office 1997–2005), the government paid special attention to developing the country’s oil and gas industry. Oil was defined as inter-generational capital and an indispensable foundation of economic development. Thus, between 1997 and 2004 Iran invested more than US$40 billion in expanding the capacity of existing oil fields and discovering and exploring new fields and deposits. These projects were financed either in the form of joint investments with foreign companies
or domestic contractors or through direct investment by the NIOC. In accordance with the law, foreign investment in oil discovery was possible only in the form of buyback agreements under which the NIOC was required to reimburse expenses and retain complete ownership of an oil field. Marketing of crude oil to potential buyers was managed by the NIOC and by a government enterprise called Nicoo. Nicoo marketed Iranian oil to Africa, and the NIOC marketed to Asia and Europe.
producer and exporter of crude oil and the fourth-largest producer in the world. After a lengthy decline in the 1980s, production of crude oil began to increase steadily in 1987. In 2008 Iran produced 3.9 Moilbbl per day (bpd) and exported 2.4 Moilbbl/d. Accounting for 5 percent of world production, it returned to its previous position as OPEC’s second-largest producer. According to estimates, in 2005 Iran had the capacity to produce 4.5 Moilbbl/d; it was believed that production capacity could increase to 5 Moilbbl/d by 2010, but only with a substantial increase in foreign investment
. Iran’s long-term sustainable oil production rate is estimated at 3.8 Moilbbl/d.
In 2006 Iran reported crude oil reserves of 132.5 Goilbbl, accounting for about 15 percent of OPEC’s proven reserves and 11.4 percent of world proven reserves. While the estimate of world crude oil reserves remained nearly steady between 2001 and 2006, at 1154 Goilbbl, the estimate of Iran’s oil reserves
was revised upward by 32 percent when a new field was discovered near Bushehr
. Market value of Iran's total oil
reserves at international crude price
of $75 per barrel stands at ~US $10 trillion.
In the early 2000s, leading international oil firms from China
, France
, India
, Italy
, the Netherlands
, Norway
, Russia
, Spain
, and the United Kingdom
had agreements to develop Iran’s oil and gas fields
. In 2004 China signed a major agreement to buy oil and gas from Iran, as well as to develop Iran’s Yadavaran oil field
. The value of this contract was estimated at US$150 billion to US$200 billion over 25 years. In 2009, China National Petroleum Corp (CNPC) signed a deal with the National Iranian Oil Company whereby the former took ownership of
a 70% stake upon promising to pay 90 percent of the development costs for the South Azadegan oil field, with the project needing investment of up to $2.5 billion. Earlier that year, CNPC also won a $2 billion deal to develop the first phase of the North Azadegan oilfield.
A more modest yet important agreement was signed with India
to explore and produce oil and natural gas in southern Iran. In 2006 the rate of production decline was 8 percent for Iran’s existing onshore oil fields (furnishing the majority of oil output) and 10 percent for existing offshore fields. Little exploration, upgrading, or establishment of new fields occurred in 2005–6. However, the threat of American retaliation kept the investment way below the desired levels. It only allowed Iran to continue to keep its oil export at or below its OPEC determined quota level.
, kerosene
, fuel oil
, and lubricants.
Between 1981 and 2004, domestic consumption of oil products increased from 0.6 Moilbbl/d to 1.1 Moilbbl/d—an average annual growth rate of 2.6 percent. Most of this growth in consumption occurred between 1980 and 2001. Between 1981 and 2004, consumption of gasoline grew by 6 percent annually, but domestic production met only 75 percent of demand for this product. In 2004 the country imported US$1.6 billion worth of gasoline. By 2006 it imported 41 percent of its gasoline. Most imported gasoline is purchased at very high prices from the Middle East
and Venezuela
. Iran had invested between US$100 million and US$150 million to expand gasoline production to 42 million liters per day by 2007.
because of the U.S. trade embargo on Iran and the marketing strategy of the NIOC
. Initially, Iran’s post-revolutionary crude oil export policy was based on foreign currency requirements and the need for long-term preservation of the natural resource. In addition, the government expanded oil trade with other developing countries. While the shares of Europe, Japan, and the United States declined from an average of 87 percent of oil exports before the Revolution to 52 percent in the early 2000s, the share of exports to East Asia (excluding Japan) increased significantly. In addition to crude oil exports, Iran exports oil products. In 2006 it exported 282000 barrels (44,834.4 m³) of oil products, or about 21 percent of its total oil product output. Officials in Iran estimate that Iran's annual oil and gas revenues could reach $250 billion by 2015 once the current projects come on stream. Iran plans to invest $500 billion in the oil sector until 2025.
 In addition to the natural gas
In addition to the natural gas
associated with oil exploration and extraction, an estimated 62 percent of Iran’s 32.3 trillion cubic meters of proven natural gas reserves in 2006 were located in independent natural gas fields, an amount second only to those of Russia. In 2006 annual production reached 105 billion cubic meters, with fastest growth occurring over the previous 15 years. In 2006 natural gas accounted for abut 50 percent of domestic energy consumption
, in part because domestic gas prices were heavily subsidized. Natural gas production will reach 700 million cubic meter/day by 2012 and 900 million cubic meter/day by 2015.
Since 1979, infrastructure investment by Iranian and foreign oil firms has increased pipeline capacity to support the Iranian gas industry. Between 1979 and 2003, pipelines to transport natural gas to refineries and to domestic consumers increased from 2,000 kilometers to 12,000 kilometers. In the same period, natural gas distribution pipelines increased from 2,000 kilometers to 45,000 kilometers in response to growing domestic consumption. Gas processing plants are located at Ahvaz, Dalan, Kangan, and Marun, in a corridor along the northern Persian Gulf
close to the major gas fields. South Pars, Iran’s largest natural gas field, has received substantial foreign investment. With its output intended for both export and domestic consumption, South Pars is expected to reach full production in 2015. The output of South Pars is the basis of the Pars Special Economic Energy Zone, a complex of petrochemical and natural gas processing plants and port facilities established in 1998 on the Persian Gulf south of Kangan.
In the 1980s, Iran began to replace oil, coal, charcoal, and other fossil-fuel energy sources with natural gas, which is environmentally safer. The share of natural gas in household energy consumption, which averaged 54 percent in 2004, was projected to increase to 69 percent by 2009. Overall, natural gas consumption in Iran was expected to grow by more than 10 percent per annum between 2005 and 2009.
With international oil prices increasing and projected to continue increasing, international demand for natural gas and investment in production and transportation of natural gas to consumer markets both increased in the early 2000s. Iran set a goal of increasing its natural gas production capacity to 300 billion cubic meters by 2015 while keeping oil production stable. To achieve this capacity, the government has planned a joint investment worth US$100 billion in the oil and gas industry through 2015. In 2004 Iran signed a contract with France and Malaysia for production and export of natural gas and another agreement with European and Asian companies for expansion and marketing of its natural gas resources. In 2005 Iran exported natural gas to Turkey
and was expected to expand its market to Armenia, China, Japan, other East Asian countries, India, Pakistan, and Europe. The first section of a new line to Armenia opened in spring 2007, as a much-discussed major pipeline to India and Pakistan remained in the negotiation stage.
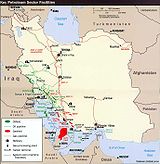 Among some more recent deals, Switzerland’s energy company EGL, signed a 25-year LNG export deal with Iran’s National Iranian Gas Export Company on March 17, 2007, reportedly valued at 18 billion. Switzerland
Among some more recent deals, Switzerland’s energy company EGL, signed a 25-year LNG export deal with Iran’s National Iranian Gas Export Company on March 17, 2007, reportedly valued at 18 billion. Switzerland
will buy 5.5 billion cubic meters of Iranian natural gas each year, beginning in 2011. In April 2007, OMV
, the Austria
n partially state-owned energy company, signed letters of intent with Iran, worth an estimated $22.8 billion (22 billion euros), for Iran
to supply Europe with gas. The United States has expressed strong opposition to both the Swiss and Austrian deals with Iran.
The National Iranian Gas Company
(NIGC) is expected to finalize a natural gas export deal with Pakistan
, with exports set to begin in 2011. The gas would be transported through a “Peace pipeline”, worth about $7.4 billion. The plan initially also included exporting gas to India
, but negotiations have stalled over pricing. Iran also is discussing a gas production and export deal with Turkey
. Under the plan, Turkey would assist in developing Iran’s South Pars field in exchange for cash or natural gas. Gas would be shipped from Iran to Turkey and Europe via a new pipeline
that Turkey plans to build.
Other notable petroleum sector development deals include those with Russia
and China
. On February 19, 2008, Russian state gas company Gazprom
announced a deal to establish a joint venture company to develop the offshore Iranian South Pars gas field. A China National Offshore Oil Corporation
(CNOOC) investment deal, valued at $16 billion, to develop Iran’s North Pars
gas field and to build a liquid natural gas (LNG) plant, was supposed to be signed on February 27, 2008 but has been delayed. The state-operated National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) and CNOOC signed a memorandum of understanding in December 2006 for the project, under which CNOOC would purchase 10 million metric tons per year of LNG for 25 years. In 2011, Iran signed a contract with Baghdad and Damascus in order to export Iran’s gas to Iraq
, Syria
, Lebanon
, the Mediterranean region and eventually Europe.
Market value of Iran's total natural gas
reserves at comparative international energy price of $75 per barrel of oil
stands at ~US $4 trillion.
and India
were the major trading partners in this industry. Iran’s domestic resource base gives it a unique comparative advantage in producing petrochemicals when international crude oil prices rise. The gain has been greatest in those plants that use liquid gas as their main input. For FY 2006, the petrochemical industry’s share of GDP was projected to be about 2 percent. Iran plans to invest $500 billion in the oil sector until 2025.
Iran’s petrochemical industries have absorbed a large amount of private and public investment. In the early 2000s, 43 percent of these investments was financed by Iran’s National Petrochemical Company
, a subsidiary of the Ministry of Petroleum
, which administers the entire petrochemical sector. Another 53 percent is owned by foreign creditors (more than 100 foreign banks and foreign companies), 3 percent by banks, and 1 percent by the capital market. Most of the petrochemical industry’s physical capital is imported, and the industry does not have strong backward linkages to manufacturing industries. In 2006 new petrochemical plants came online at Marun
and Asaluyeh, and construction began on three others.
Videos
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
produced 5.1 percent of the world’s total crude oil (3.9 Moilbbl per day), which generated revenues of US$25 billion to US$30 billion and was the country’s primary source of foreign currency. At 2006 levels of production, oil proceeds represented about 18.7 percent of gross domestic product
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
(GDP). However, the importance of the hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
sector to Iran’s economy
Economy of Iran
The economy of Iran is the eighteenth largest in the world by purchasing power parity and according to Iranian officials' claims is going to become the 12th largest by 2015. The economy of Iran is a mixed and transition economy with a large public sector and some 50% of the economy centrally planned...
has been far greater. The oil and gas industry has been the engine of economic growth, directly affecting public development projects, the government’s annual budget, and most foreign exchange sources.
In FY 2009, for example, the sector accounted for 60 percent of total government revenues and 80 percent of the total annual value of both exports and foreign currency earnings. However, oil and gas revenues are affected by the value of crude oil on the international market. It has been estimated that at the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) quota level (December 2004), a one-dollar change in the price of crude oil on the international market would alter Iran’s oil revenues by US$1 billion. Iran plans to invest $500 billion in the oil sector until 2025. Officials in Iran estimate that Iran's annual oil and gas revenues could reach $250 billion by 2015.
History
The era of international control, 1901–79
The history of Iran’s oil industry began in 1901, when BritishUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
speculator William D’Arcy
William Knox D'Arcy
William Knox D'Arcy was one of the principal founders of the oil and petrochemical industry in Persia .-Early life:...
received a concession from Iran to explore and develop southern Iran’s oil resources. The discovery of oil in 1908 led to the formation in 1909 of the London-based Anglo-Persian Oil Company (APOC). By purchasing a majority of the company’s shares in 1914, the British government gained direct control of the Iranian oil industry, which it would not relinquish for 37 years. After 1935 the APOC was called the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company (AIOC). A 60-year agreement signed in 1933 established a flat payment to Iran of four British pounds for every ton of crude oil exported and denied Iran any right to control oil exports.
In 1950 ongoing popular demand prompted a vote in the Majlis
Majlis of Iran
The National Consultative Assembly of Iran , also called The Iranian Parliament or People's House, is the national legislative body of Iran...
to nationalize the petroleum industry. A year later, the government of Prime Minister Mohammad Mossadeq formed the National Iranian Oil Company
National Iranian Oil Company
The National Iranian Oil Company , a government-owned corporation under the direction of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran, is an oil and natural gas producer and distributor headquartered in Tehran. It was established in 1948...
(NIOC). A 1953 coup d’état led by British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and U.S. intelligence
Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency is a civilian intelligence agency of the United States government. It is an executive agency and reports directly to the Director of National Intelligence, responsible for providing national security intelligence assessment to senior United States policymakers...
agencies ousted the Mossadeq government and paved the way for a new oil agreement. In 1954 a new agreement divided profits equally between the NIOC and a multinational consortium that had replaced the AIOC. In 1973 Iran signed a new 20-year concession with the consortium.
Beginning in the late 1950s, many of Iran’s international oil agreements did not produce the expected outcomes; even those oil companies that managed to extract oil in their designated areas contributed very little to the country’s total oil production. By the time of the Islamic Revolution of 1978–79, the five largest international companies that had agreements with the NIOC accounted for only 10.4 percent of total oil production. During this period, Iran’s oil industry remained disconnected from other industries, particularly manufacturing. This separation promoted inefficiencies in the country’s overall industrial economy
Industry of Iran
According to a report by the Economist, Iran has been ranked 39th for producing $23 billion of industrial products in 2008. From 2008 to 2009 Iran has leaped to 28th place from 69th place in annual industrial production growth rate. A recent report by the World Fact Book ranks Iran 3rd among...
.
The era of nationalized oil, 1979–
Following the Revolution, the NIOC took control of Iran’s petroleum industry and canceled Iran’s international oil agreements. In 1980 the exploration, production, sale, andexport of oil were delegated to the Ministry of Petroleum. Initially Iran’s post-revolutionary oil policy was based on foreign currency requirements and the long-term preservation of the natural resource
Environmental issues in Iran
Environmental issues in Iran include, especially in urban areas, vehicle emissions, refinery operations, and industrial effluents which contribute to poor air quality. Most cars use leaded gas and lack emissions control equipment. Tehran is rated as one of the world’s most polluted cities...
. Following the Iran–Iraq War, however, this policy was replaced by a more aggressive approach: maximizing exports and accelerating economic growth
Economic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
. From 1979 until 1998, Iran did not sign any oil agreements with foreign oil companies. Early in the first administration of President Mohammad Khatami
Mohammad Khatami
Sayyid Mohammad Khātamī is an Iranian scholar, philosopher, Shiite theologian and Reformist politician. He served as the fifth President of Iran from August 2, 1997 to August 3, 2005. He also served as Iran's Minister of Culture in both the 1980s and 1990s...
(in office 1997–2005), the government paid special attention to developing the country’s oil and gas industry. Oil was defined as inter-generational capital and an indispensable foundation of economic development. Thus, between 1997 and 2004 Iran invested more than US$40 billion in expanding the capacity of existing oil fields and discovering and exploring new fields and deposits. These projects were financed either in the form of joint investments with foreign companies
Foreign Direct Investment in Iran
Foreign direct investment in Iran has been hindered by unfavorable or complex operating requirements and by international sanctions, although in the early 2000s the Iranian government liberalized investment regulations. Iran ranks 62nd in the World Economic Forum's 2011 analysis of the global...
or domestic contractors or through direct investment by the NIOC. In accordance with the law, foreign investment in oil discovery was possible only in the form of buyback agreements under which the NIOC was required to reimburse expenses and retain complete ownership of an oil field. Marketing of crude oil to potential buyers was managed by the NIOC and by a government enterprise called Nicoo. Nicoo marketed Iranian oil to Africa, and the NIOC marketed to Asia and Europe.
Oil production and reserves
Total oil production reached a peak level of 6.6 Moilbbl/d in 1976. By 1978, Iran had become the second-largest OPECOPEC
OPEC is an intergovernmental organization of twelve developing countries made up of Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. OPEC has maintained its headquarters in Vienna since 1965, and hosts regular meetings...
producer and exporter of crude oil and the fourth-largest producer in the world. After a lengthy decline in the 1980s, production of crude oil began to increase steadily in 1987. In 2008 Iran produced 3.9 Moilbbl per day (bpd) and exported 2.4 Moilbbl/d. Accounting for 5 percent of world production, it returned to its previous position as OPEC’s second-largest producer. According to estimates, in 2005 Iran had the capacity to produce 4.5 Moilbbl/d; it was believed that production capacity could increase to 5 Moilbbl/d by 2010, but only with a substantial increase in foreign investment
Foreign Direct Investment in Iran
Foreign direct investment in Iran has been hindered by unfavorable or complex operating requirements and by international sanctions, although in the early 2000s the Iranian government liberalized investment regulations. Iran ranks 62nd in the World Economic Forum's 2011 analysis of the global...
. Iran’s long-term sustainable oil production rate is estimated at 3.8 Moilbbl/d.
In 2006 Iran reported crude oil reserves of 132.5 Goilbbl, accounting for about 15 percent of OPEC’s proven reserves and 11.4 percent of world proven reserves. While the estimate of world crude oil reserves remained nearly steady between 2001 and 2006, at 1154 Goilbbl, the estimate of Iran’s oil reserves
National Iranian Oil Company
The National Iranian Oil Company , a government-owned corporation under the direction of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran, is an oil and natural gas producer and distributor headquartered in Tehran. It was established in 1948...
was revised upward by 32 percent when a new field was discovered near Bushehr
Bushehr
Bushehr Bushehr lies in a vast plain running along the coastal region on the Persian Gulf coast of southwestern Iran. It is the chief seaport of the country and the administrative centre of its province. Its location is about south of Tehran. The local climate is hot and humid.The city...
. Market value of Iran's total oil
Oil
An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils....
reserves at international crude price
Price of petroleum
The price of petroleum as quoted in news generally refers to the spot price per barrel of either WTI/light crude as traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange for delivery at Cushing, Oklahoma, or of Brent as traded on the Intercontinental Exchange for delivery at Sullom Voe.The price...
of $75 per barrel stands at ~US $10 trillion.
In the early 2000s, leading international oil firms from China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
had agreements to develop Iran’s oil and gas fields
National Iranian Oil Company
The National Iranian Oil Company , a government-owned corporation under the direction of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran, is an oil and natural gas producer and distributor headquartered in Tehran. It was established in 1948...
. In 2004 China signed a major agreement to buy oil and gas from Iran, as well as to develop Iran’s Yadavaran oil field
Yadavaran Field
Yadavaran Field oil field is one of the NIOC Recent Discoveries which is located in Khuzestan, Iran.The name is new, as the field is made up of two former fields, Koushk and Hosseinieh...
. The value of this contract was estimated at US$150 billion to US$200 billion over 25 years. In 2009, China National Petroleum Corp (CNPC) signed a deal with the National Iranian Oil Company whereby the former took ownership of
a 70% stake upon promising to pay 90 percent of the development costs for the South Azadegan oil field, with the project needing investment of up to $2.5 billion. Earlier that year, CNPC also won a $2 billion deal to develop the first phase of the North Azadegan oilfield.
A more modest yet important agreement was signed with India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
to explore and produce oil and natural gas in southern Iran. In 2006 the rate of production decline was 8 percent for Iran’s existing onshore oil fields (furnishing the majority of oil output) and 10 percent for existing offshore fields. Little exploration, upgrading, or establishment of new fields occurred in 2005–6. However, the threat of American retaliation kept the investment way below the desired levels. It only allowed Iran to continue to keep its oil export at or below its OPEC determined quota level.
Oil refining and consumption
In 2006 Iran’s refineries had a combined capacity of 1.64 Moilbbl/d. The largest refineries have the following capacities: Abadan, 400000 oilbbl/d; Esfahan, 265000 oilbbl/d; Bandar-e Abbas, 232000 oilbbl/d; Tehran, 225000 oilbbl/d; Arak, 150000 oilbbl/d; and Tabriz, 112000 oilbbl/d. In 2004 pipelines conveyed 69 percent of total refined products; trucks, 20 percent; rail, 7 percent; and tankers, 4 percent. Oil refining produces a wide range of oil products, such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), gasolineGasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
, kerosene
Kerosene
Kerosene, sometimes spelled kerosine in scientific and industrial usage, also known as paraffin or paraffin oil in the United Kingdom, Hong Kong, Ireland and South Africa, is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid. The name is derived from Greek keros...
, fuel oil
Fuel oil
Fuel oil is a fraction obtained from petroleum distillation, either as a distillate or a residue. Broadly speaking, fuel oil is any liquid petroleum product that is burned in a furnace or boiler for the generation of heat or used in an engine for the generation of power, except oils having a flash...
, and lubricants.
Between 1981 and 2004, domestic consumption of oil products increased from 0.6 Moilbbl/d to 1.1 Moilbbl/d—an average annual growth rate of 2.6 percent. Most of this growth in consumption occurred between 1980 and 2001. Between 1981 and 2004, consumption of gasoline grew by 6 percent annually, but domestic production met only 75 percent of demand for this product. In 2004 the country imported US$1.6 billion worth of gasoline. By 2006 it imported 41 percent of its gasoline. Most imported gasoline is purchased at very high prices from the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
and Venezuela
Venezuela
Venezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
. Iran had invested between US$100 million and US$150 million to expand gasoline production to 42 million liters per day by 2007.
Trade in oil and oil products
In 2006 exports of crude oil totaled 2.5 Moilbbl/d, or about 62.5 percent of the country’s crude oil production. The direction of crude oil exports changed after the RevolutionIranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution refers to events involving the overthrow of Iran's monarchy under Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi and its replacement with an Islamic republic under Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, the leader of the...
because of the U.S. trade embargo on Iran and the marketing strategy of the NIOC
National Iranian Oil Company
The National Iranian Oil Company , a government-owned corporation under the direction of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran, is an oil and natural gas producer and distributor headquartered in Tehran. It was established in 1948...
. Initially, Iran’s post-revolutionary crude oil export policy was based on foreign currency requirements and the need for long-term preservation of the natural resource. In addition, the government expanded oil trade with other developing countries. While the shares of Europe, Japan, and the United States declined from an average of 87 percent of oil exports before the Revolution to 52 percent in the early 2000s, the share of exports to East Asia (excluding Japan) increased significantly. In addition to crude oil exports, Iran exports oil products. In 2006 it exported 282000 barrels (44,834.4 m³) of oil products, or about 21 percent of its total oil product output. Officials in Iran estimate that Iran's annual oil and gas revenues could reach $250 billion by 2015 once the current projects come on stream. Iran plans to invest $500 billion in the oil sector until 2025.
Natural gas

Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
associated with oil exploration and extraction, an estimated 62 percent of Iran’s 32.3 trillion cubic meters of proven natural gas reserves in 2006 were located in independent natural gas fields, an amount second only to those of Russia. In 2006 annual production reached 105 billion cubic meters, with fastest growth occurring over the previous 15 years. In 2006 natural gas accounted for abut 50 percent of domestic energy consumption
Energy in Iran
Energy resources in Iran consist of the third largest oil reserves and the second largest natural gas reserves in the world. Iran is in a constant battle to use its energy resources more effectively in the face of subsidization and the need for technological advances in energy exploration and...
, in part because domestic gas prices were heavily subsidized. Natural gas production will reach 700 million cubic meter/day by 2012 and 900 million cubic meter/day by 2015.
Since 1979, infrastructure investment by Iranian and foreign oil firms has increased pipeline capacity to support the Iranian gas industry. Between 1979 and 2003, pipelines to transport natural gas to refineries and to domestic consumers increased from 2,000 kilometers to 12,000 kilometers. In the same period, natural gas distribution pipelines increased from 2,000 kilometers to 45,000 kilometers in response to growing domestic consumption. Gas processing plants are located at Ahvaz, Dalan, Kangan, and Marun, in a corridor along the northern Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
close to the major gas fields. South Pars, Iran’s largest natural gas field, has received substantial foreign investment. With its output intended for both export and domestic consumption, South Pars is expected to reach full production in 2015. The output of South Pars is the basis of the Pars Special Economic Energy Zone, a complex of petrochemical and natural gas processing plants and port facilities established in 1998 on the Persian Gulf south of Kangan.
In the 1980s, Iran began to replace oil, coal, charcoal, and other fossil-fuel energy sources with natural gas, which is environmentally safer. The share of natural gas in household energy consumption, which averaged 54 percent in 2004, was projected to increase to 69 percent by 2009. Overall, natural gas consumption in Iran was expected to grow by more than 10 percent per annum between 2005 and 2009.
With international oil prices increasing and projected to continue increasing, international demand for natural gas and investment in production and transportation of natural gas to consumer markets both increased in the early 2000s. Iran set a goal of increasing its natural gas production capacity to 300 billion cubic meters by 2015 while keeping oil production stable. To achieve this capacity, the government has planned a joint investment worth US$100 billion in the oil and gas industry through 2015. In 2004 Iran signed a contract with France and Malaysia for production and export of natural gas and another agreement with European and Asian companies for expansion and marketing of its natural gas resources. In 2005 Iran exported natural gas to Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
and was expected to expand its market to Armenia, China, Japan, other East Asian countries, India, Pakistan, and Europe. The first section of a new line to Armenia opened in spring 2007, as a much-discussed major pipeline to India and Pakistan remained in the negotiation stage.
Major foreign projects

Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
will buy 5.5 billion cubic meters of Iranian natural gas each year, beginning in 2011. In April 2007, OMV
OMV
OMV is Austria's largest oil-producing, refining and gas station operating company with important activities in other Central European countries...
, the Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
n partially state-owned energy company, signed letters of intent with Iran, worth an estimated $22.8 billion (22 billion euros), for Iran
to supply Europe with gas. The United States has expressed strong opposition to both the Swiss and Austrian deals with Iran.
The National Iranian Gas Company
National Iranian Gas Company
The National Iranian Gas Company was established in 1965 as one of the four principal companies affiliated to the Ministry of Petroleum of the Islamic Republic of Iran with 25,000 million Rials initial capital....
(NIGC) is expected to finalize a natural gas export deal with Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, with exports set to begin in 2011. The gas would be transported through a “Peace pipeline”, worth about $7.4 billion. The plan initially also included exporting gas to India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, but negotiations have stalled over pricing. Iran also is discussing a gas production and export deal with Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
. Under the plan, Turkey would assist in developing Iran’s South Pars field in exchange for cash or natural gas. Gas would be shipped from Iran to Turkey and Europe via a new pipeline
Persian Pipeline
Persian Pipeline is a proposed natural gas pipeline to transfer Iranian gas from the Persian gulf to European markets.-Route:...
that Turkey plans to build.
Other notable petroleum sector development deals include those with Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. On February 19, 2008, Russian state gas company Gazprom
Gazprom
Open Joint Stock Company Gazprom is the largest extractor of natural gas in the world and the largest Russian company. Its headquarters are in Cheryomushki District, South-Western Administrative Okrug, Moscow...
announced a deal to establish a joint venture company to develop the offshore Iranian South Pars gas field. A China National Offshore Oil Corporation
China National Offshore Oil Corporation
China National Offshore Oil Corporation is one of the three major national oil companies of China....
(CNOOC) investment deal, valued at $16 billion, to develop Iran’s North Pars
North Pars
North Pars Gas Field is one of the biggest independent gas fields of the world. This field which was discovered in 1967 is located some 120 kilometers south east of Bushehr province in water depths of 2 to 30 meters in the Persian Gulf....
gas field and to build a liquid natural gas (LNG) plant, was supposed to be signed on February 27, 2008 but has been delayed. The state-operated National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) and CNOOC signed a memorandum of understanding in December 2006 for the project, under which CNOOC would purchase 10 million metric tons per year of LNG for 25 years. In 2011, Iran signed a contract with Baghdad and Damascus in order to export Iran’s gas to Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
, the Mediterranean region and eventually Europe.
Market value of Iran's total natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
reserves at comparative international energy price of $75 per barrel of oil
Oil
An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils....
stands at ~US $4 trillion.
Petrochemicals
In the early 2000s, an ambitious state petrochemicals project called for expansion of annual output in that industry from 9 million tons in 2001 to 100 million tons in 2015. Output capacity in 2006 was estimated at 15 million tons. The goal of this expansion is to increase the percentage of Iran’s processed petroleum-based exports, which are more profitable than raw materials. In 2005 Iran exported US$1.8 billion of petrochemical products (about one-third of total nonoil exports in that year). Receiving 30 percent of Iran’s petrochemical exports between them, ChinaChina
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
and India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
were the major trading partners in this industry. Iran’s domestic resource base gives it a unique comparative advantage in producing petrochemicals when international crude oil prices rise. The gain has been greatest in those plants that use liquid gas as their main input. For FY 2006, the petrochemical industry’s share of GDP was projected to be about 2 percent. Iran plans to invest $500 billion in the oil sector until 2025.
Iran’s petrochemical industries have absorbed a large amount of private and public investment. In the early 2000s, 43 percent of these investments was financed by Iran’s National Petrochemical Company
National Iranian Petrochemical Company
The National Iranian Petrochemical Company , a subsidiary to the Iranian Petroleum Ministry, is owned by the government of the Islamic Republic of Iran. It is responsible for the development and operation of the country's petrochemical sector. Founded in 1964, NIPC began its activities by operating...
, a subsidiary of the Ministry of Petroleum
Ministry of Petroleum of Iran
The Ministry of Petroleum manages the oil industry, the producer of oil and petrochemical products. MoP is in charge of all issues pertaining to exploration, extraction, exploitation, distribution and exportation of crude oil and oil products. In addition, according to the "", issuing import...
, which administers the entire petrochemical sector. Another 53 percent is owned by foreign creditors (more than 100 foreign banks and foreign companies), 3 percent by banks, and 1 percent by the capital market. Most of the petrochemical industry’s physical capital is imported, and the industry does not have strong backward linkages to manufacturing industries. In 2006 new petrochemical plants came online at Marun
Marun petrochemical complex
Marun Petrochemical Complex , is a petrochemical complex in Mahshahr, Khuzestan, Iran.The complex consists of LDPE, HDPE, PP, Olefin, EO/EG and UT plants.The main plant is Olefin which feeds the others....
and Asaluyeh, and construction began on three others.
See also
- Economy of IranEconomy of IranThe economy of Iran is the eighteenth largest in the world by purchasing power parity and according to Iranian officials' claims is going to become the 12th largest by 2015. The economy of Iran is a mixed and transition economy with a large public sector and some 50% of the economy centrally planned...
- Iranian Oil BourseIranian oil bourseThe Iranian Oil Bourse International Oil Bourse, Iran Petroleum Exchange Kish Exchange or Oil Bourse in Kish is a commodity exchange which opened on February 17, 2008. It was created by cooperation between Iranian ministries, the Iran Mercantile Exchange and other state and private institutions...
- Ministry of Petroleum of IranMinistry of Petroleum of IranThe Ministry of Petroleum manages the oil industry, the producer of oil and petrochemical products. MoP is in charge of all issues pertaining to exploration, extraction, exploitation, distribution and exportation of crude oil and oil products. In addition, according to the "", issuing import...
- National Iranian Oil CompanyNational Iranian Oil CompanyThe National Iranian Oil Company , a government-owned corporation under the direction of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran, is an oil and natural gas producer and distributor headquartered in Tehran. It was established in 1948...
- National Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution CompanyNational Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution CompanyNational Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution Company is part of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran. NIORDC was established on March 8, 1992 and undertook to perform all operations relating to refining and distribution of oil products....
- National Iranian Petrochemical CompanyNational Iranian Petrochemical CompanyThe National Iranian Petrochemical Company , a subsidiary to the Iranian Petroleum Ministry, is owned by the government of the Islamic Republic of Iran. It is responsible for the development and operation of the country's petrochemical sector. Founded in 1964, NIPC began its activities by operating...
- National Iranian Gas CompanyNational Iranian Gas CompanyThe National Iranian Gas Company was established in 1965 as one of the four principal companies affiliated to the Ministry of Petroleum of the Islamic Republic of Iran with 25,000 million Rials initial capital....
- Tehran Stock ExchangeTehran Stock ExchangeThe Tehran Stock Exchange is Iran's largest stock exchange, which first opened in 1967. The TSE is based in Tehran. As of July 2010, 337 companies with a market capitalization of US$72 billion were listed on TSE...
- Iranian targeted subsidy plan
External links
- US Department of Energy - Iran
- SHANA - Official News Service for Oil and Gas in Iran
- Oil & Gas Industry in Iran - 2003 Study (history, market overview, domestic suppliers, major projects, buy-backs)
- FACTBOX-Iran's crude export and fuel import customers - ReutersReutersReuters is a news agency headquartered in New York City. Until 2008 the Reuters news agency formed part of a British independent company, Reuters Group plc, which was also a provider of financial market data...
- Offshore Middle East and Caspian Sea Oil and Gas Market Report 2011
- Iran Gas Markets Report, 2011 - GlobalData
Videos
- Iranian Oil and Gas Industry in the Midst of Latest UNSC Sanctions - PressTV video (2010)

