
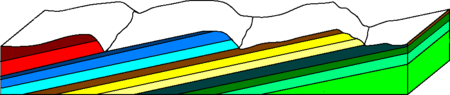
Dip slope
Encyclopedia
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
formation often created by erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
of tilted strata
Stratum
In geology and related fields, a stratum is a layer of sedimentary rock or soil with internally consistent characteristics that distinguish it from other layers...
. Dip slopes are found on homoclinal ridges with one side that is steep and irregular (an escarpment
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that occurs from erosion or faulting and separates two relatively level areas of differing elevations.-Description and variants:...
) and another side, the dip slope, that is generally planar with a dip
Strike and dip
Strike and dip refer to the orientation or attitude of a geologic feature. The strike line of a bed, fault, or other planar feature is a line representing the intersection of that feature with a horizontal plane. On a geologic map, this is represented with a short straight line segment oriented...
parallel to the bedding. The orientation of the dip slope is referred to as the strike
Strike and dip
Strike and dip refer to the orientation or attitude of a geologic feature. The strike line of a bed, fault, or other planar feature is a line representing the intersection of that feature with a horizontal plane. On a geologic map, this is represented with a short straight line segment oriented...
.
Formation
Some rocks (usually softer ones) erodeErosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
more rapidly than others. For example, shale
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite. The ratio of clay to other minerals is variable. Shale is characterized by breaks along thin laminae or parallel layering...
most frequently erodes faster than limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
. In situations like this, an entire layer of the easily erodible rock can be weathered away while a layer of a more durable rock will remain largely unchanged. This results in a nearly flat surface created by the top of the more durable layer. When this happens to beds that are not tilted mesa
Mesa
A mesa or table mountain is an elevated area of land with a flat top and sides that are usually steep cliffs. It takes its name from its characteristic table-top shape....
s are formed. With tilted beds, structures called cuesta
Cuesta
In structural geology and geomorphology, a cuesta is a ridge formed by gently tilted sedimentary rock strata in a homoclinal structure. Cuestas have a steep slope, where the rock layers are exposed on their edges, called an escarpment or, if more steep, a cliff...
s and hogbacks
Hogback (geology)
A hogback is a homoclinal ridge, formed from a monocline, composed of steeply tilted strata of rock protruding from the surrounding area. The name comes from the ridge resembling the high, knobby spine between the shoulders of a hog. In most cases, the two strata that compose a hogback are...
are formed. Mesas will have a flat top, while cuestas and hogbacks will look like ridges, with one side that is a dip slope and a steeper escarpment on the other.
Dip slopes can also be formed by igneous structures such as sill
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or even along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. The term sill is synonymous with concordant intrusive sheet...
s. Any generally planar geological structure can form dip slopes, when it is tilted away from horizontal.
Landslides
Dip slopes are quite prone to landslideLandslide
A landslide or landslip is a geological phenomenon which includes a wide range of ground movement, such as rockfalls, deep failure of slopes and shallow debris flows, which can occur in offshore, coastal and onshore environments...
s, due to the dipping flat erosional surface. Large sheets of rock have a tendency to slide down dip slopes.

